Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5w5y; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.8 Å)
- Summary
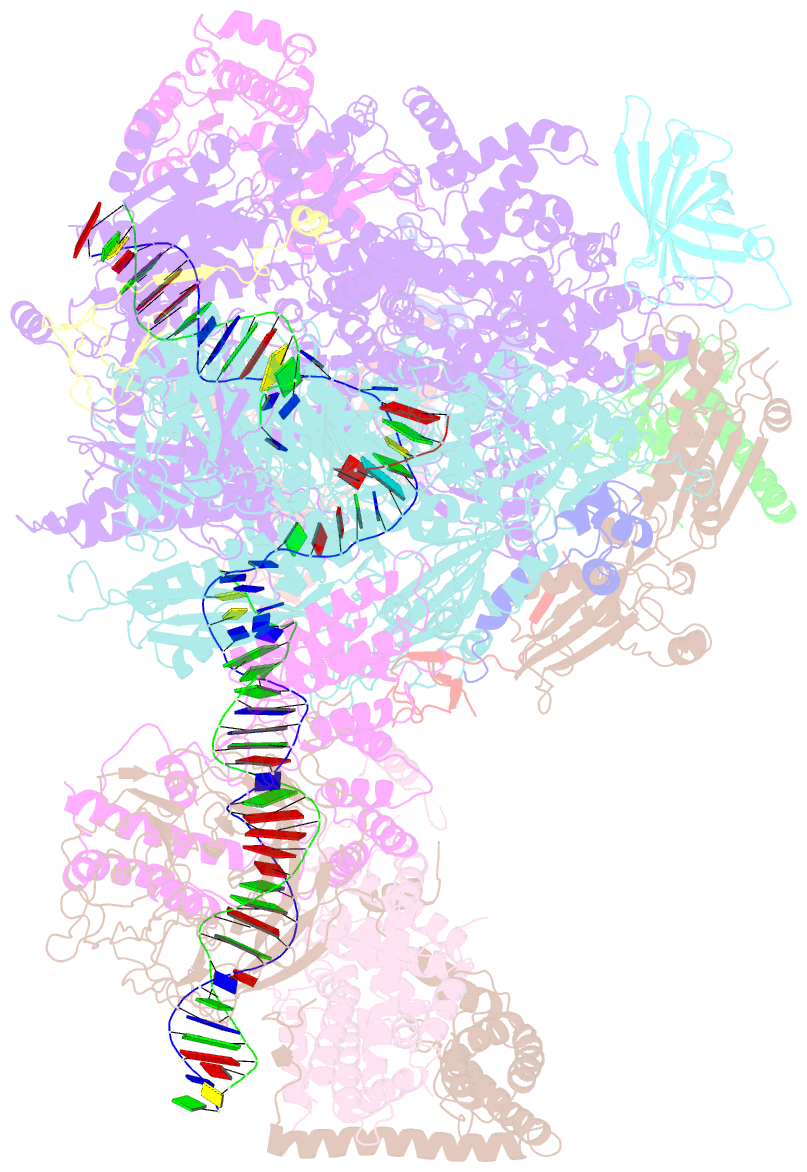
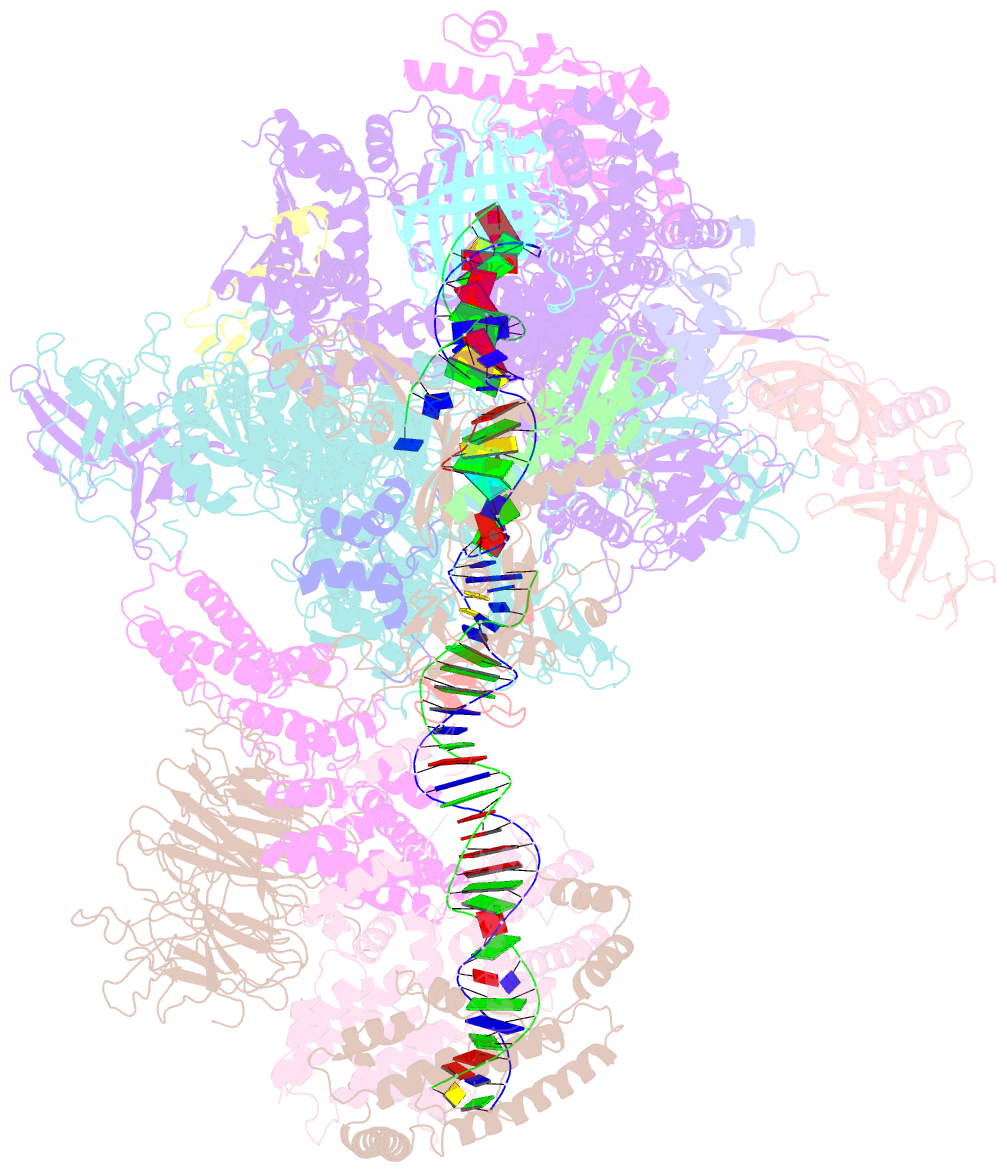
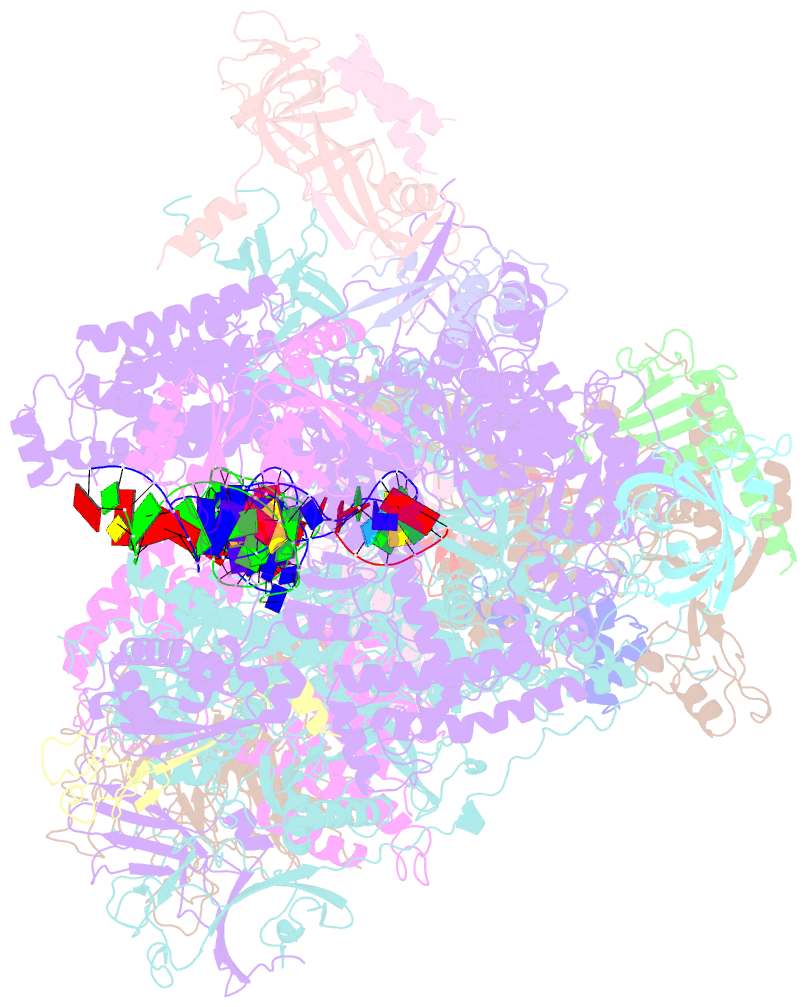
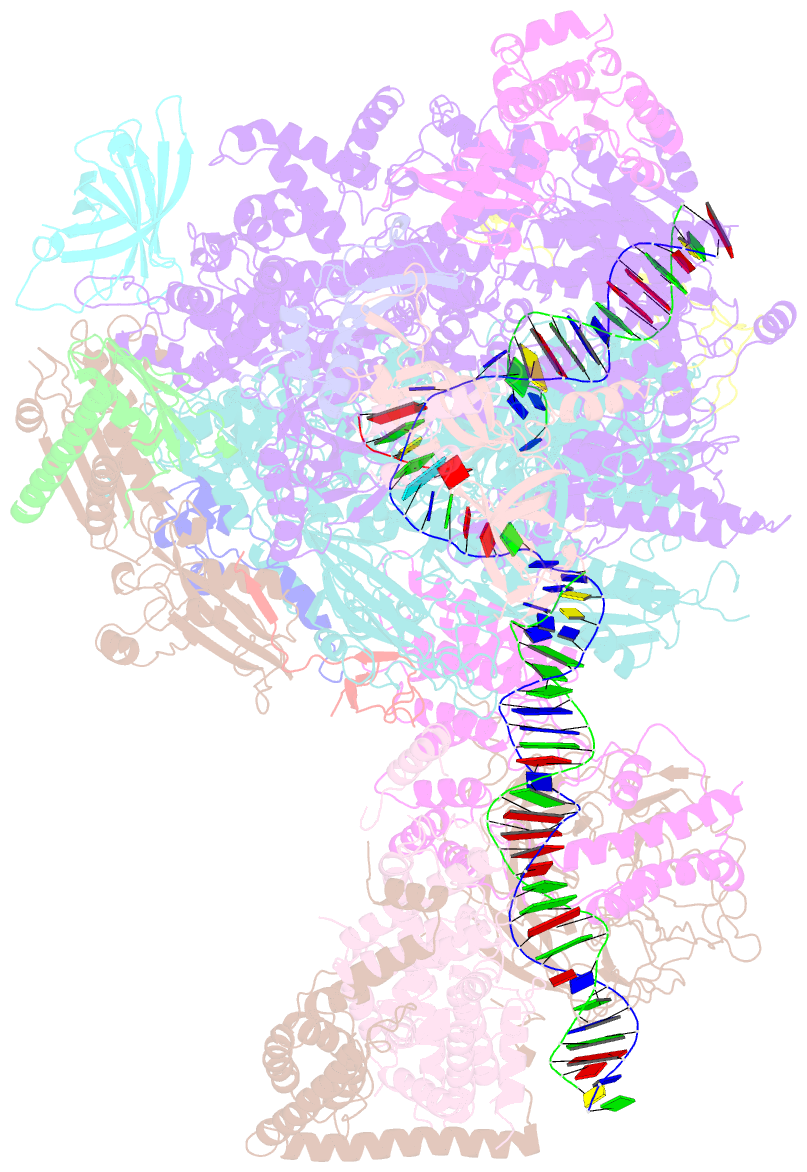
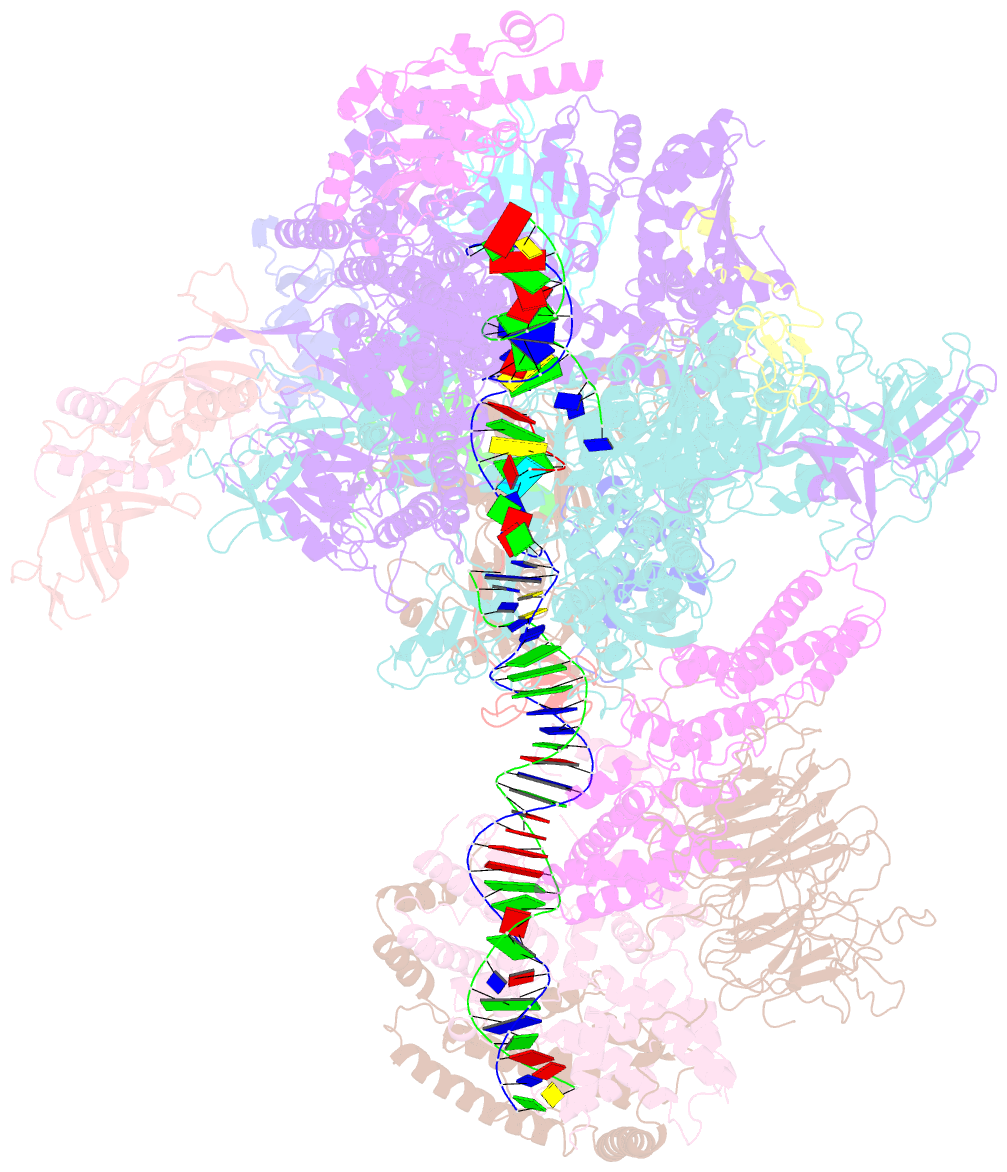
