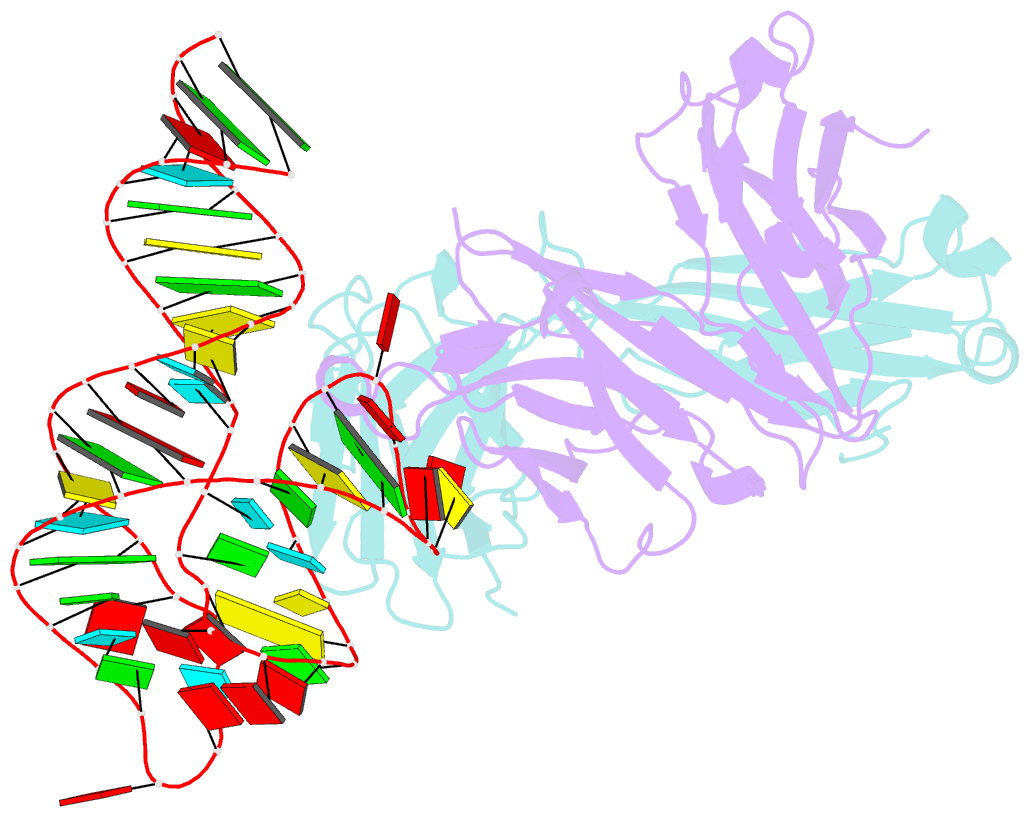
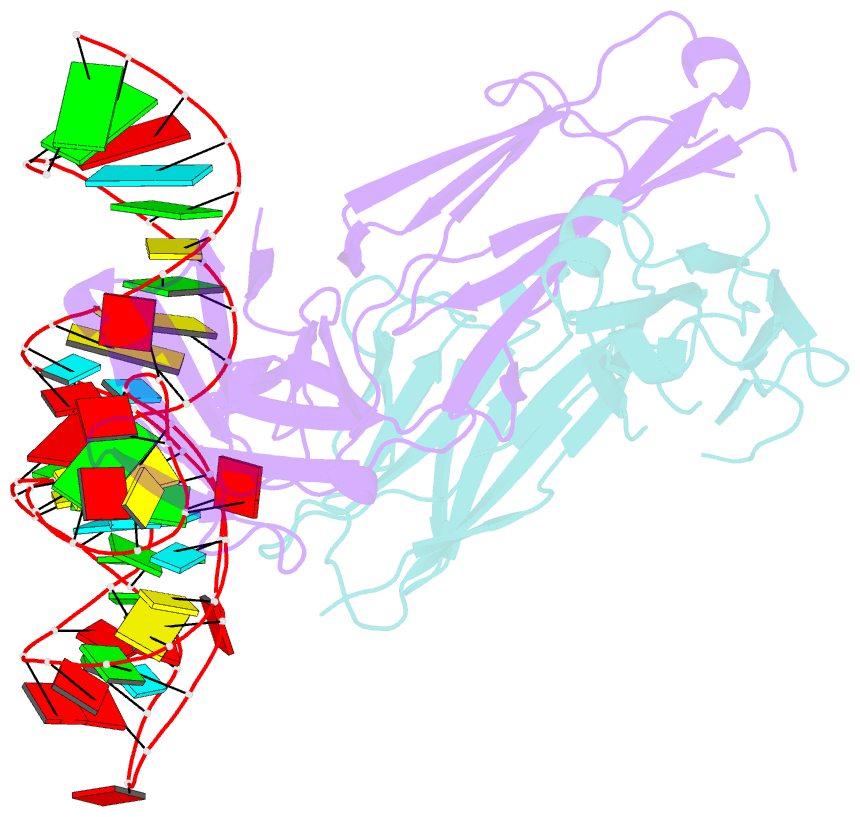
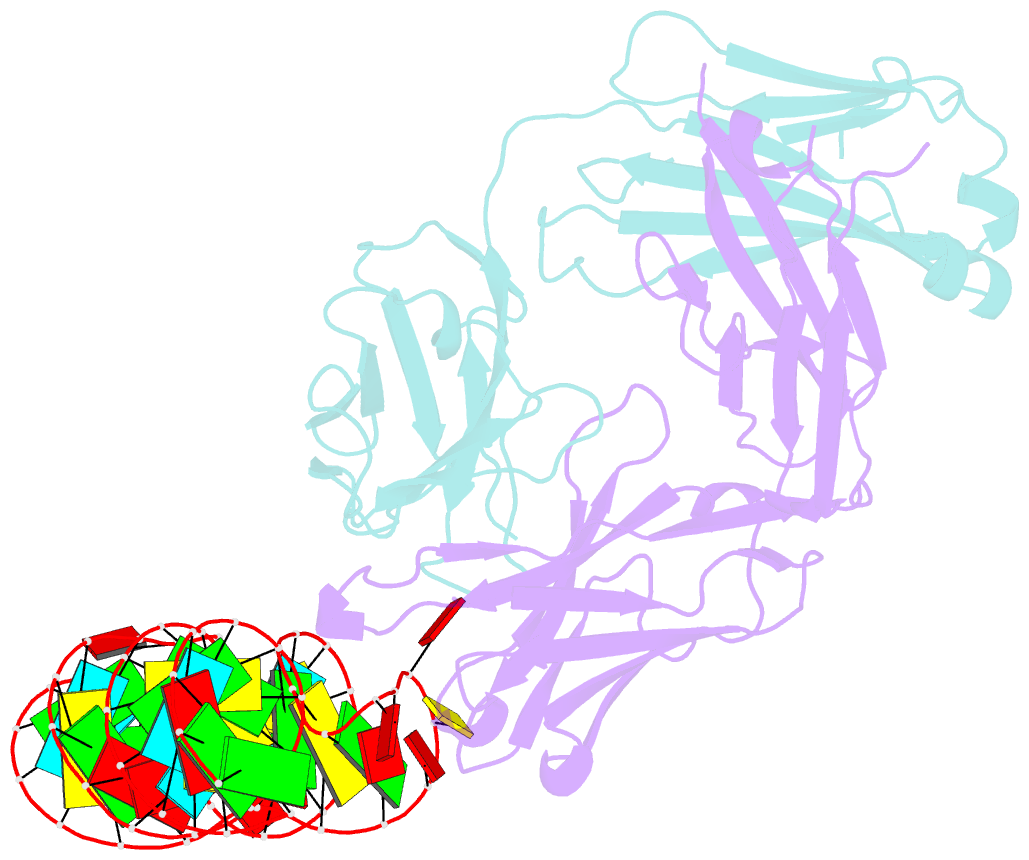
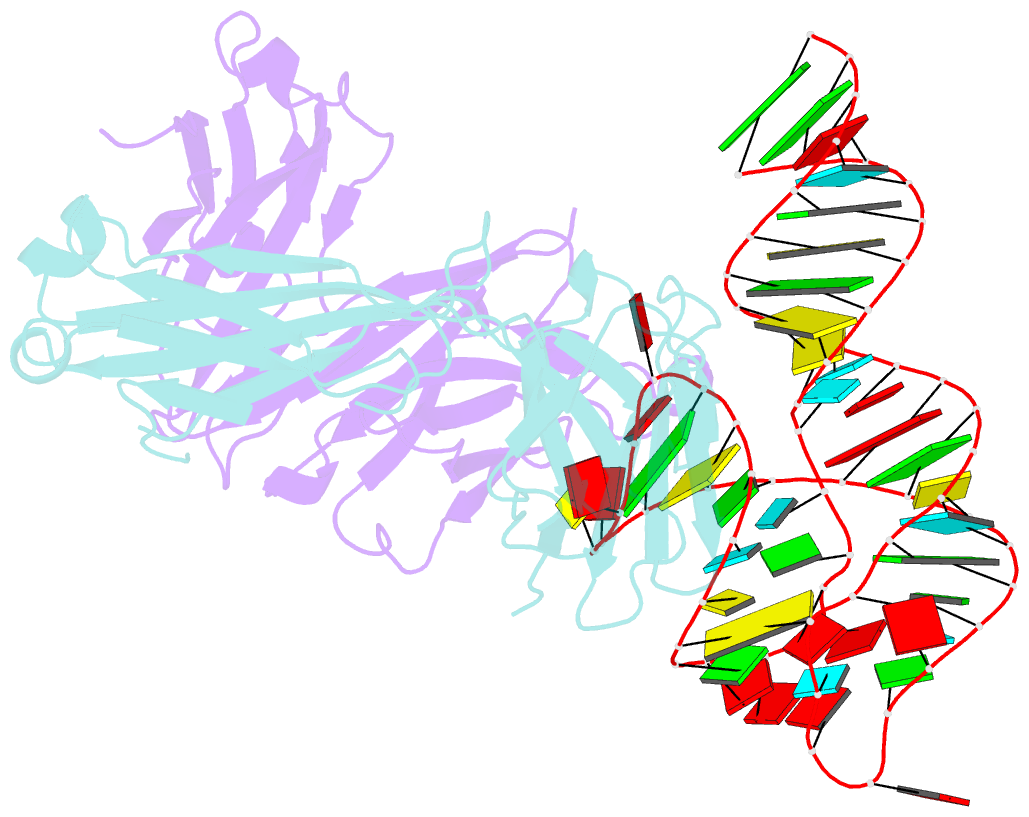
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6db9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA-immune system
- Method
- X-ray (2.025 Å)
- Summary
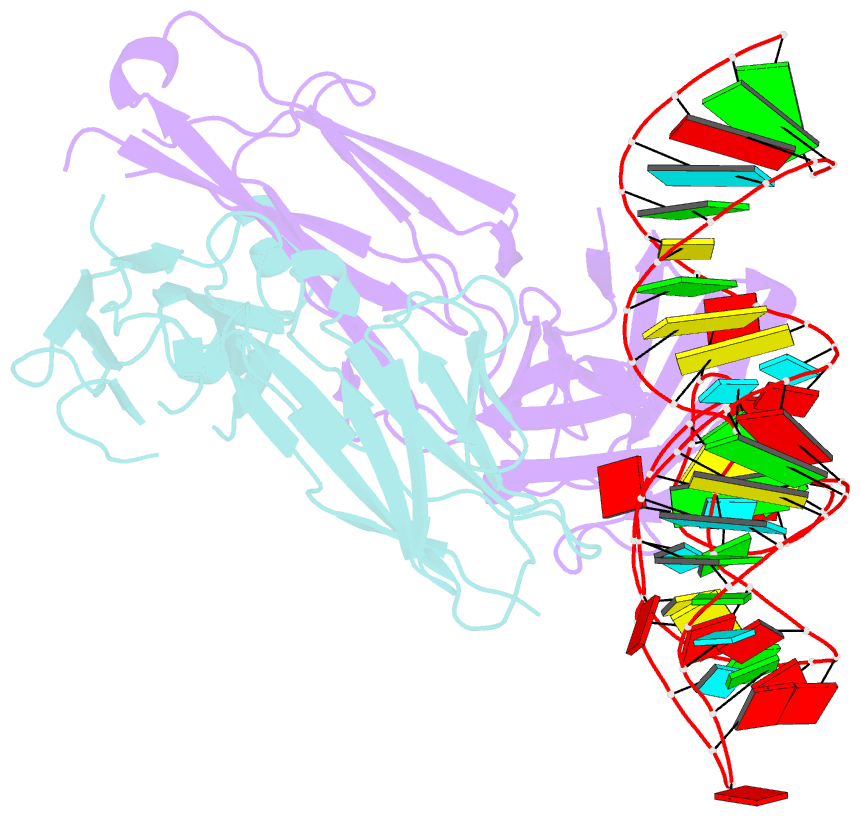
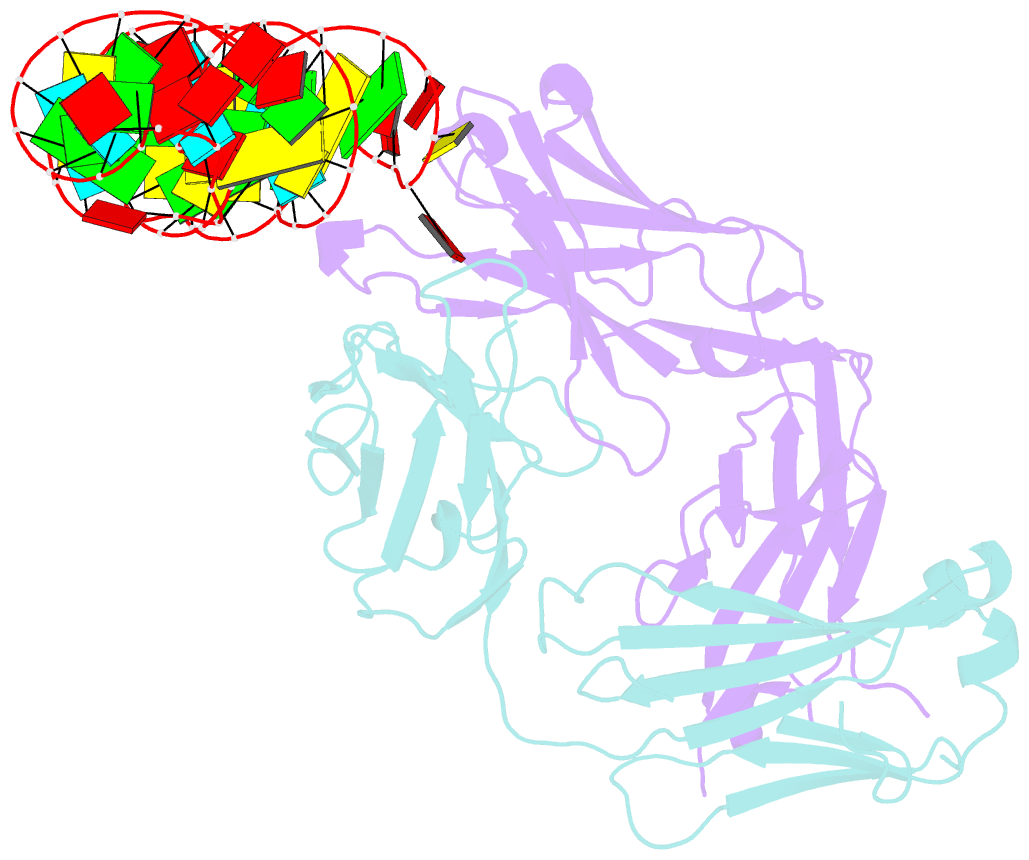
- Structural basis for promiscuous binding and activation of fluorogenic dyes by dir2s RNA aptamer
