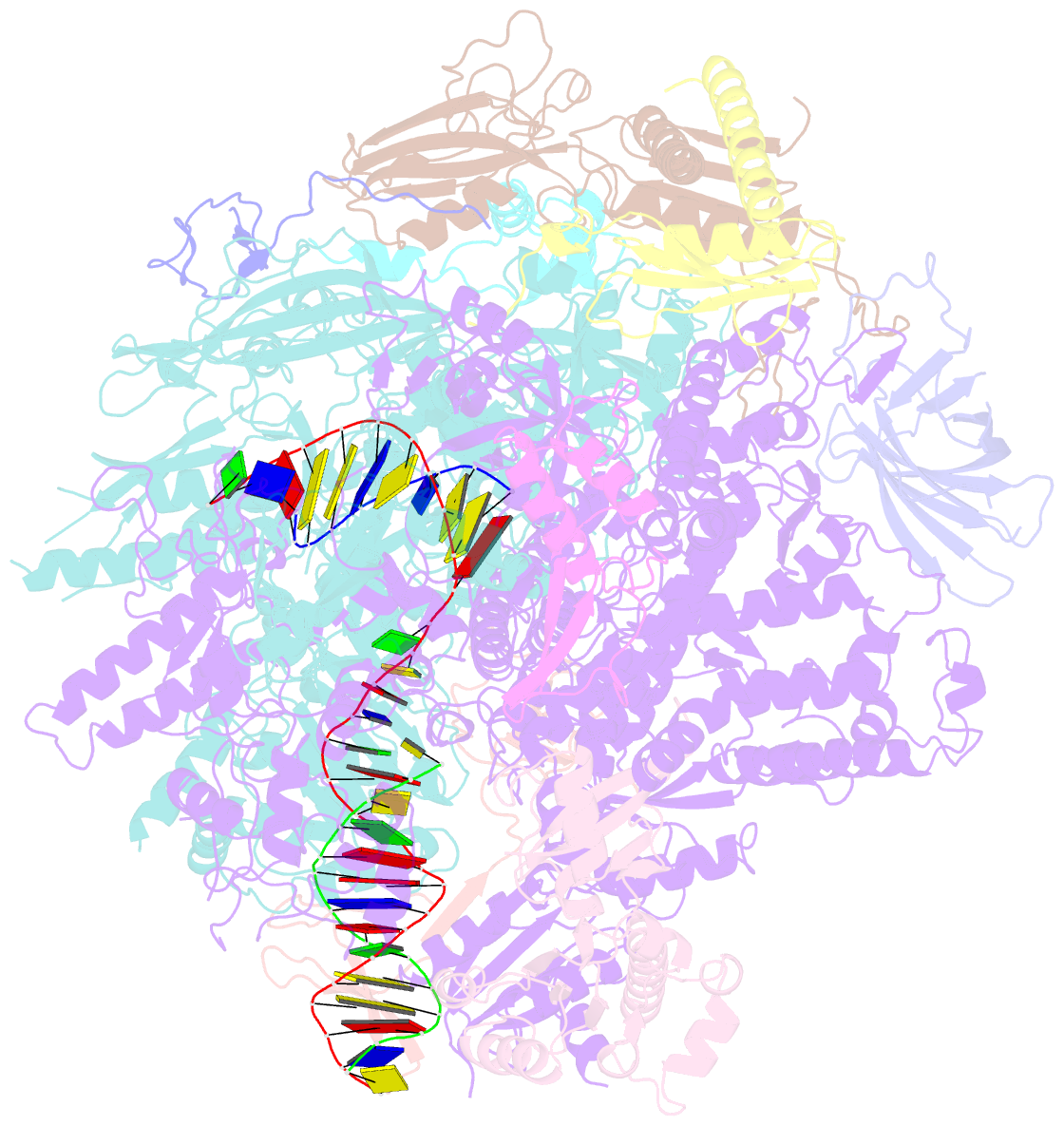
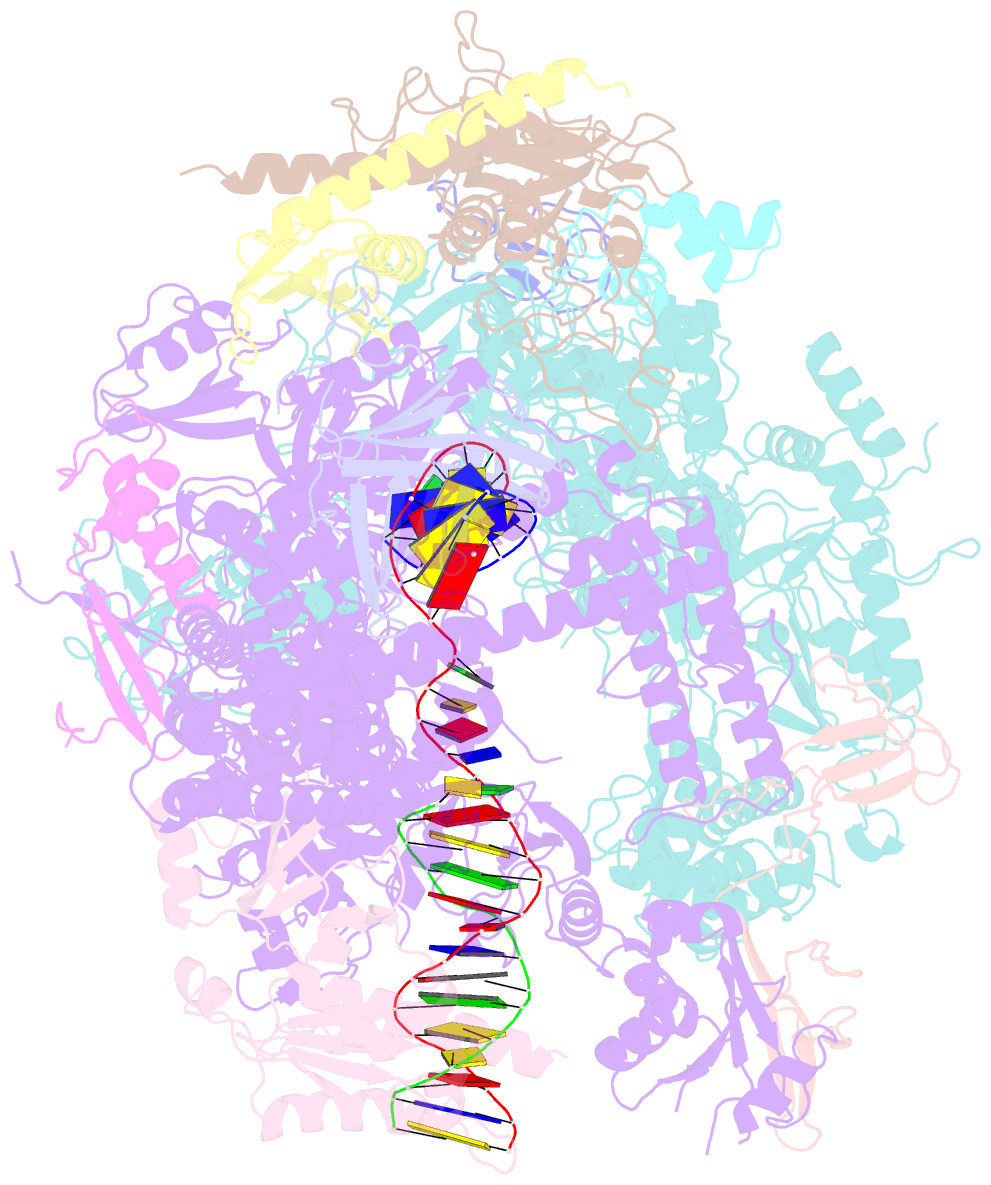
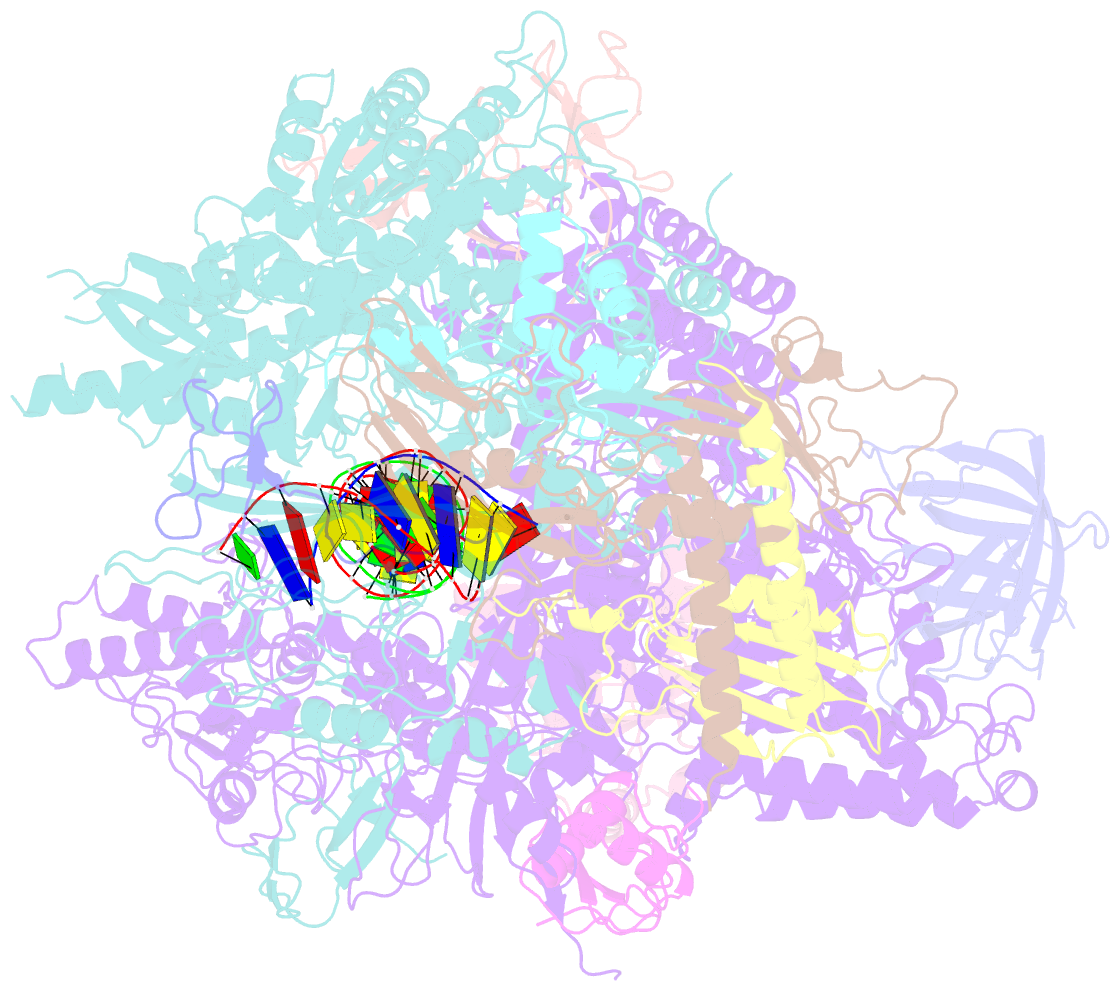
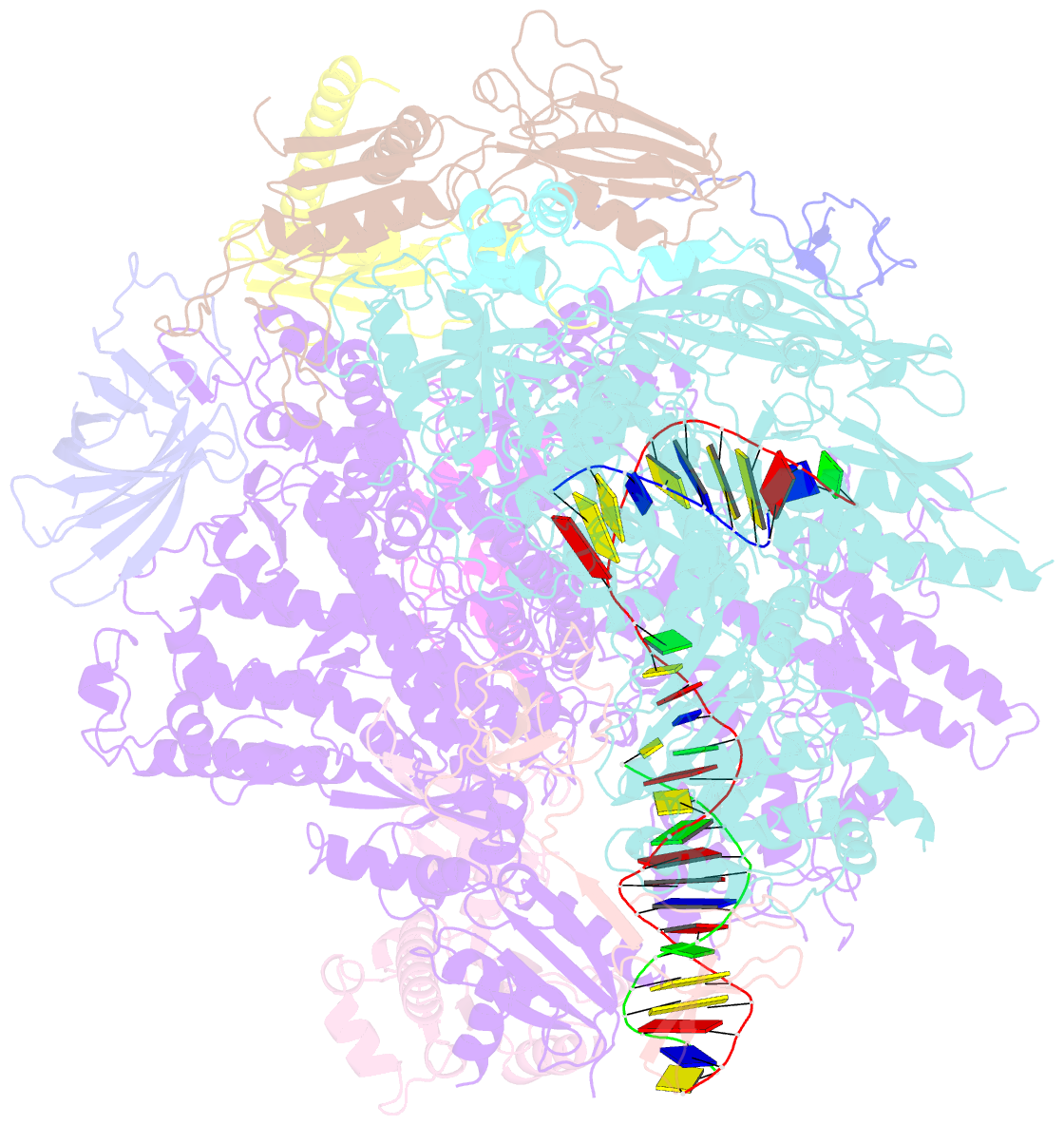
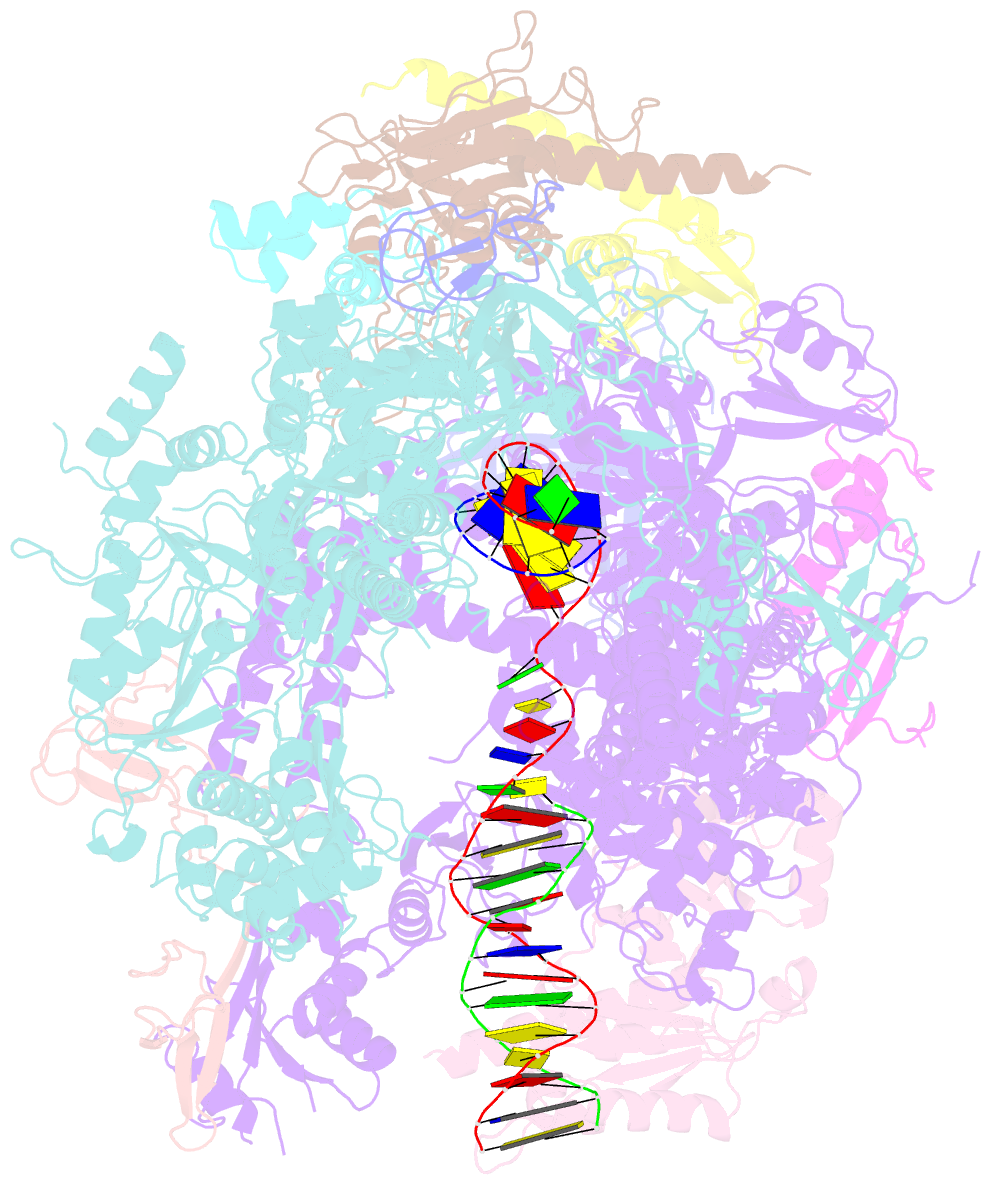
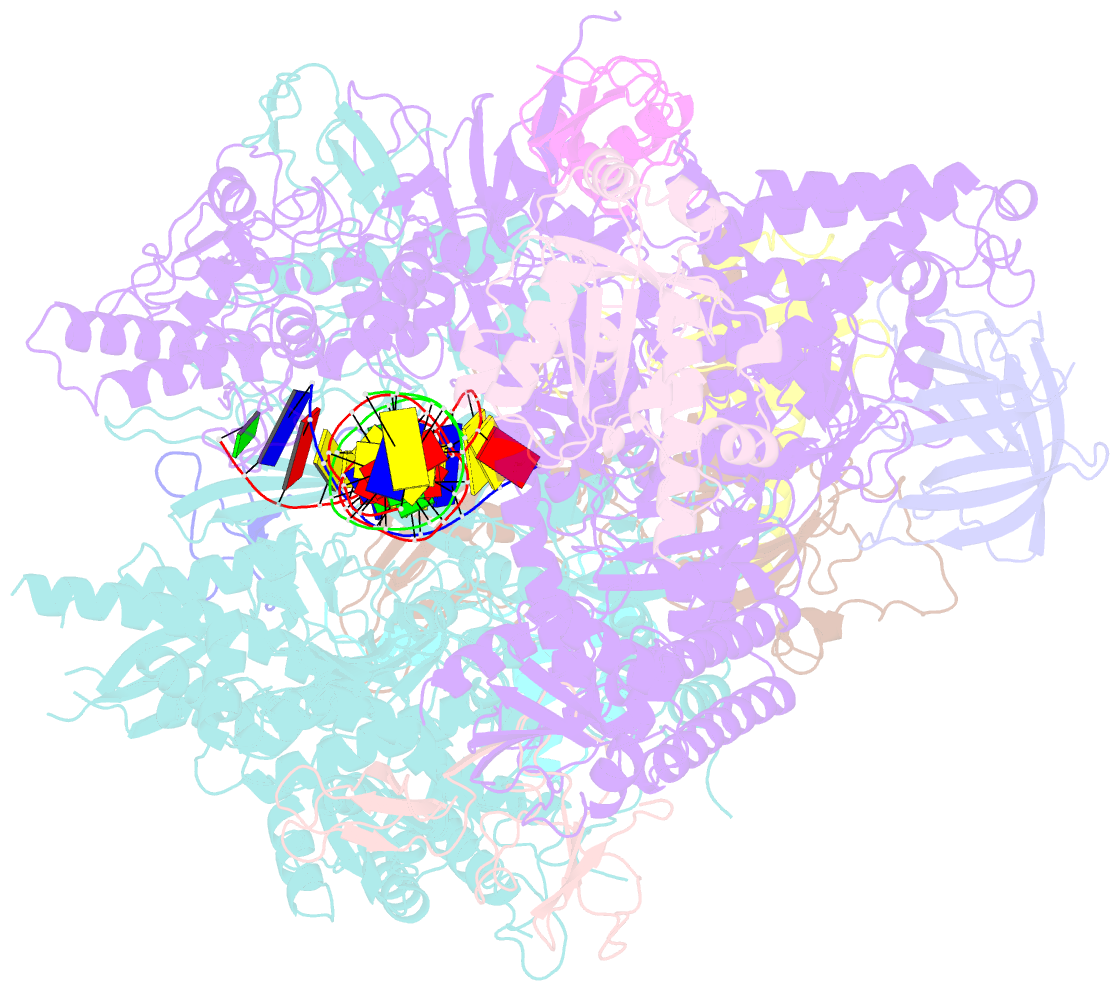
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5w51; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.404 Å)