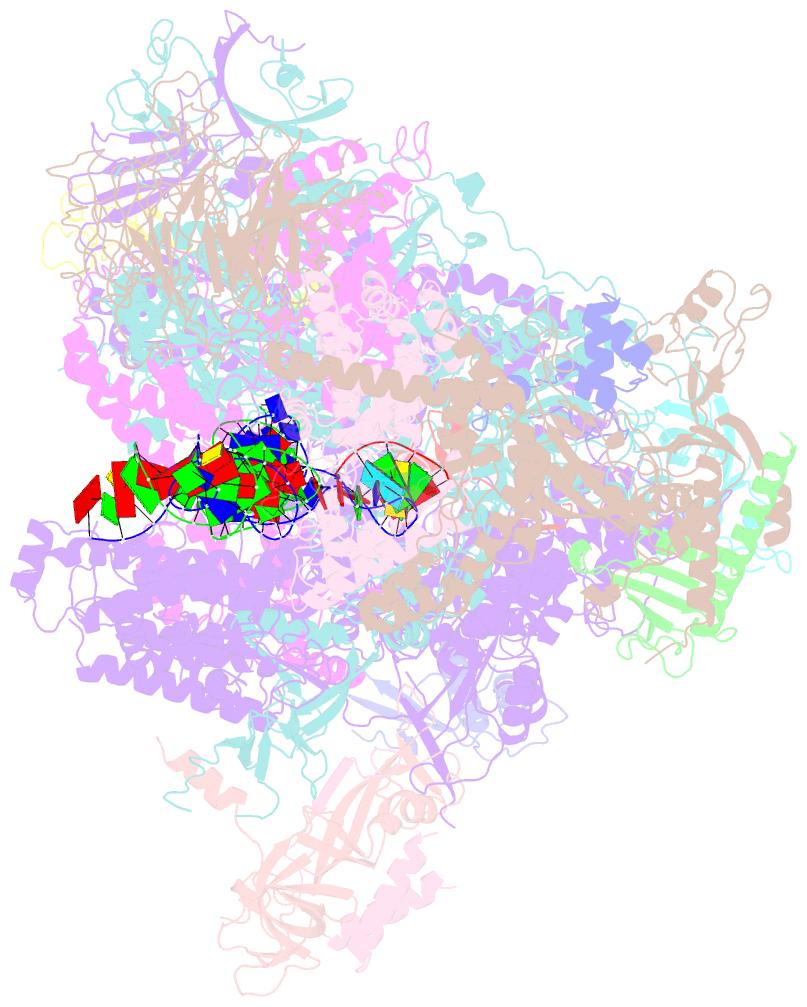
- RNA polymerase i initial transcribing complex
- Reference
- Han Y, Yan C, Nguyen THD, Jackobel AJ, Ivanov I, Knutson BA, He Y (2017): "Structural mechanism of ATP-independent transcription initiation by RNA polymerase I." Elife, 6. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27414.
- Abstract
- Transcription initiation by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) depends on the Core Factor (CF) complex to recognize the upstream promoter and assemble into a Pre-Initiation Complex (PIC). Here, we solve a structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pol I-CF-DNA to 3.8 Å resolution using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. The structure reveals a bipartite architecture of Core Factor and its recognition of the promoter from -27 to -16. Core Factor's intrinsic mobility correlates well with different conformational states of the Pol I cleft, in addition to the stabilization of either Rrn7 N-terminal domain near Pol I wall or the tandem winged helix domain of A49 at a partially overlapping location. Comparison of the three states in this study with the Pol II system suggests that a ratchet motion of the Core Factor-DNA sub-complex at upstream facilitates promoter melting in an ATP-independent manner, distinct from a DNA translocase actively threading the downstream DNA in the Pol II PIC.