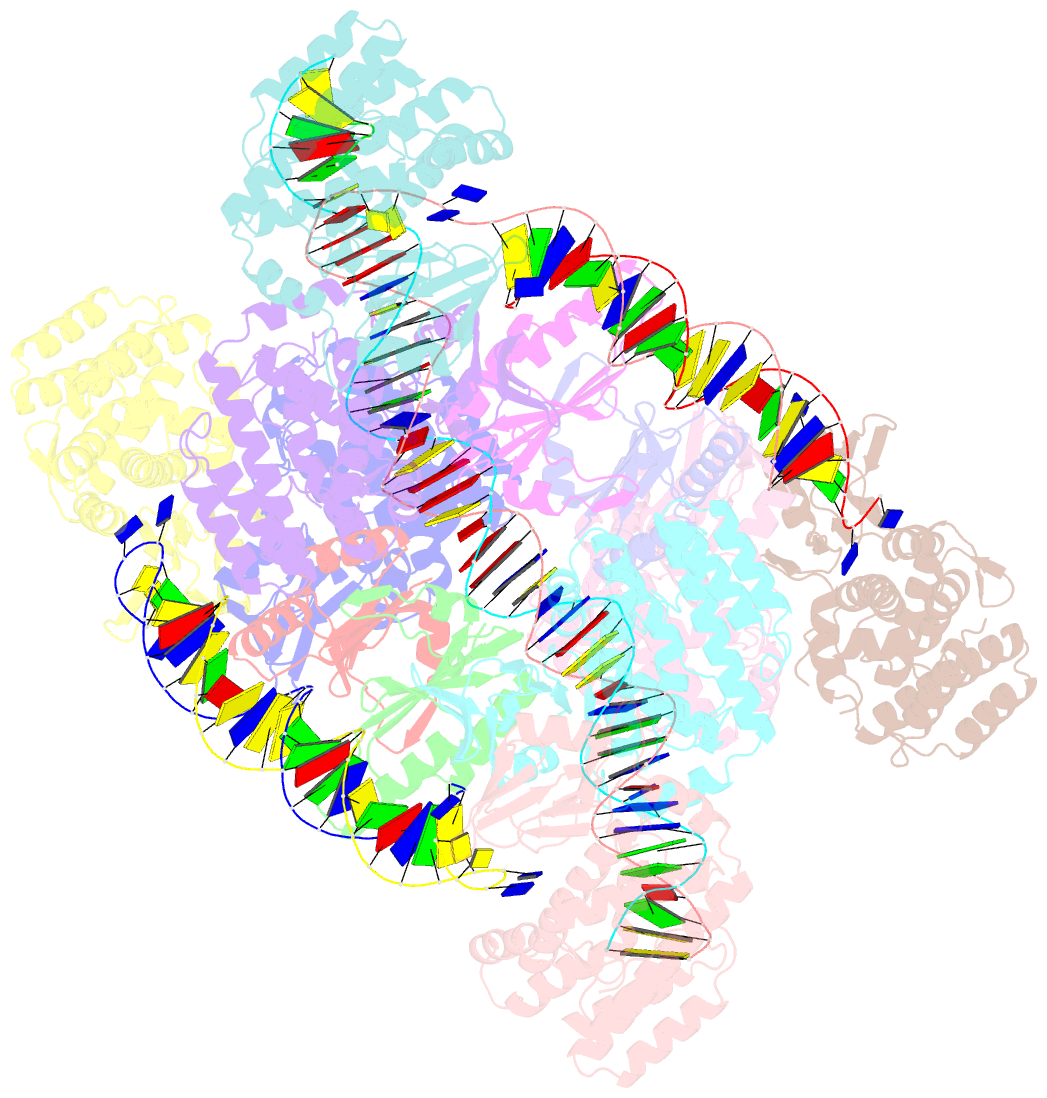
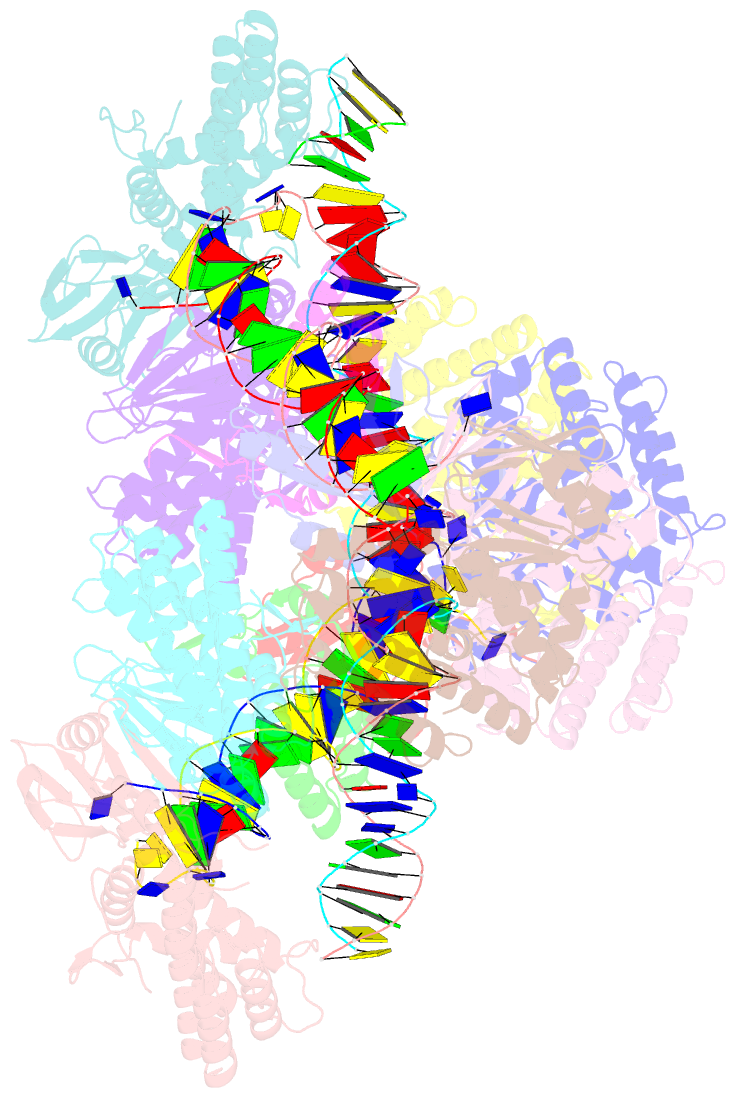
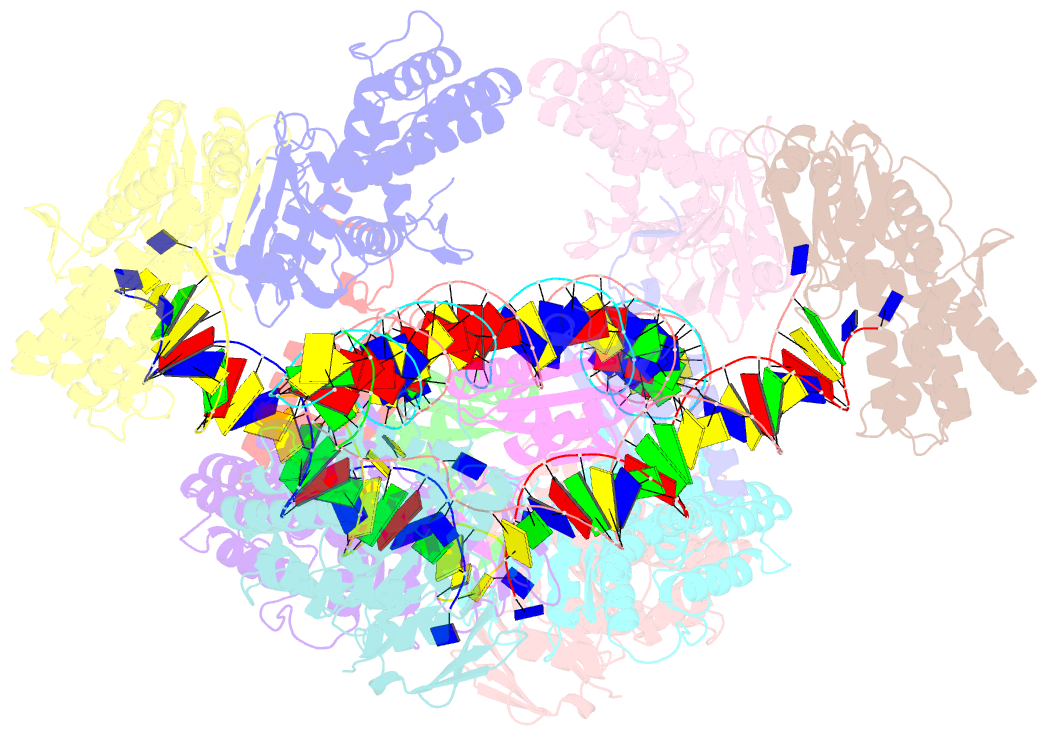
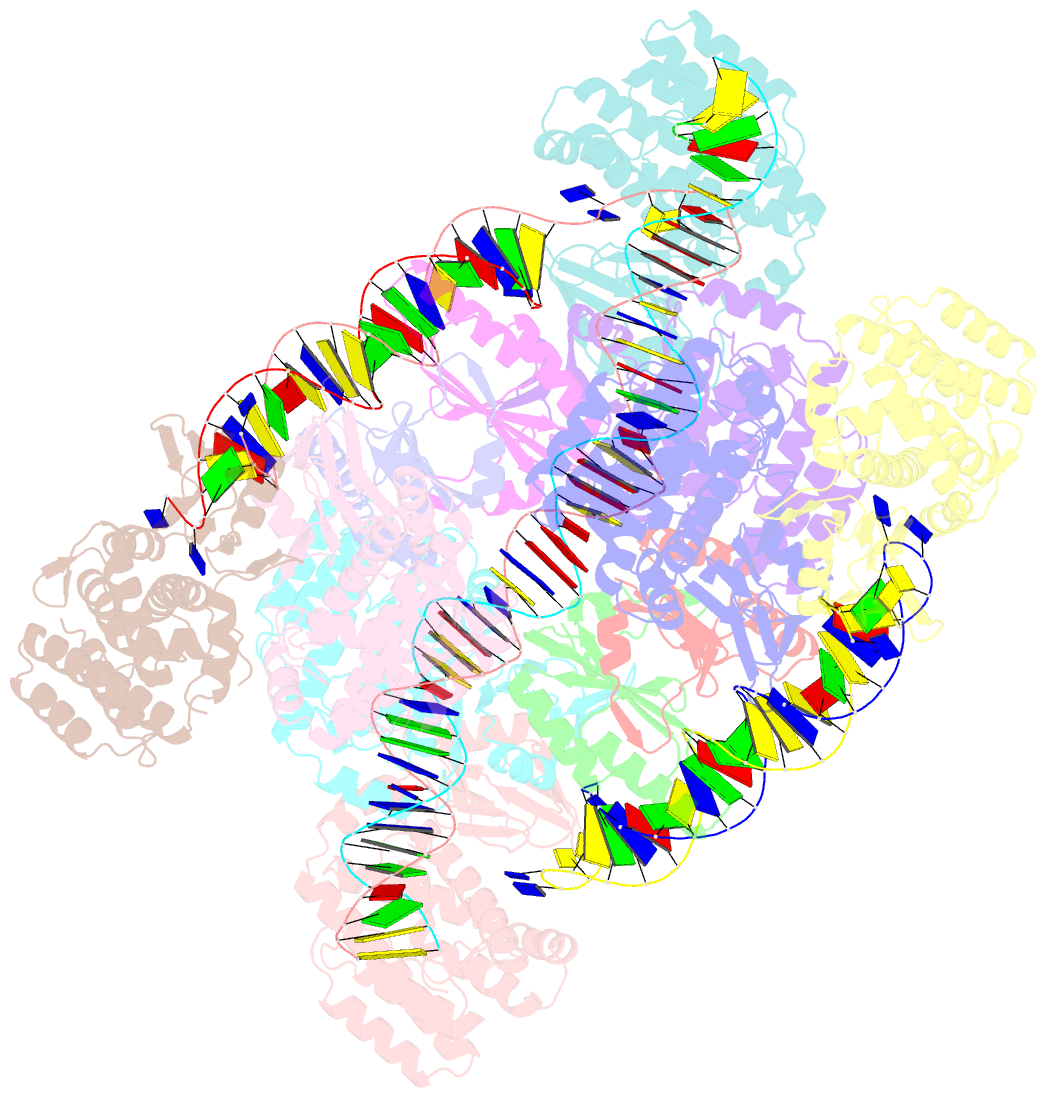
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5xvo; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- immune system
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
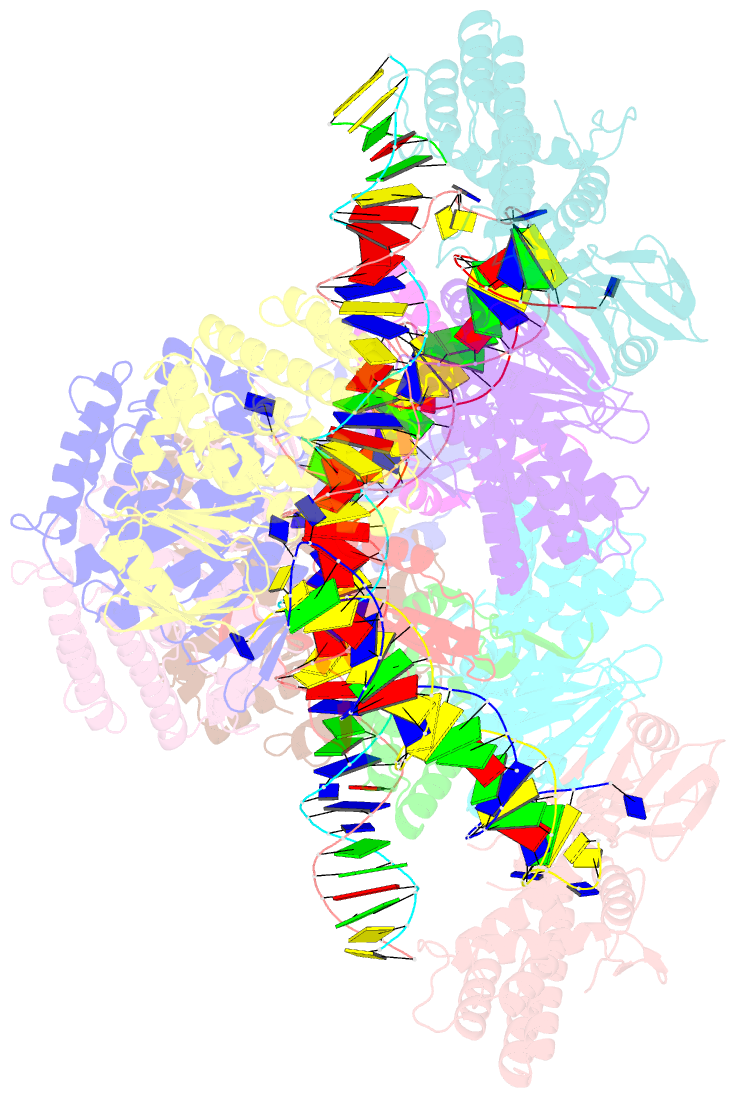
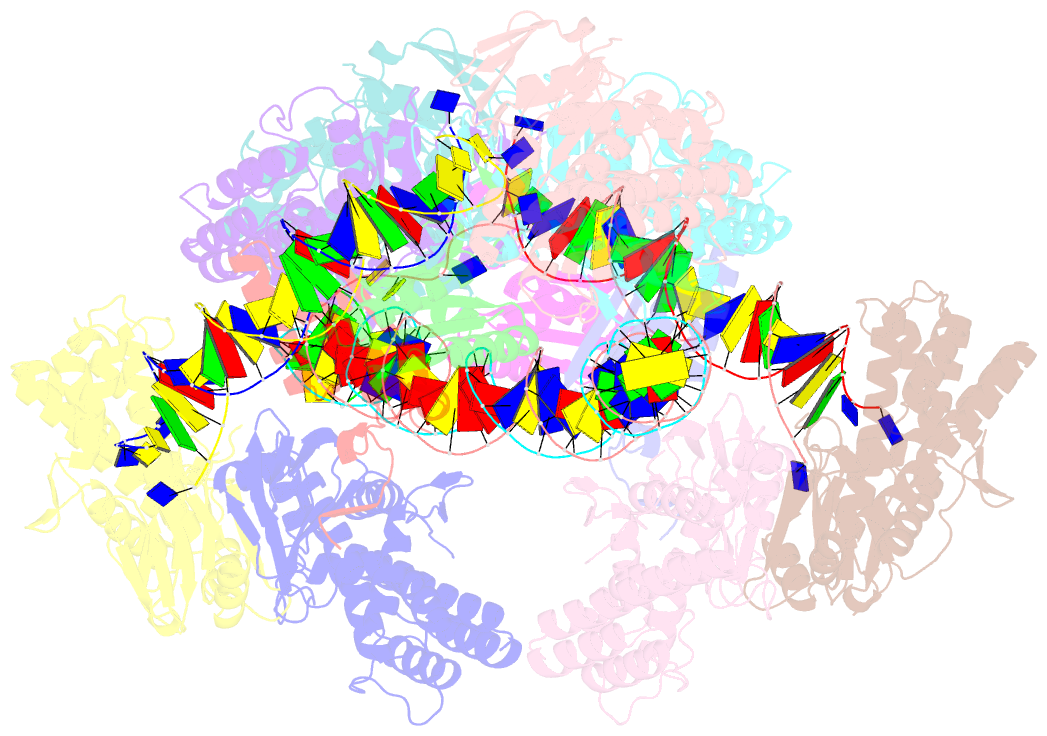
- E. fae cas1-cas2-prespacer-target ternary complex revealing DNA sampling and half-integration states
- Reference
