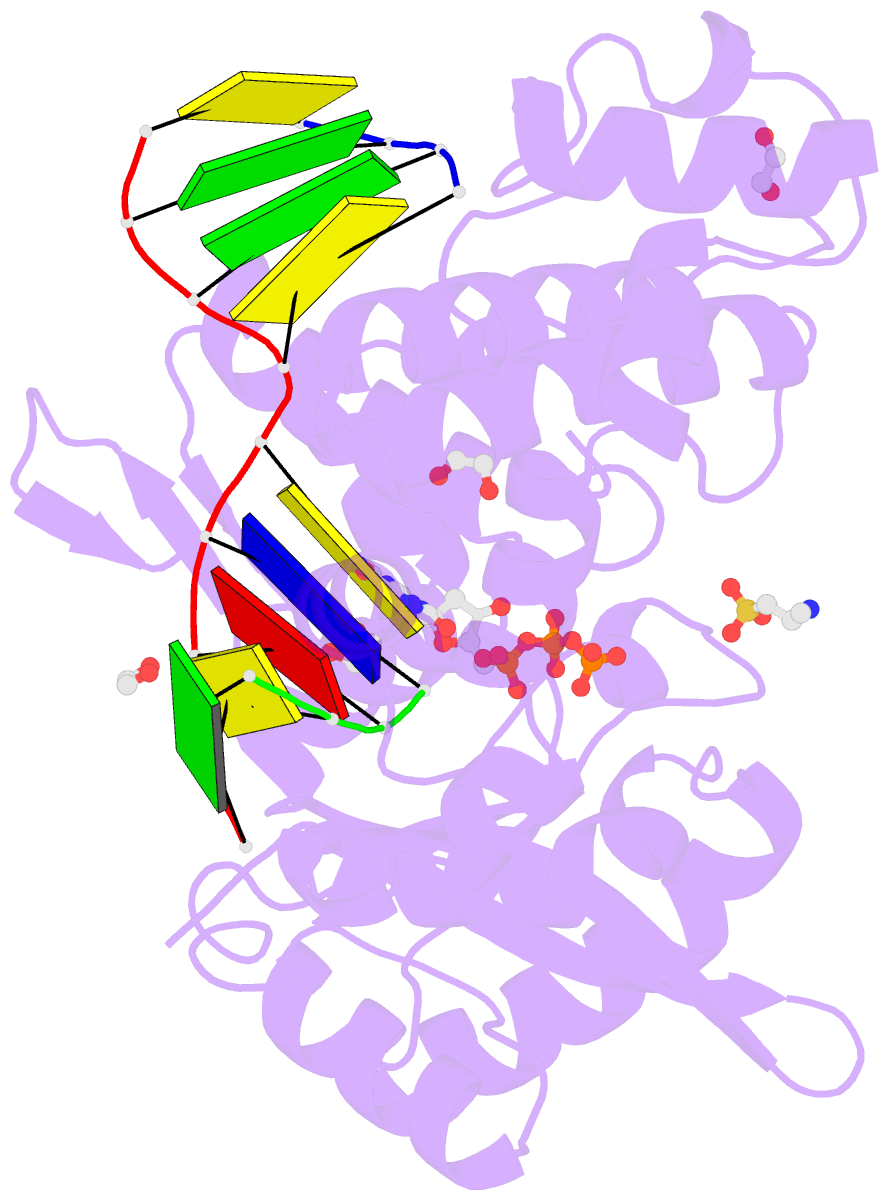
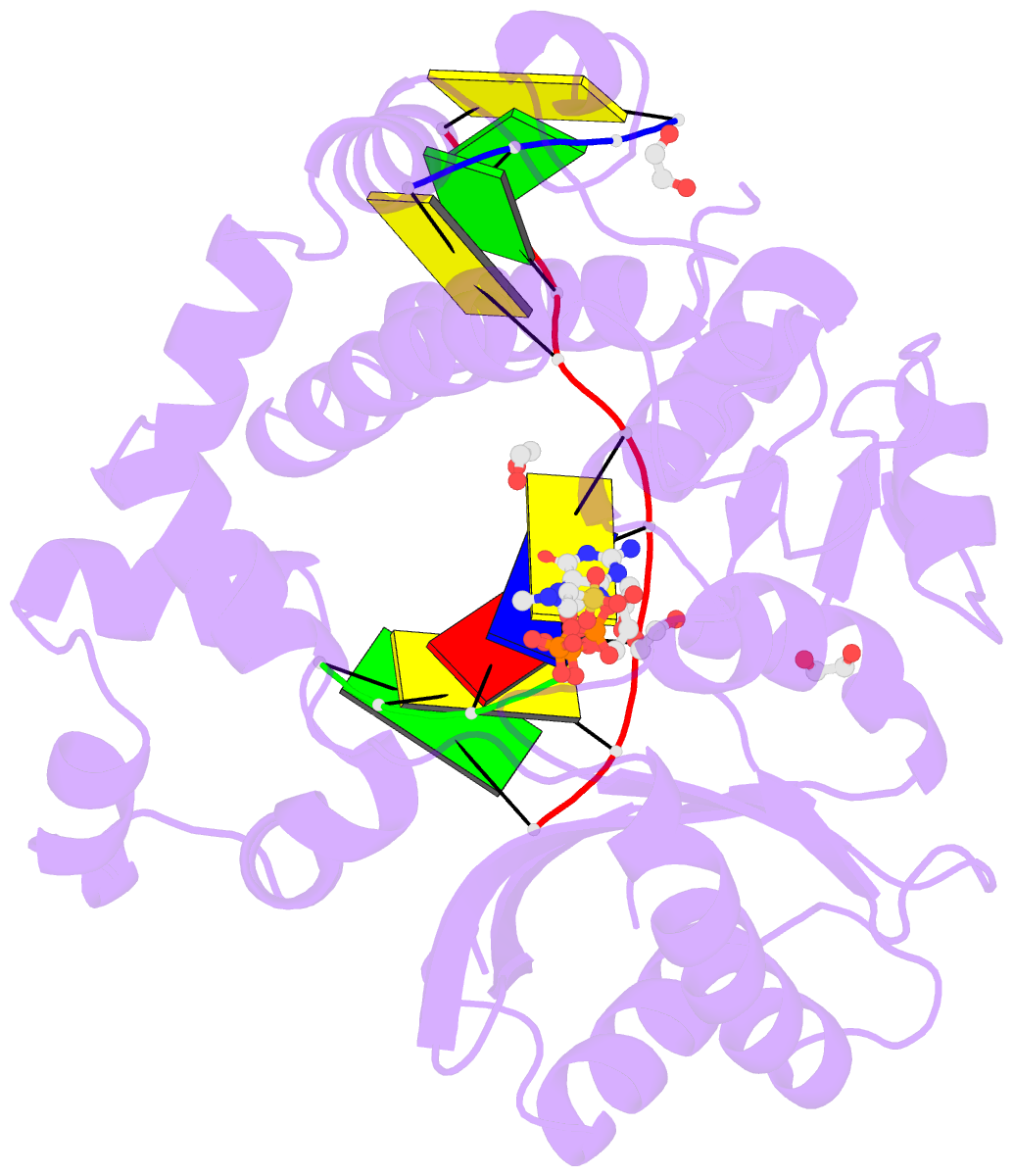
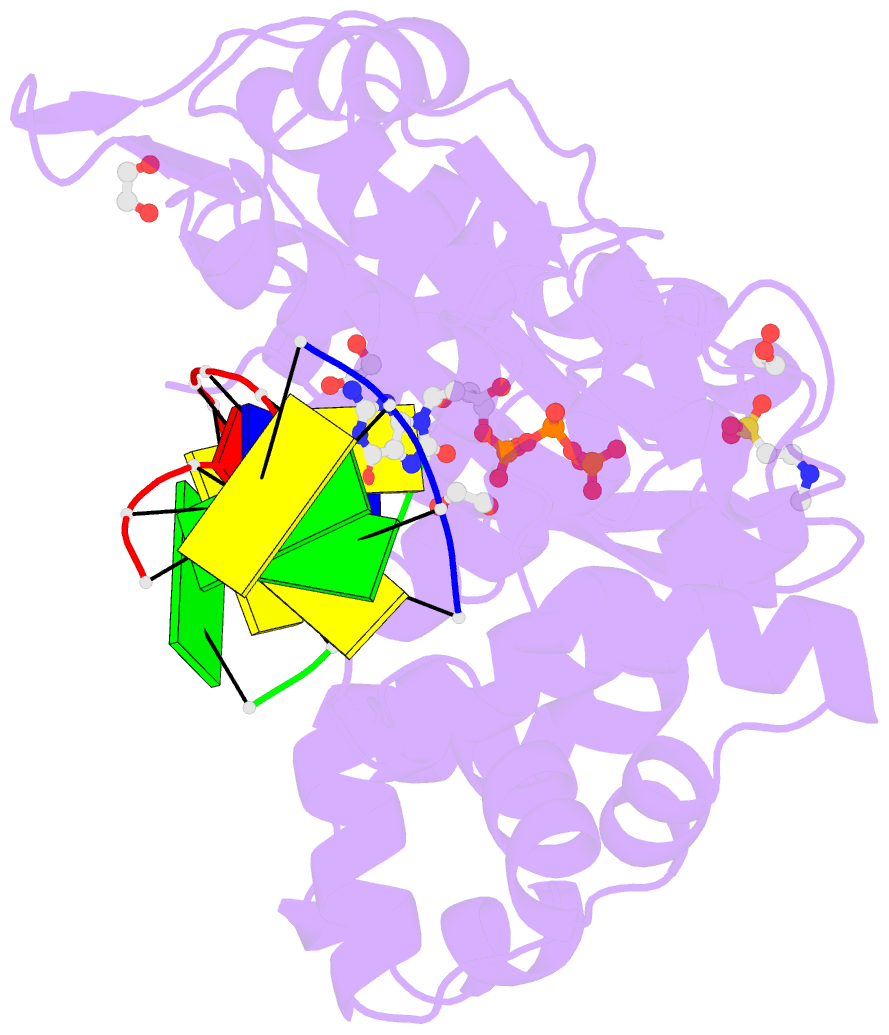
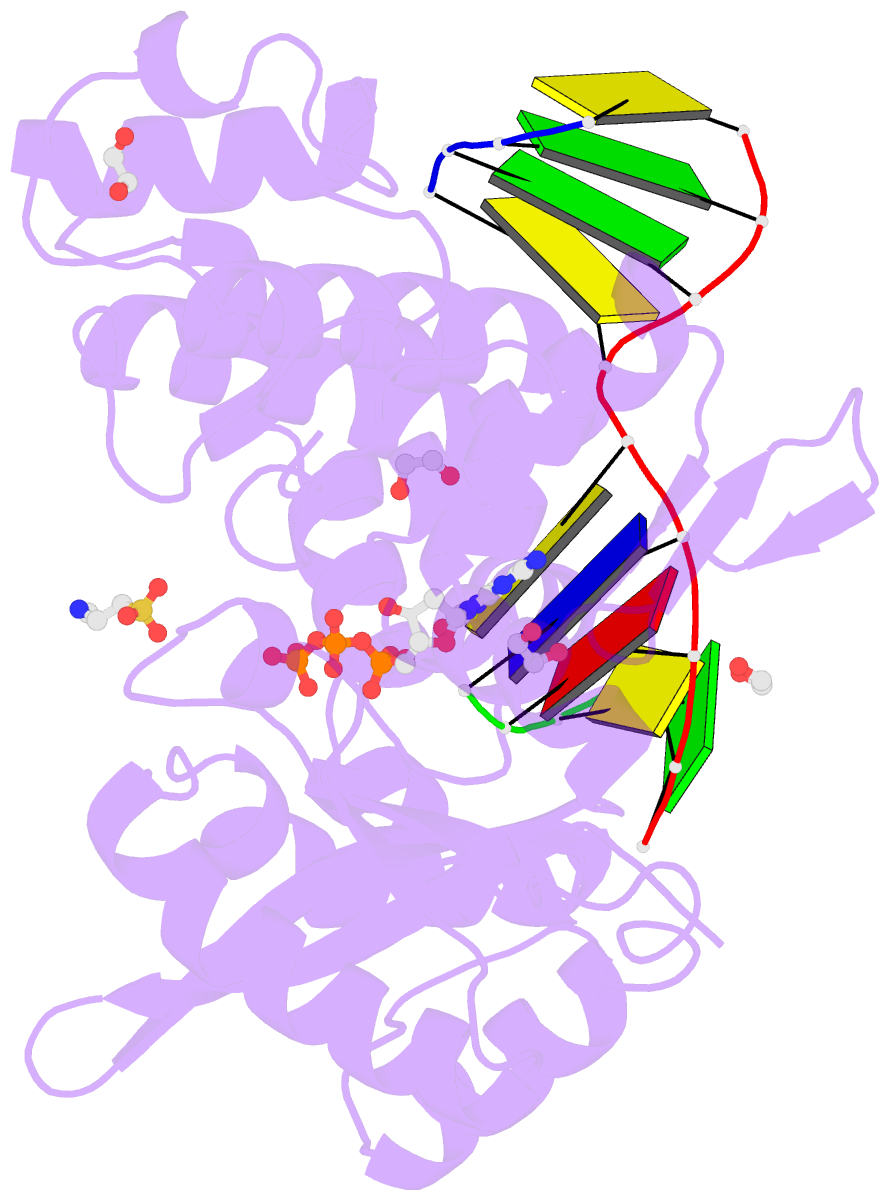
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6ak9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.91 Å)
- Summary
- Pre-catalytic ternary complex of human DNA polymerase mu with templating cytosine and incoming ca-8oxodgtp
- Reference
- Chang YK, Huang YP, Liu XX, Ko TP, Bessho Y, Kawano Y, Maestre-Reyna M, Wu WJ, Tsai MD (2019): "Human DNA Polymerase mu Can Use a Noncanonical Mechanism for Multiple Mn2+-Mediated Functions." