Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6hlr; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.18 Å)
- Summary
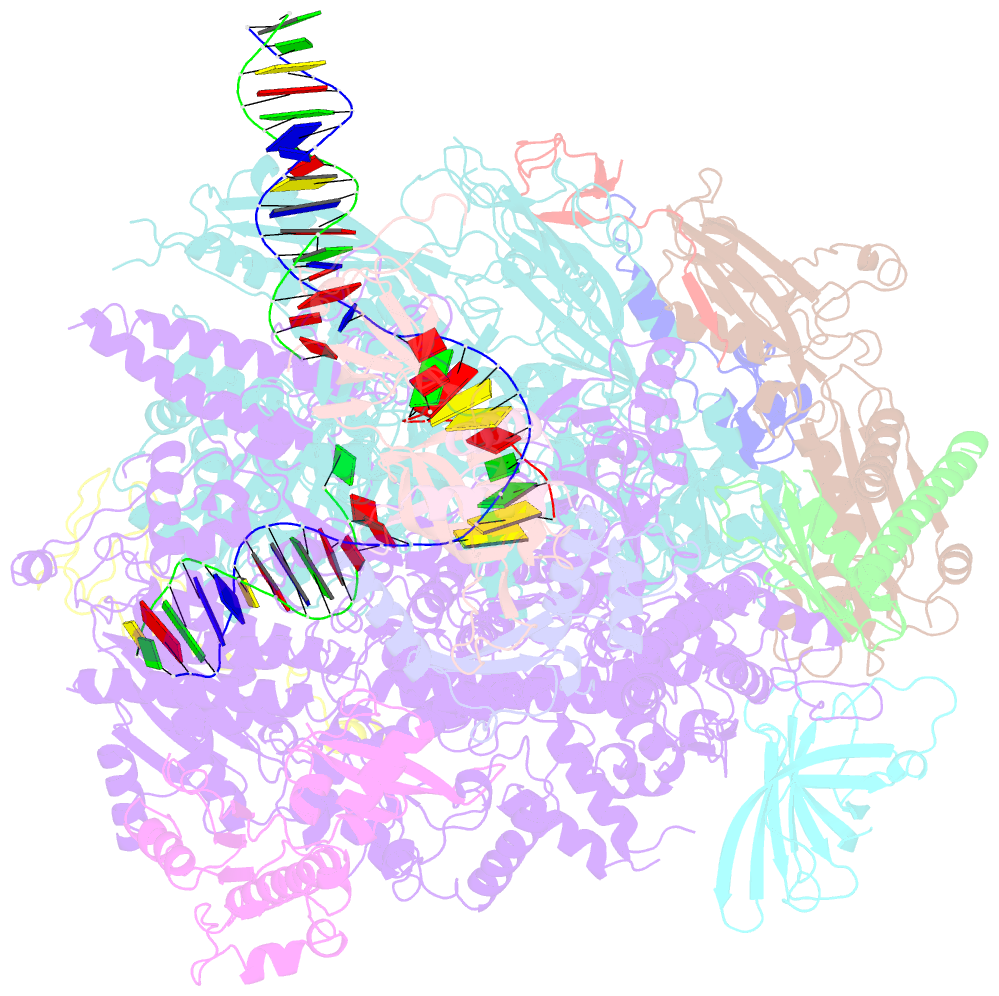
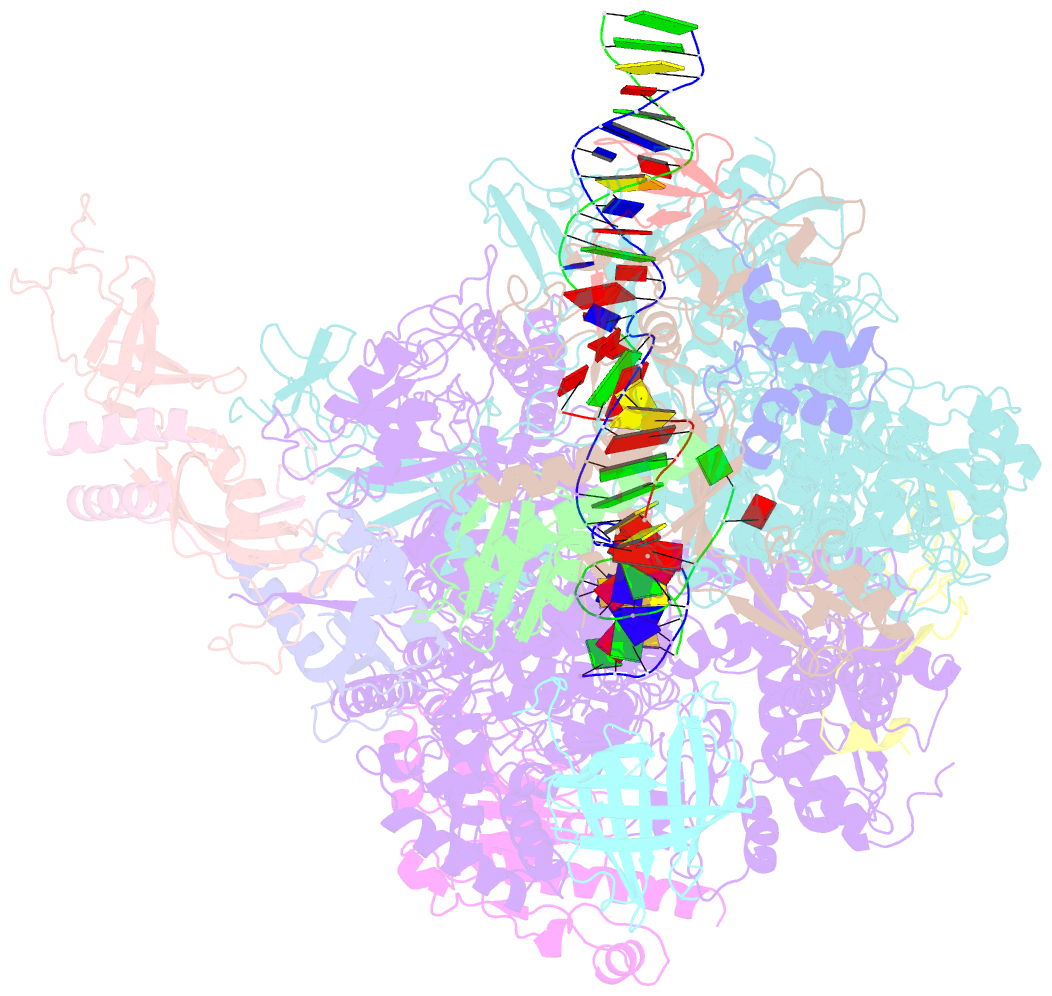
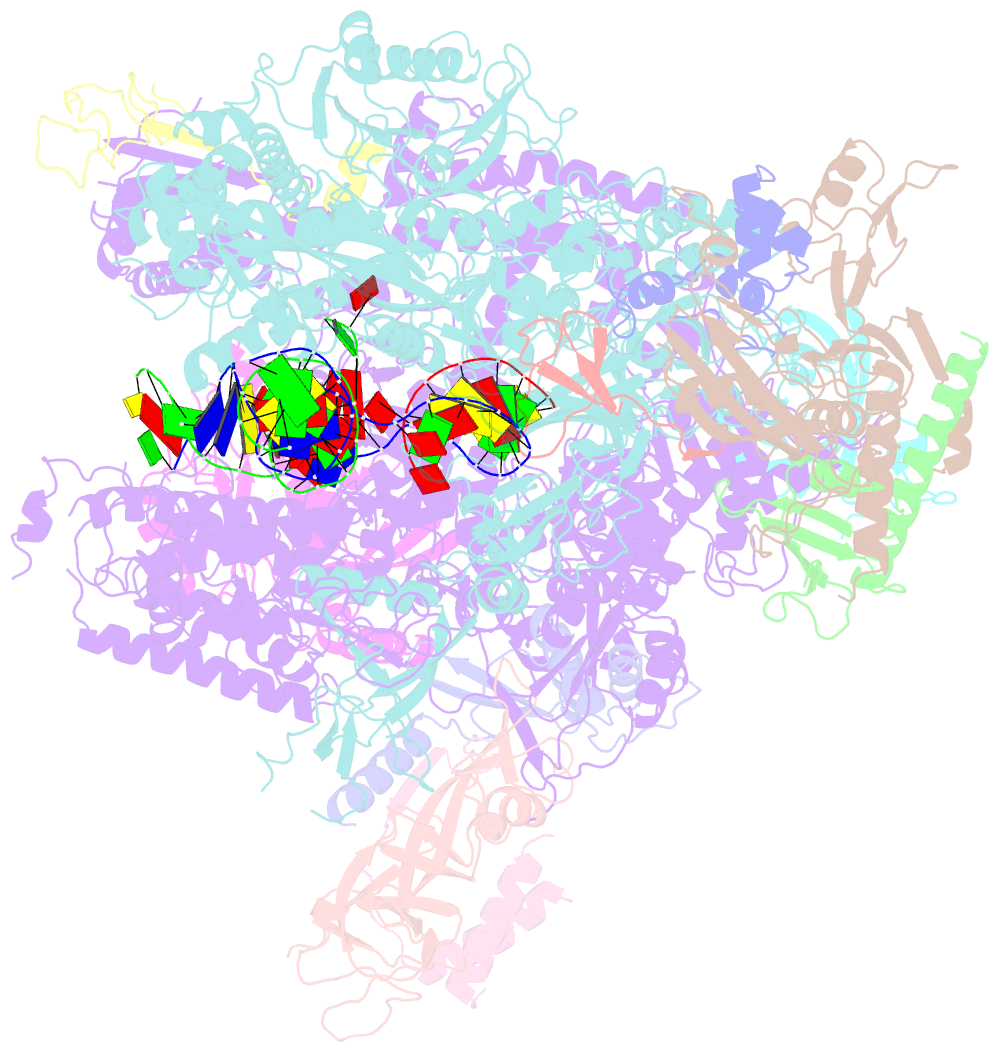
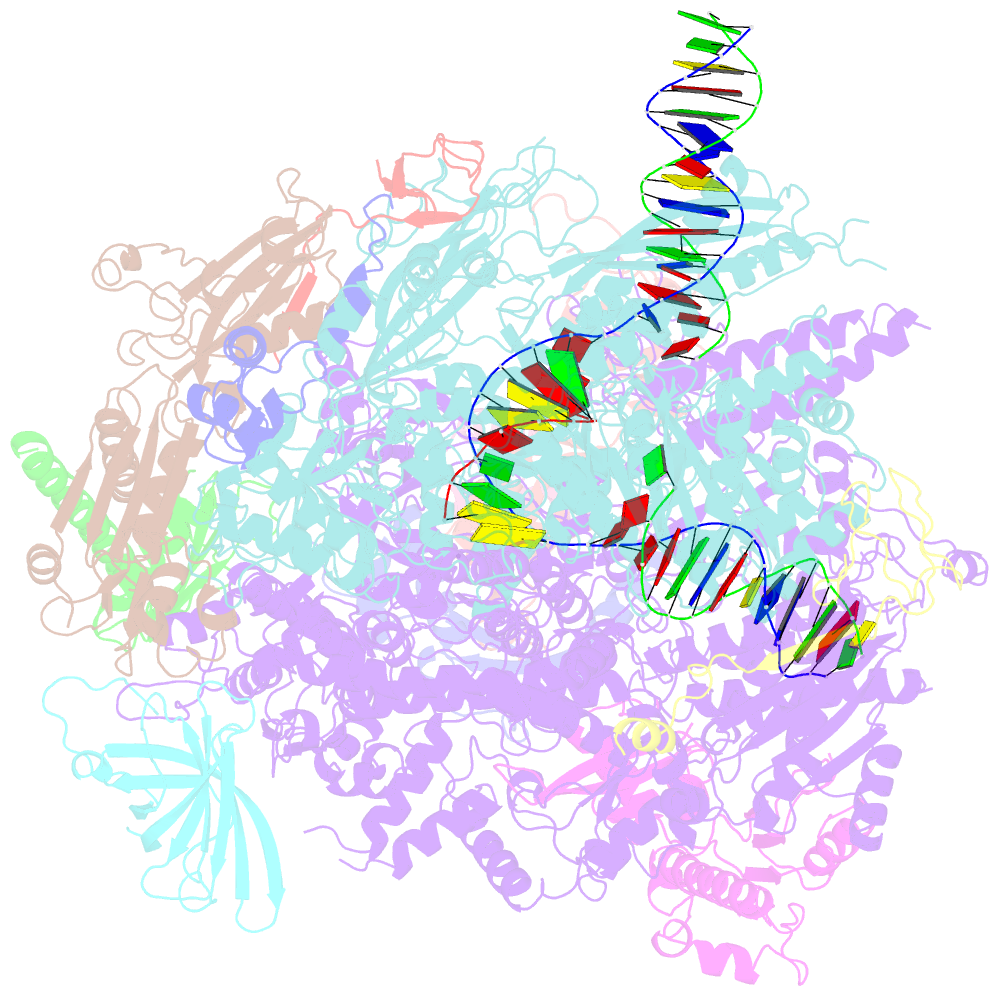
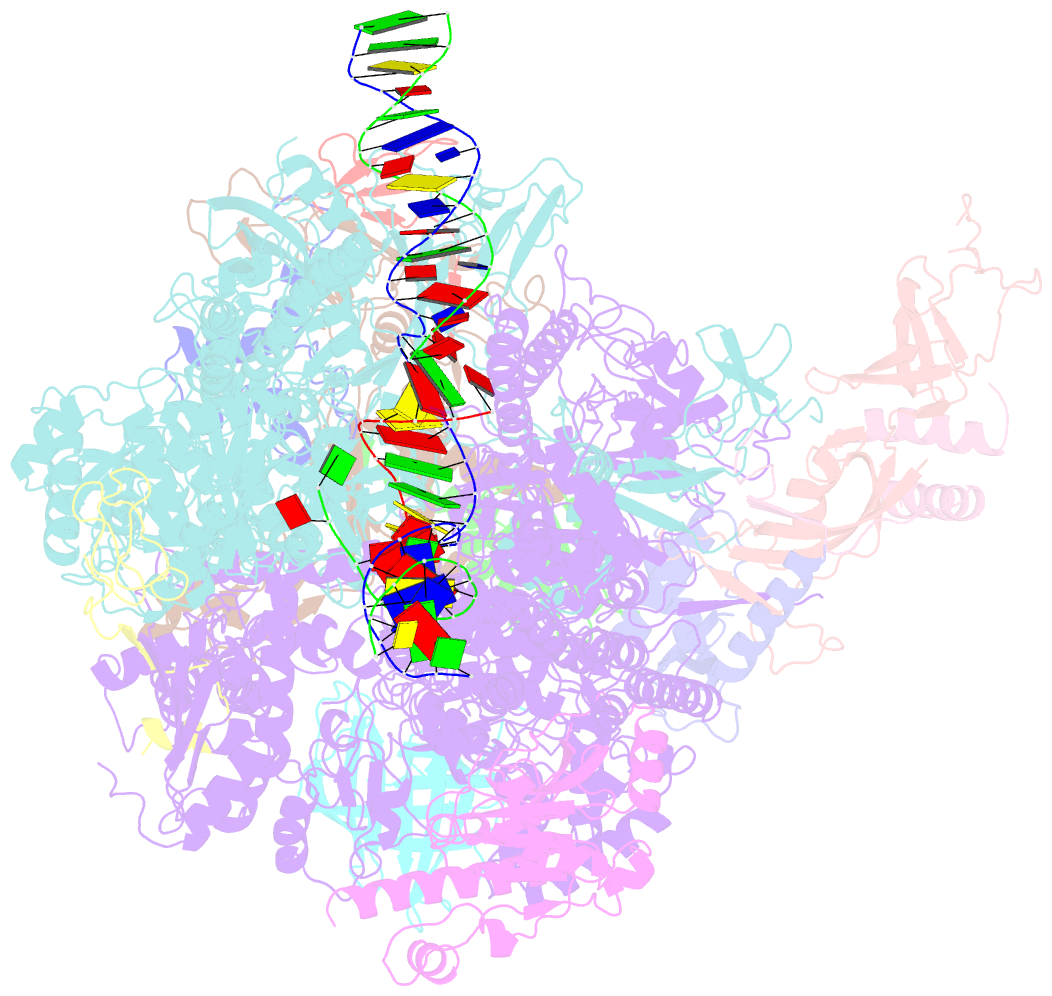
