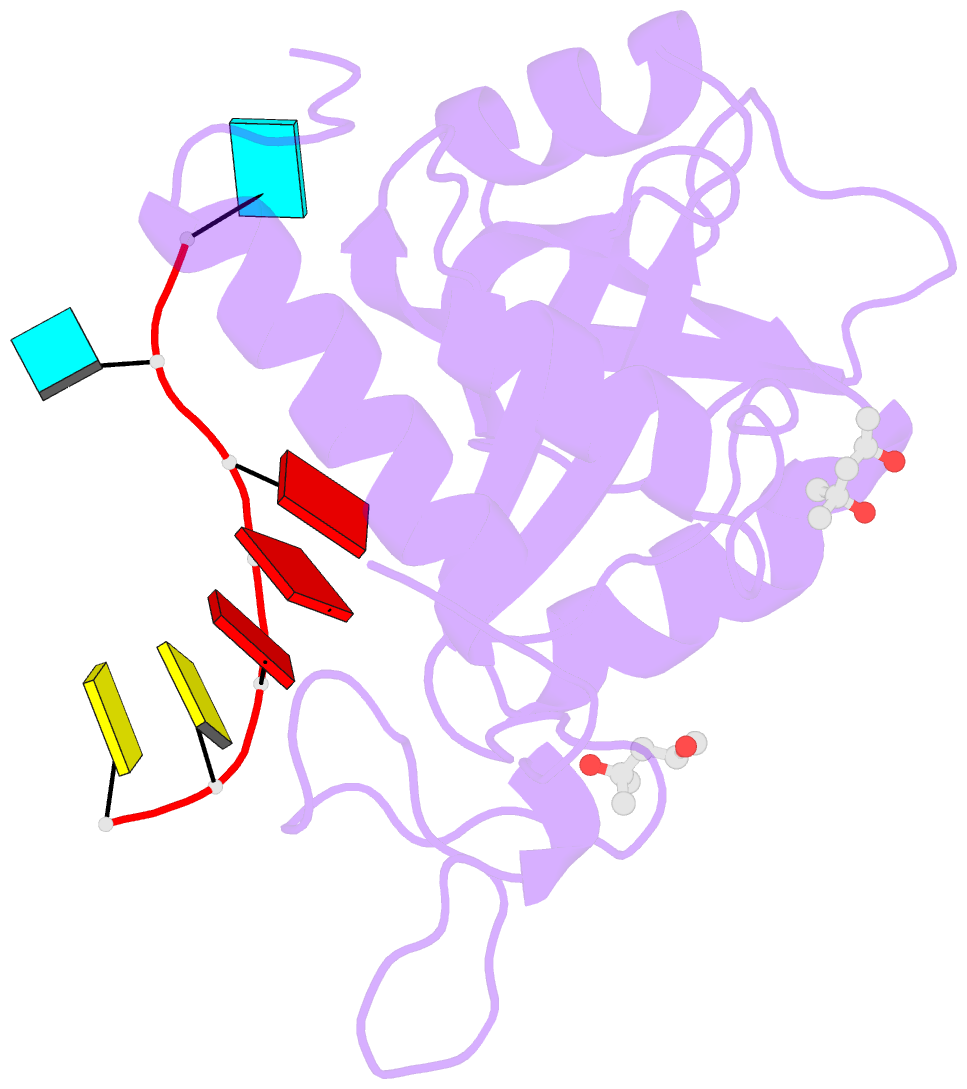
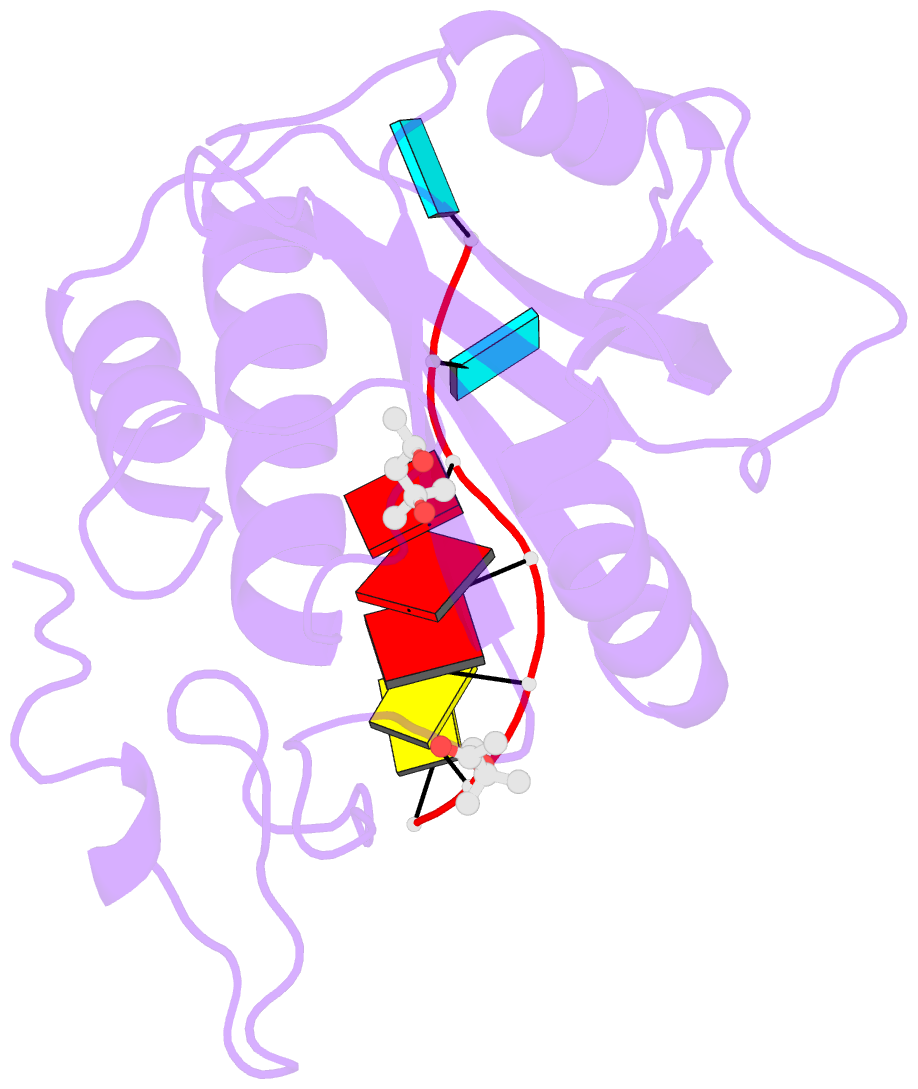
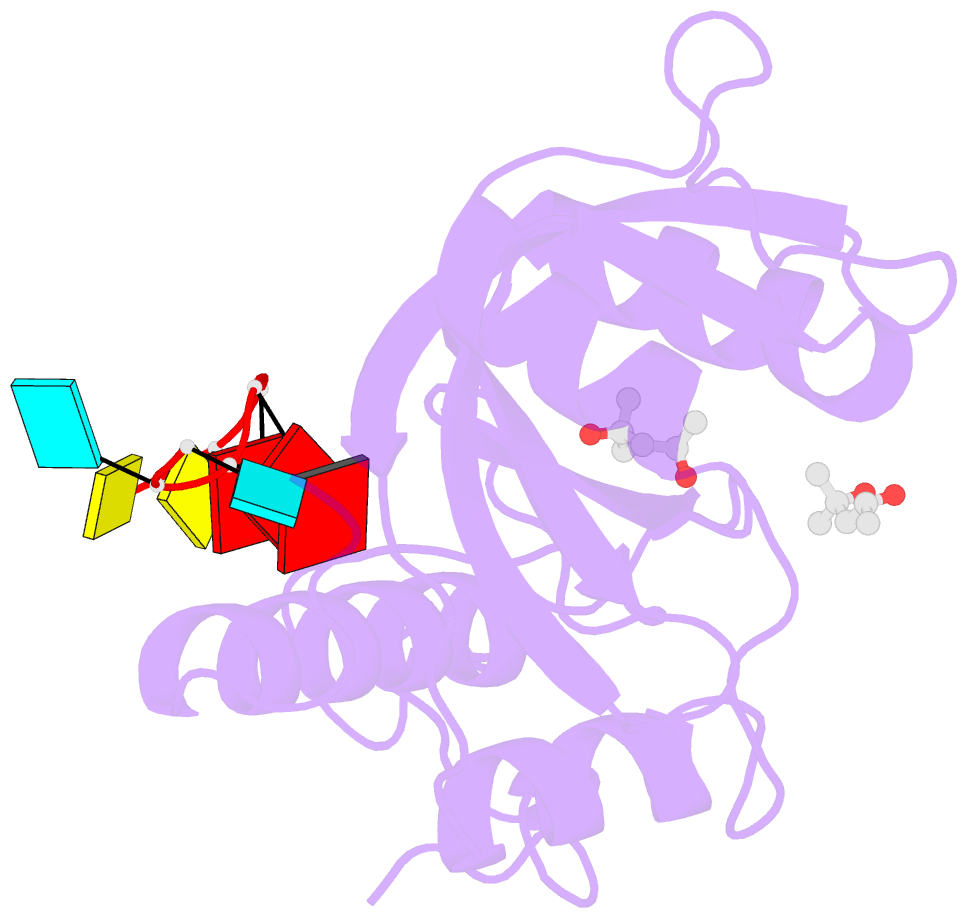
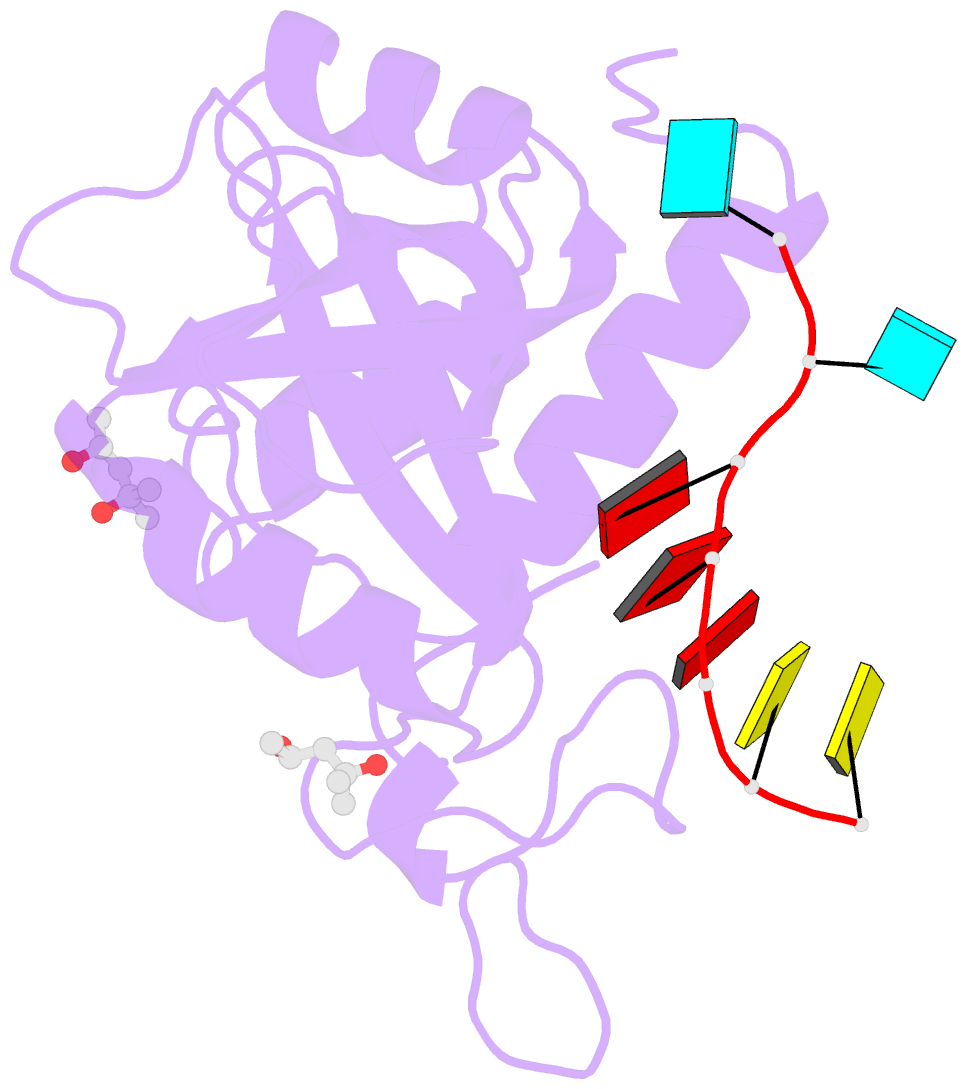
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6fpq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (1.42 Å)
- Summary
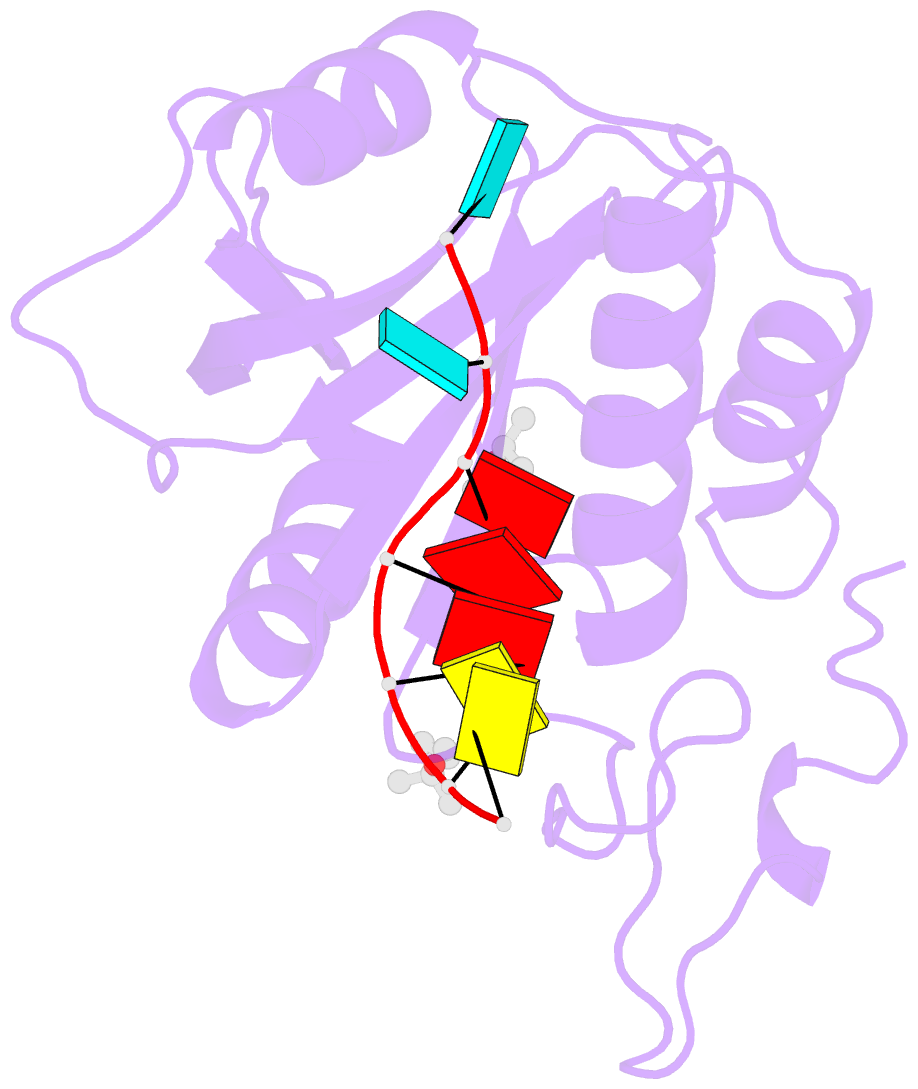
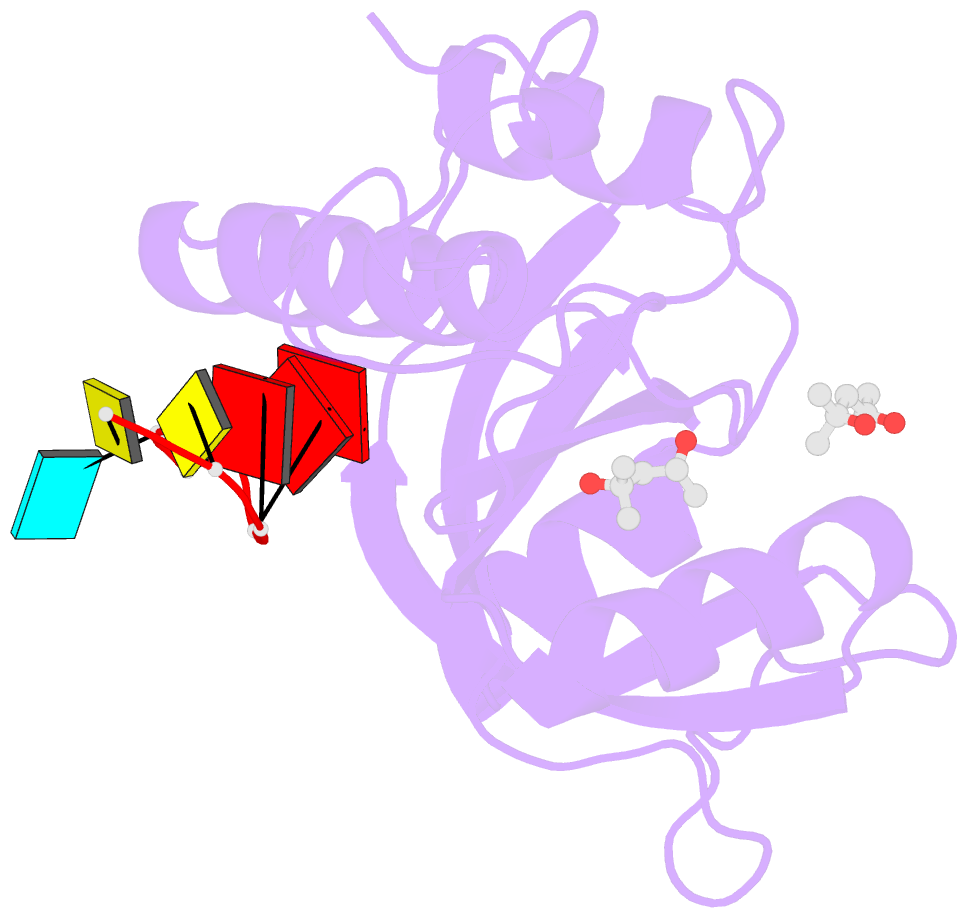
