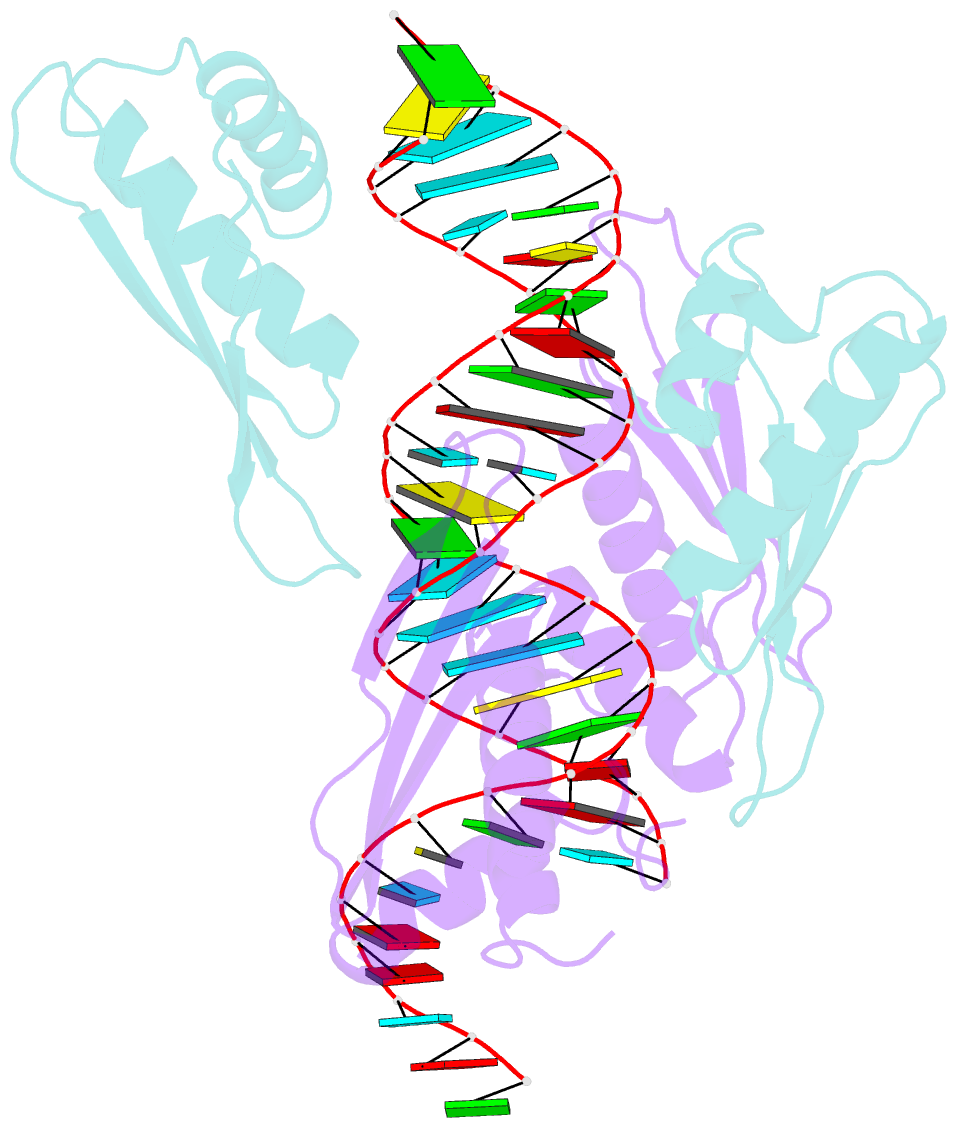
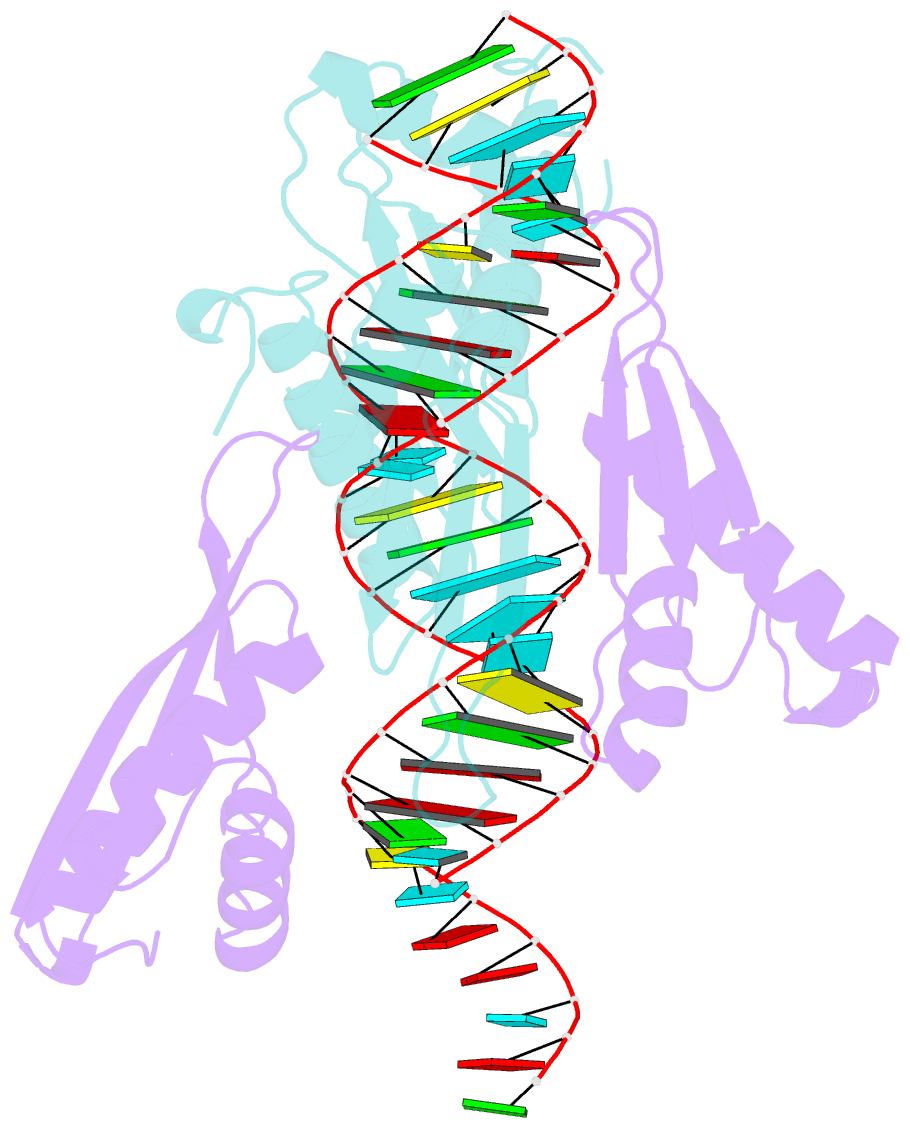
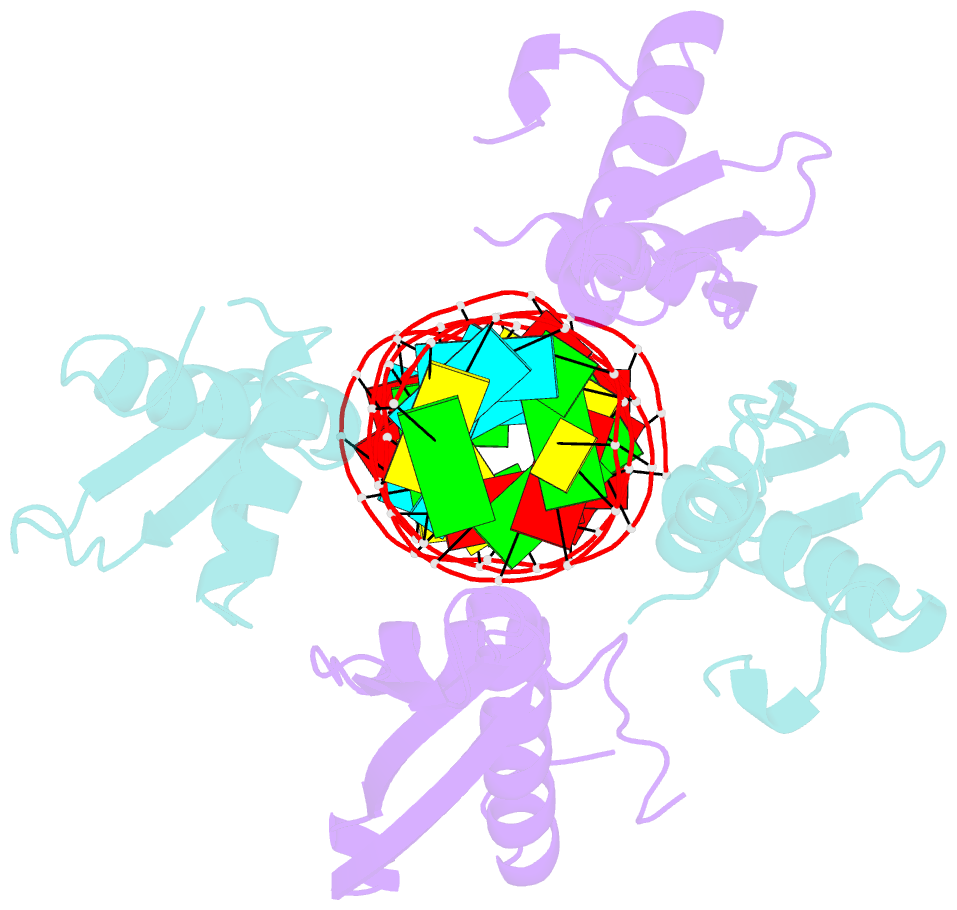
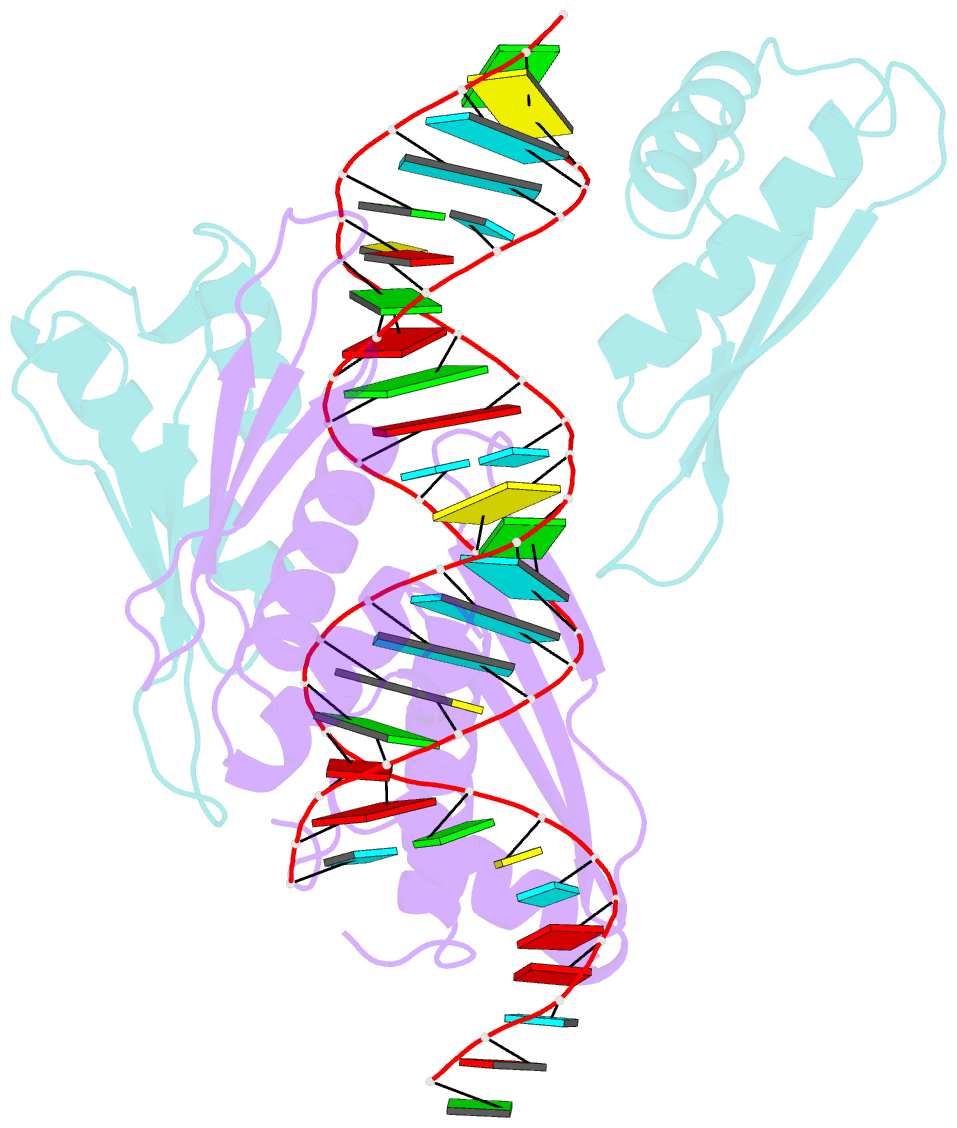
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5ztm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.899 Å)
- Summary
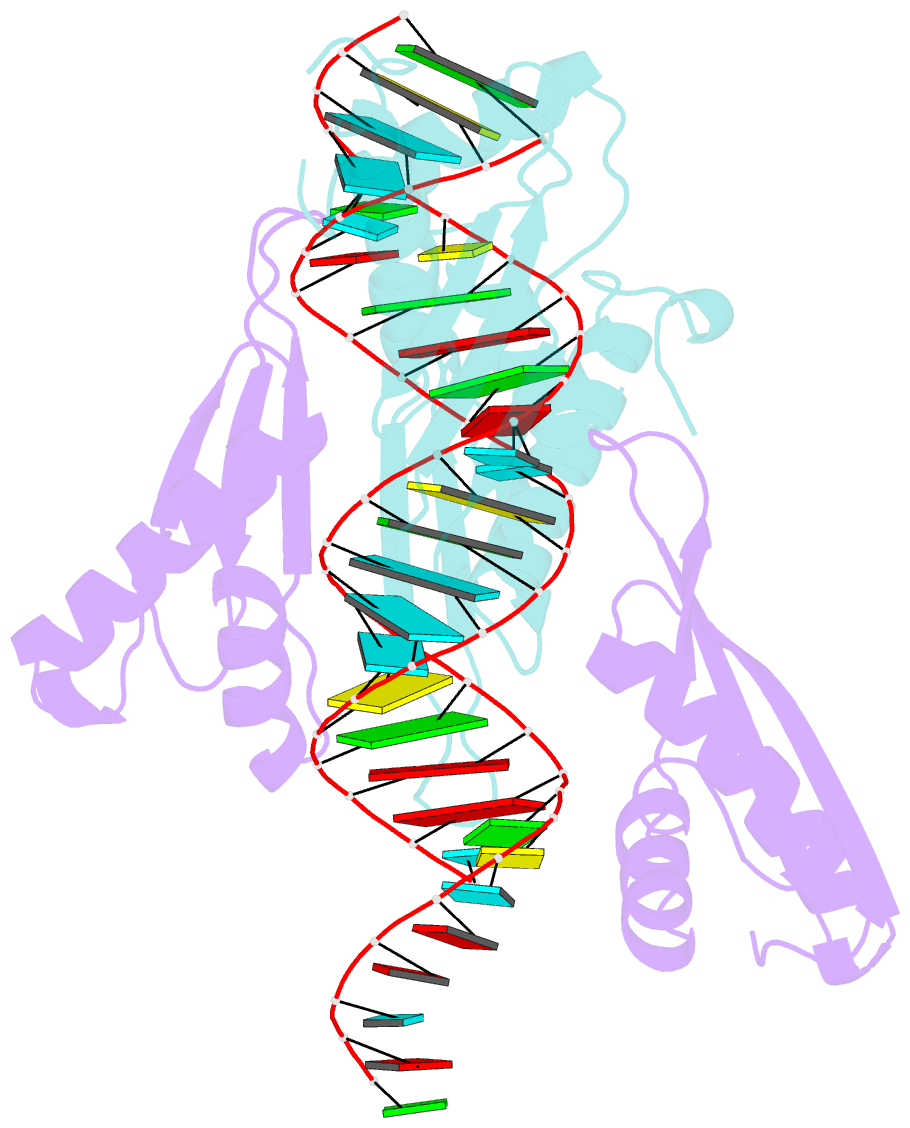
- Crystal structure of mle dsrbds in complex with rox2 (r2h1)
- Reference
- Lv M, Yao Y, Li F, Xu L, Yang L, Gong Q, Xu YZ, Shi Y, Fan YJ, Tang Y (2019): "Structural insights reveal the specific