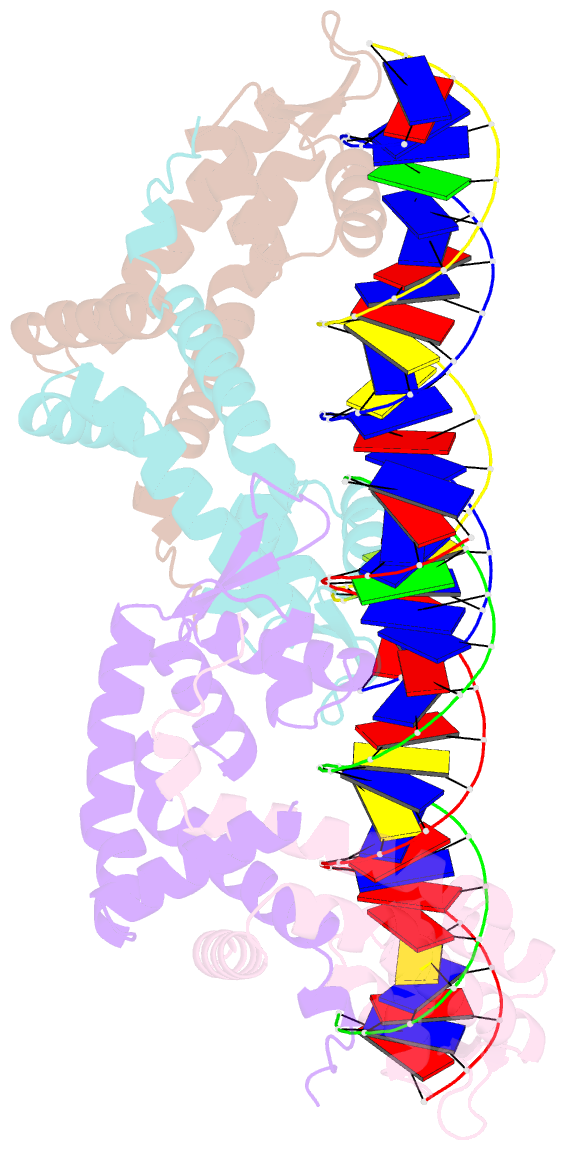
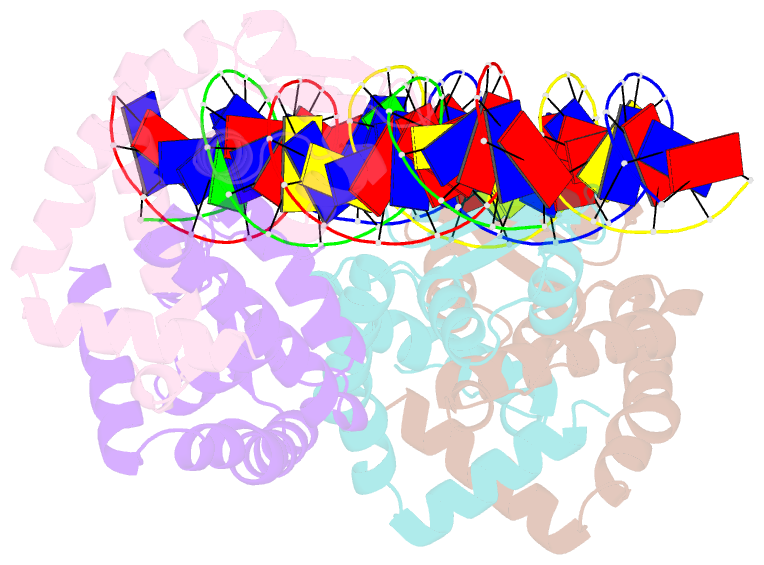
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6c2s; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.85 Å)
- Summary
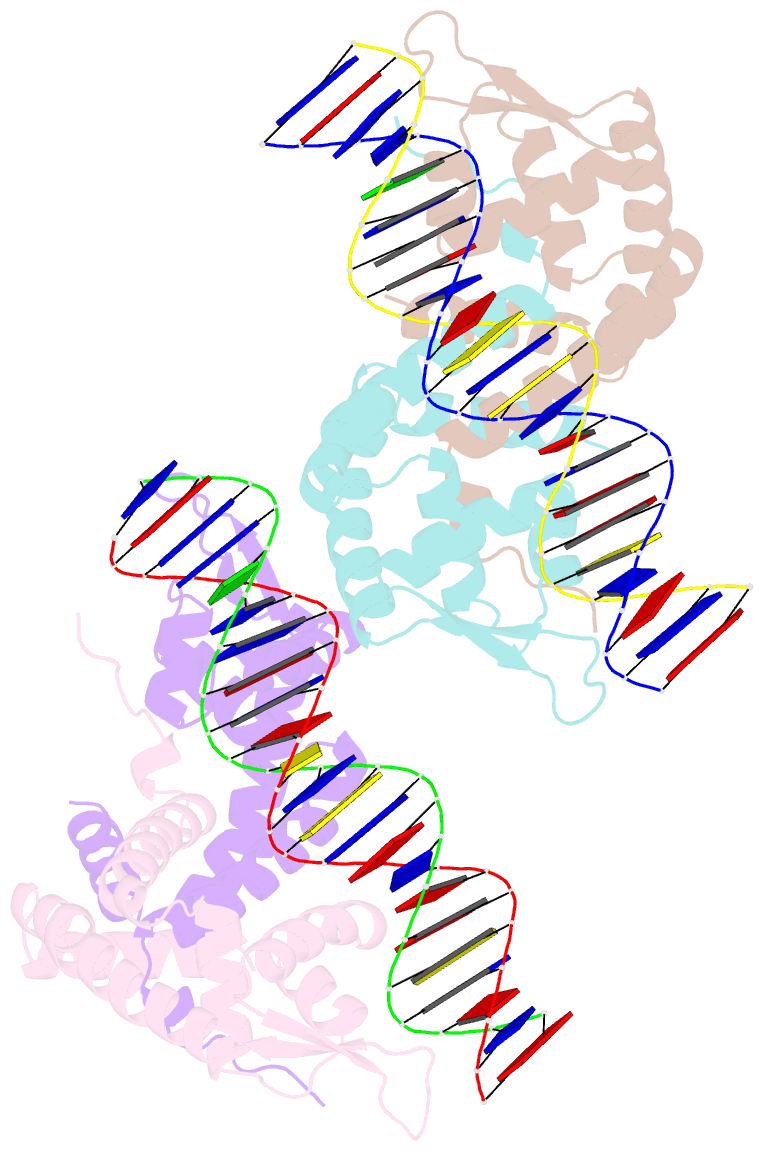
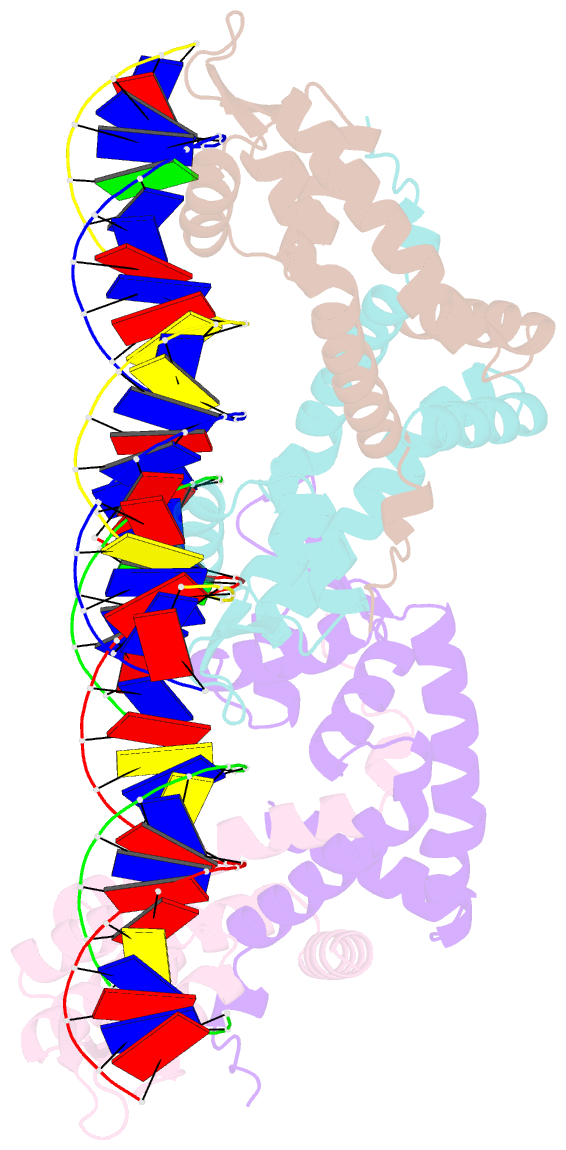
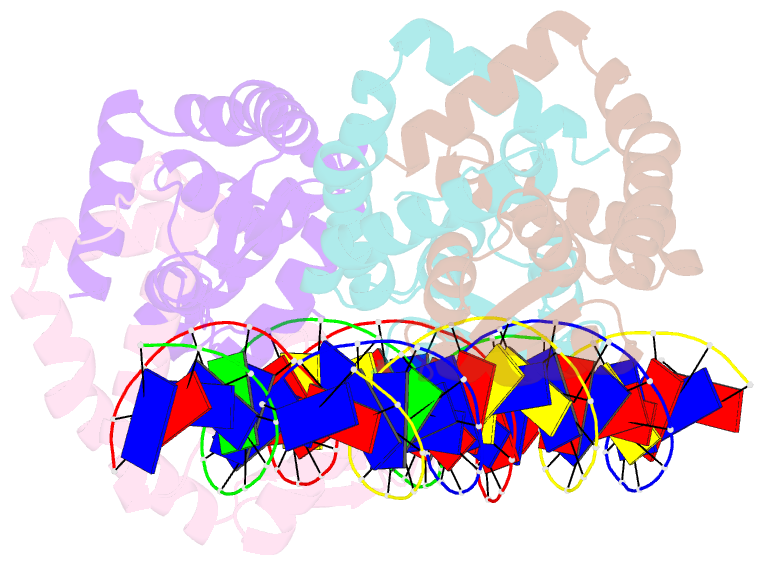
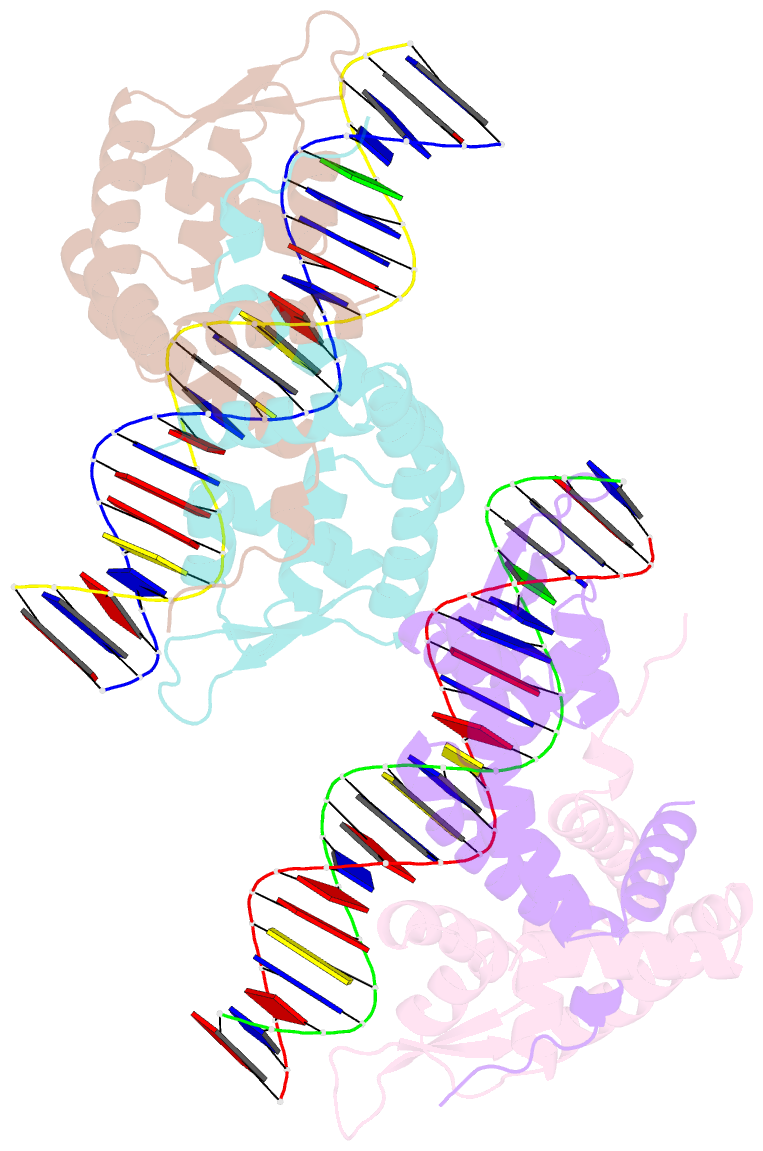
- Transcriptional repressor, cour, bound to a 23-mer DNA duplex
- Reference
- Cogan DP, Baraquet C, Harwood CS, Nair SK (2018): "Structural basis of transcriptional regulation by CouR, a repressor of coumarate catabolism, inRhodopseudomonas palustris." J. Biol. Chem., 293, 11727-11735. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003561.
- Abstract
- The MarR family transcriptional regulator CouR, from the soil bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009, has recently been shown to negatively regulate a p-coumarate catabolic operon. Unlike most characterized MarR repressors that respond to small metabolites at concentrations in the millimolar range, repression by CouR is alleviated by the 800-Da ligand p-coumaroyl-CoA with high affinity and specificity. Here we report the crystal structures of ligand-free CouR as well as the complex with p-coumaroyl-CoA, each to 2.1-Å resolution, and the 2.85-Å resolution cocrystal structure of CouR bound to an oligonucleotide bearing the cognate DNA operator sequence. In combination with binding experiments that uncover specific residues important for ligand and DNA recognition, these structures provide glimpses of a MarR family repressor in all possible states, providing an understanding of the molecular basis of DNA binding and the conformation alterations that accompany ligand-induced dissociation for activation of the operon.