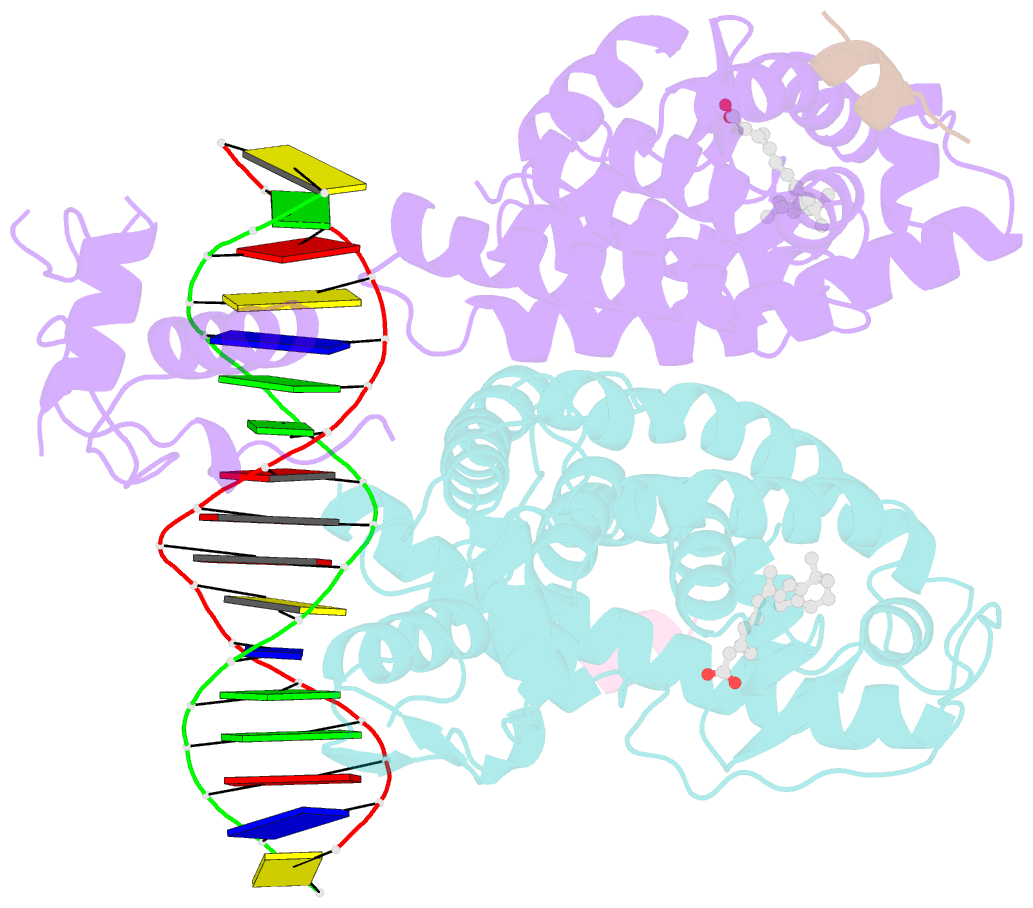
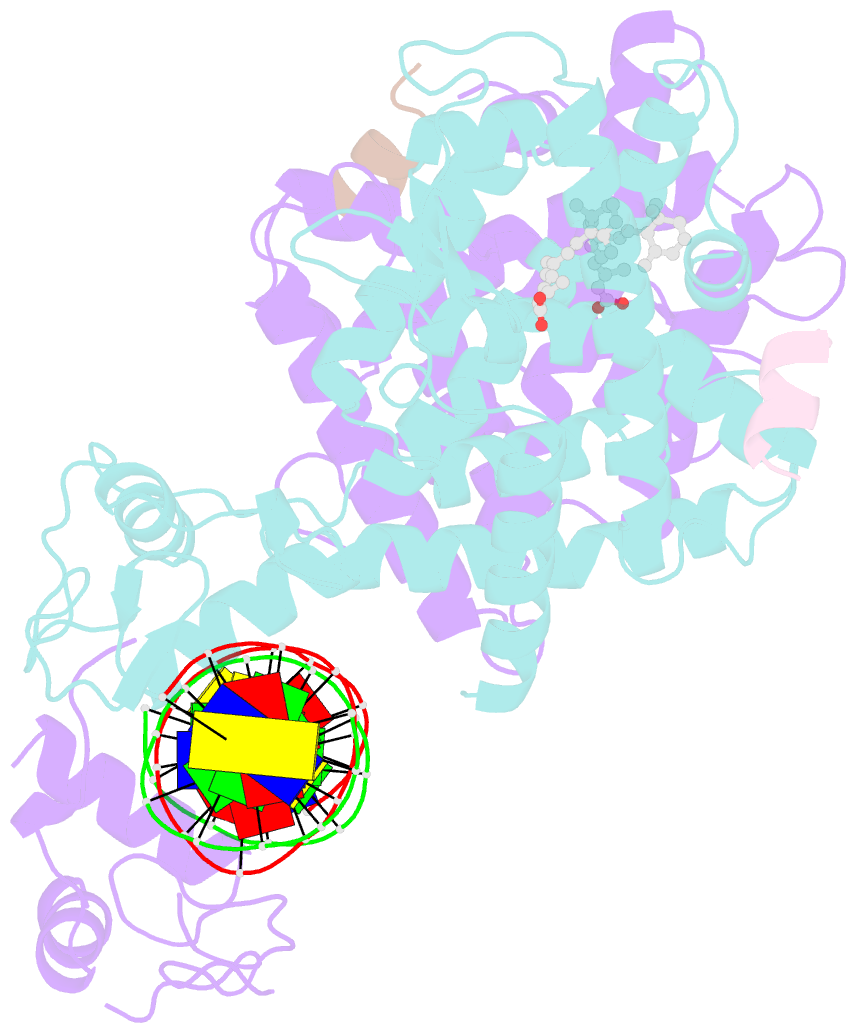
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5uan; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.508 Å)
- Summary
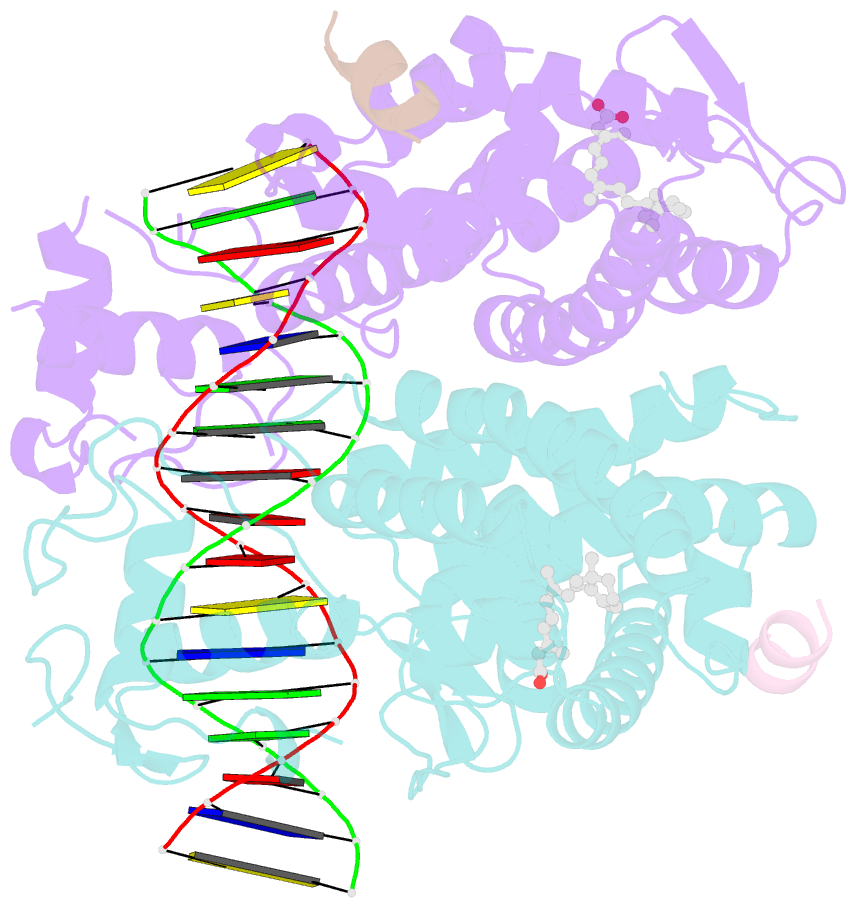
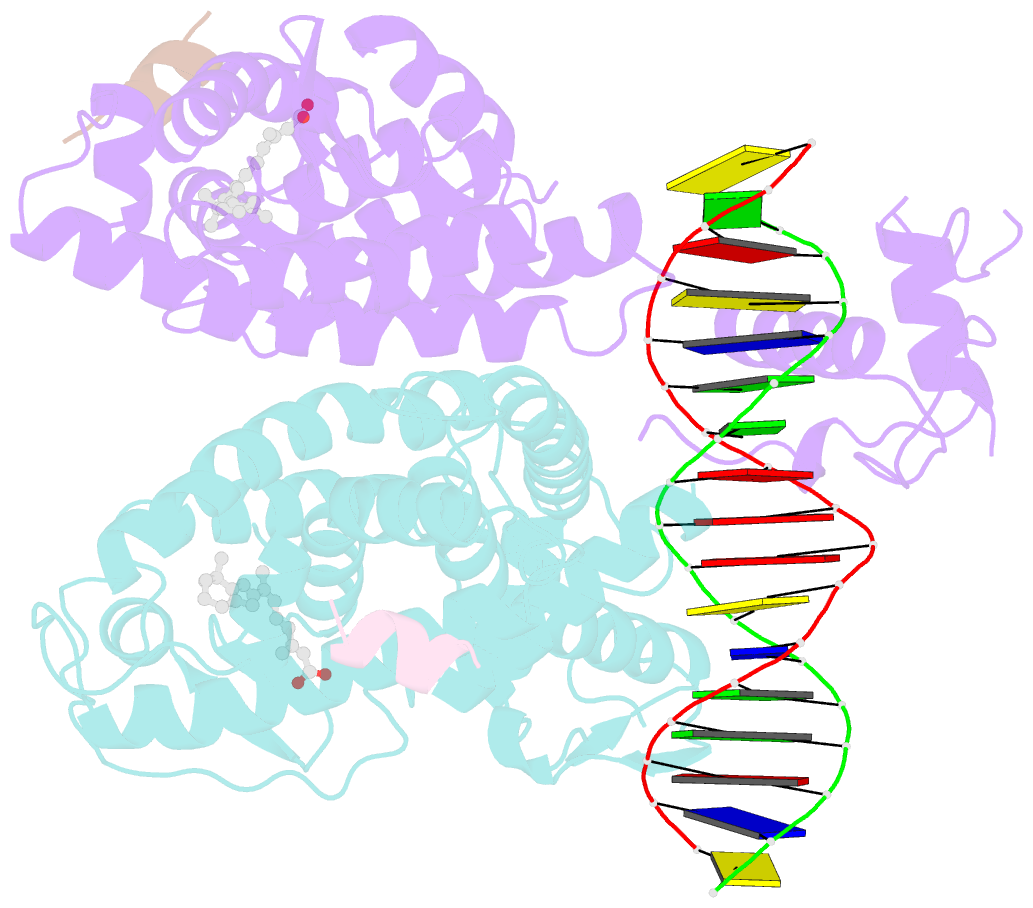
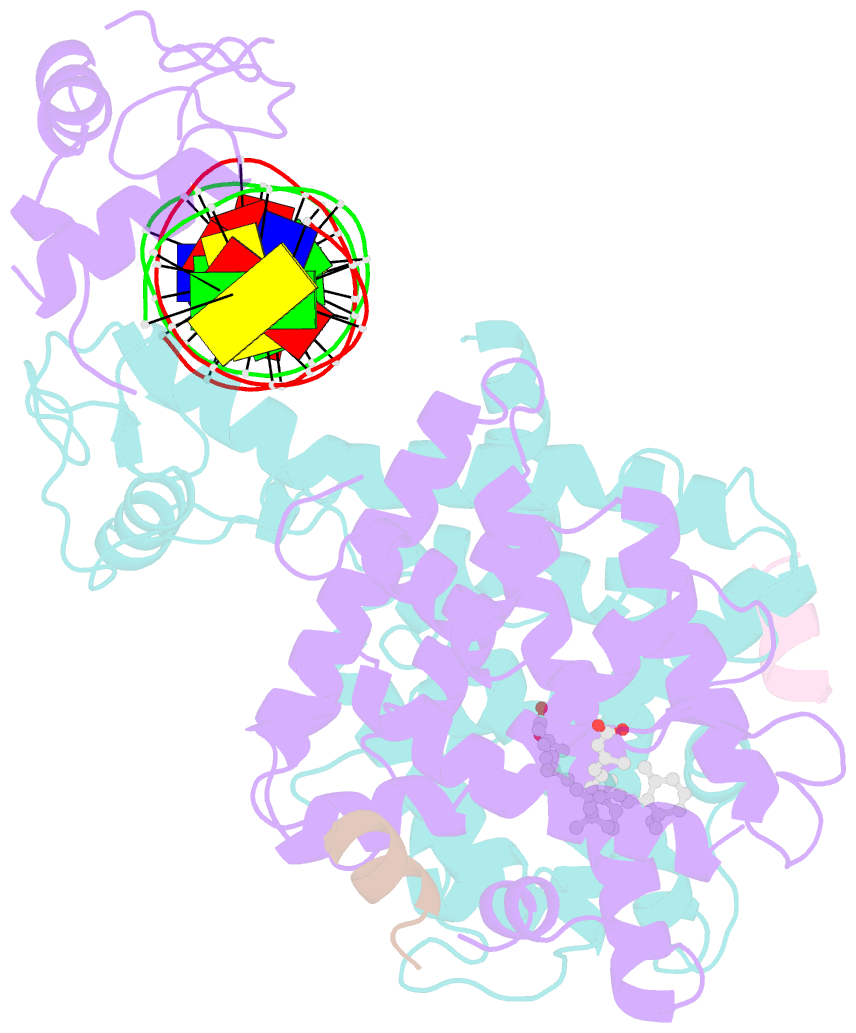
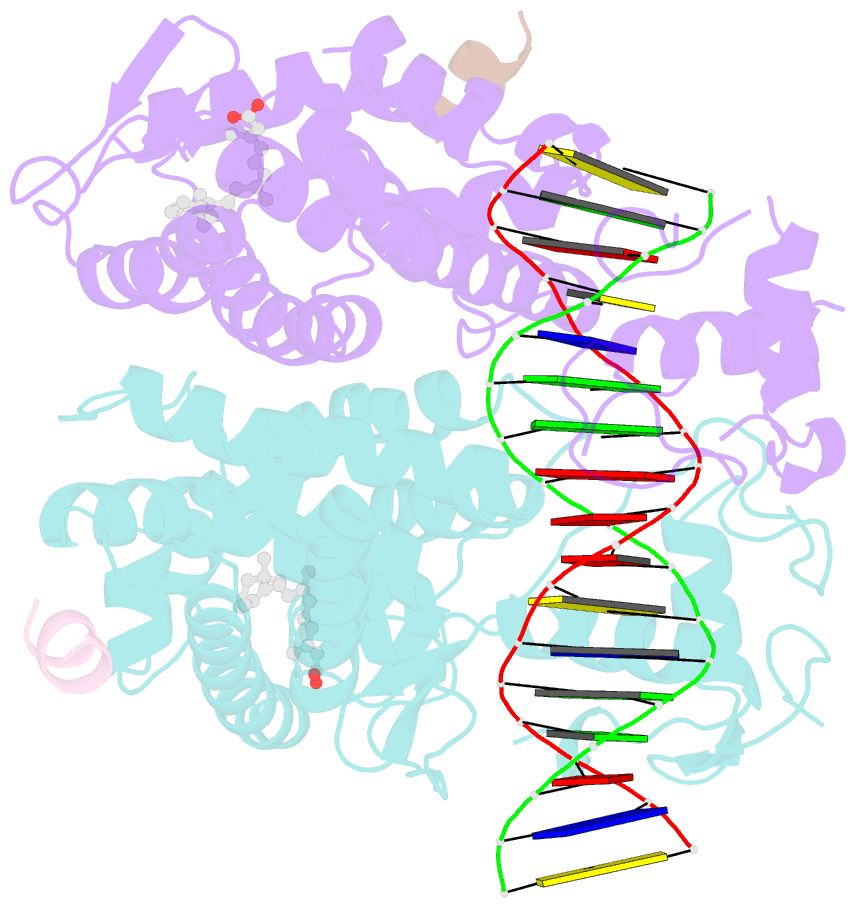
- Crystal structure of multi-domain rar-beta-rxr-alpha heterodimer on DNA
- Reference