recognition of roX RNA by the dsRNA-binding domains of the RNA helicase MLE and its indispensable role in dosage compensation in Drosophila." Nucleic Acids Res., 47, 3142-3157. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1308.
- Abstract
- In Drosophila, dosage compensation globally upregulates the expression of genes located on male single X-chromosome. Maleless (MLE) helicase plays an essential role to incorporate the roX lncRNA into the dosage compensation complex (MSL-DCC), and such function is essentially dependent on its dsRNA-binding domains (dsRBDs). Here, we report a 2.90Å crystal structure of tandem dsRBDs of MLE in complex with a 55mer stem-loop of roX2 (R2H1). MLE dsRBDs bind to R2H1 cooperatively and interact with two successive minor grooves and a major groove of R2H1, respectively. The recognition of R2H1 by MLE dsRBDs involves both shape- and sequence-specificity. Moreover, dsRBD2 displays a stronger RNA affinity than dsRBD1, and mutations of key residues in either MLE dsRBD remarkably reduce their affinities for roX2 both in vitro and in vivo. In Drosophila, the structure-based mle mutations generated using the CRISPR/Cas9 system, are partially male-lethal and indicate the inter-regulation among the components of the MSL-DCC at multiple levels. Hence, our research provides structural insights into the interactions between MLE dsRBDs and R2H1 and facilitates a deeper understanding of the mechanism by which MLE tandem dsRBDs play an indispensable role in specific recognition of roX and the assembly of the MSL-DCC in Drosophila dosage compensation.