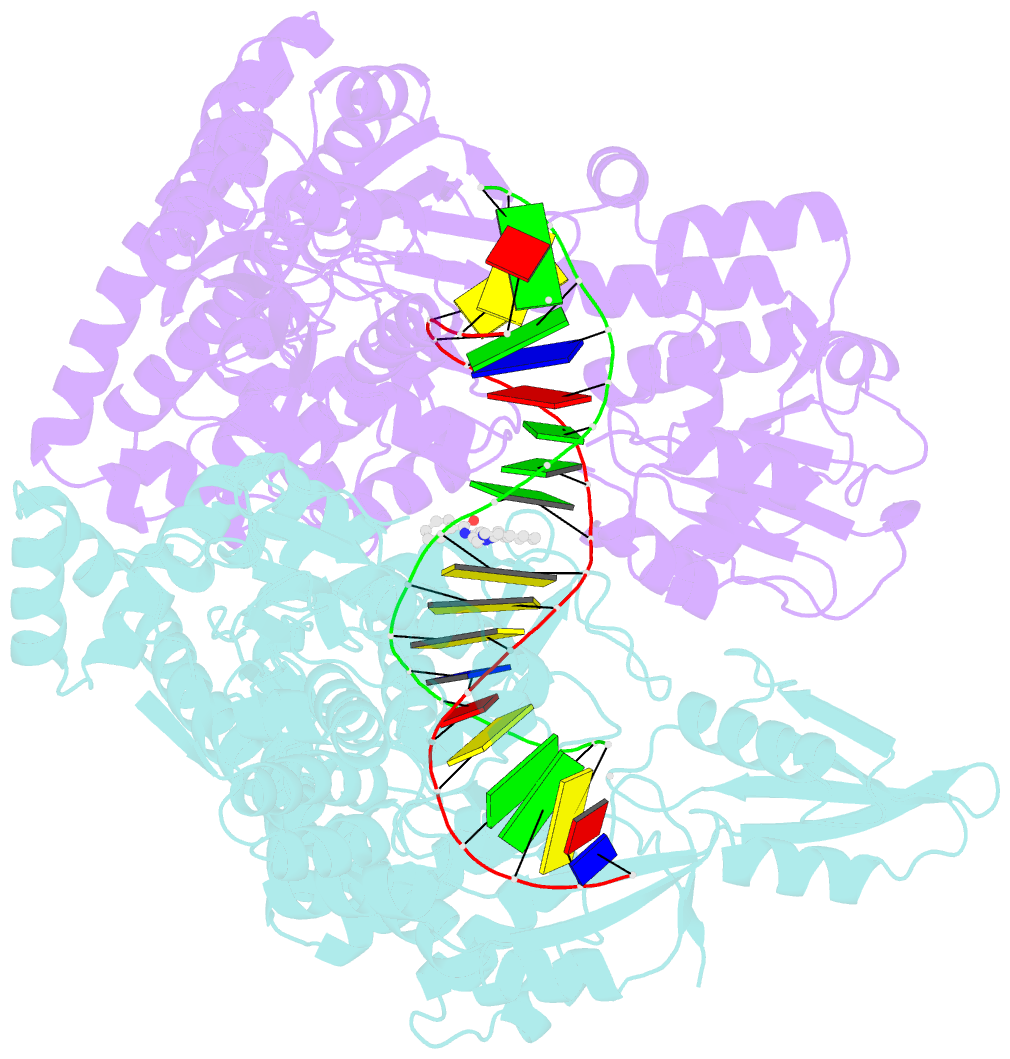
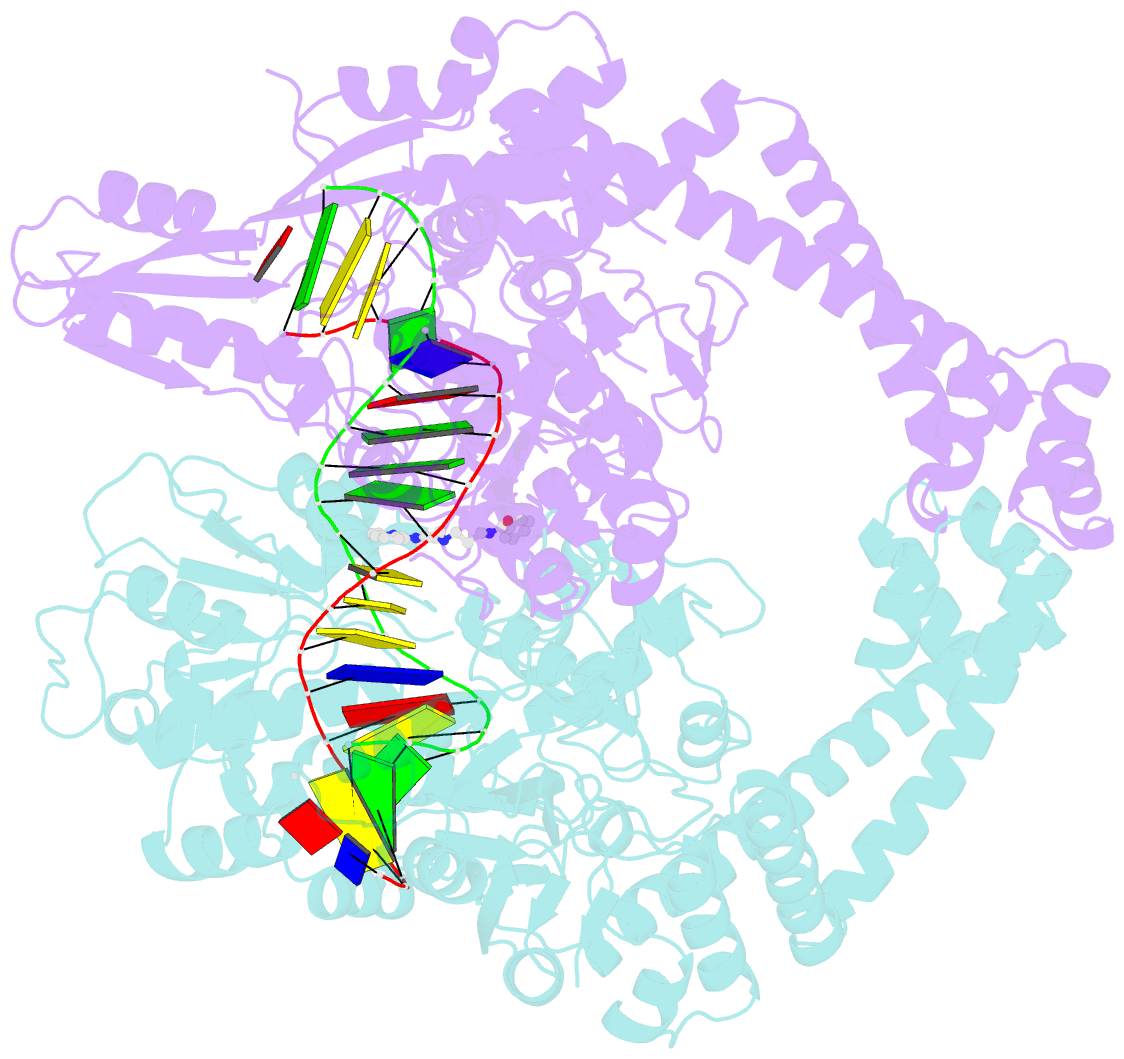
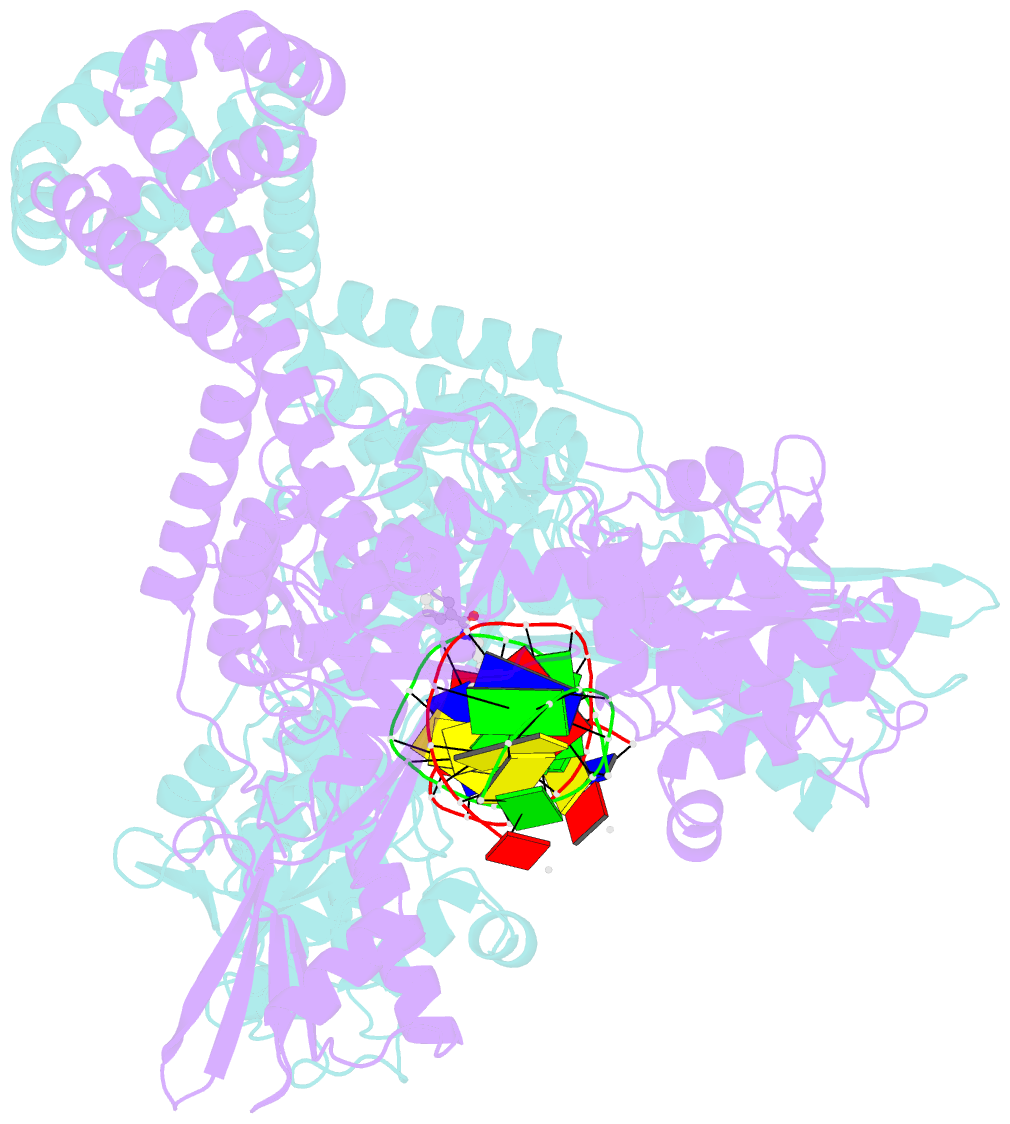
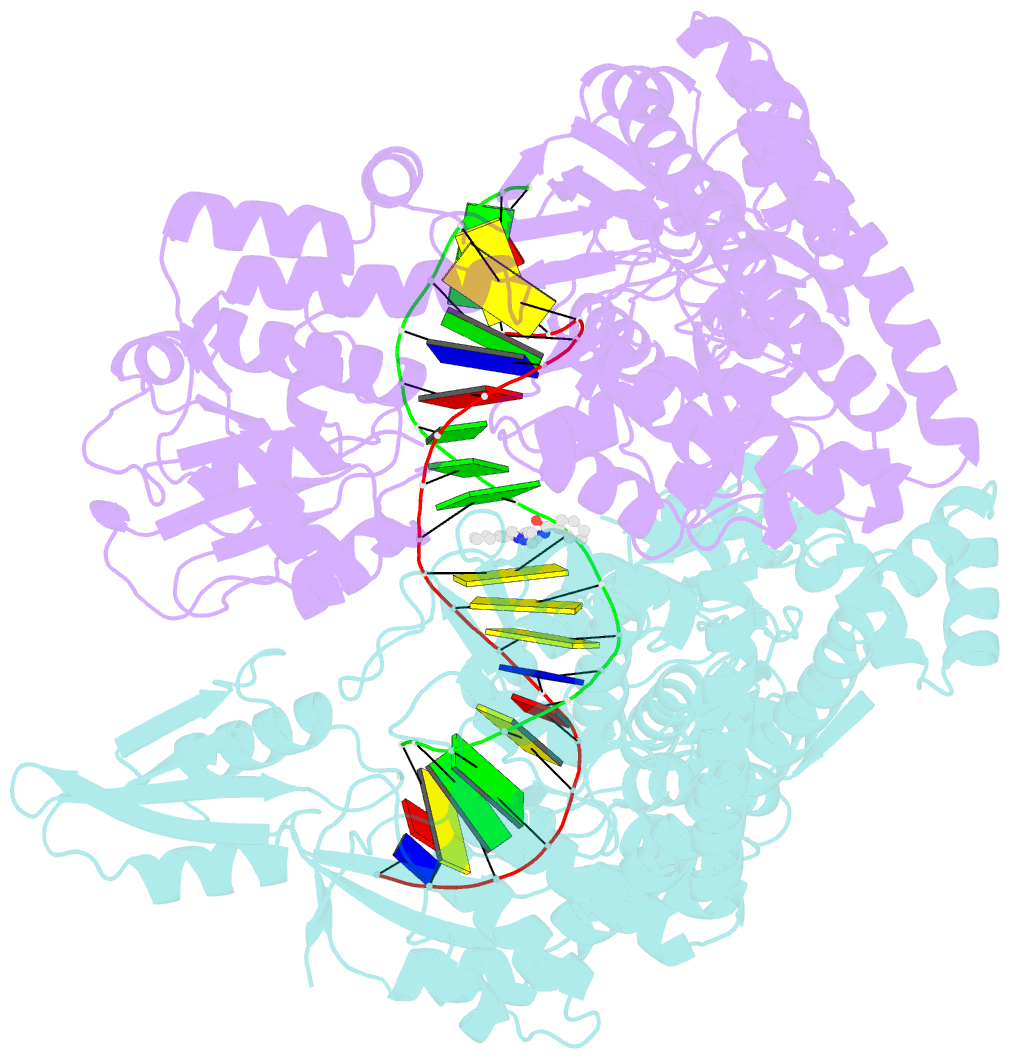
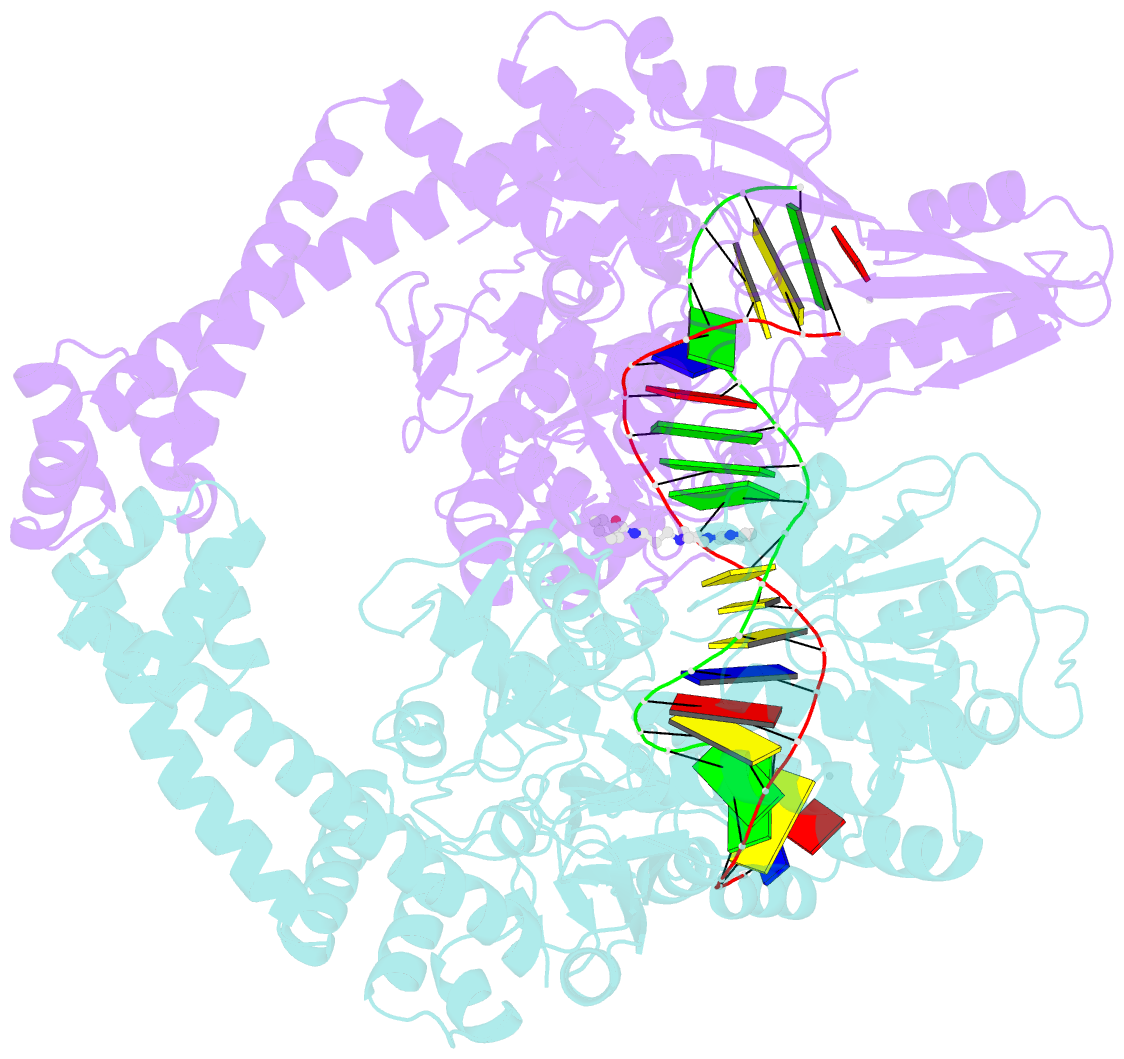
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6fm4; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- isomerase
- Method
- X-ray (2.7 Å)
- Summary
- The crystal structure of s. aureus gyrase complex with id-130 and DNA
- Reference
- Magaro G, Prati F, Garofalo B, Corso G, Furlotti G, Apicella C, Mangano G, D'Atanasio N, Robinson D, Di Giorgio FP, Ombrato R (2019): "Virtual Screening Approach and Investigation of Structure-Activity Relationships To Discover Novel Bacterial Topoisomerase Inhibitors Targeting Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Pathogens." J.Med.Chem., 62, 7445-7472. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00394.
- Abstract
- Bacterial resistance is increasing rapidly, requiring urgent identification of new antibacterial drugs that are effective against multidrug-resistant pathogens. Novel bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors (NBTIs) provide a new strategy for investigating the well-validated DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV targets while preventing cross-resistance issues. On this basis, starting from a virtual screening campaign and subsequent structure-based hit optimization guided by X-ray studies, a novel class of piperazine-like NBTIs with outstanding enzymatic activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV was identified. Notably, compounds