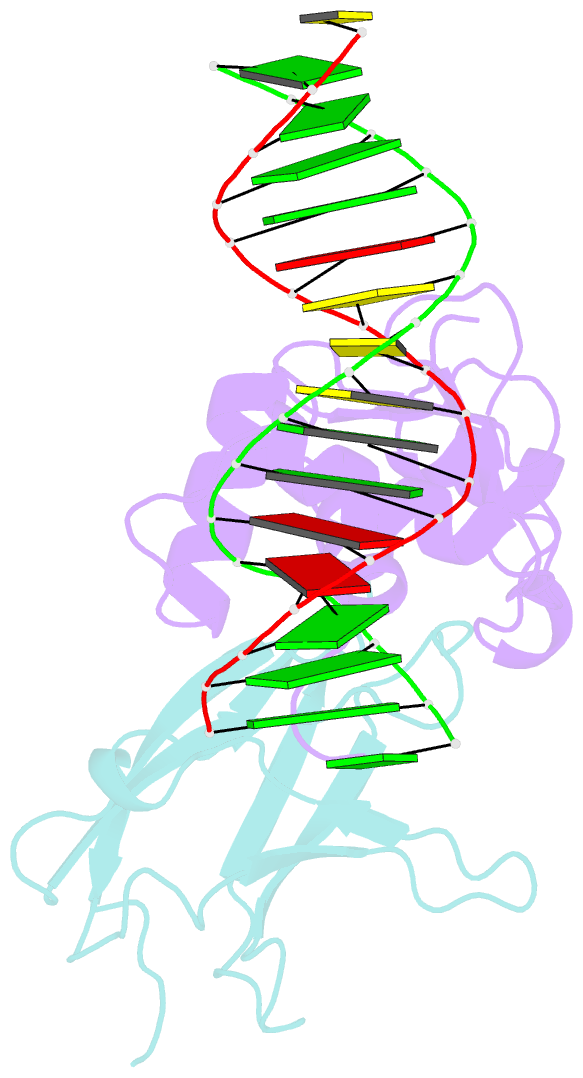
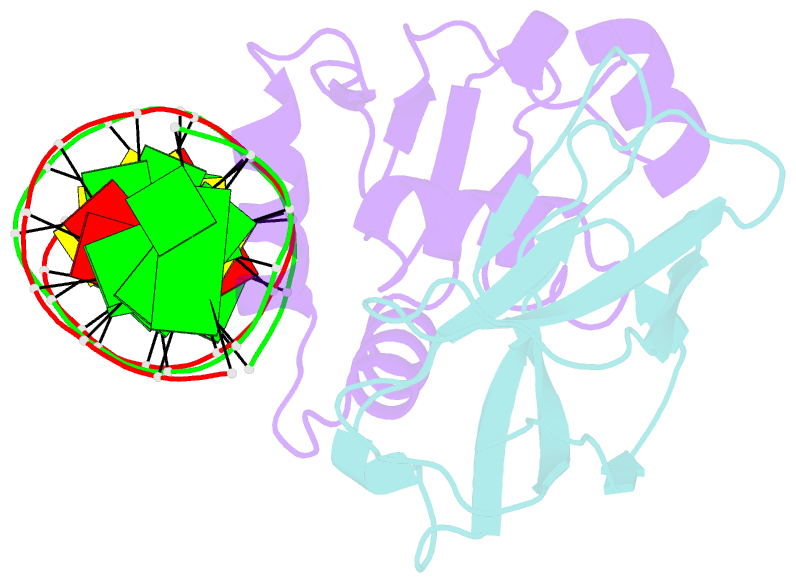
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5zmc; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.99 Å)
- Summary
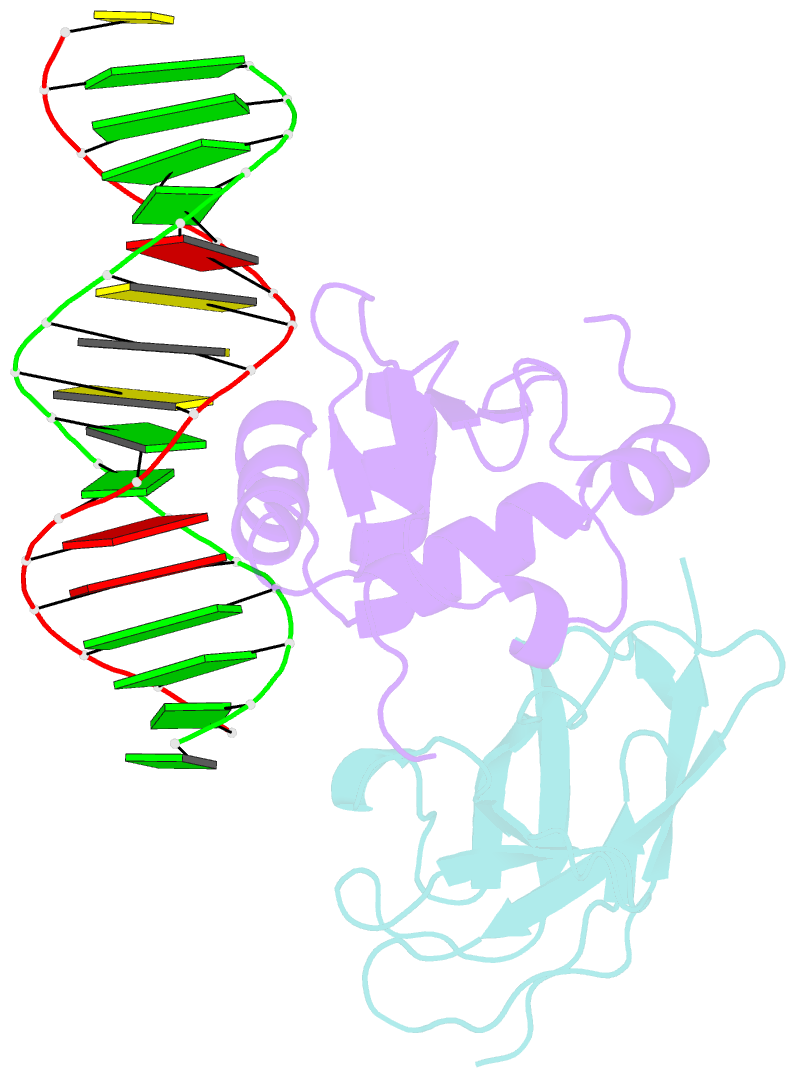
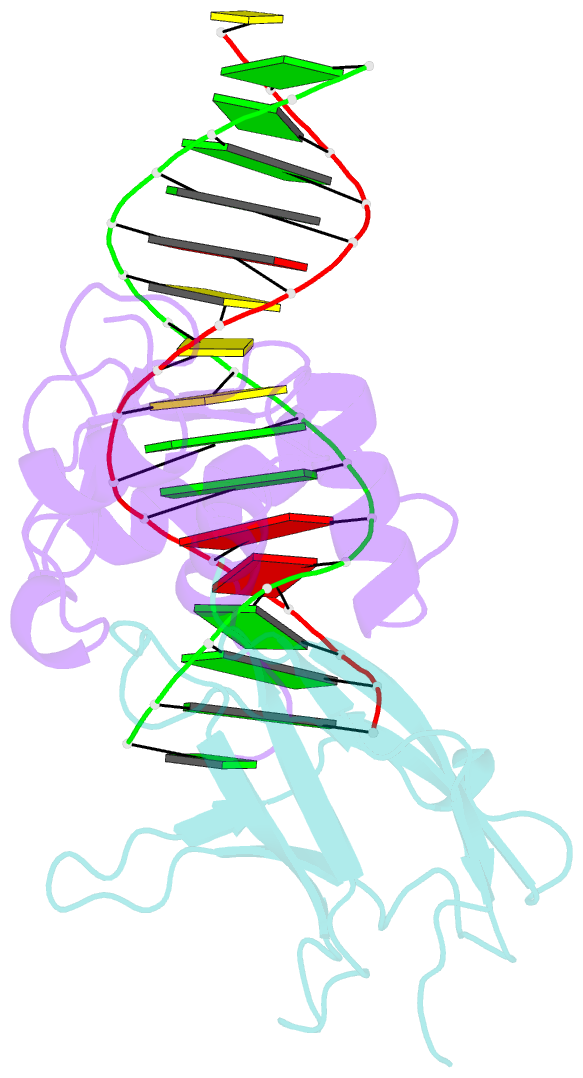
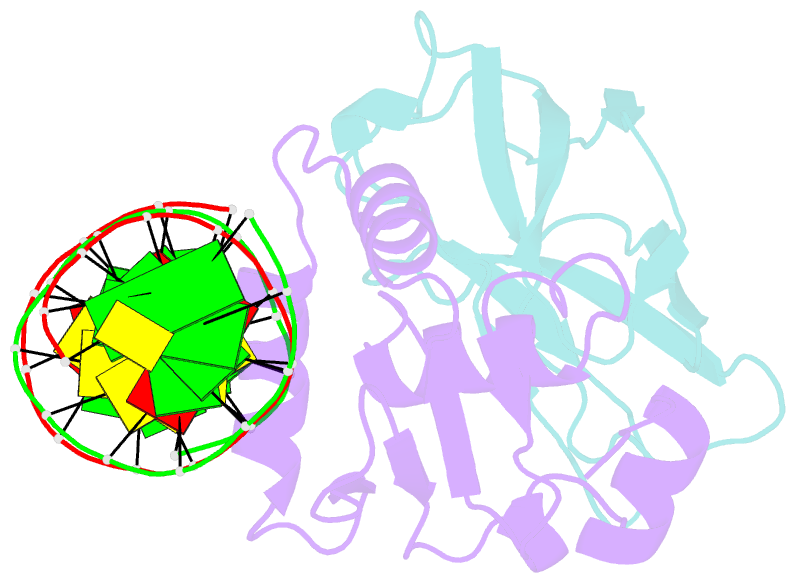
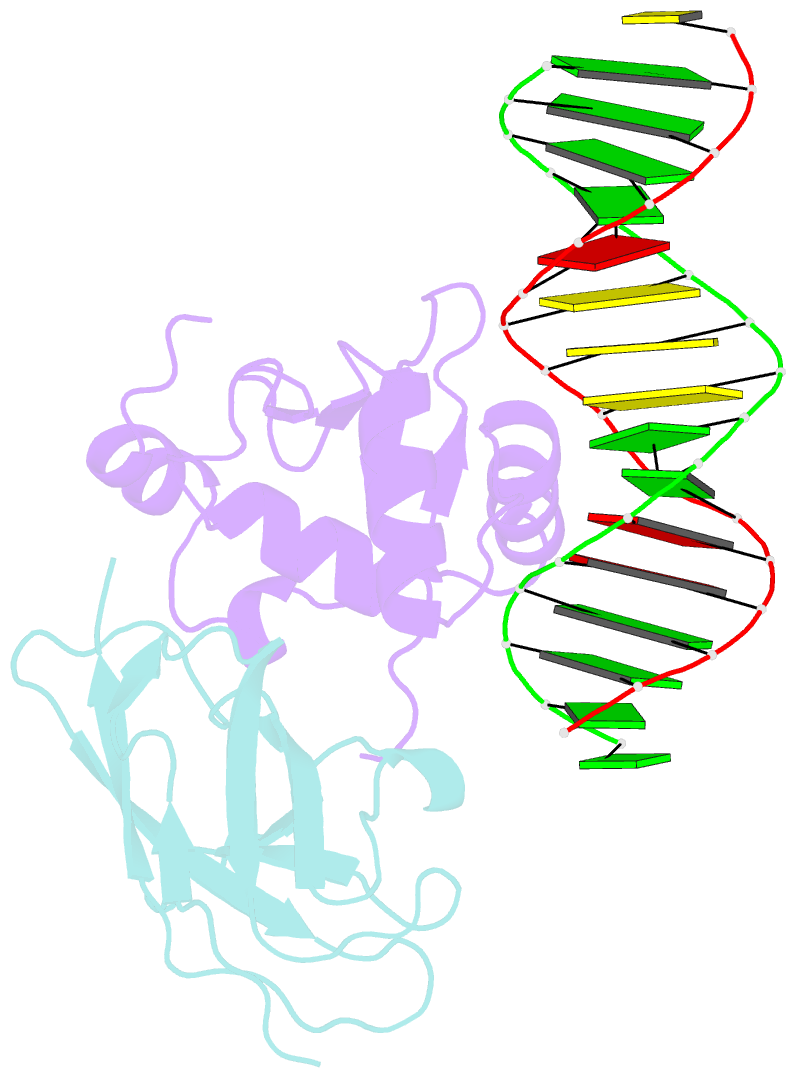
- Structural basis for reactivation of -146c>t mutant tert promoter by cooperative binding of p52 and ets1-2
- Reference
- Xu X, Li Y, Bharath SR, Ozturk MB, Bowler MW, Loo BZL, Tergaonkar V, Song H (2018): "Structural basis for reactivating the mutant TERT promoter by cooperative binding of p52 and ETS1." Nat Commun, 9, 3183. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05644-0.
- Abstract
- Transcriptional factors ETS1/2 and p52 synergize downstream of non-canonical NF-κB signaling to drive reactivation of the -146C>T mutant TERT promoter in multiple cancer types, but the mechanism underlying this cooperativity remains unknown. Here we report the crystal structure of a ternary p52/ETS1/-146C>T TERT promoter complex. While p52 needs to associate with consensus κB sites on the DNA to function during non-canonical NF-κB signaling, we show that p52 can activate the -146C>T TERT promoter without binding DNA. Instead, p52 interacts with ETS1 to form a heterotetramer, counteracting autoinhibition of ETS1. Analogous to observations with the GABPA/GABPB heterotetramer, the native flanking ETS motifs are required for sustained activation of the -146C>T TERT promoter by the p52/ETS1 heterotetramer. These observations provide a unifying mechanism for transcriptional activation by GABP and ETS1, and suggest that genome-wide targets of non-canonical NF-κB signaling are not limited to those driven by consensus κB sequences.