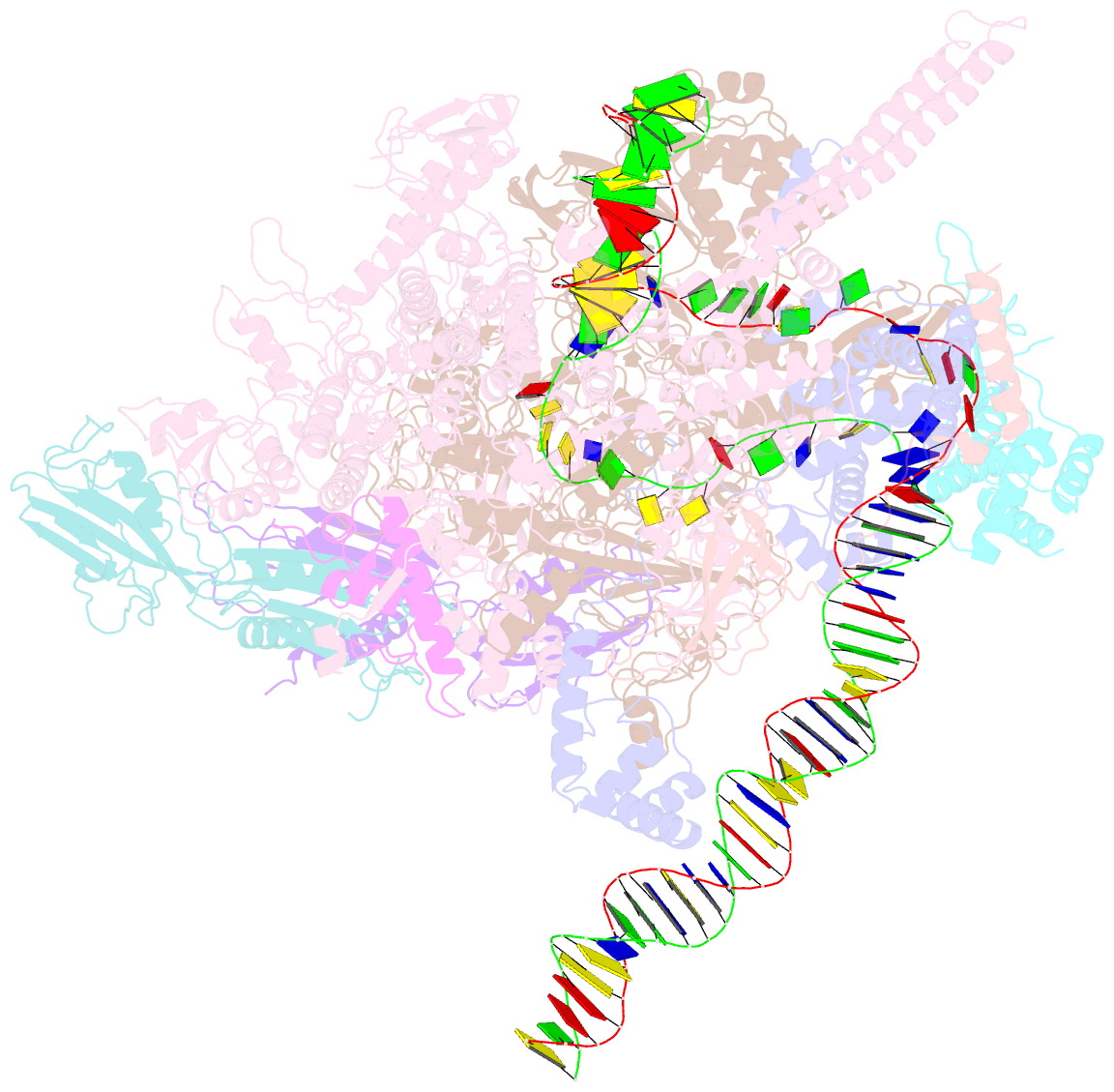
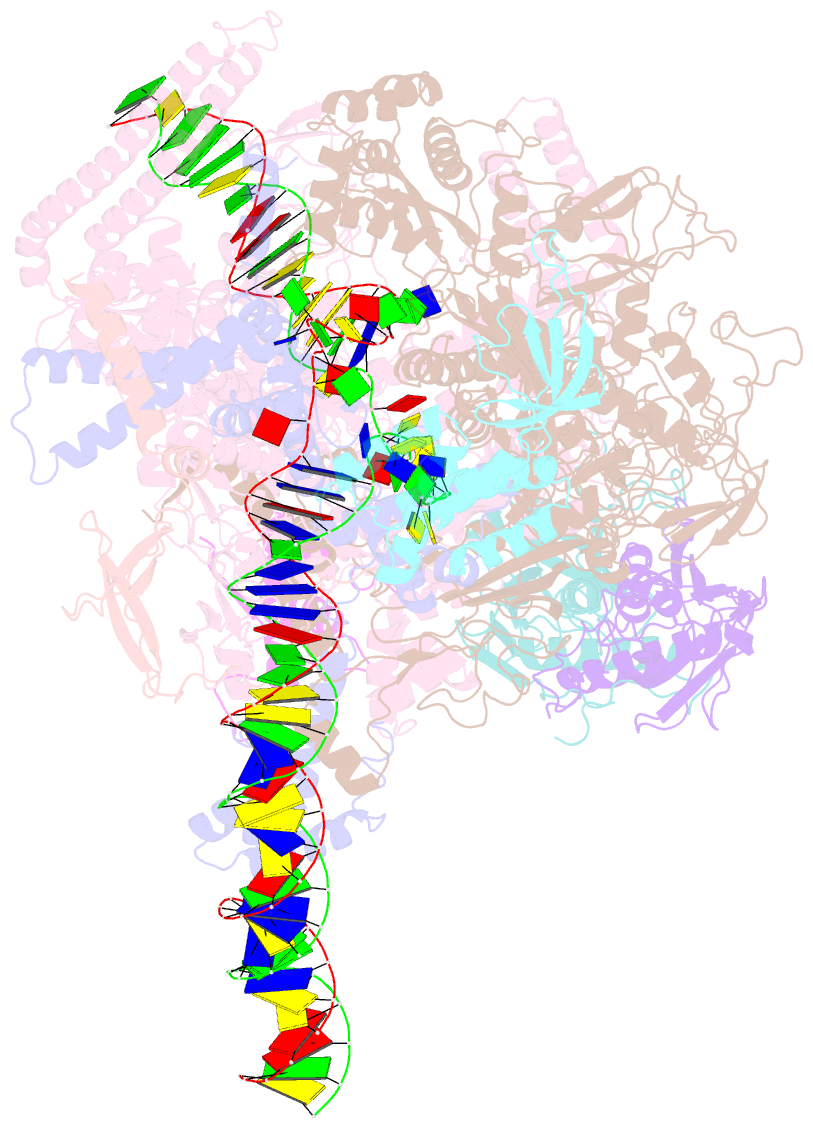
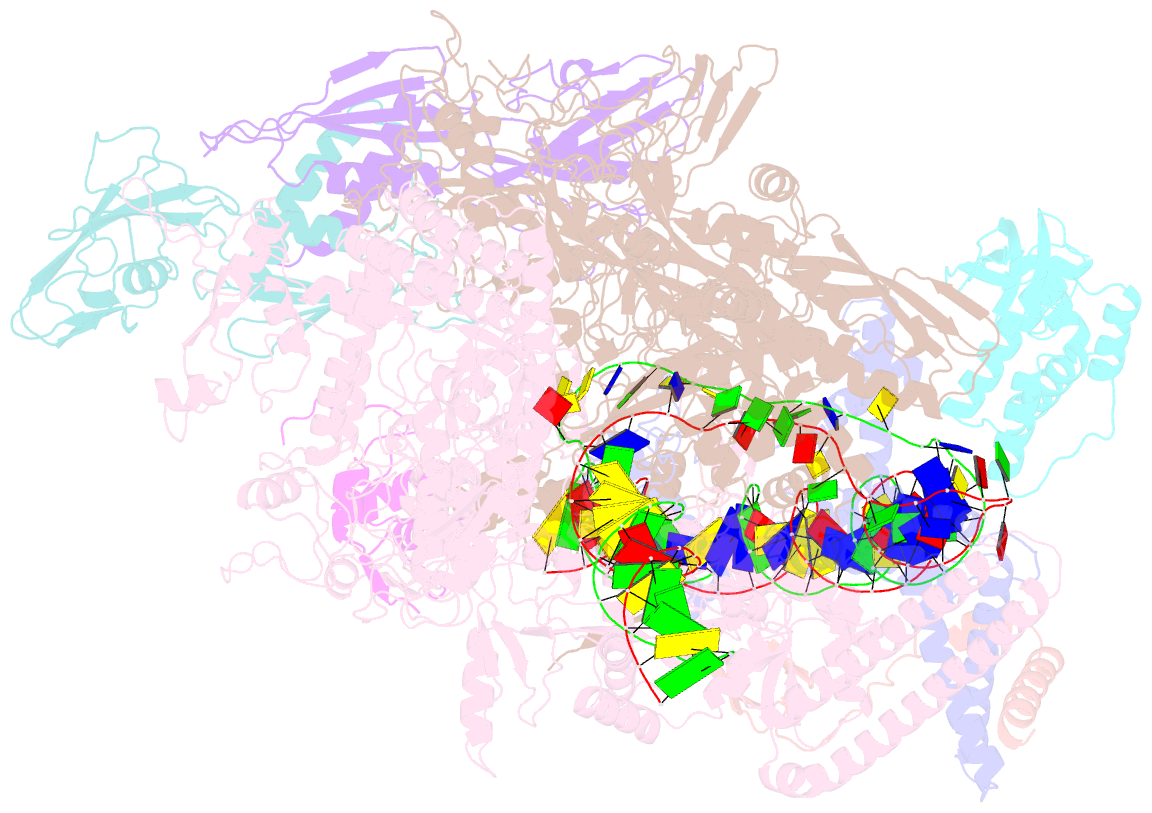
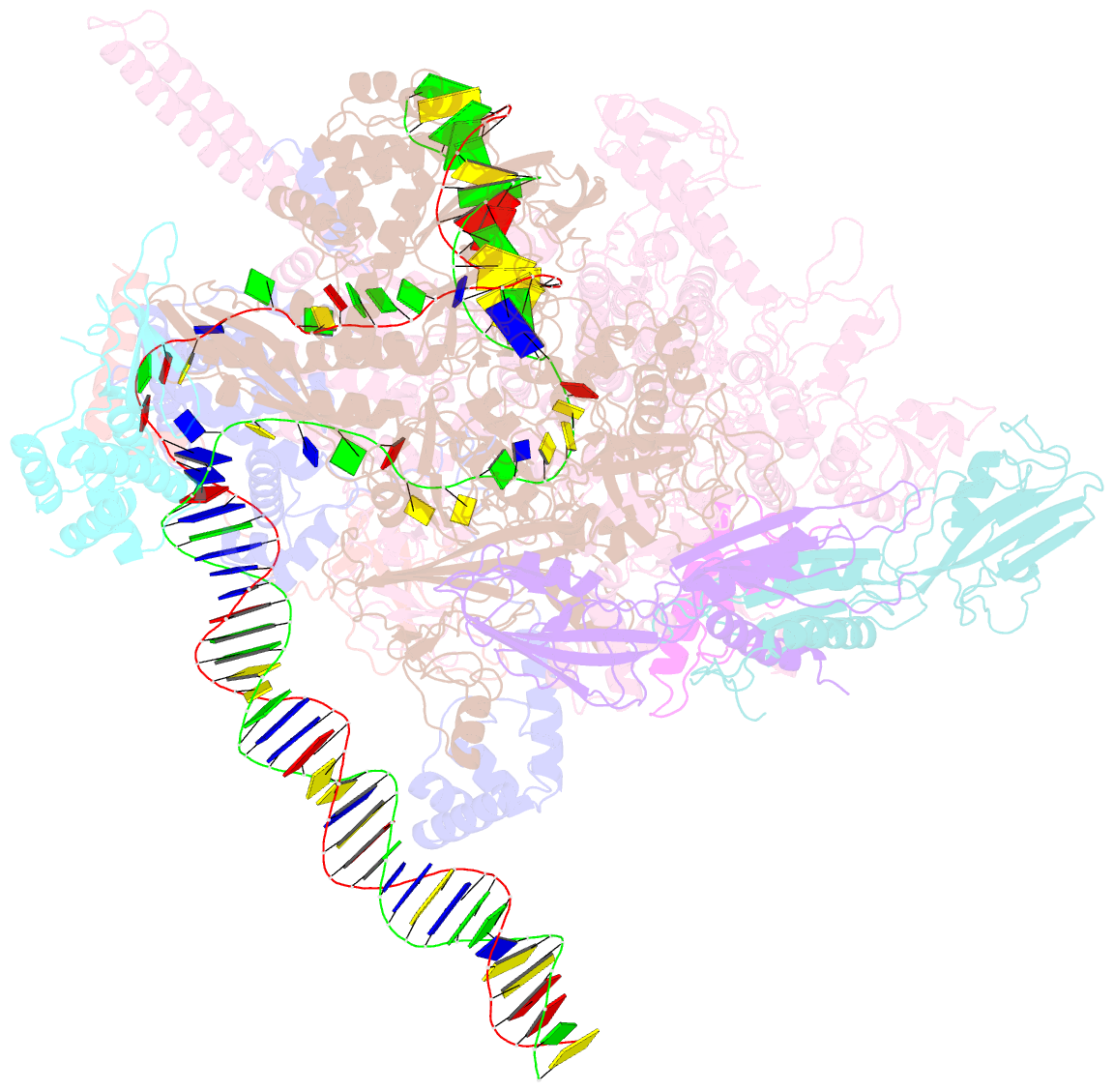
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6edt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM
- Summary
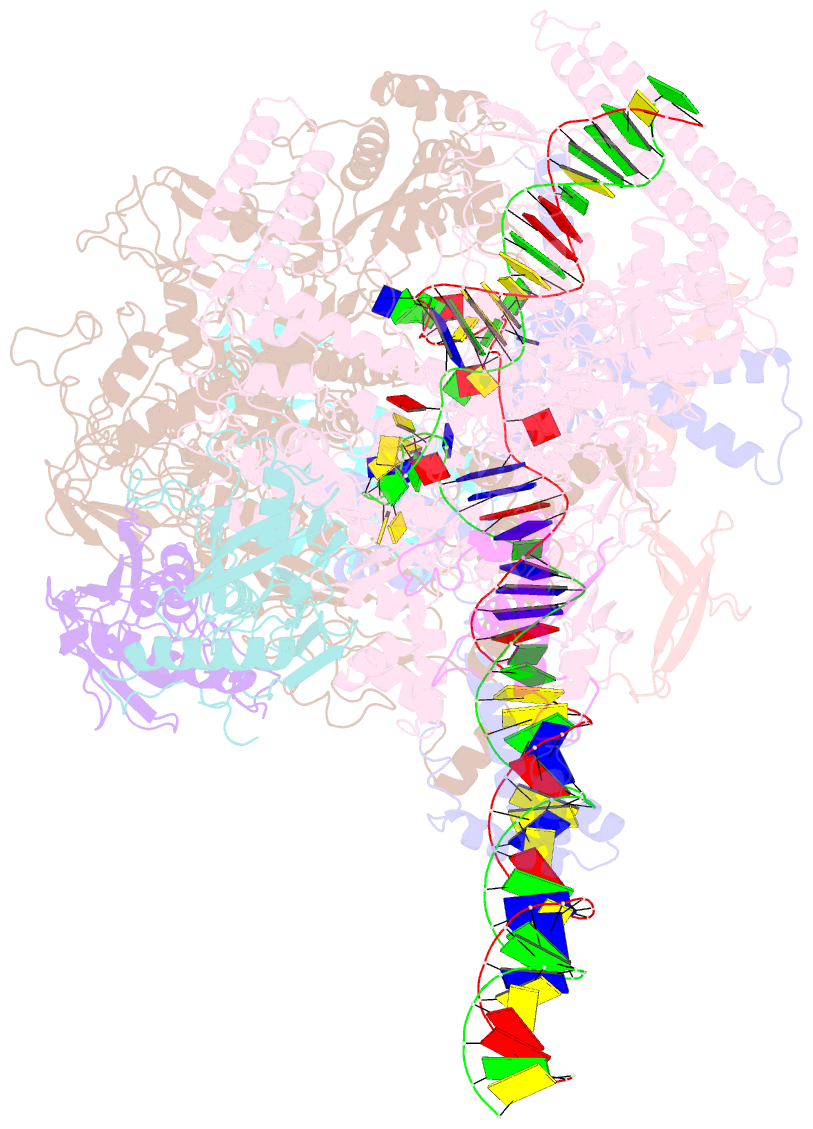
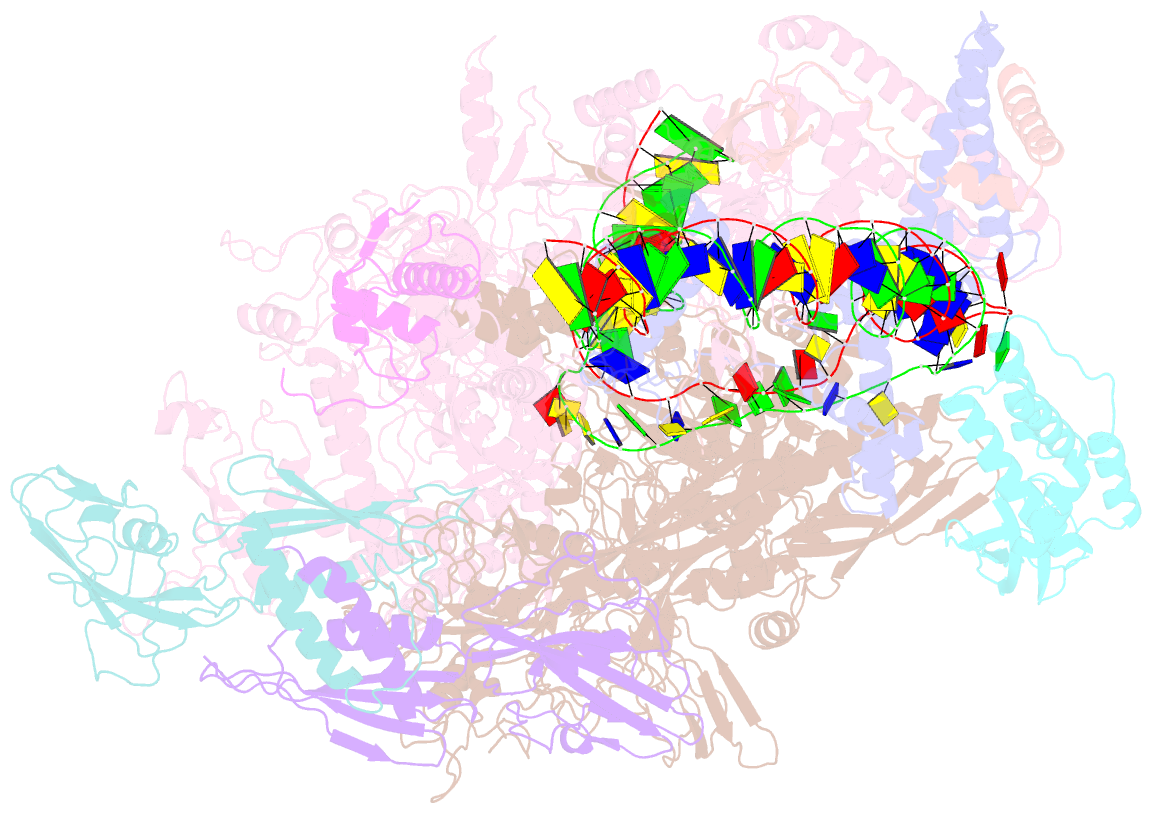
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis rnap open promoter complex with rbpa-card and ap3 promoter
- Reference
- Boyaci H, Chen J, Jansen R, Darst SA, Campbell EA (2019): "Structures of an RNA polymerase promoter melting intermediate elucidate DNA unwinding." Nature, 565, 382-385. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0840-5.
- Abstract
- A key regulated step of transcription is promoter melting by RNA polymerase (RNAP) to form the open promoter complex1-3. To generate the open complex, the conserved catalytic core of the RNAP combines with initiation factors to locate promoter DNA, unwind 12-14 base pairs of the DNA duplex and load the template-strand DNA into the RNAP active site. Formation of the open complex is a multi-step process during which transient intermediates of unknown structure are formed4-6. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of bacterial RNAP-promoter DNA complexes, including structures of partially melted intermediates. The structures show that late steps of promoter melting occur within the RNAP cleft, delineate key roles for fork-loop 2 and switch 2-universal structural features of RNAP-in restricting access of DNA to the RNAP active site, and explain why clamp opening is required to allow entry of single-stranded template DNA into the active site. The key roles of fork-loop 2 and switch 2 suggest a common mechanism for late steps in promoter DNA opening to enable gene expression across all domains of life.