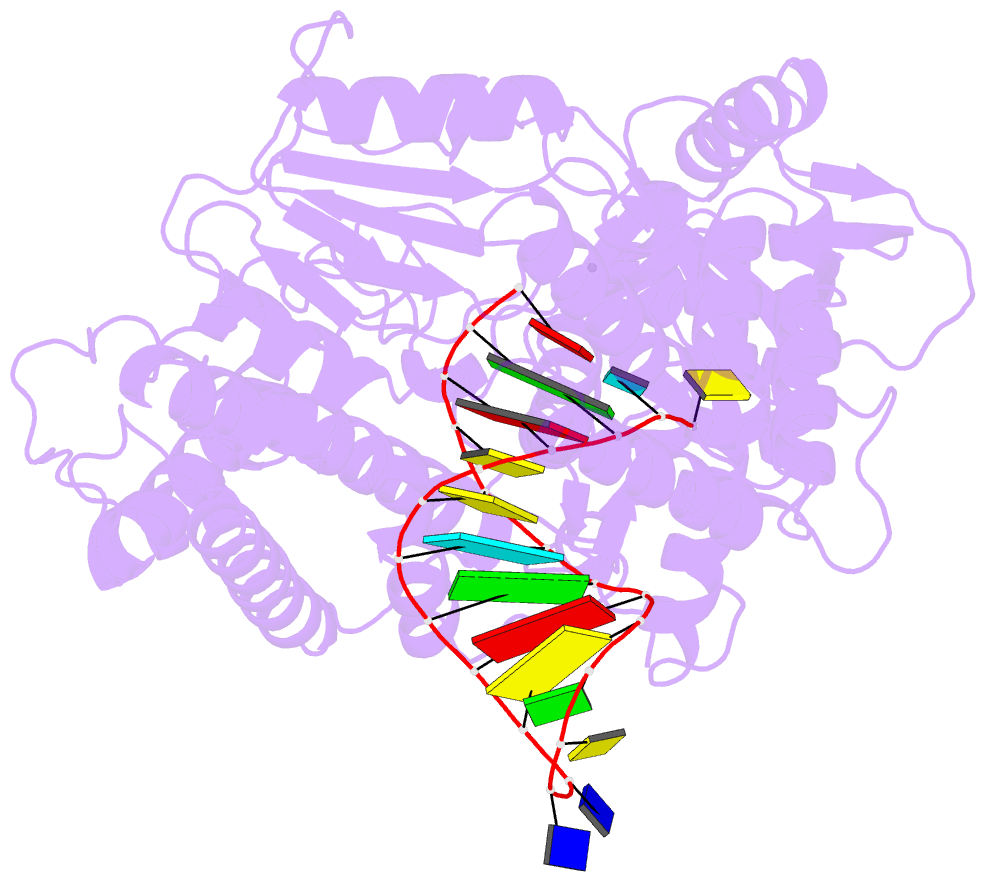
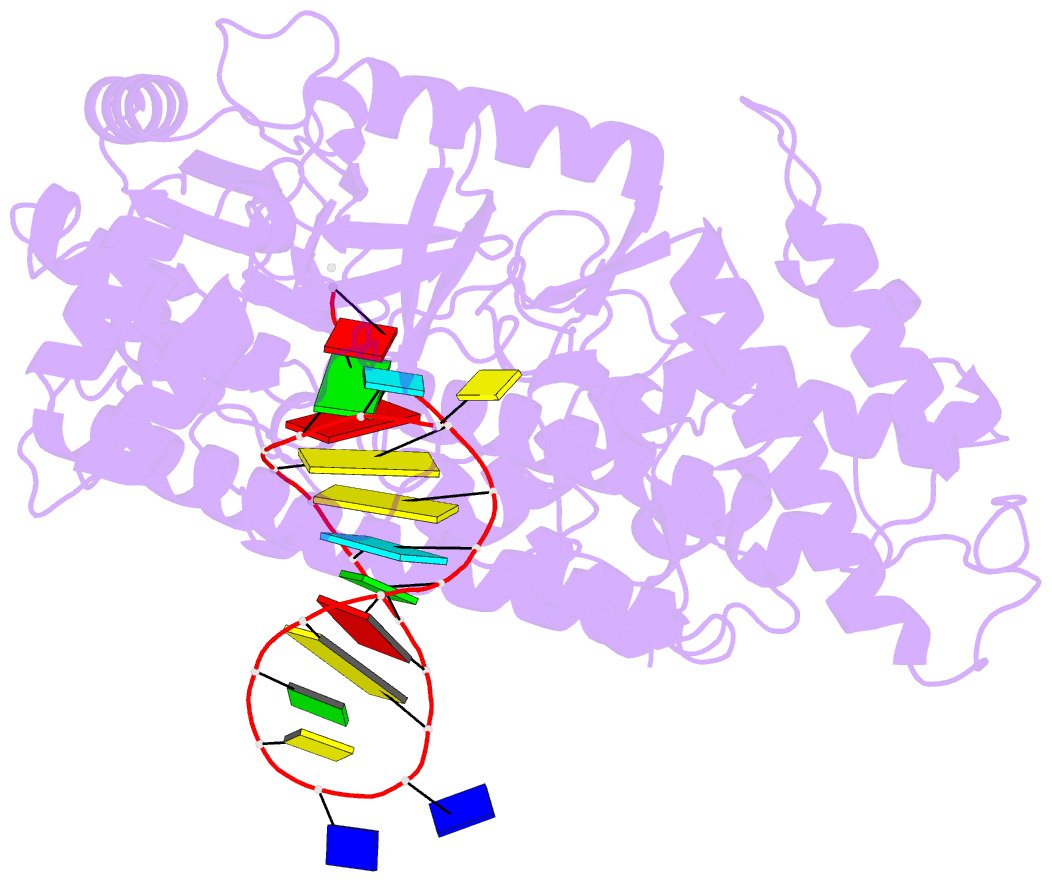
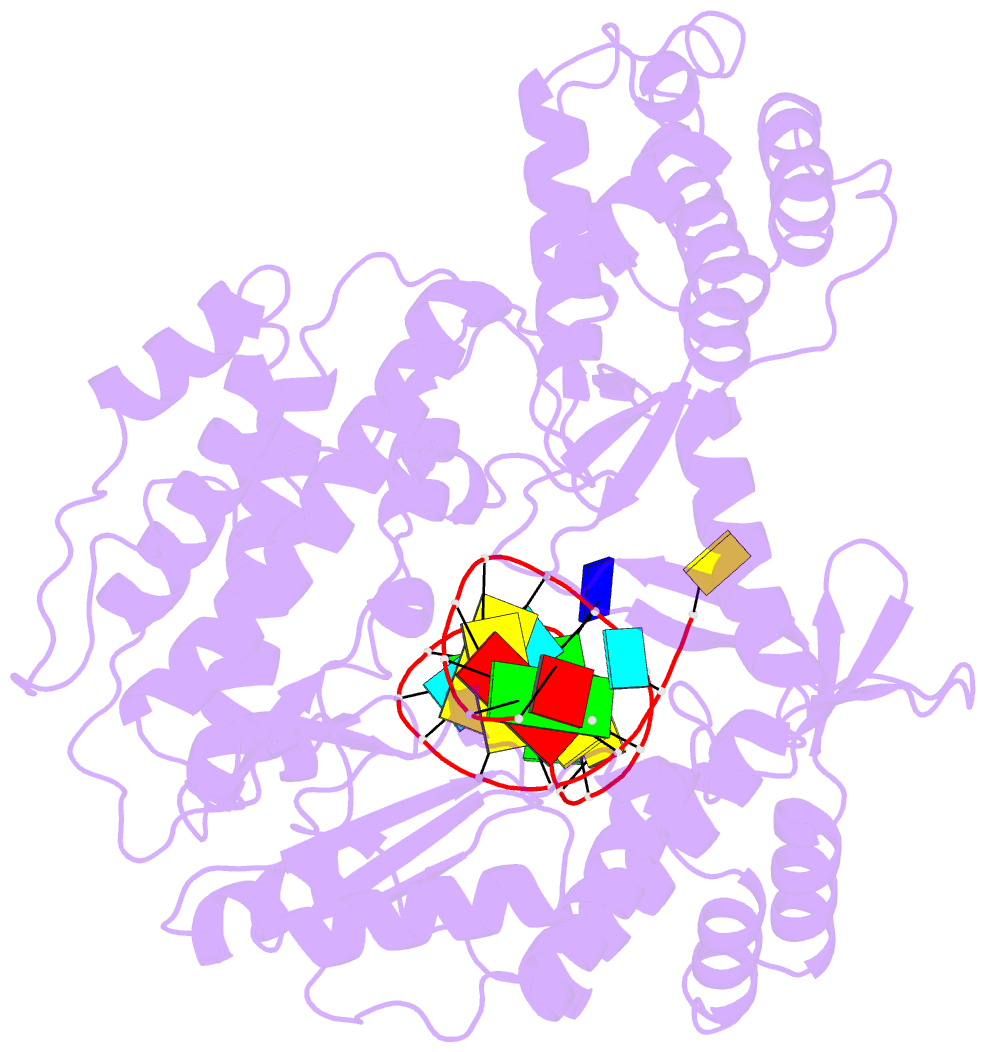
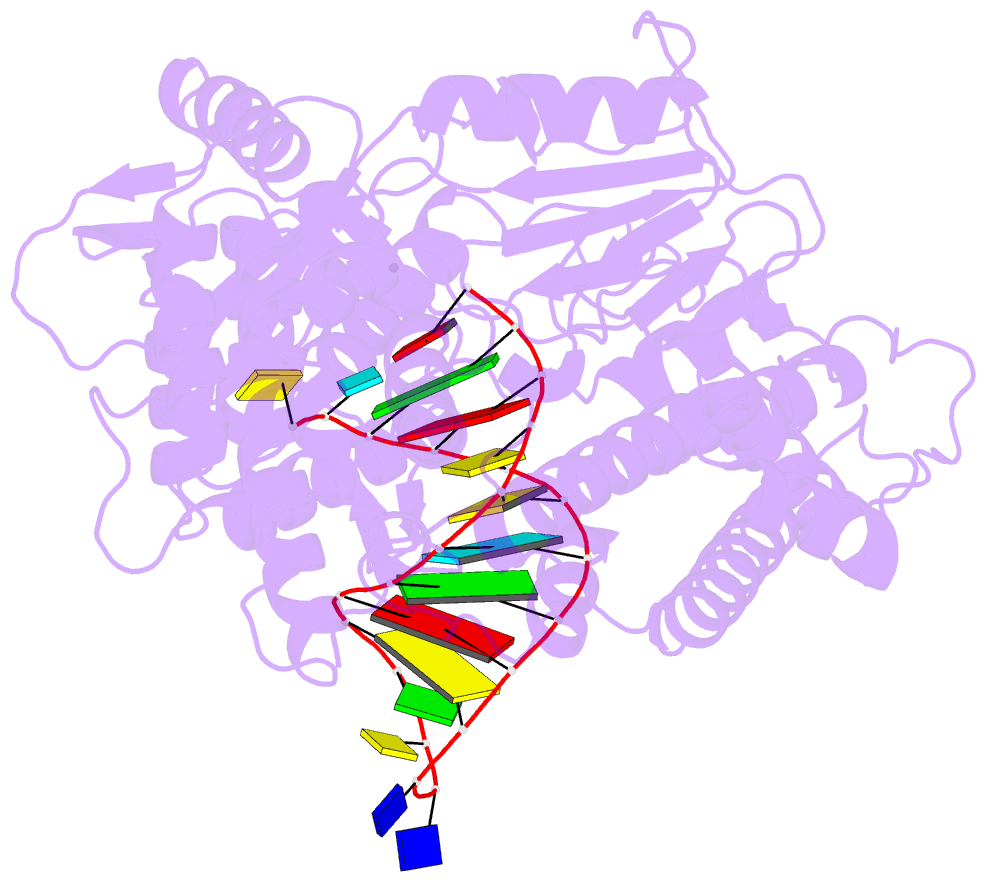
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6e53; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-transferase inhibitor
- Method
- X-ray (2.8 Å)
- Summary
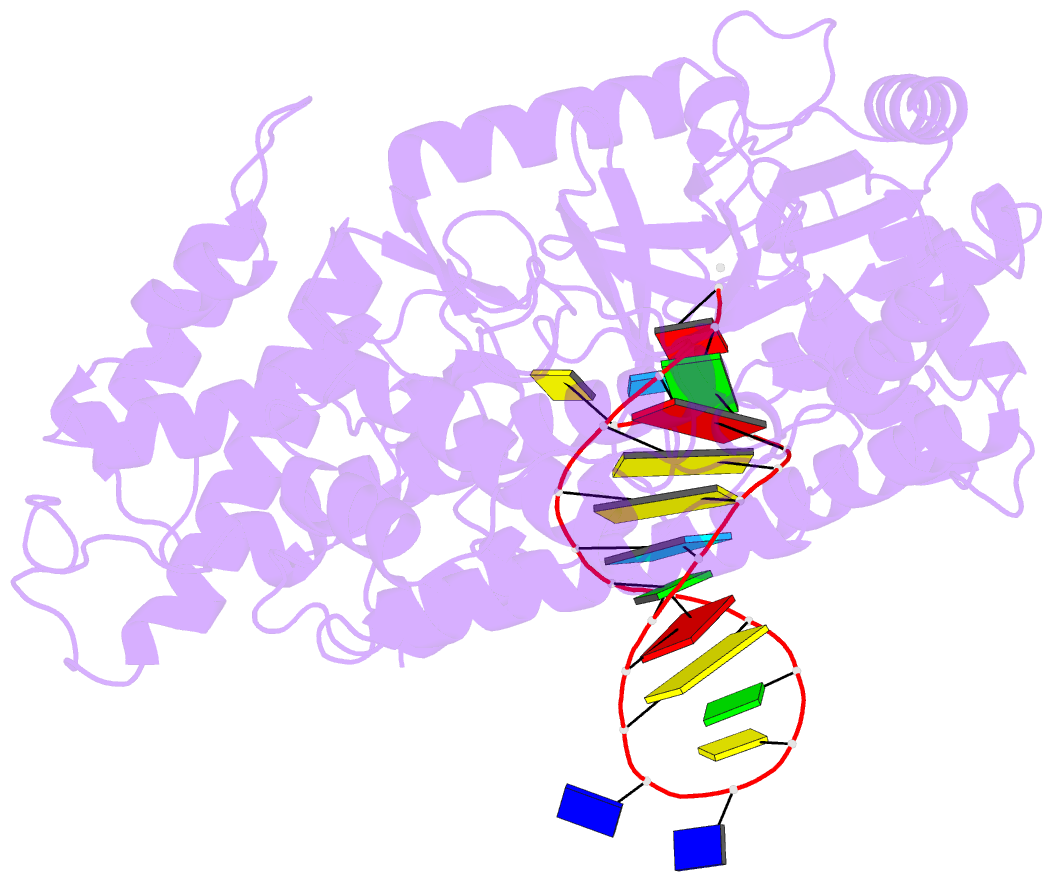
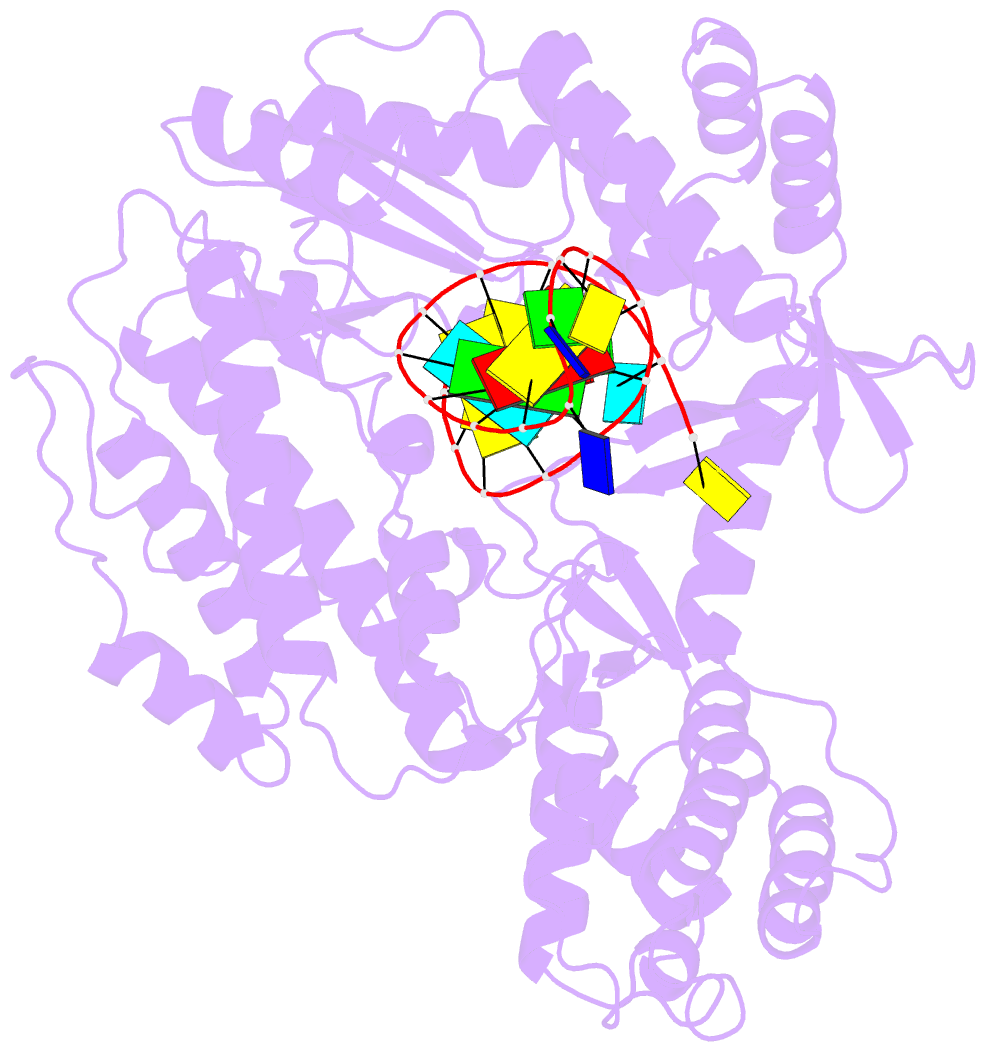