- Xiao Y, Ng S, Hyun Nam K, Ke A (2017): "How type II CRISPR-Cas establish immunity through Cas1-Cas2-mediated spacer integration." Nature, 550, 137-141. doi: 10.1038/nature24020.
- Abstract
- CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) and the nearby Cas (CRISPR-associated) operon establish an RNA-based adaptive immunity system in prokaryotes. Molecular memory is created when a short foreign DNA-derived prespacer is integrated into the CRISPR array as a new spacer. Whereas the RNA-guided CRISPR interference mechanism varies widely among CRISPR-Cas systems, the spacer integration mechanism is essentially identical. The conserved Cas1 and Cas2 proteins form an integrase complex consisting of two distal Cas1 dimers bridged by a Cas2 dimer. The prespacer is bound by Cas1-Cas2 as a dual-forked DNA, and the terminal 3'-OH of each 3' overhang serves as an attacking nucleophile during integration. The prespacer is preferentially integrated into the leader-proximal region of the CRISPR array, guided by the leader sequence and a pair of inverted repeats inside the CRISPR repeat. Spacer integration in the well-studied Escherichia coli type I-E CRISPR system also relies on the bacterial integration host factor. In type II-A CRISPR, however, Cas1-Cas2 alone integrates spacers efficiently in vitro; other Cas proteins (such as Cas9 and Csn2) have accessory roles in the biogenesis phase of prespacers. Here we present four structural snapshots from the type II-A system of Enterococcus faecalis Cas1 and Cas2 during spacer integration. Enterococcus faecalis Cas1-Cas2 selectively binds to a splayed 30-base-pair prespacer bearing 4-nucleotide 3' overhangs. Three molecular events take place upon encountering a target: first, the Cas1-Cas2-prespacer complex searches for half-sites stochastically, then it preferentially interacts with the leader-side CRISPR repeat, and finally, it catalyses a nucleophilic attack that connects one strand of the leader-proximal repeat to the prespacer 3' overhang. Recognition of the spacer half-site requires DNA bending and leads to full integration. We derive a mechanistic framework to explain the stepwise spacer integration process and the leader-proximal preference.