- Structure of s. pombe mmi1 in complex with 7-mer RNA
- Reference
- Stowell JAW, Wagstaff JL, Hill CH, Yu M, McLaughlin SH, Freund SMV, Passmore LA (2018): "A low-complexity region in the YTH domain protein Mmi1 enhances RNA binding." J. Biol. Chem., 293, 9210-9222. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002291.
- Abstract
- Mmi1 is an essential RNA-binding protein in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe that eliminates meiotic transcripts during normal vegetative growth. Mmi1 contains a YTH domain that binds specific RNA sequences, targeting mRNAs for degradation. The YTH domain of Mmi1 uses a noncanonical RNA-binding surface that includes contacts outside the conserved fold. Here, we report that an N-terminal extension that is proximal to the YTH domain enhances RNA binding. Using X-ray crystallography, NMR, and biophysical methods, we show that this low-complexity region becomes more ordered upon RNA binding. This enhances the affinity of the interaction of the Mmi1 YTH domain with specific RNAs by reducing the dissociation rate of the Mmi1-RNA complex. We propose that the low-complexity region influences RNA binding indirectly by reducing dynamic motions of the RNA-binding groove and stabilizing a conformation of the YTH domain that binds to RNA with high affinity. Taken together, our work reveals how a low-complexity region proximal to a conserved folded domain can adopt an ordered structure to aid nucleic acid binding.