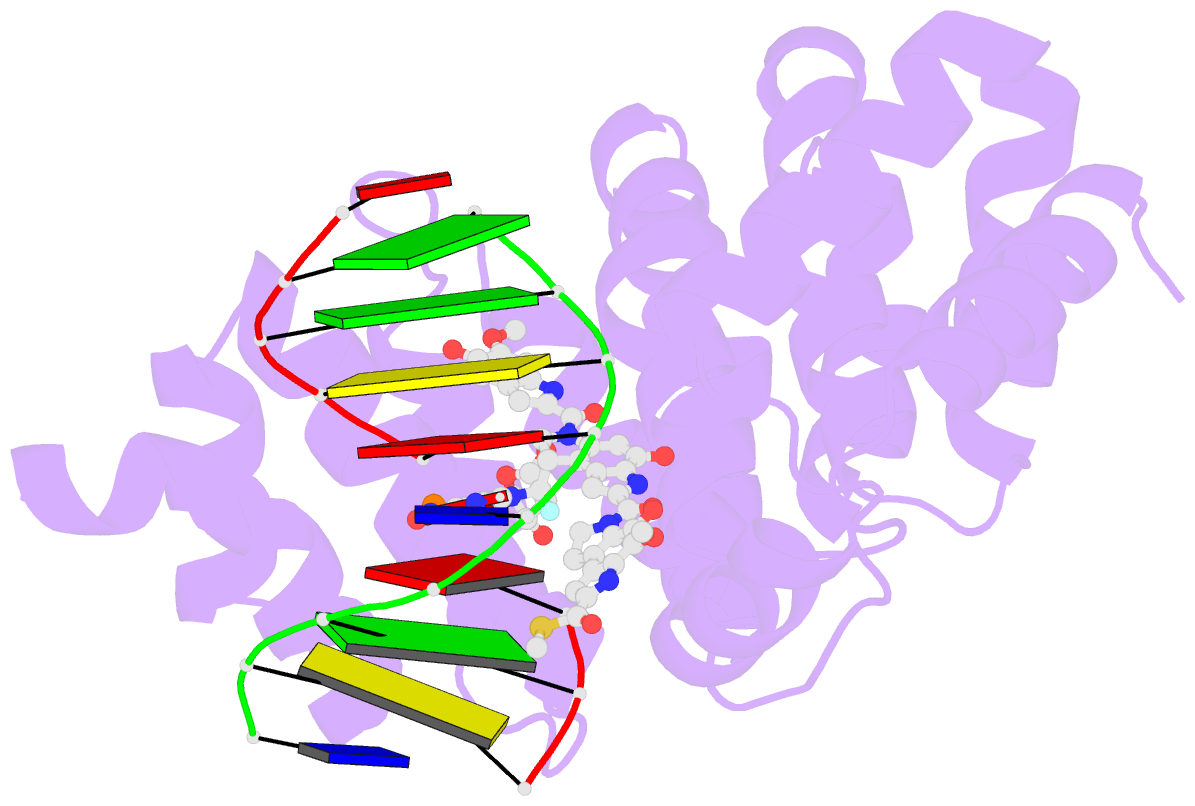
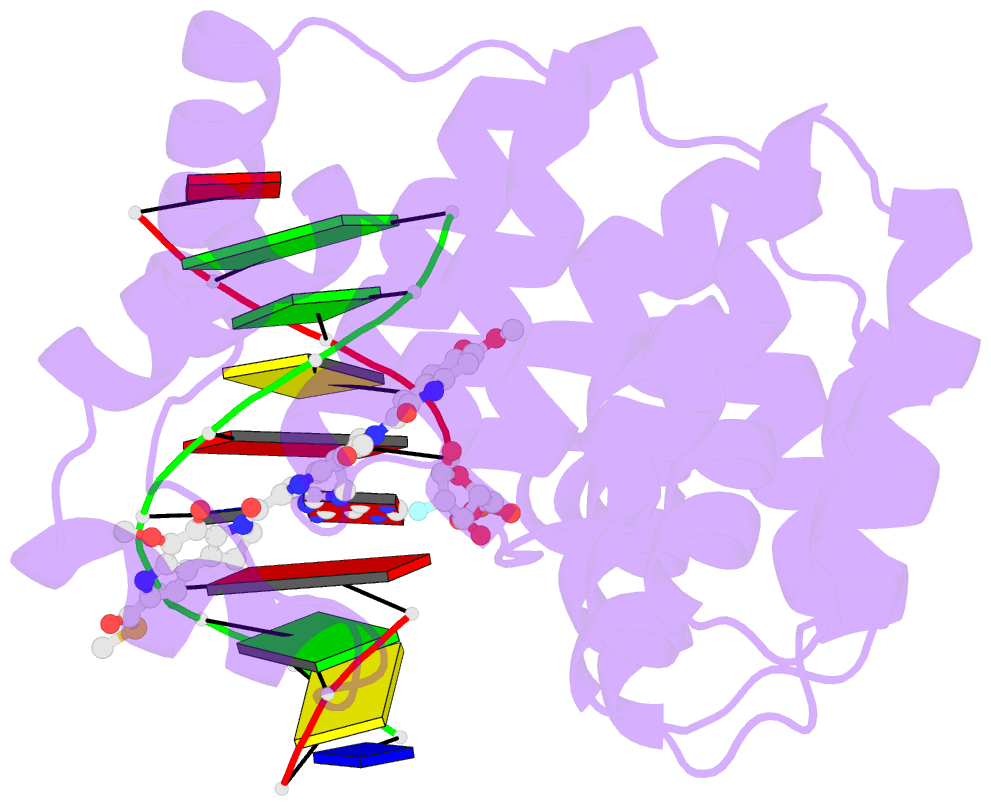
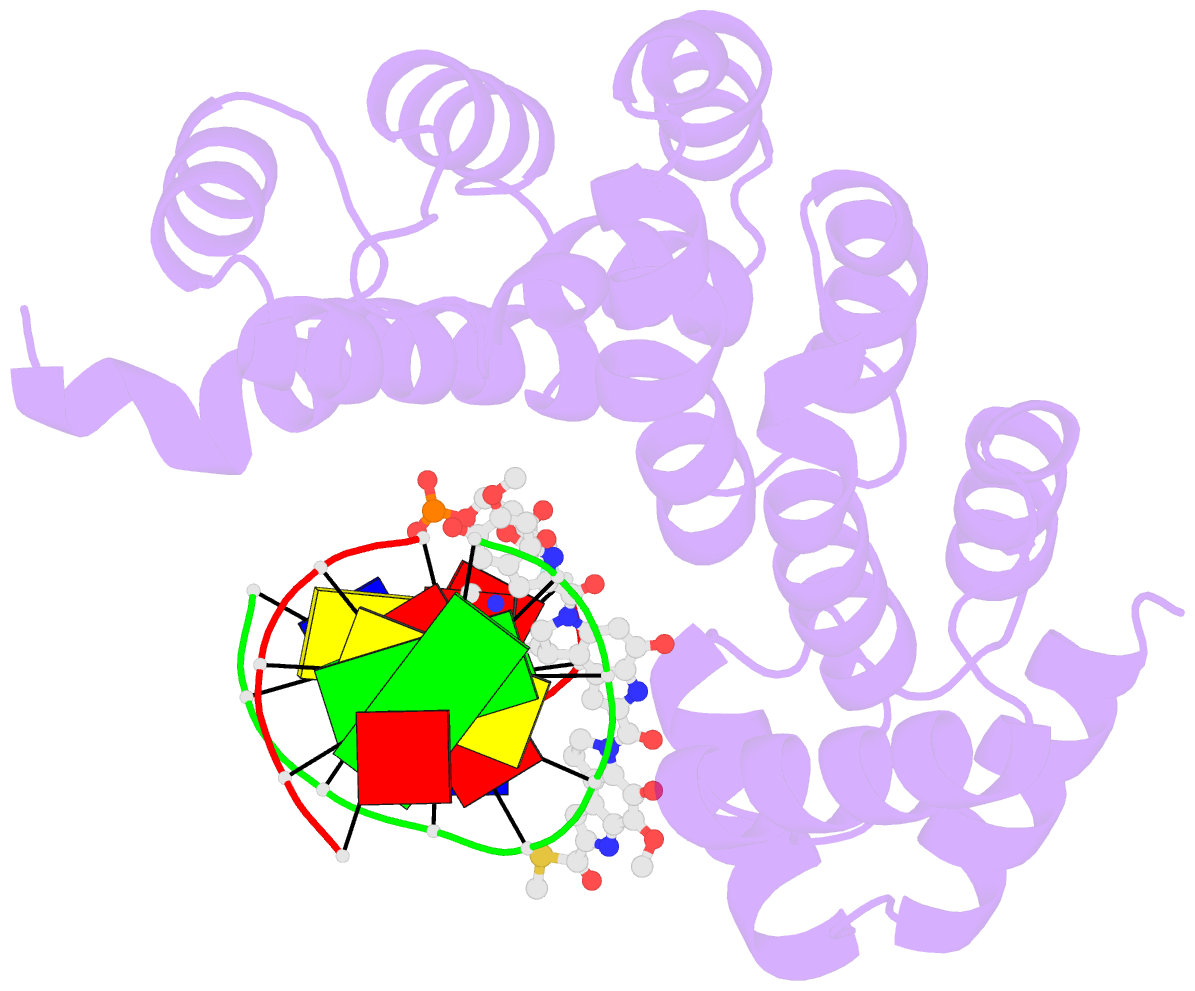
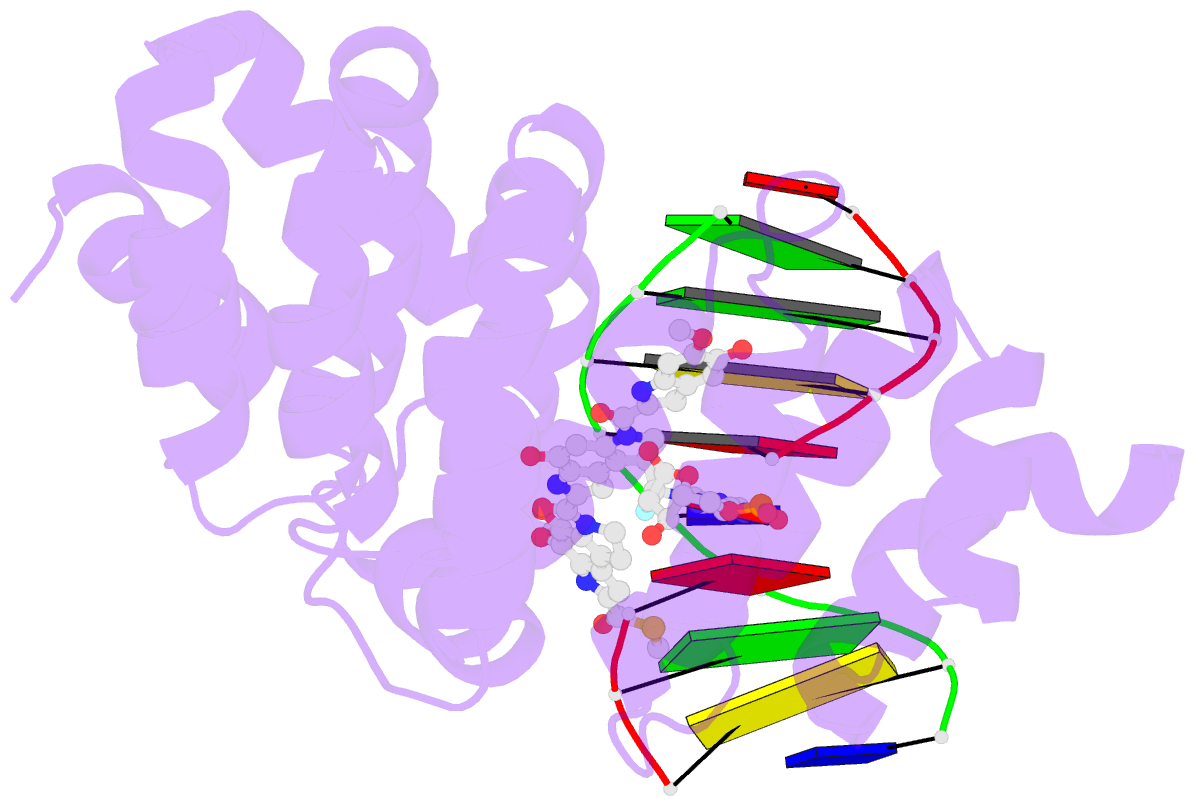
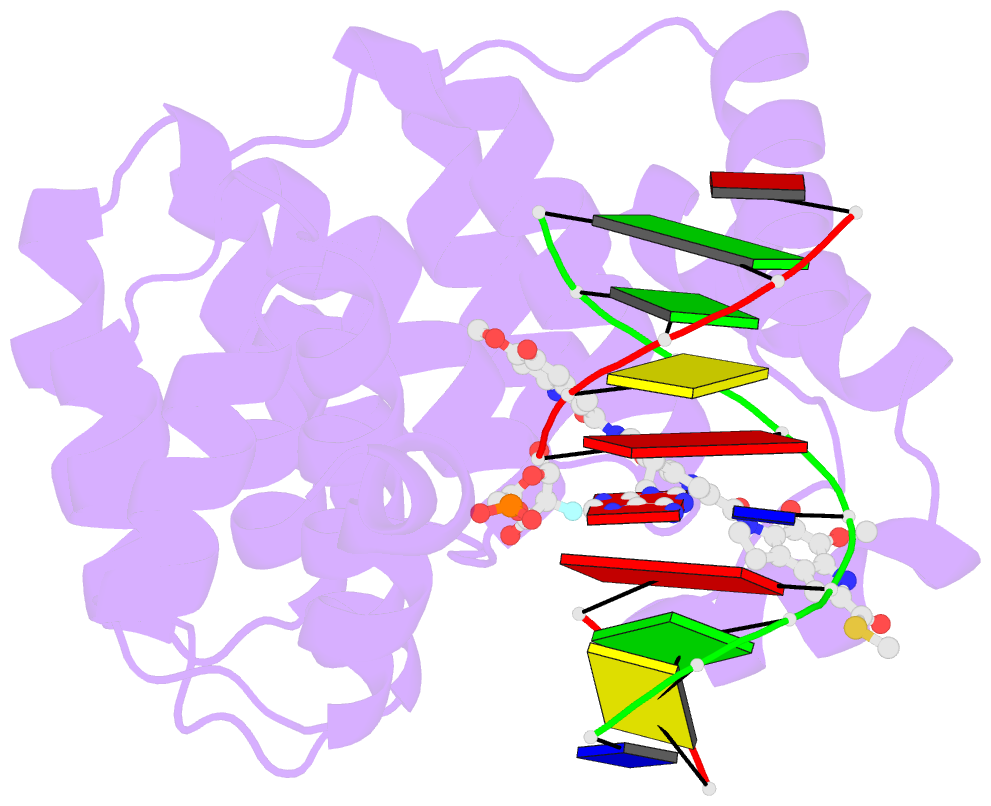
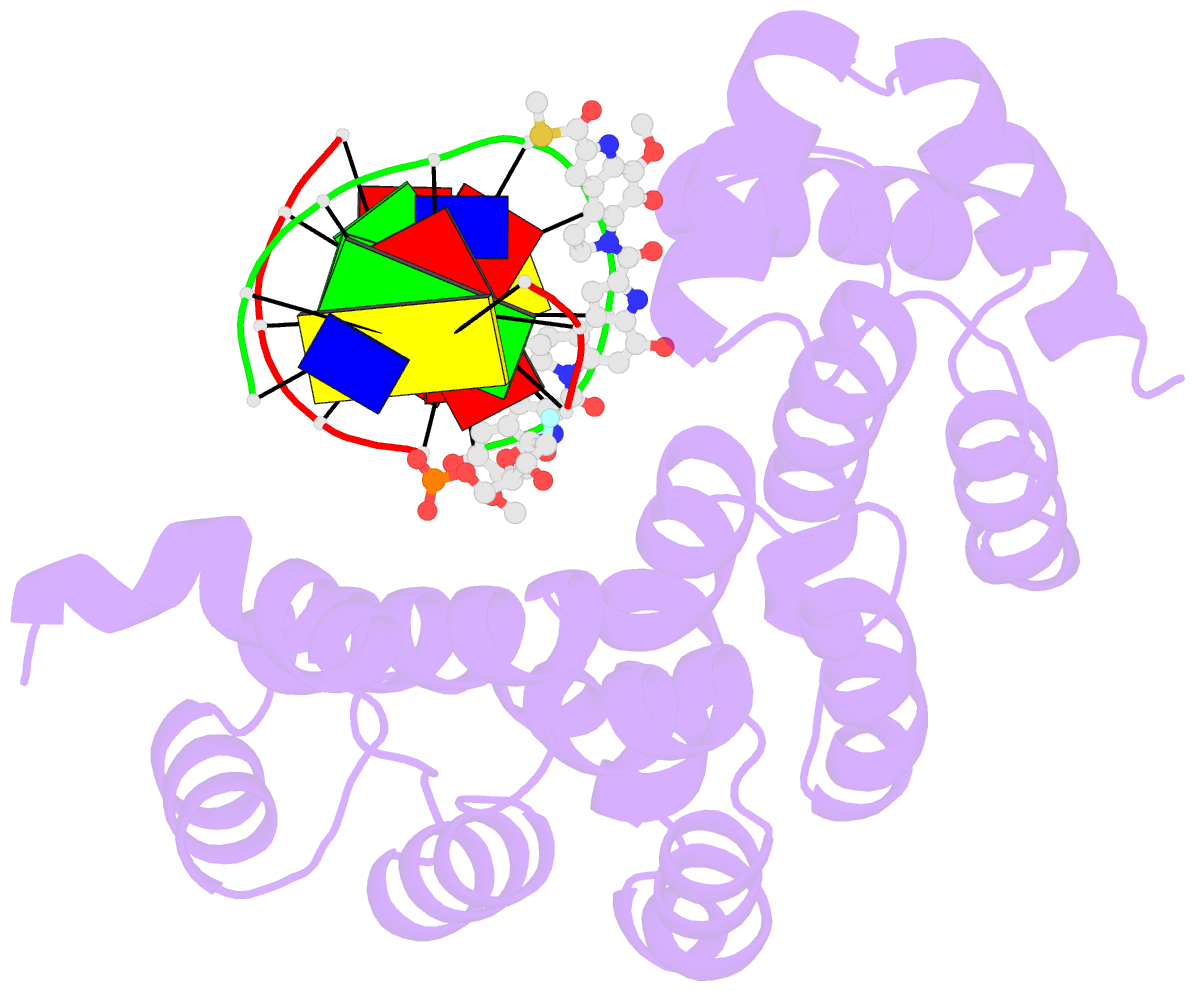
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5uuh; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA-antibiotic
