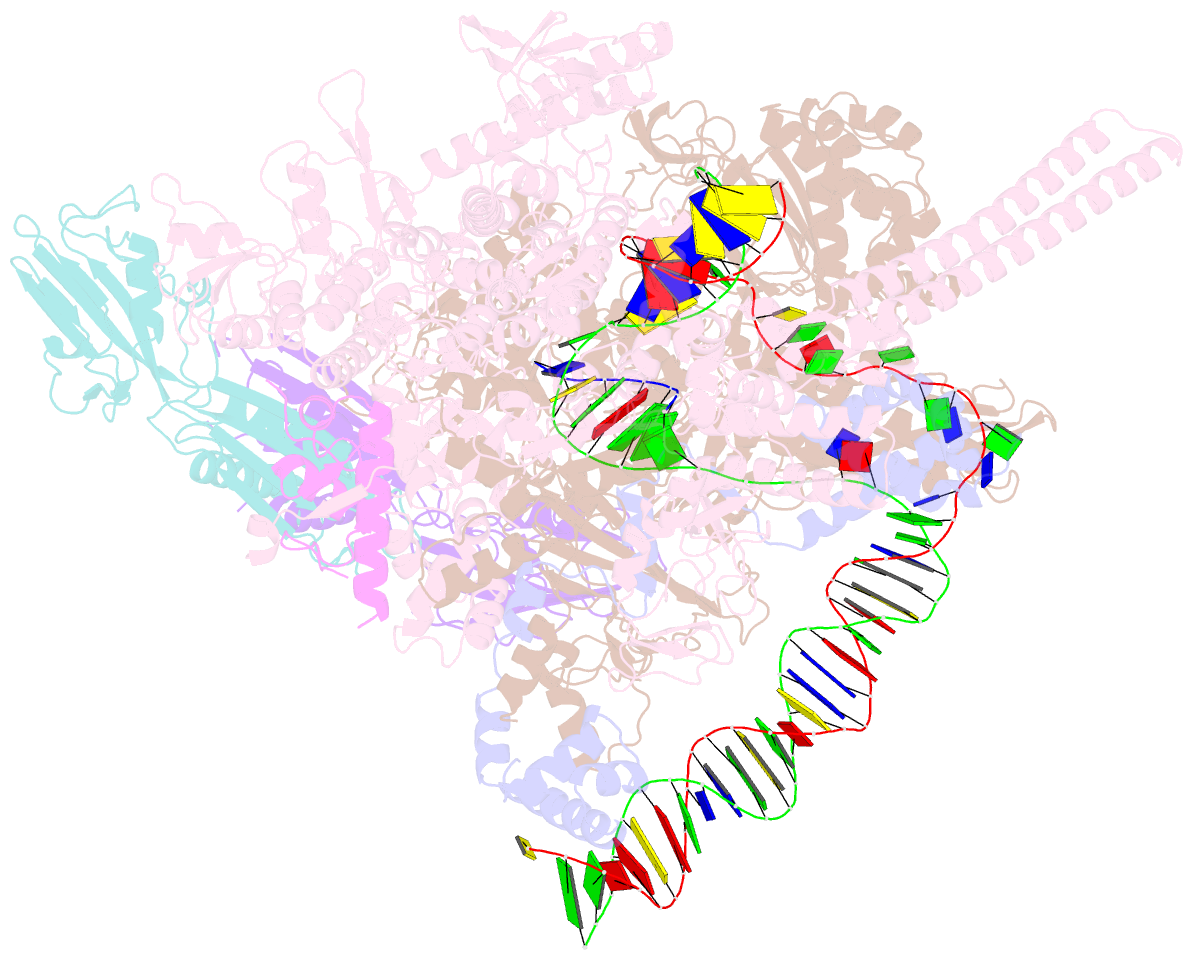
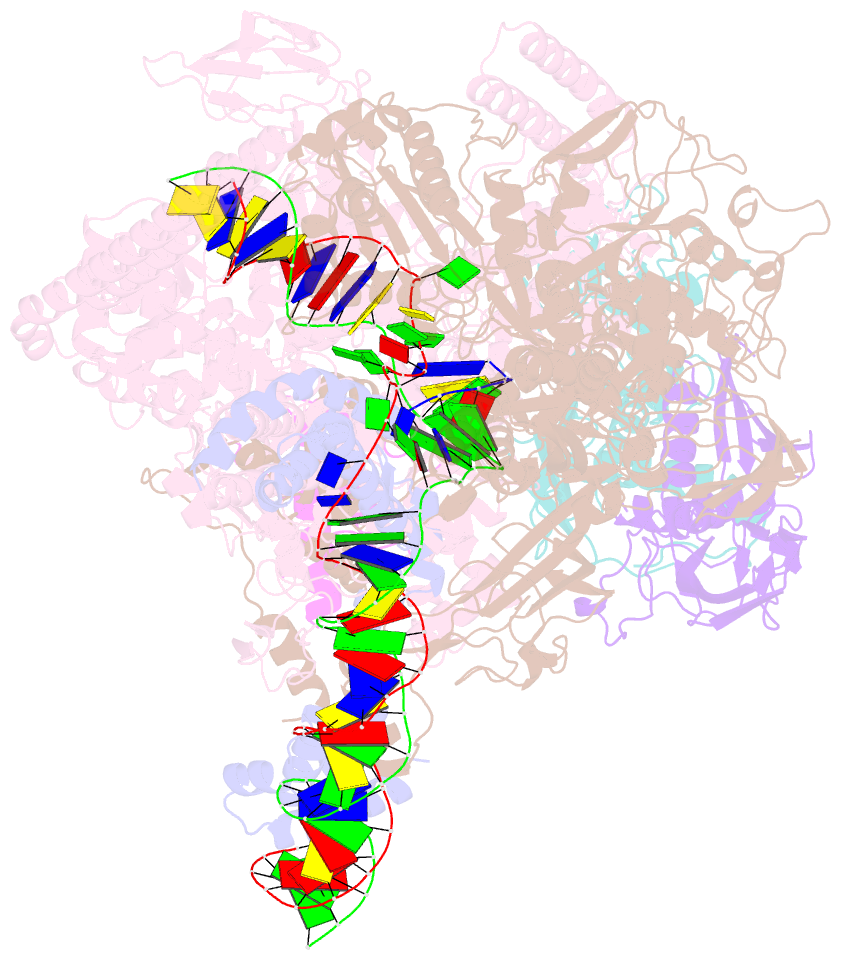
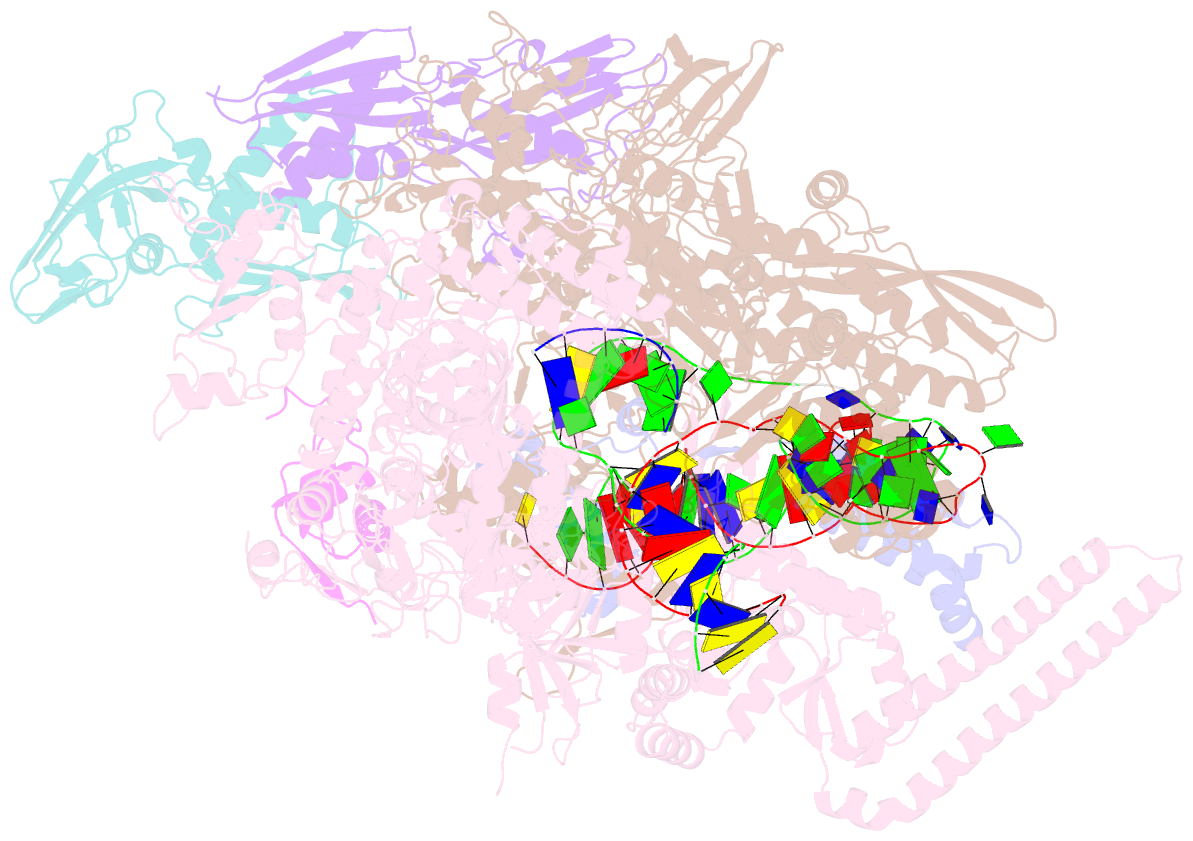
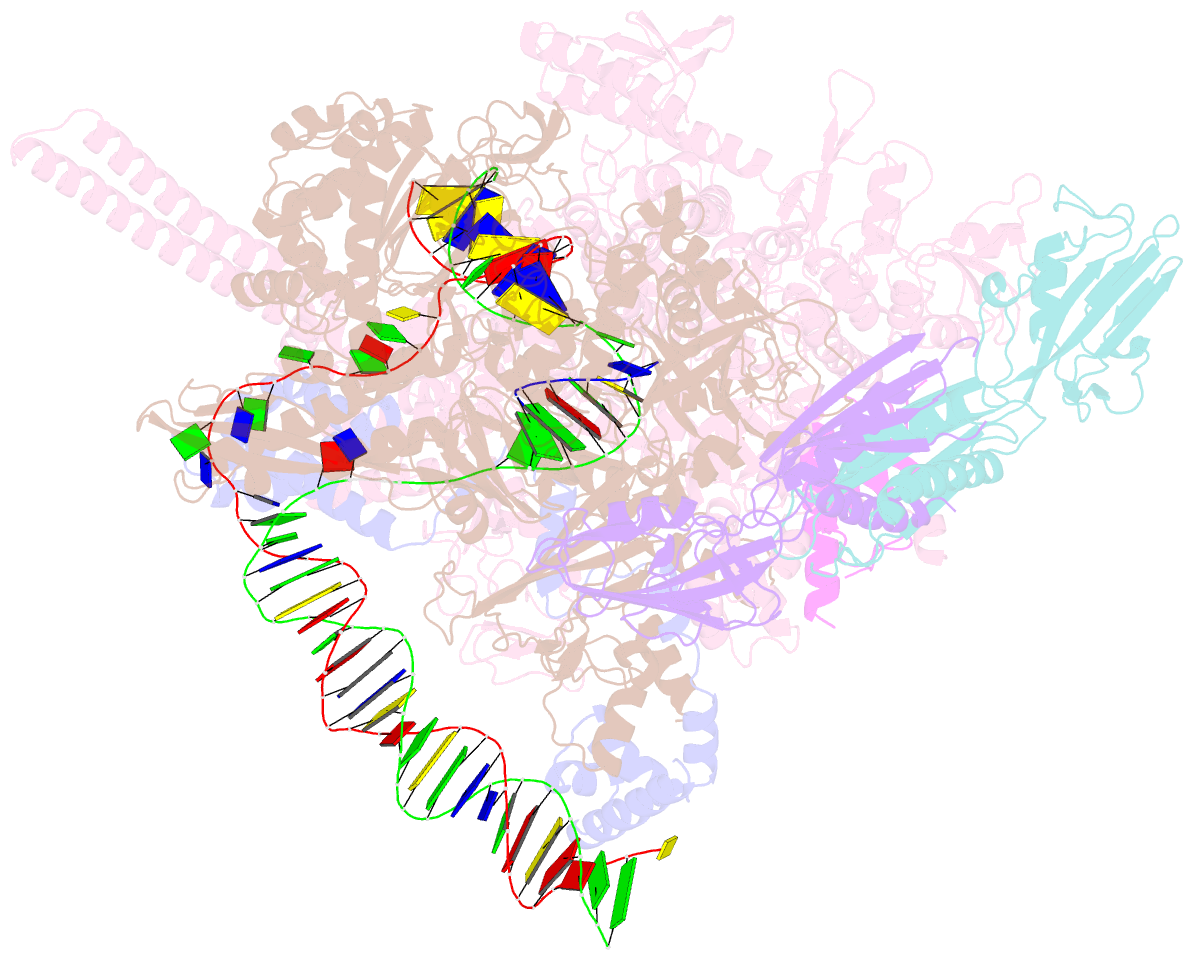
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 5zx2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
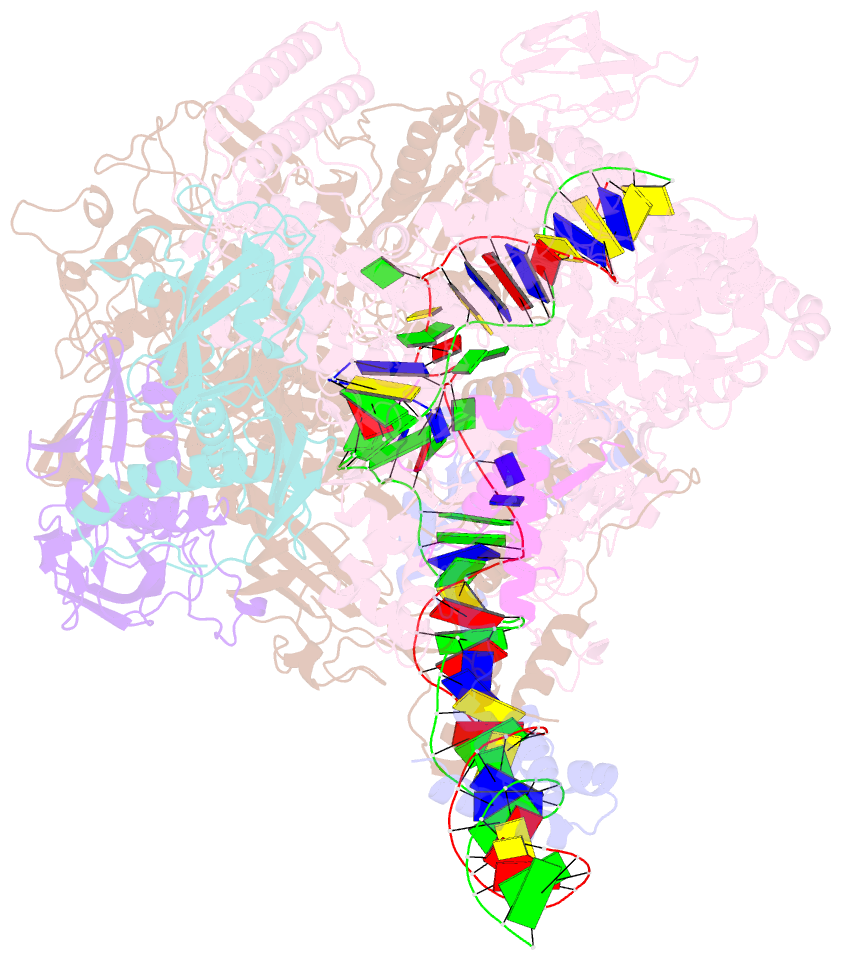
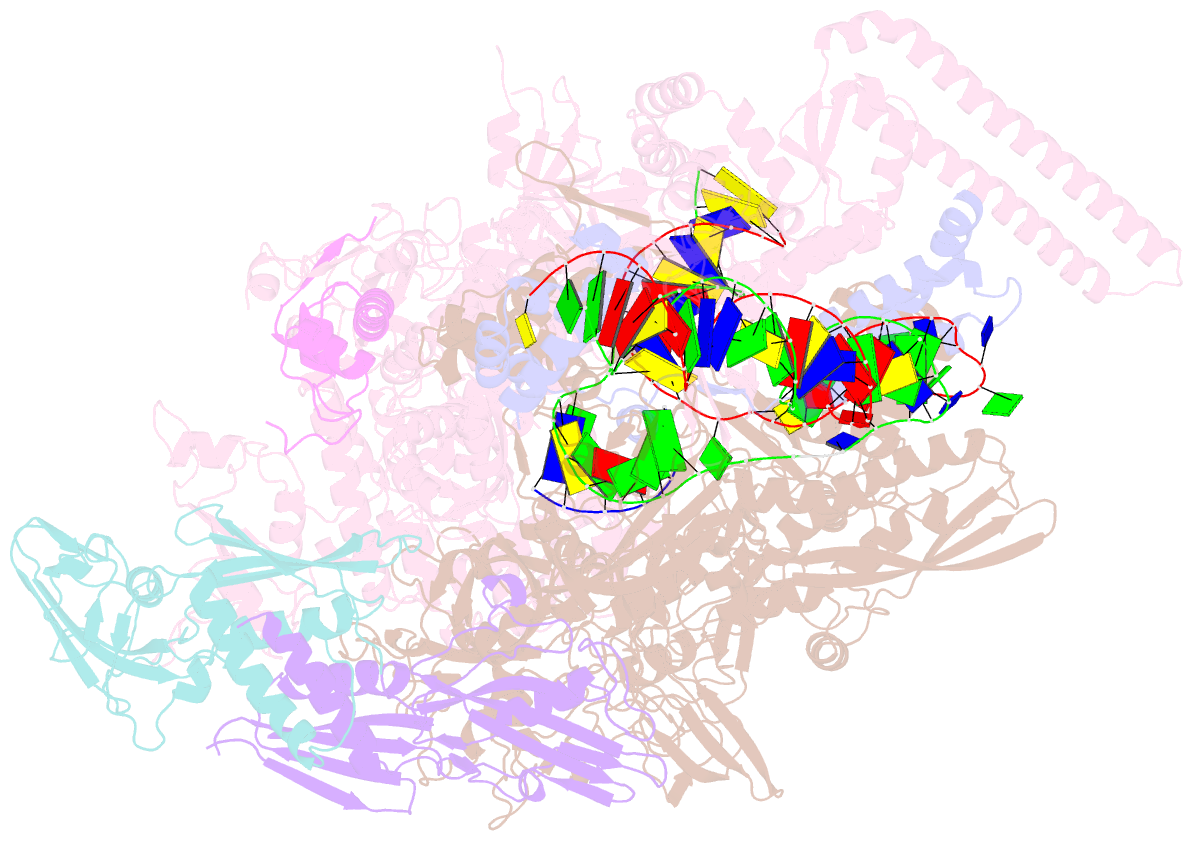
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA polymerase transcription initiation complex with ecf sigma factor sigma h and 7nt RNA
- Reference
- Li L, Fang C, Zhuang N, Wang T, Zhang Y (2019): "Structural basis for transcription initiation by bacterial ECF sigma factors." Nat Commun, 10, 1153. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09096-y.
- Abstract
- Bacterial RNA polymerase employs extra-cytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factors to regulate context-specific gene expression programs. Despite being the most abundant and divergent σ factor class, the structural basis of ECF σ factor-mediated transcription initiation remains unknown. Here, we determine a crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) RNAP holoenzyme comprising an RNAP core enzyme and the ECF σ factor σH (σH-RNAP) at 2.7 Å, and solve another crystal structure of a transcription initiation complex of Mtb σH-RNAP (σH-RPo) comprising promoter DNA and an RNA primer at 2.8 Å. The two structures together reveal the interactions between σH and RNAP that are essential for σH-RNAP holoenzyme assembly as well as the interactions between σH-RNAP and promoter DNA responsible for stringent promoter recognition and for promoter unwinding. Our study establishes that ECF σ factors and primary σ factors employ distinct mechanisms for promoter recognition and for promoter unwinding.