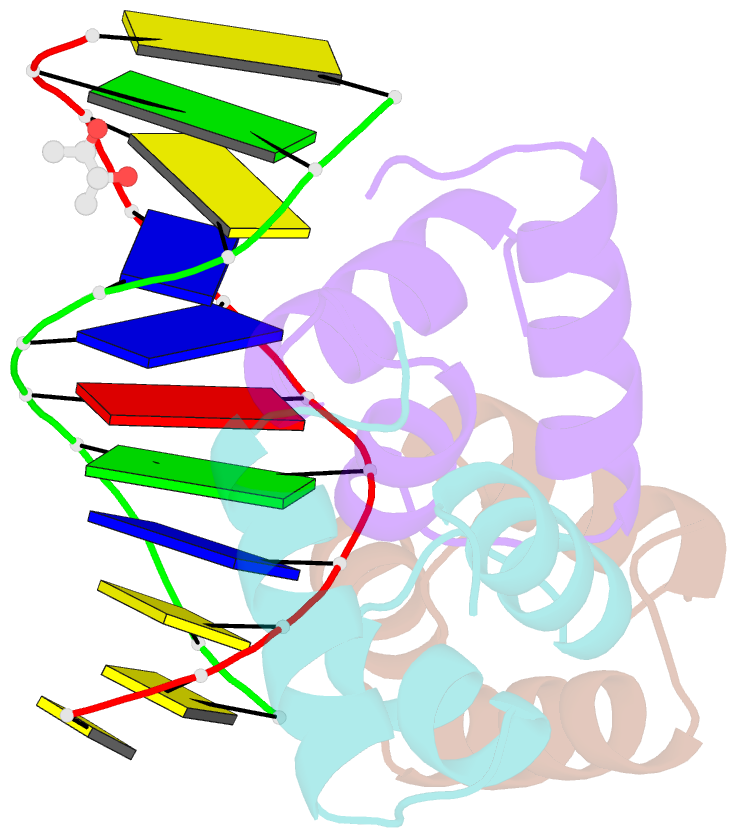
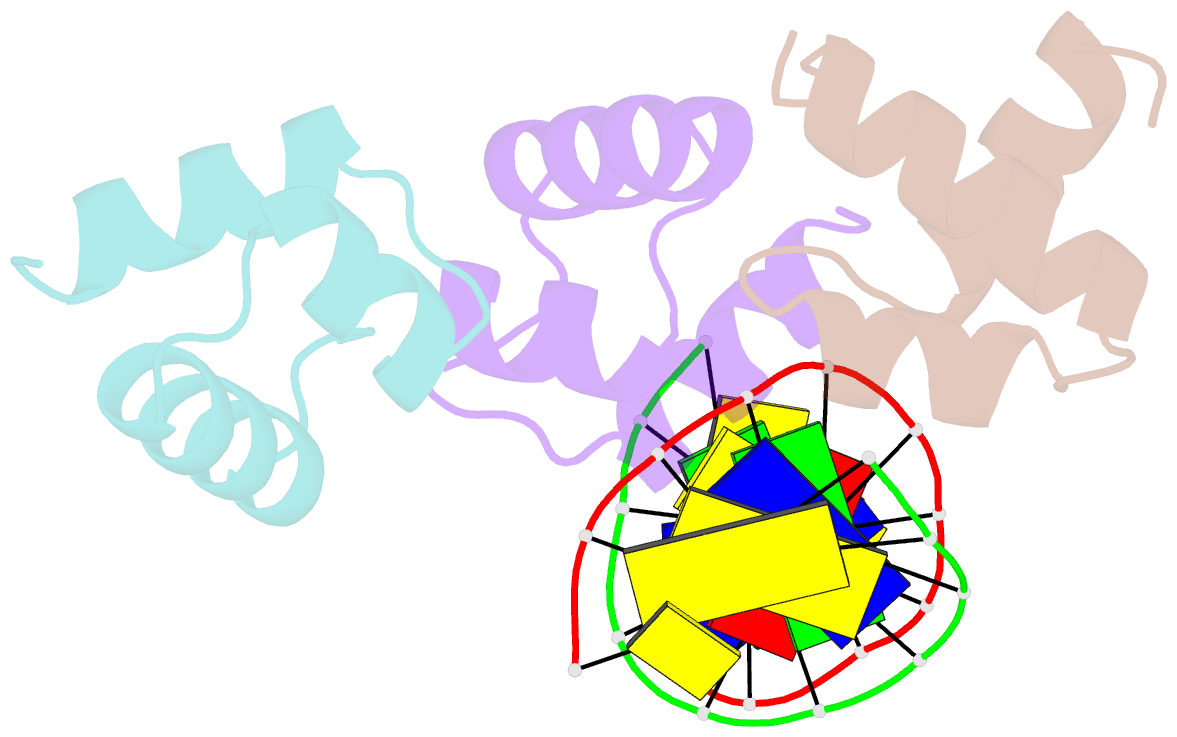
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5z7i; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.601 Å)
- Summary
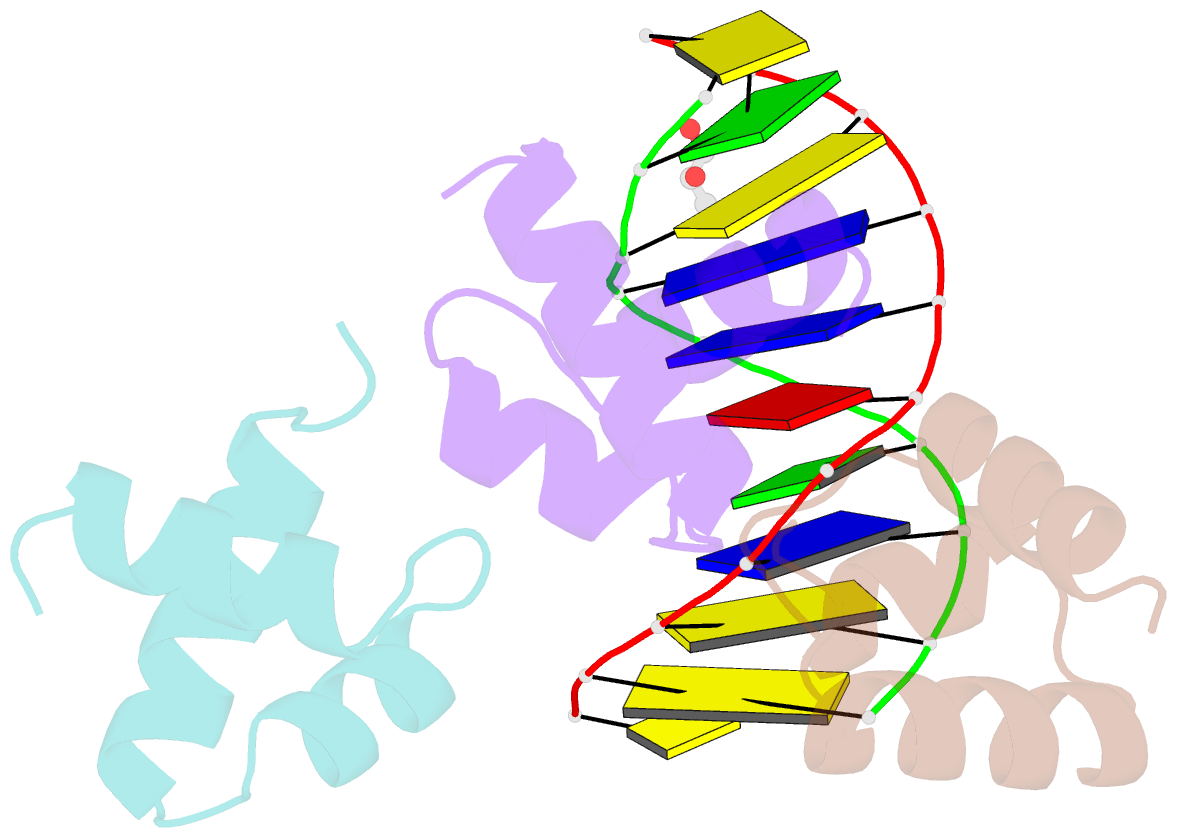
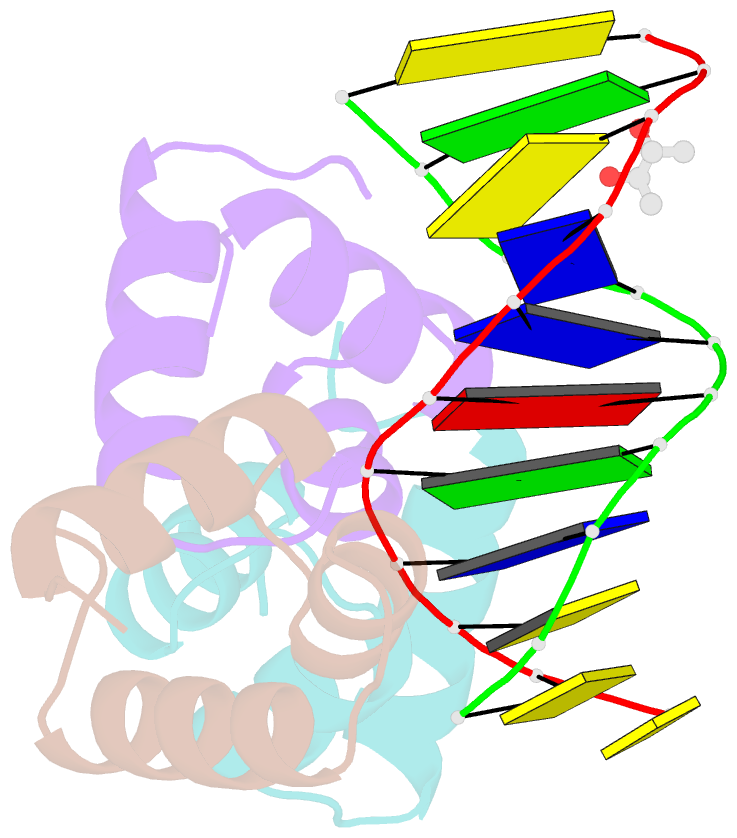
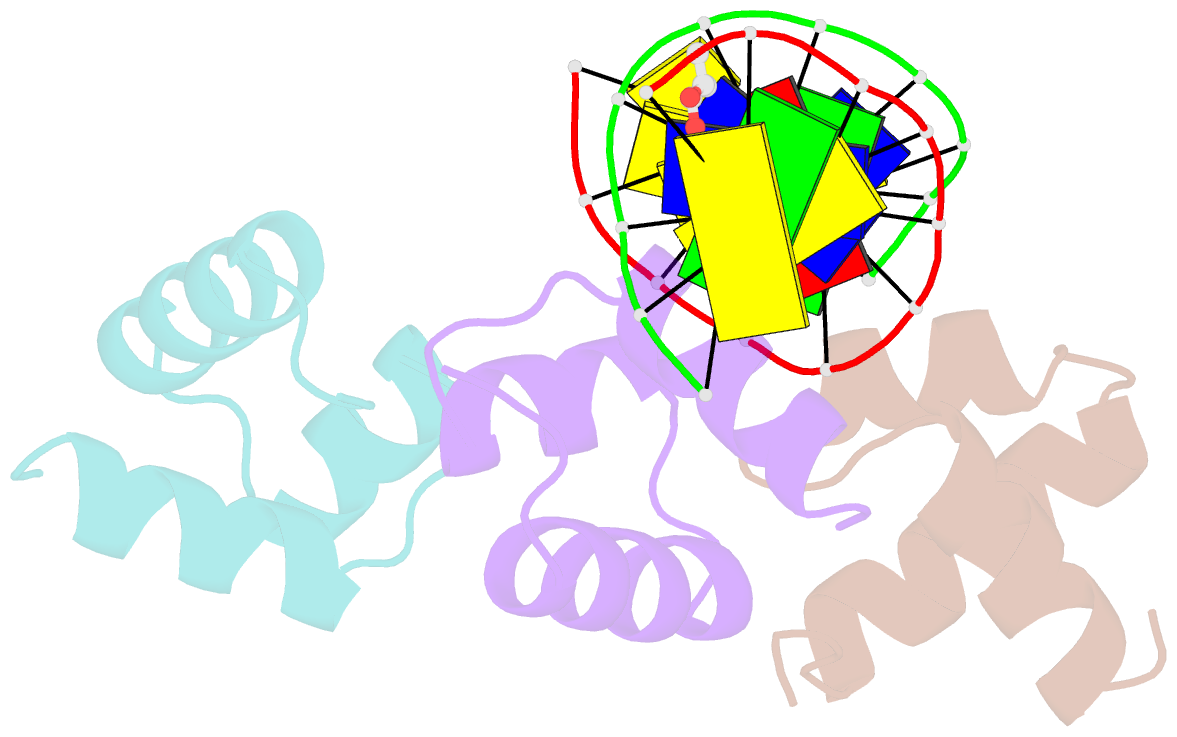
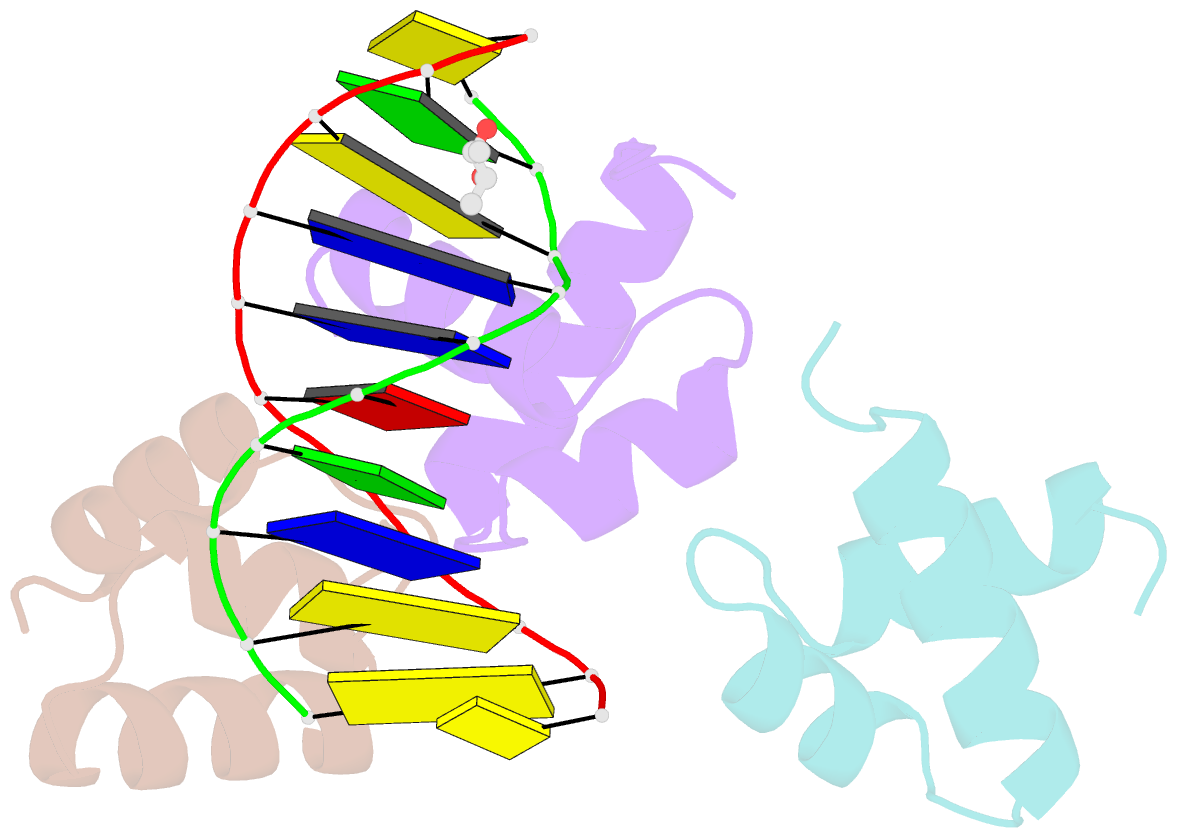
- Caulobacter crescentus gcra DNA-binding domain(dbd)in complex with unmethylated dsDNA
- Reference
