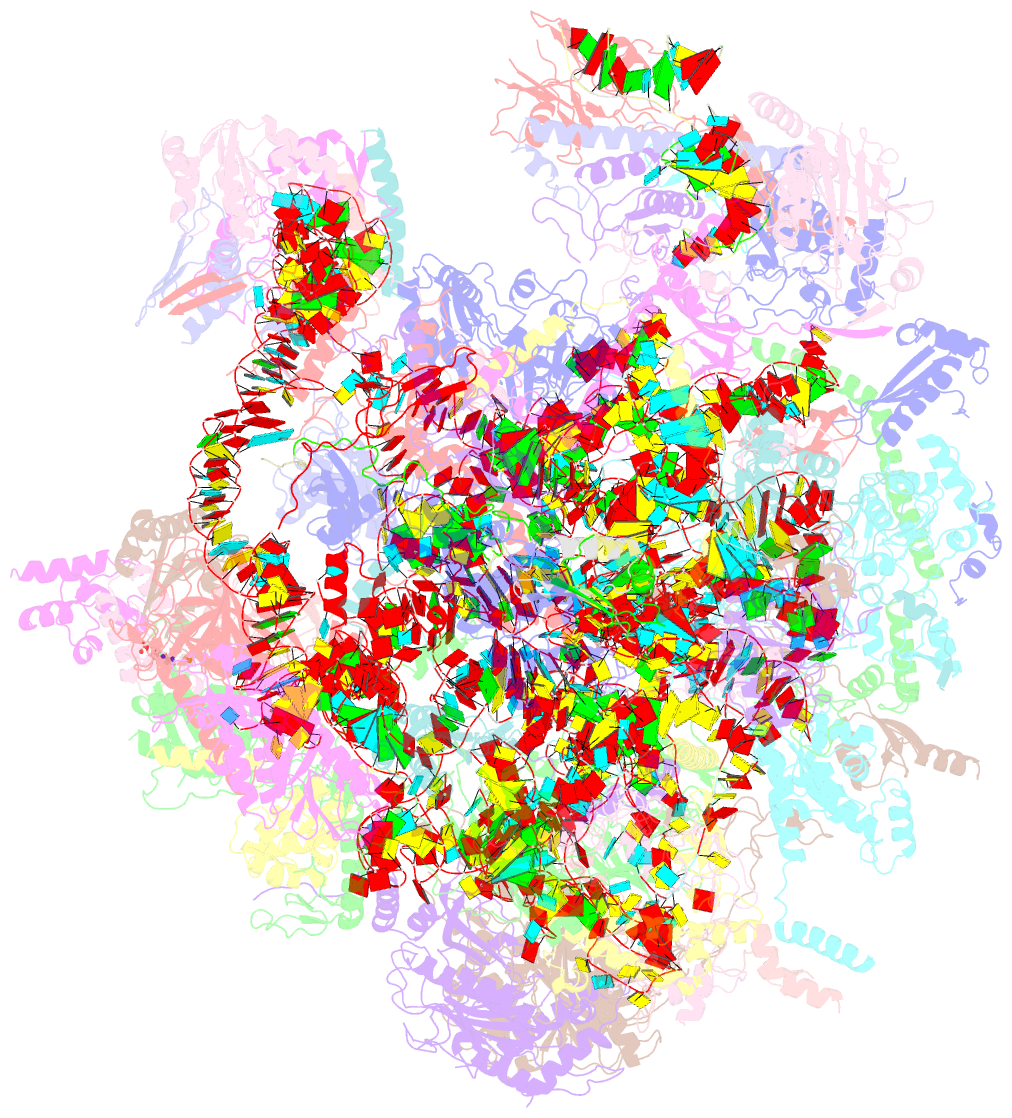
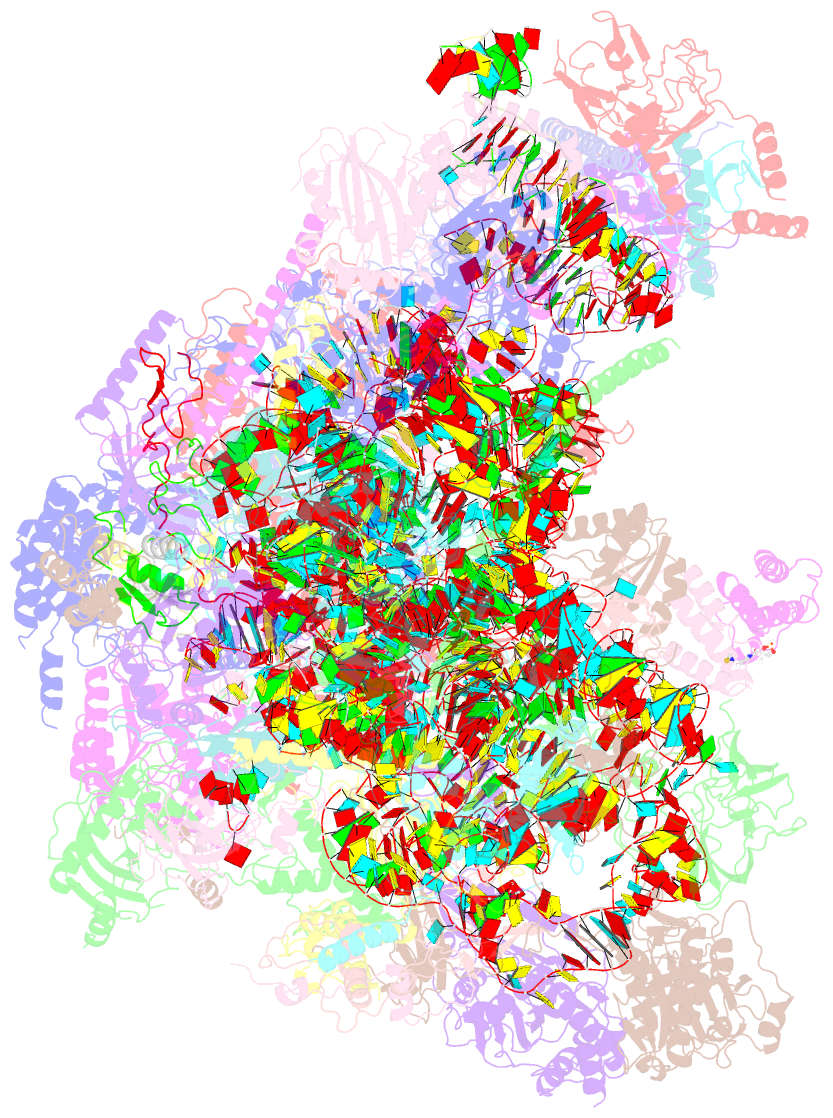
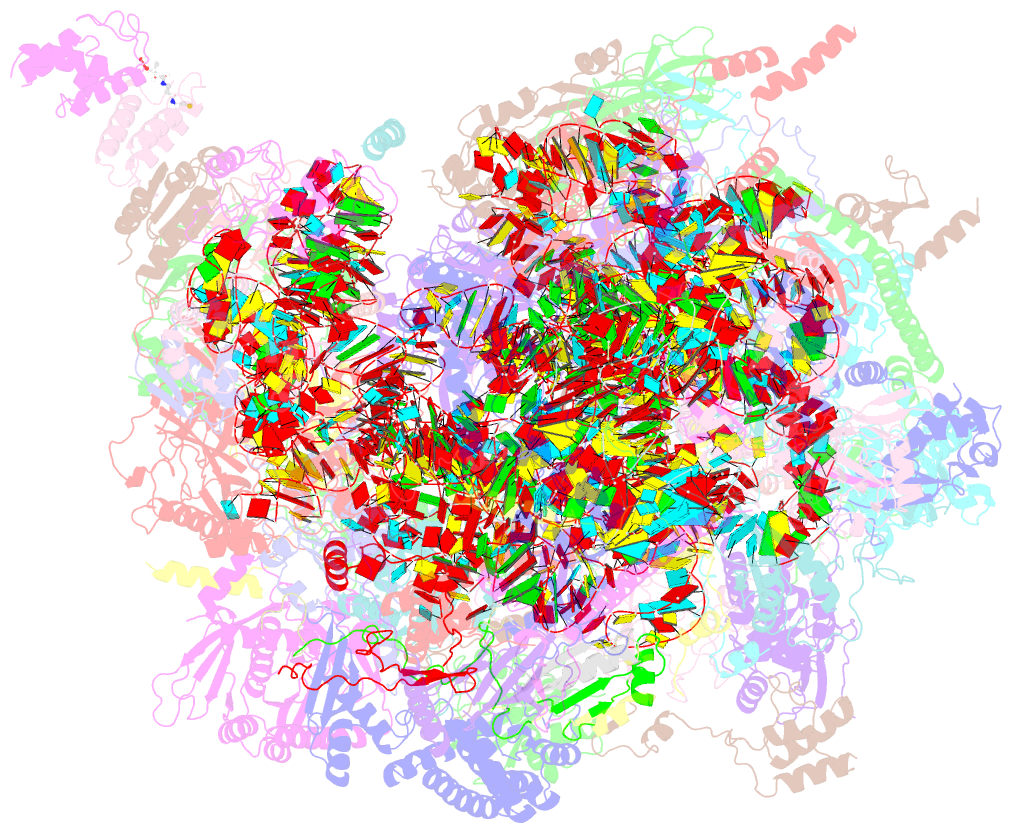
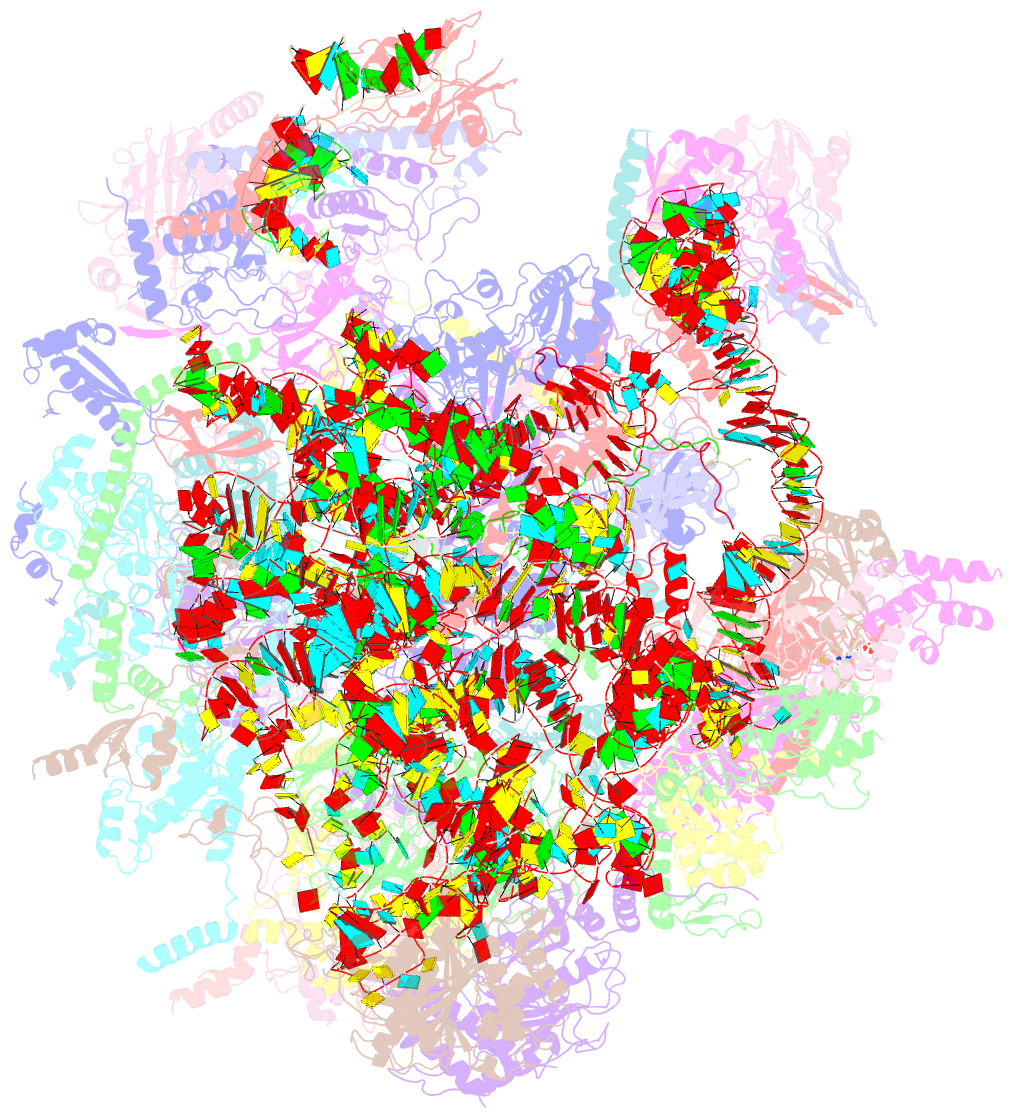
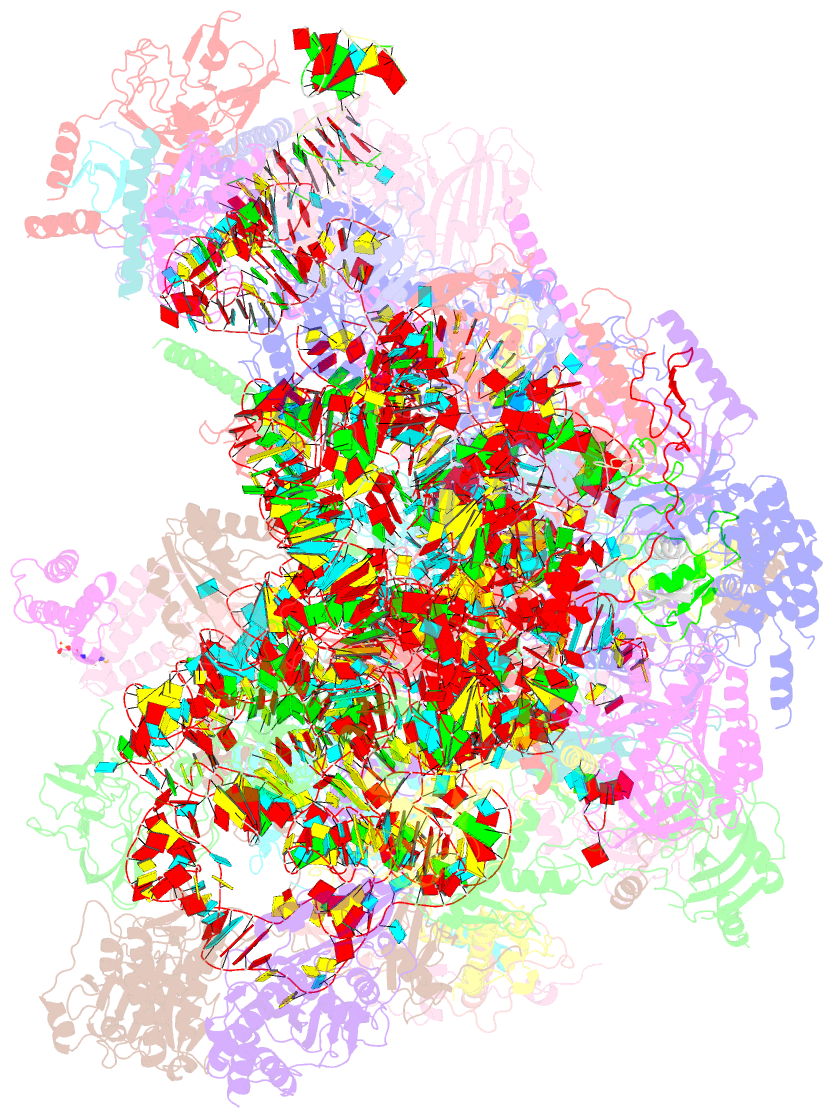
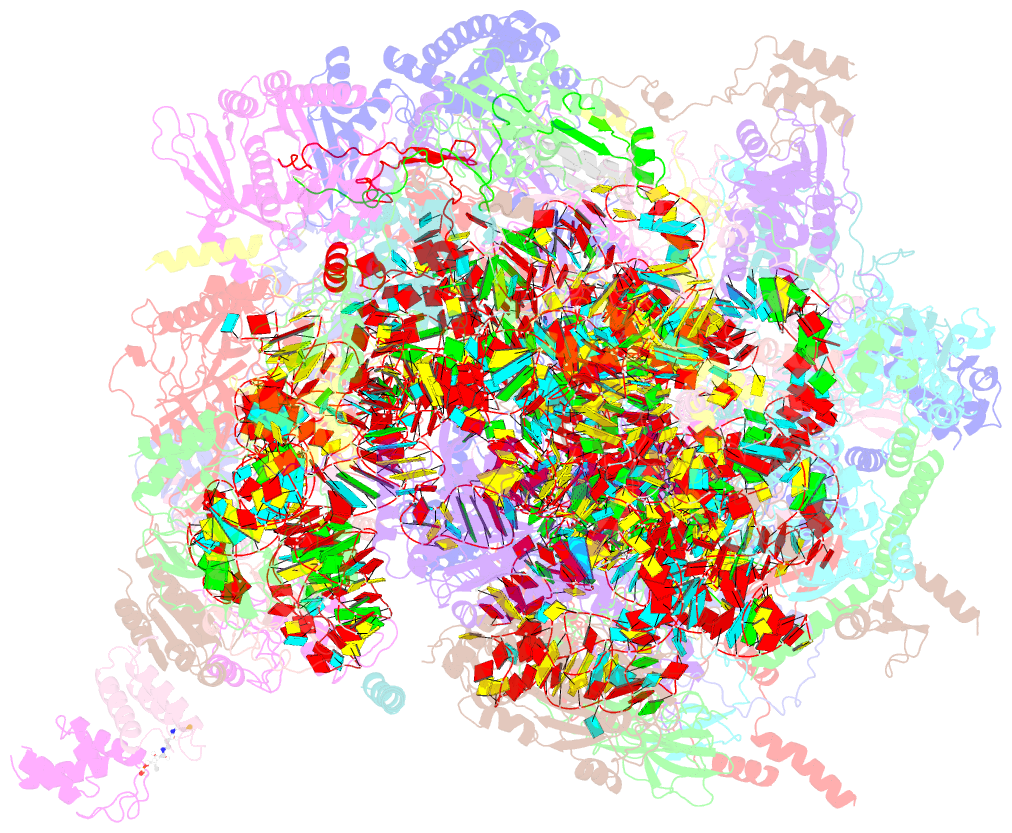
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5oom; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.03 