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 141, 8489-8502. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b01741.
- Abstract
- Recent research on the structure and mechanism of DNA polymerases has continued to generate fundamentally important features, including a noncanonical pathway involving "prebinding" of metal-bound dNTP (MdNTP) in the absence of DNA. While this noncanonical mechanism was shown to be a possible subset for African swine fever DNA polymerase X (Pol X) and human Pol λ, it remains unknown whether it could be the primary pathway for a DNA polymerase. Pol μ is a unique member of the X-family with multiple functions and with unusual Mn2+ preference. Here we report that Pol μ not only prebinds MdNTP in a catalytically active conformation but also exerts a Mn2+ over Mg2+ preference at this early stage of catalysis, for various functions: incorporation of dNTP into a single nucleotide gapped DNA, incorporation of rNTP in the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) repair, incorporation of dNTP to an ssDNA, and incorporation of an 8-oxo-dGTP opposite template dA (mismatched) or dC (matched). The structural basis of this noncanonical mechanism and Mn2+ over Mg2+ preference in these functions was analyzed by solving 19 structures of prebinding binary complexes, precatalytic ternary complexes, and product complexes. The results suggest that the noncanonical pathway is functionally relevant for the multiple functions of Pol μ. Overall, this work provides the structural and mechanistic basis for the long-standing puzzle in the Mn2+ preference of Pol μ and expands the landscape of the possible mechanisms of DNA polymerases to include both mechanistic pathways.