- Reference
- Shelke SA, Shao Y, Laski A, Koirala D, Weissman BP, Fuller JR, Tan X, Constantin TP, Waggoner AS, Bruchez MP, Armitage BA, Piccirilli JA (2018): "Structural basis for activation of fluorogenic dyes by an RNA aptamer lacking a G-quadruplex motif." Nat Commun, 9, 4542. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06942-3.
- Abstract
- The DIR2s RNA aptamer, a second-generation, in-vitro selected binder to dimethylindole red (DIR), activates the fluorescence of cyanine dyes, DIR and oxazole thiazole blue (OTB), allowing detection of two well-resolved emission colors. Using Fab BL3-6 and its cognate hairpin as a crystallization module, we solved the crystal structures of both the apo and OTB-SO3 bound forms of DIR2s at 2.0 Å and 1.8 Å resolution, respectively. DIR2s adopts a compact, tuning fork-like architecture comprised of a helix and two short stem-loops oriented in parallel to create the ligand binding site through tertiary interactions. The OTB-SO3 fluorophore binds in a planar conformation to a claw-like structure formed by a purine base-triple, which provides a stacking platform for OTB-SO3, and an unpaired nucleotide, which partially caps the binding site from the top. The absence of a G-quartet or base tetrad makes the DIR2s aptamer unique among fluorogenic RNAs with known 3D structure.