Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6f5o; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (9.8 Å)
- Summary
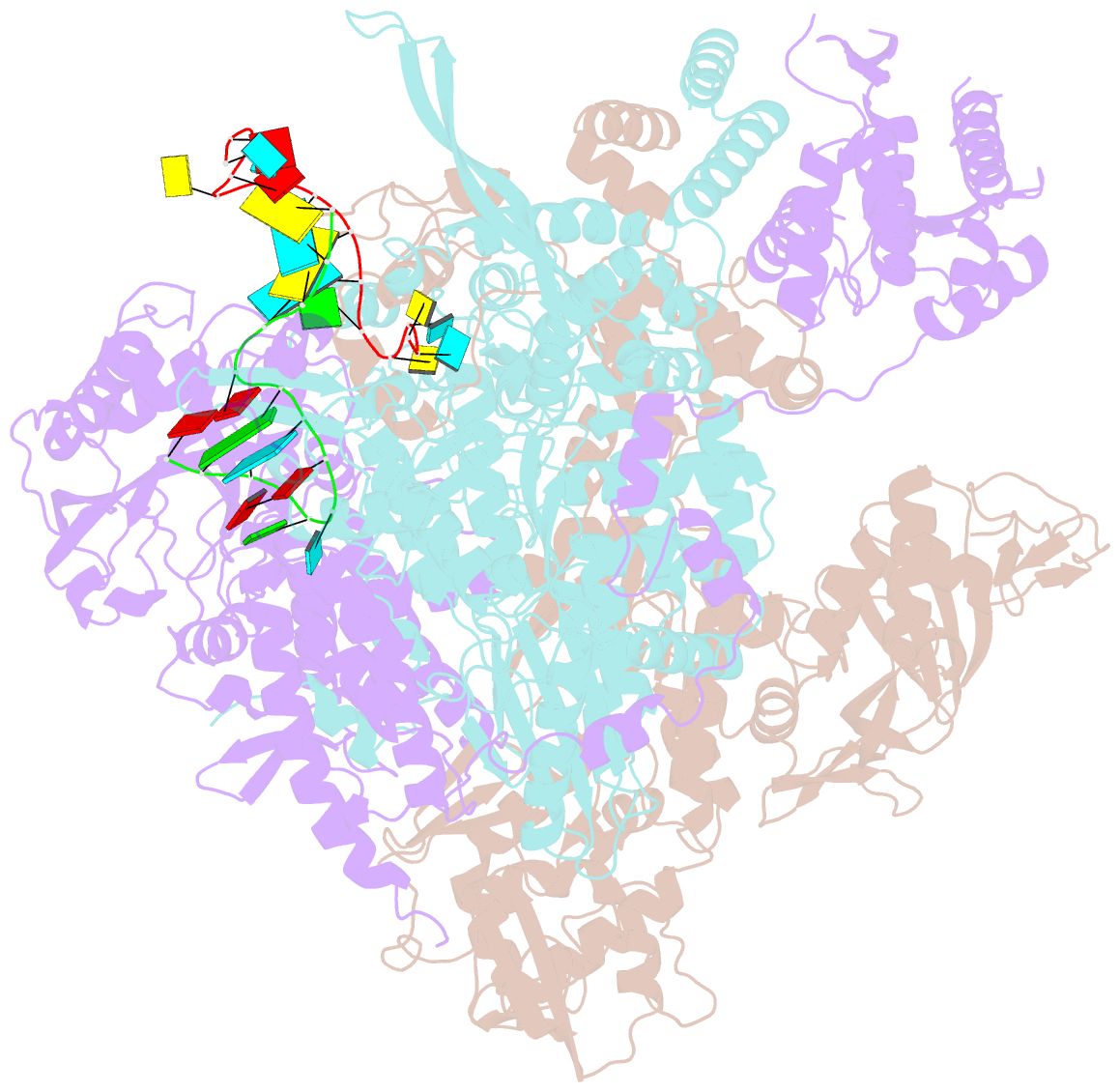
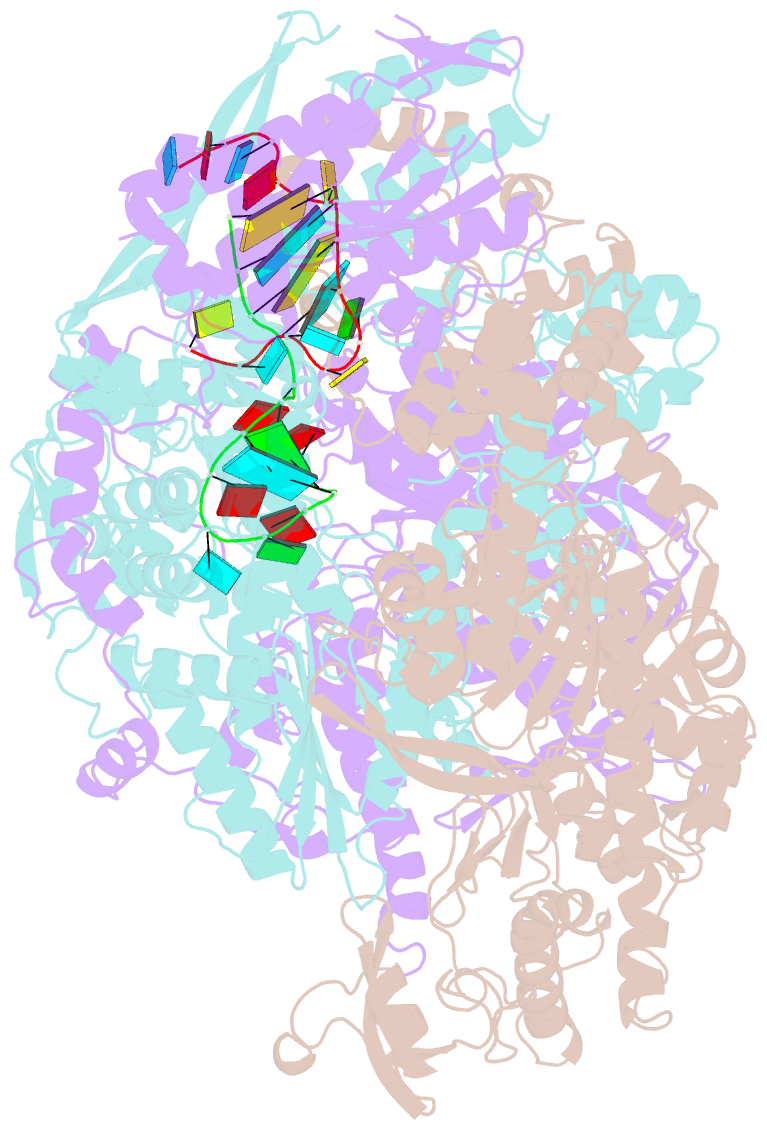
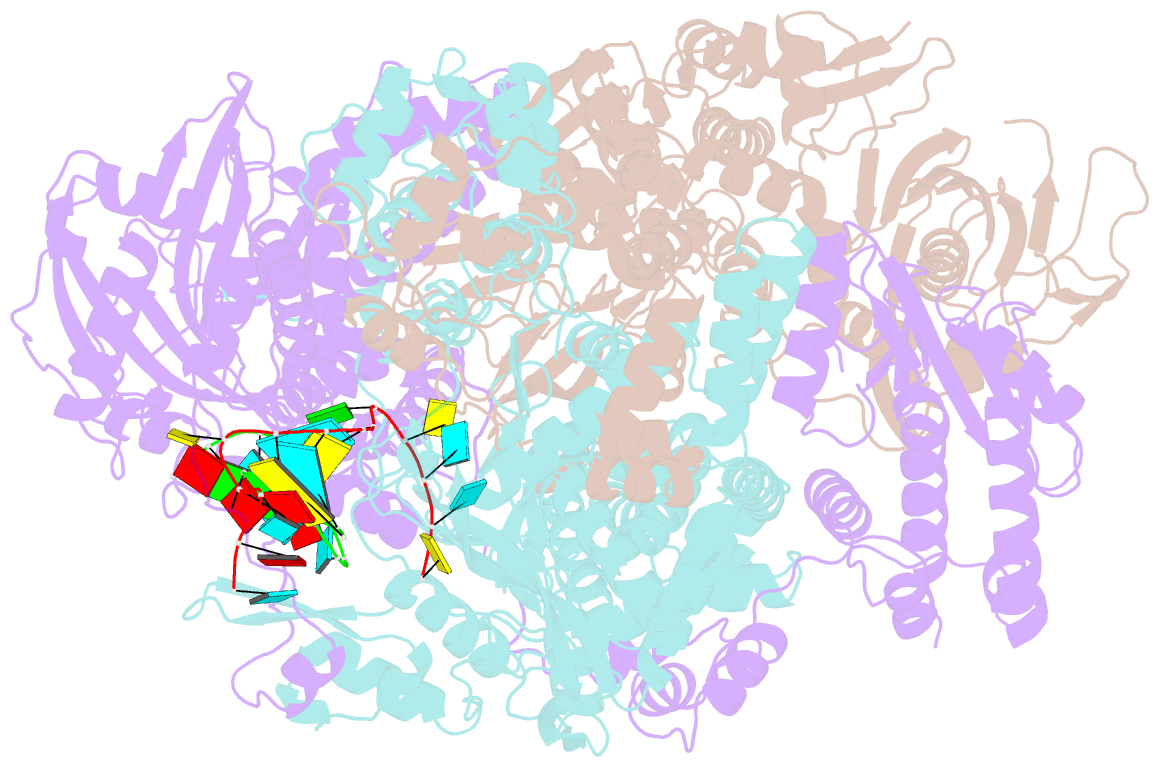
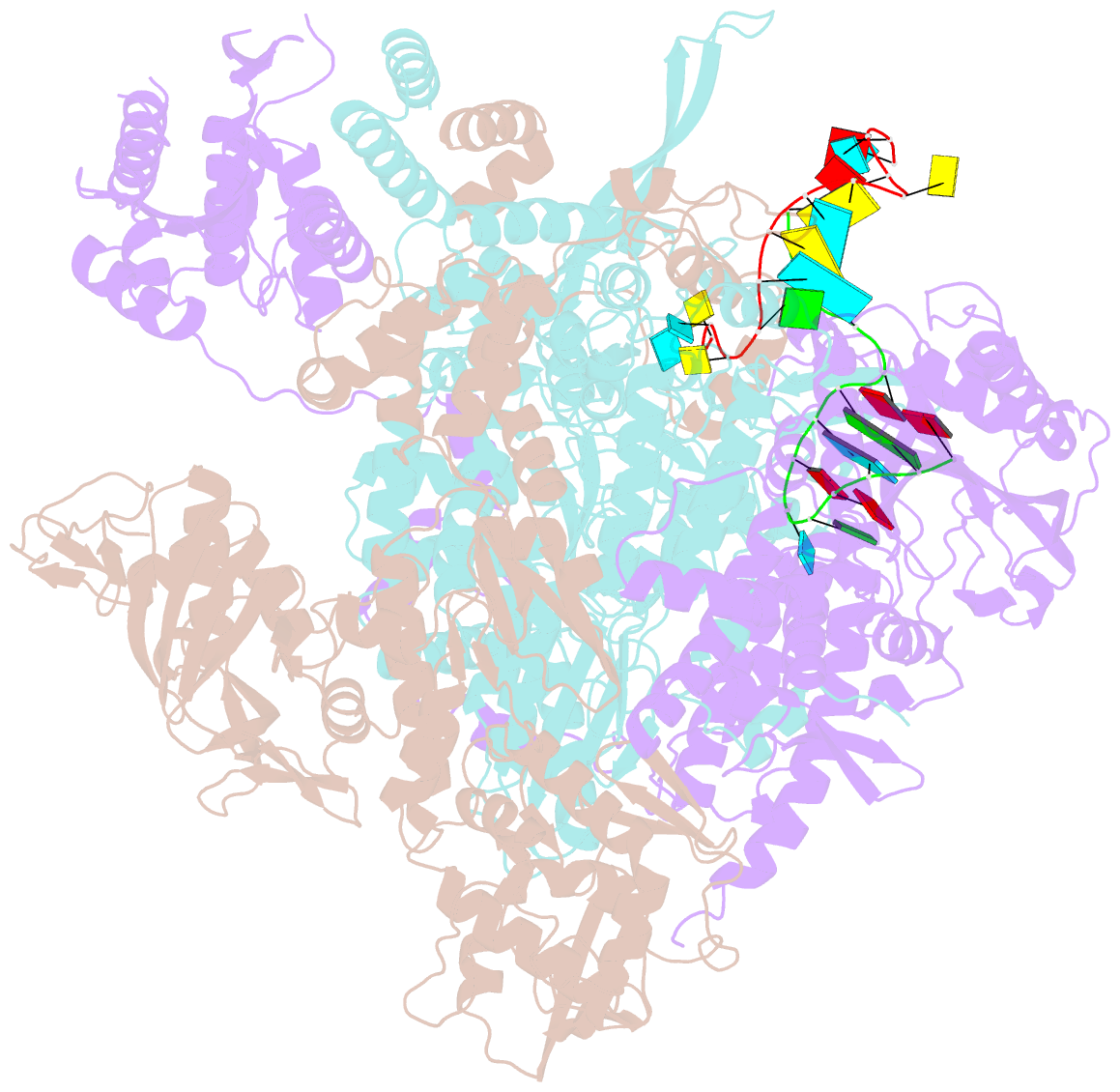
- A mechanism for the activation of the influenza virus transcriptase
- Reference
- Serna Martin I, Hengrung N, Renner M, Sharps J, Martinez-Alonso M, Masiulis S, Grimes JM, Fodor E (2018): "A Mechanism for the Activation of the Influenza Virus Transcriptase." Mol. Cell, 70, 1101-1110.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.011.
- Abstract
- Influenza virus RNA polymerase (FluPol), a heterotrimer composed of PB1, PB2, and PA subunits (P3 in influenza C), performs both transcription and replication of the viral RNA genome. For transcription, FluPol interacts with the C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which enables FluPol to snatch capped RNA primers from nascent host RNAs. Here, we describe the co-crystal structure of influenza C virus polymerase (FluPolC) bound to a Ser5-phosphorylated CTD (pS5-CTD) peptide. The position of the CTD-binding site at the interface of PB1, P3, and the flexible PB2 C-terminal domains suggests that CTD binding stabilizes the transcription-competent conformation of FluPol. In agreement, both cap snatching and capped primer-dependent transcription initiation by FluPolC are enhanced in the presence of pS5-CTD. Mutations of amino acids in the CTD-binding site reduce viral mRNA synthesis. We propose a model for the activation of the influenza virus transcriptase through its association with pS5-CTD of Pol II.