- Wu X, Haakonsen DL, Sanderlin AG, Liu YJ, Shen L, Zhuang N, Laub MT, Zhang Y (2018): "Structural insights into the unique mechanism of transcription activation by Caulobacter crescentus GcrA." Nucleic Acids Res., 46, 3245-3256. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky161.
- Abstract
- Canonical bacterial transcription activators bind to non-transcribed promoter elements to increase transcription of their target genes. Here we report crystal structures of binary complexes comprising domains of Caulobacter crescentus GcrA, a noncanonical bacterial transcription factor, that support a novel mechanism for transcription activation through the preferential binding of methylated cis-regulatory elements and the promotion of open complex formation through an interaction with region 2 of the principal σ factor, σ70. We present crystal structures of the C-terminal, σ factor-interacting domain (GcrA-SID) in complex with domain 2 of σ70 (σ702), and the N-terminal, DNA-binding domain (GcrA-DBD) in complex with methylated double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). The structures reveal interactions essential for transcription activation and DNA recognition by GcrA. These structures, along with mutational analyses, support a mechanism of transcription activation in which GcrA associates with RNA polymerase (RNAP) prior to promoter binding through GcrA-SID, arming RNAP with a flexible GcrA-DBD. The RNAP-GcrA complex then binds and activates target promoters harboring a methylated GcrA binding site either upstream or downstream of the transcription start site.