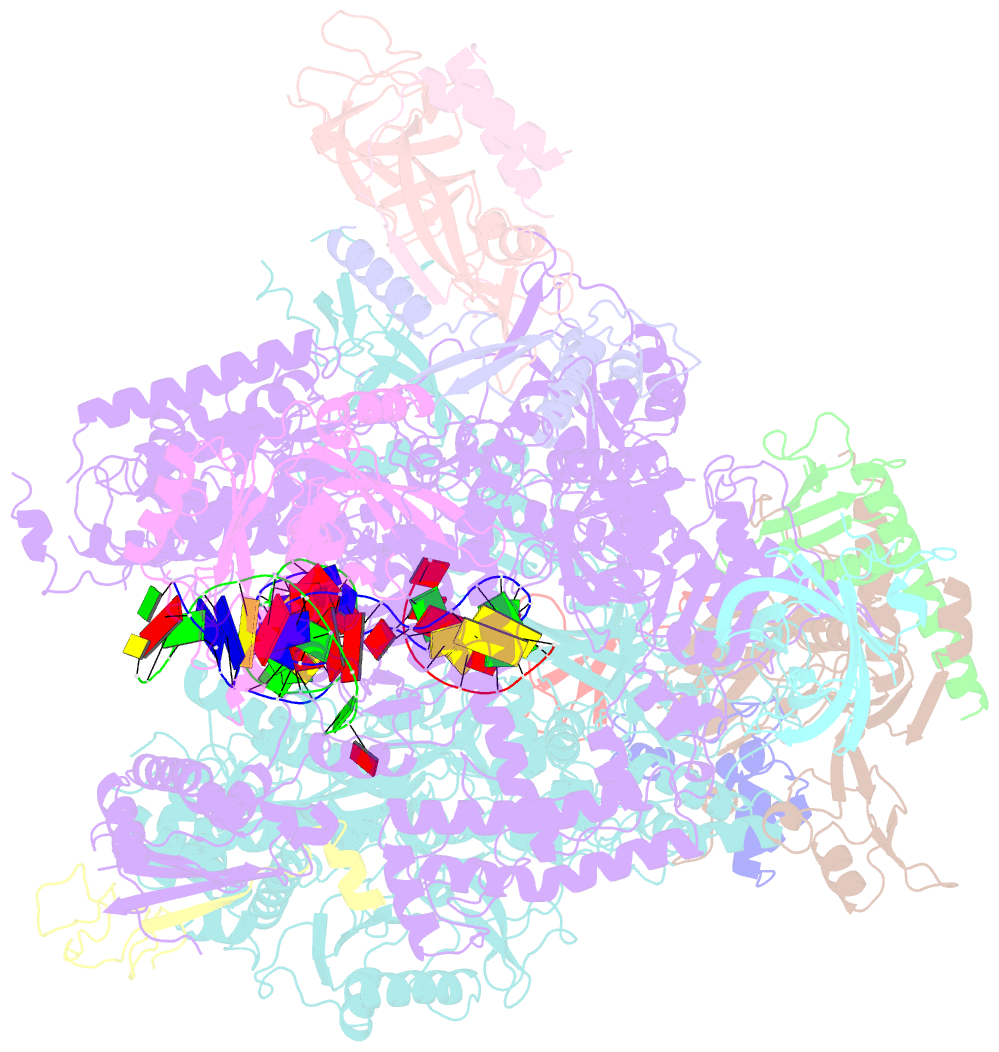
- Yeast RNA polymerase i elongation complex bound to nucleotide analog gmpcpp (core focused)
- Reference
- Tafur L, Sadian Y, Hanske J, Wetzel R, Weis F, Muller CW (2019): "The cryo-EM structure of a 12-subunit variant of RNA polymerase I reveals dissociation of the A49-A34.5 heterodimer and rearrangement of subunit A12.2." Elife, 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43204.
- Abstract
- RNA polymerase (Pol) I is a 14-subunit enzyme that solely transcribes pre-ribosomal RNA. Cryo-electron microscopy (EM) structures of Pol I initiation and elongation complexes have given first insights into the molecular mechanisms of Pol I transcription. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of yeast Pol I elongation complexes (ECs) bound to the nucleotide analog GMPCPP at 3.2 to 3.4 Å resolution that provide additional insight into the functional interplay between the Pol I-specific transcription-like factors A49-A34.5 and A12.2. Strikingly, most of the nucleotide-bound ECs lack the A49-A34.5 heterodimer and adopt a Pol II-like conformation, in which the A12.2 C-terminal domain is bound in a previously unobserved position at the A135 surface. Our structural and biochemical data suggest a mechanism where reversible binding of the A49-A34.5 heterodimer could contribute to the regulation of Pol I transcription initiation and elongation.