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of a native assembly intermediate of the human mitochondrial ribosome with unfolded interfacial rrna
- Reference
- Brown A, Rathore S, Kimanius D, Aibara S, Bai XC, Rorbach J, Amunts A, Ramakrishnan V (2017): "Structures of the human mitochondrial ribosome in native states of assembly." Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 24, 866-869. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3464.
- Abstract
- Mammalian mitochondrial ribosomes (mitoribosomes) have less rRNA content and 36 additional proteins compared with the evolutionarily related bacterial ribosome. These differences make the assembly of mitoribosomes more complex than the assembly of bacterial ribosomes, but the molecular details of mitoribosomal biogenesis remain elusive. Here, we report the structures of two late-stage assembly intermediates of the human mitoribosomal large subunit (mt-LSU) isolated from a native pool within a human cell line and solved by cryo-EM to ∼3-Å resolution. Comparison of the structures reveals insights into the timing of rRNA folding and protein incorporation during the final steps of ribosomal maturation and the evolutionary adaptations that are required to preserve biogenesis after the structural diversification of mitoribosomes. Furthermore, the structures redefine the ribosome silencing factor (RsfS) family as multifunctional biogenesis factors and identify two new assembly factors (L0R8F8 and mt-ACP) not previously implicated in mitoribosomal biogenesis.