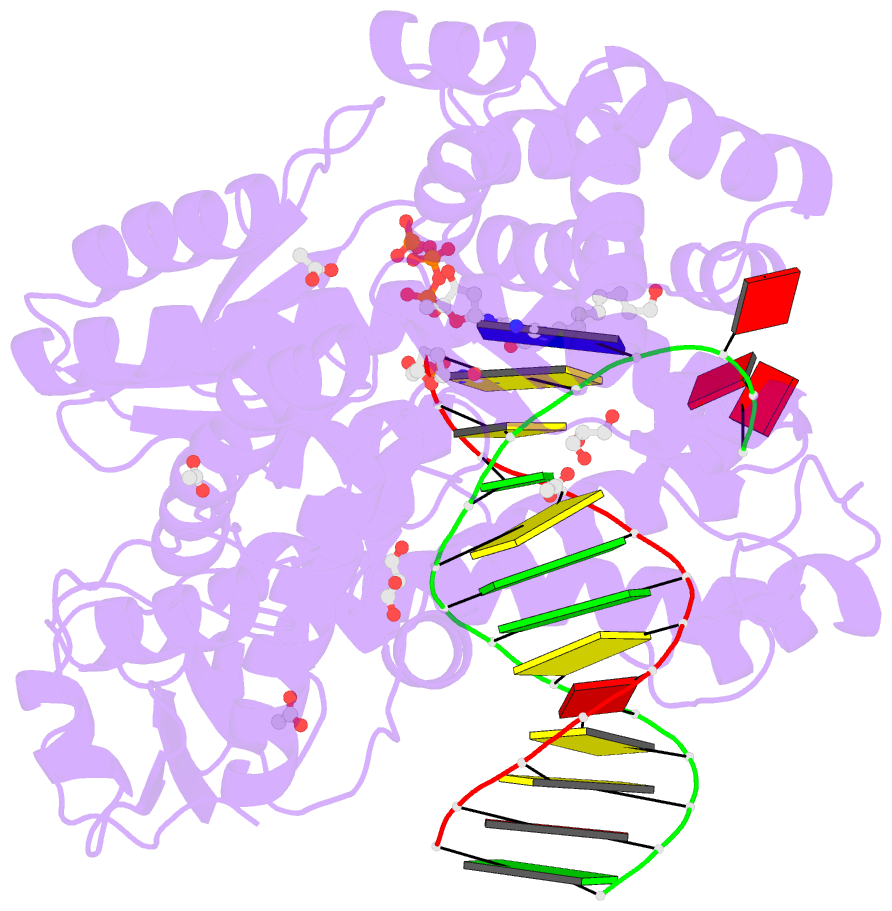
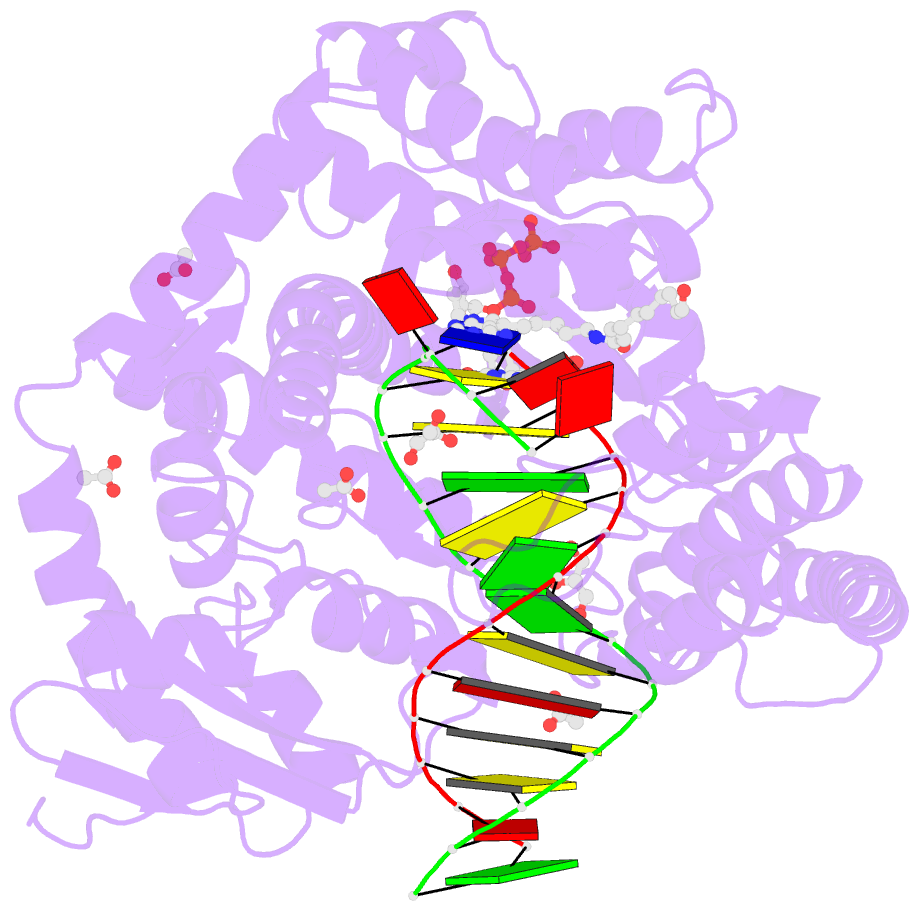
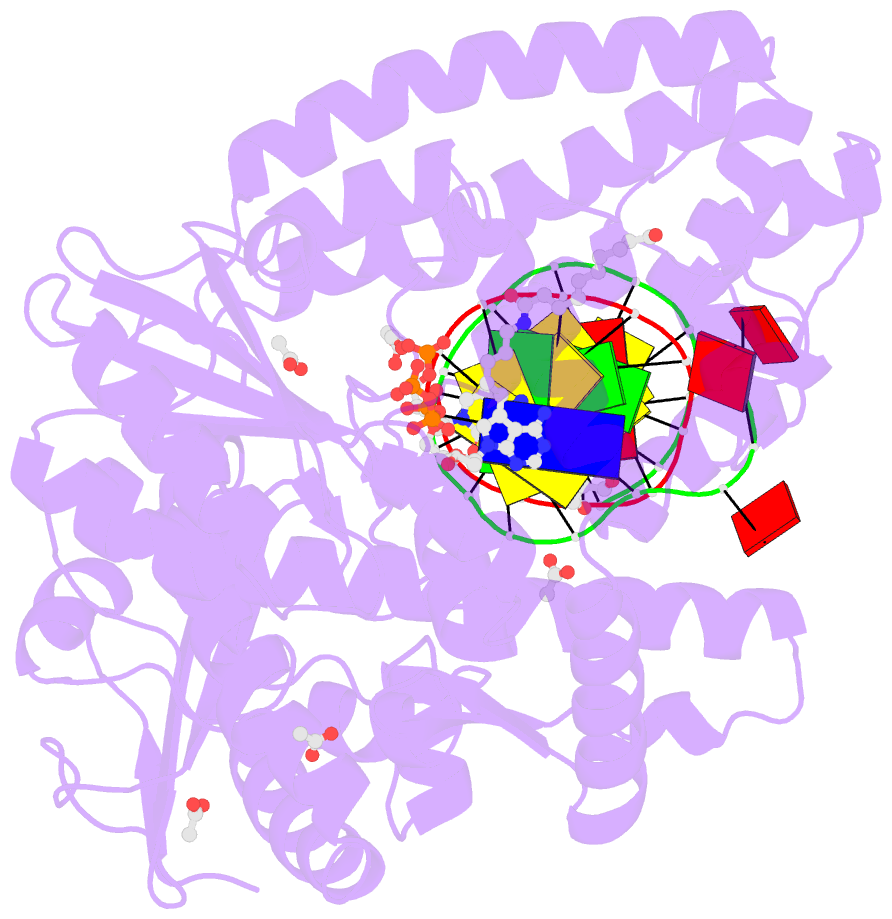
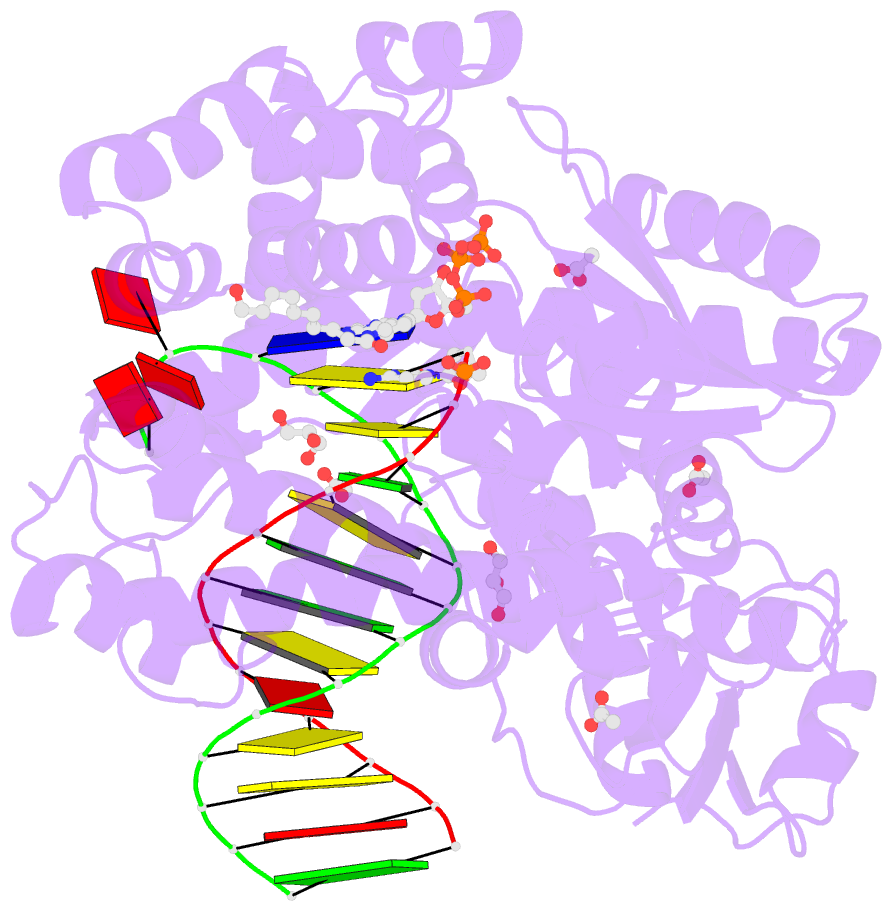
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5szt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase
- Method
- X-ray (1.8 Å)
- Summary
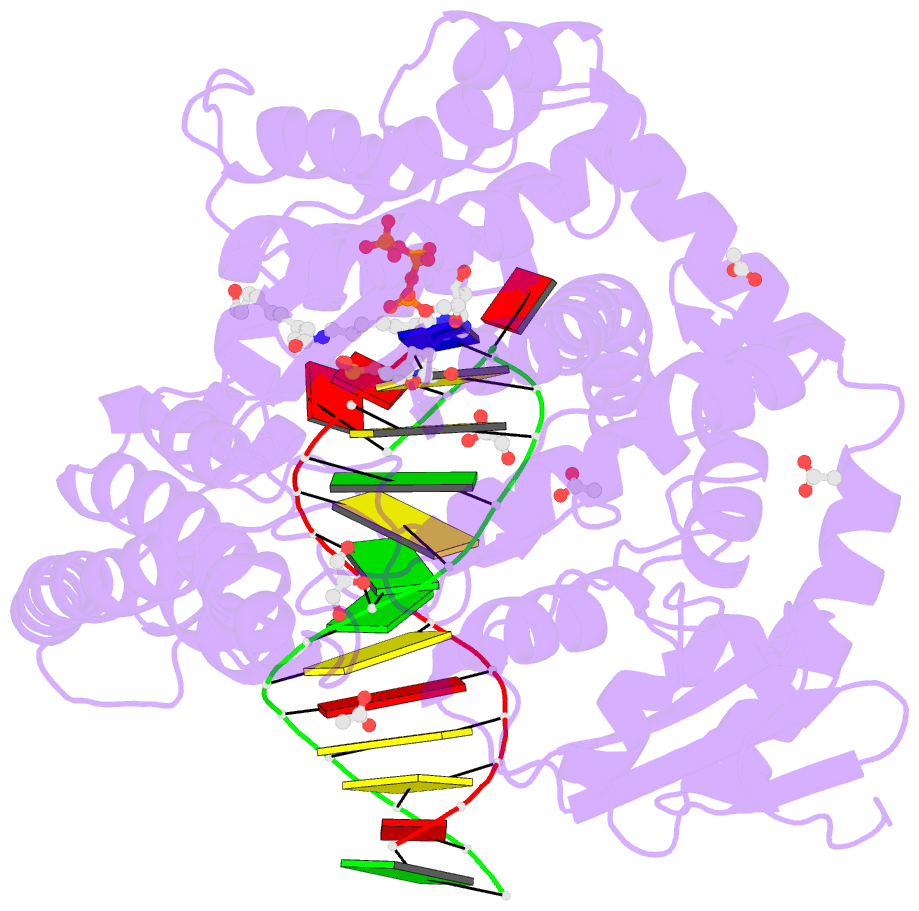