- Chandra V, Wu D, Li S, Potluri N, Kim Y, Rastinejad F (2017): "The quaternary architecture of RAR beta-RXR alpha heterodimer facilitates domain-domain signal transmission." Nat Commun, 8, 868. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00981-y.
- Abstract
- Assessing the physical connections and allosteric communications in multi-domain nuclear receptor (NR) polypeptides has remained challenging, with few crystal structures available to show their overall structural organizations. Here we report the quaternary architecture of multi-domain retinoic acid receptor β-retinoic X receptor α (RARβ-RXRα) heterodimer bound to DNA, ligands and coactivator peptides, examined through crystallographic, hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, mutagenesis and functional studies. The RARβ ligand-binding domain (LBD) and DNA-binding domain (DBD) are physically connected to foster allosteric signal transmission between them. Direct comparisons among all the multi-domain NRs studied crystallographically to date show significant variations within their quaternary architectures, rather than a common architecture adhering to strict rules. RXR remains flexible and adaptive by maintaining loosely organized domains, while its heterodimerization partners use a surface patch on their LBDs to form domain-domain interactions with DBDs.Nuclear receptors (NR) are multidomain proteins, which makes their crystallization challenging. Here the authors present the crystal structure of the retinoic acid receptor β-retinoic X receptor α (RARβ-RXRα) heterodimer bound to DNA, ligands and coactivator peptides, which shows that NR quaternary architectures are variable.