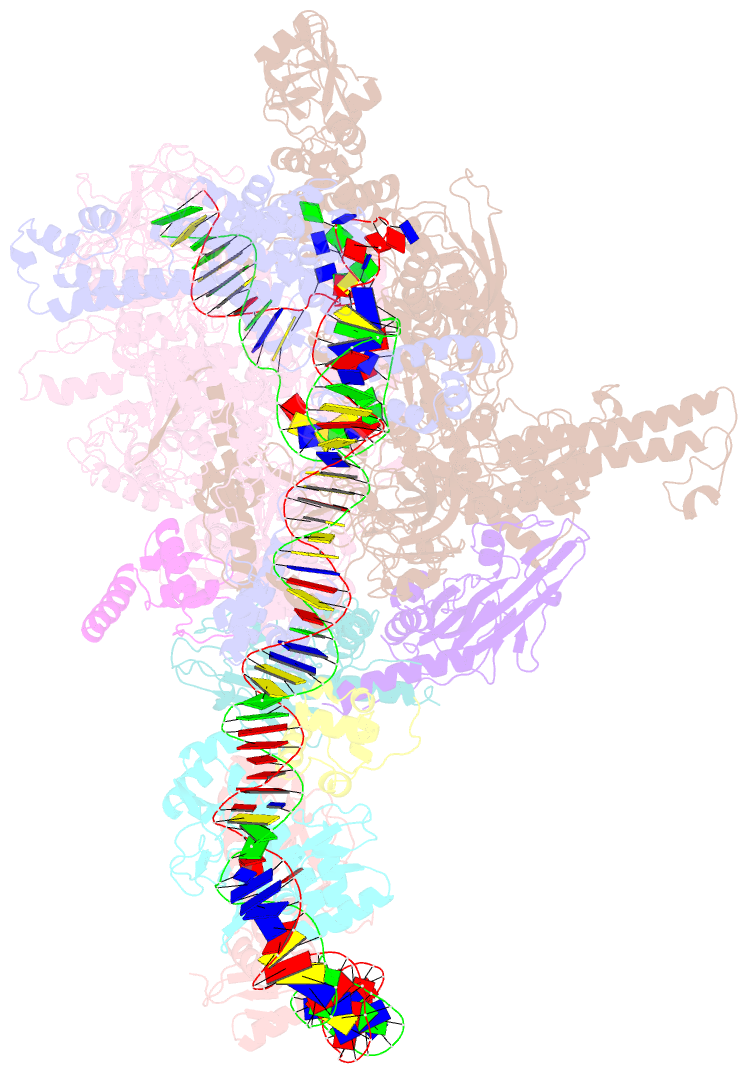
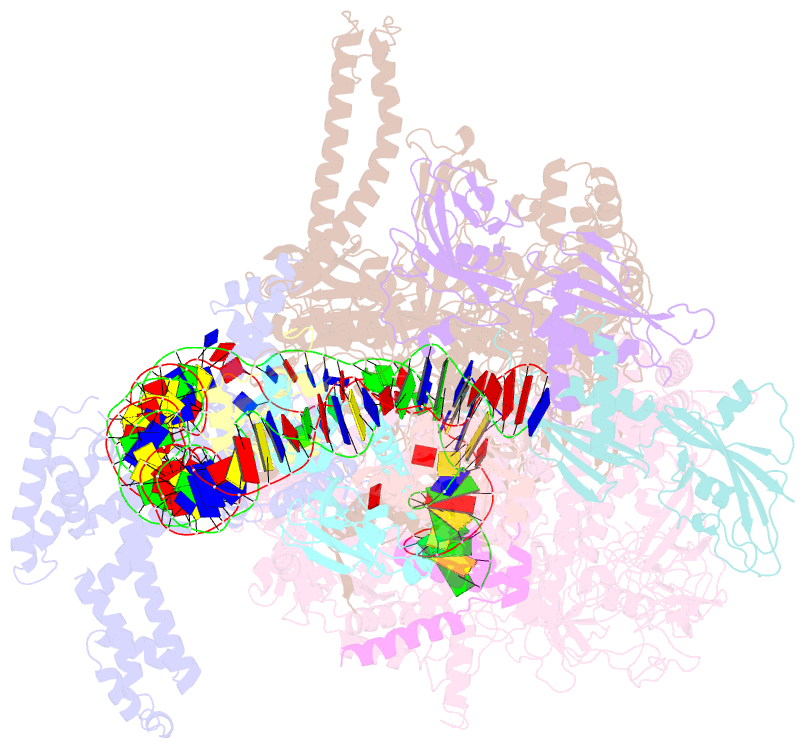
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6b6h; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-transferase-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.9 Å)
- Summary
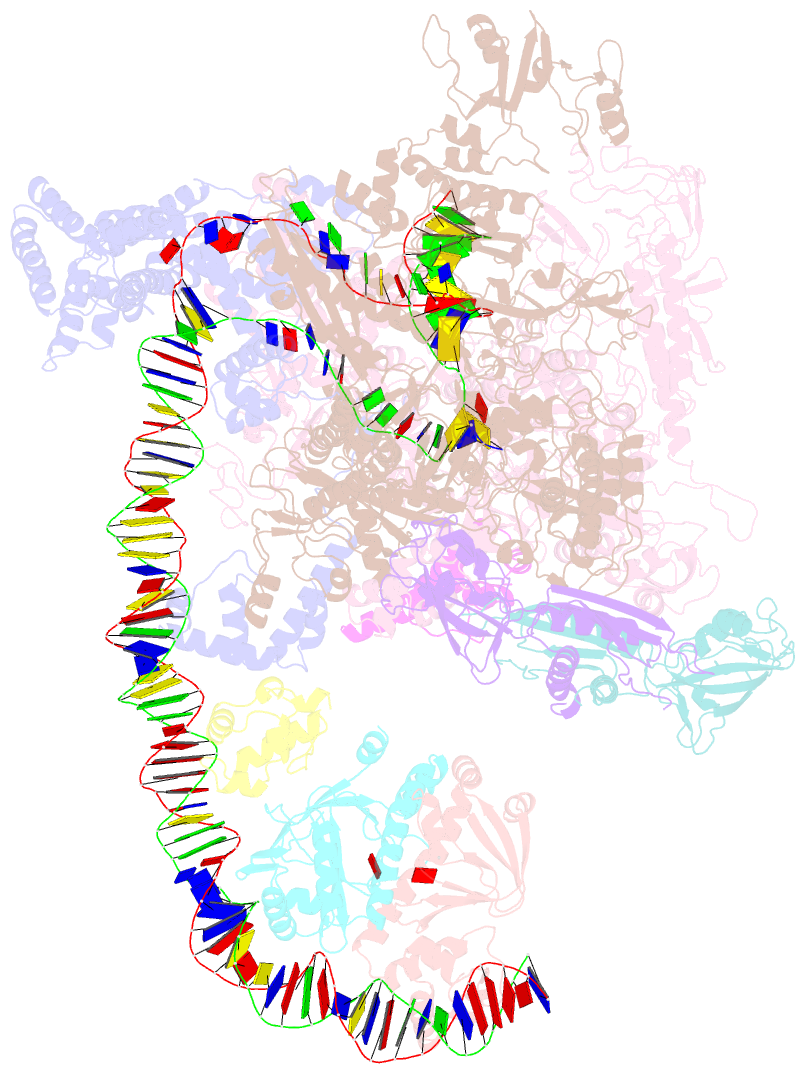
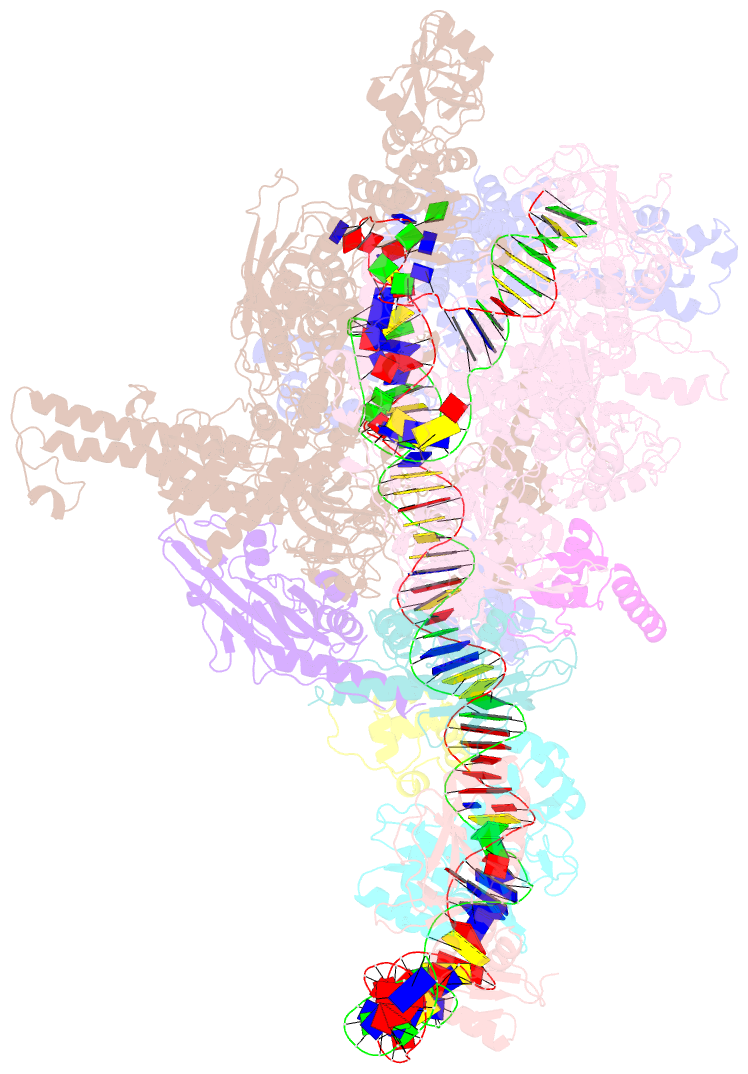
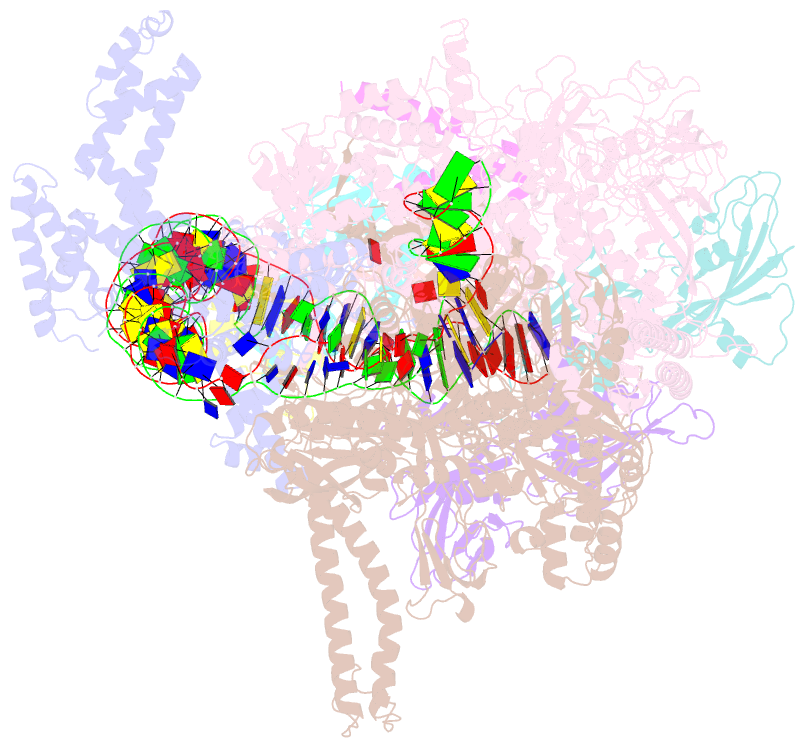