- Summary
- Pol ii elongation complex with an n6-methyladenine-containing template and a matched umpnpp
- Reference
- Wang W, Xu L, Hu L, Chong J, He C, Wang D (2017): "Epigenetic DNA Modification N6-Methyladenine Causes Site-Specific RNA Polymerase II Transcriptional Pausing." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 139, 14436-14442. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b06381.
- Abstract
- N6-Methyladenine (N6-mA or 6 mA) is an epigenetic DNA modification in eukaryotic genomes. In contrast to the well-established roles of 5-methylcytosine for epigenetic regulation of gene expression, the functional roles of N6-mA remain elusive. In particular, the impact of N6-mA modification of the DNA template on RNA polymerase II (pol II) transcription elongation is not known. In this work, using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae pol II transcriptional elongation system as a model, we investigated the molecular mechanism of pol II recognition and processing of N6-mA sites via both biochemical and structural approaches. We found that N6-mA causes site-specific pol II pausing/stalling. Structural analysis revealed that while N6-mA can reach the +1 template position, the stability of the N6-mA and UTP base pairing is compromised. Taken together, we reveal that the presence of the 6-methyl group on adenine reduces incorporation efficiency and promotes backtracking translocation. Our studies with yeast pol II provide molecular insights into understanding the impacts of N6-mA on pol II transcription dynamics in different organisms.