- Structure of tert in complex with a novel telomerase inhibitor
- Reference
- Hernandez-Sanchez W, Huang W, Plucinsky B, Garcia-Vazquez N, Robinson NJ, Schiemann WP, Berdis AJ, Skordalakes E, Taylor DJ (2019): "A non-natural nucleotide uses a specific pocket to selectively inhibit telomerase activity." Plos Biol., 17, e3000204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000204.
- Abstract
- Telomerase, a unique reverse transcriptase that specifically extends the ends of linear chromosomes, is up-regulated in the vast majority of cancer cells. Here, we show that an indole nucleotide analog, 5-methylcarboxyl-indolyl-2'-deoxyriboside 5'-triphosphate (5-MeCITP), functions as an inhibitor of telomerase activity. The crystal structure of 5-MeCITP bound to the Tribolium castaneum telomerase reverse transcriptase reveals an atypical interaction, in which the nucleobase is flipped in the active site. In this orientation, the methoxy group of 5-MeCITP extends out of the canonical active site to interact with a telomerase-specific hydrophobic pocket formed by motifs 1 and 2 in the fingers domain and T-motif in the RNA-binding domain of the telomerase reverse transcriptase. In vitro data show that 5-MeCITP inhibits telomerase with a similar potency as the clinically administered nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor azidothymidine (AZT). In addition, cell-based studies show that treatment with the cell-permeable nucleoside counterpart of 5-MeCITP leads to telomere shortening in telomerase-positive cancer cells, while resulting in significantly lower cytotoxic effects in telomerase-negative cell lines when compared with AZT treatment.