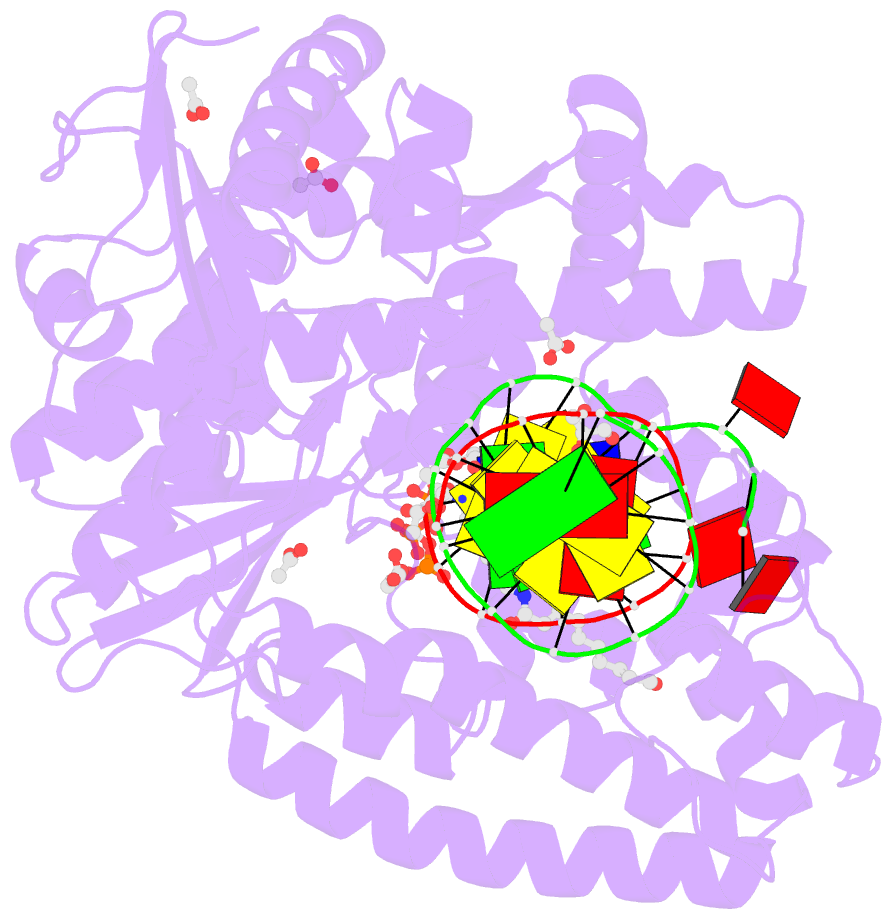
- Crystal structure of the large fragment of DNA polymerase i from thermus aquaticus in a closed ternary complex with 7-(n-(10-hydroxydecanoyl)-aminopentenyl)-7-deaza-2'-datp
- Reference
- Hottin A, Betz K, Diederichs K, Marx A (2017): "Structural Basis for the KlenTaq DNA Polymerase Catalysed Incorporation of Alkene- versus Alkyne-Modified Nucleotides." Chemistry, 23, 2109-2118. doi: 10.1002/chem.201604515.
- Abstract
- Efficient incorporation of modified nucleotides by DNA polymerases is essential for many cutting-edge biomolecular technologies. The present study compares the acceptance of either alkene- or alkyne-modified nucleotides by KlenTaq DNA polymerase and provides structural insights into how 7-deaza-adenosine and deoxyuridine with attached alkene-modifications are incorporated into the growing DNA strand. Thereby, we identified modified nucleotides that prove to be superior substrates for KlenTaq DNA polymerase compared with their natural analogues. The knowledge can be used to guide future design of functionalized nucleotide building blocks.