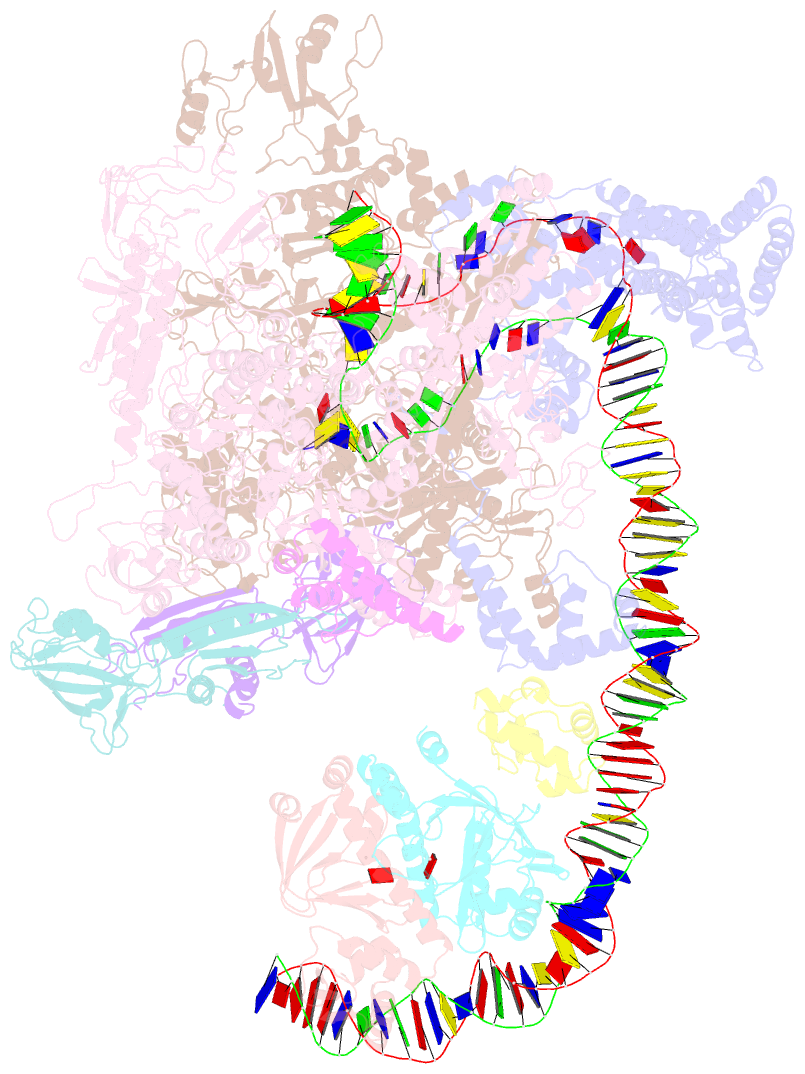
- The cryo-EM structure of a bacterial class i transcription activation complex
- Reference
- Liu B, Hong C, Huang RK, Yu Z, Steitz TA (2017): "Structural basis of bacterial transcription activation." Science, 358, 947-951. doi: 10.1126/science.aao1923.
- Abstract
- In bacteria, the activation of gene transcription at many promoters is simple and only involves a single activator. The cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor protein (CAP), a classic activator, is able to activate transcription independently through two different mechanisms. Understanding the class I mechanism requires an intact transcription activation complex (TAC) structure at a high resolution. Here we report a high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of an intact Escherichia coli class I TAC containing a CAP dimer, a σ70-RNA polymerase (RNAP) holoenzyme, a complete class I CAP-dependent promoter DNA, and a de novo synthesized RNA oligonucleotide. The structure shows how CAP wraps the upstream DNA and how the interactions recruit RNAP. Our study provides a structural basis for understanding how activators activate transcription through the class I recruitment mechanism.