- Method
- X-ray (1.569 Å)
- Summary
- Bacillus cereus DNA glycosylase alkd bound to a yatakemycin-adenine nucleobase adduct and DNA containing a fluorinated abasic site (9-mer product complex)
- Reference
- Mullins EA, Shi R, Eichman BF (2017): "Toxicity and repair of DNA adducts produced by the natural product yatakemycin." Nat. Chem. Biol., 13, 1002-1008. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2439.
- Abstract
- Yatakemycin (YTM) is an extraordinarily toxic DNA alkylating agent with potent antimicrobial and antitumor properties and is the most recent addition to the CC-1065 and duocarmycin family of natural products. Though bulky DNA lesions the size of those produced by YTM are normally removed from the genome by the nucleotide-excision repair (NER) pathway, YTM adducts are also a substrate for the bacterial DNA glycosylases AlkD and YtkR2, unexpectedly implicating base-excision repair (BER) in their elimination. The reason for the extreme toxicity of these lesions and the molecular basis for the way they are eliminated by BER have been unclear. Here, we describe the structural and biochemical properties of YTM adducts that are responsible for their toxicity, and define the mechanism by which they are excised by AlkD. These findings delineate an alternative strategy for repair of bulky DNA damage and establish the cellular utility of this pathway relative to that of NER.