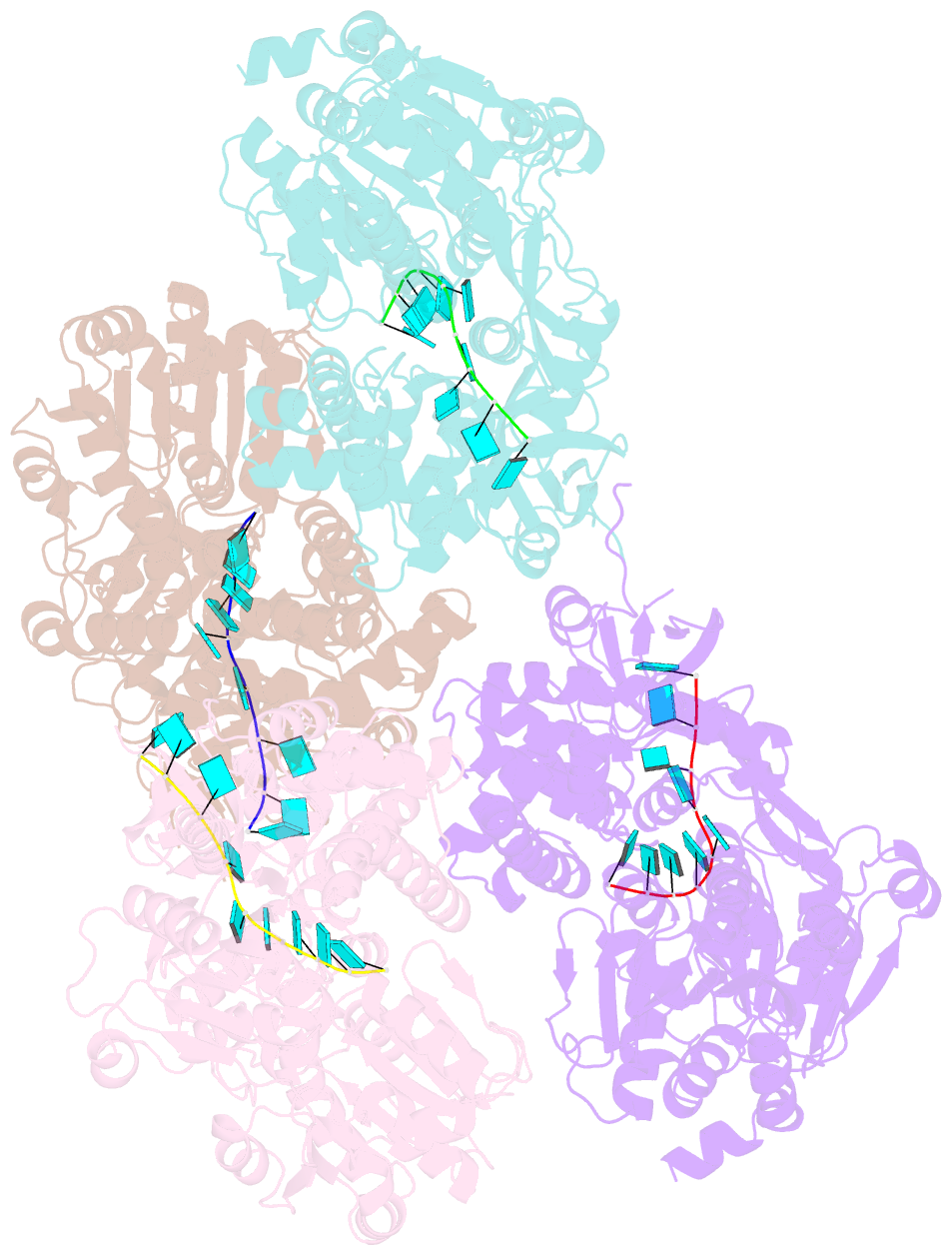
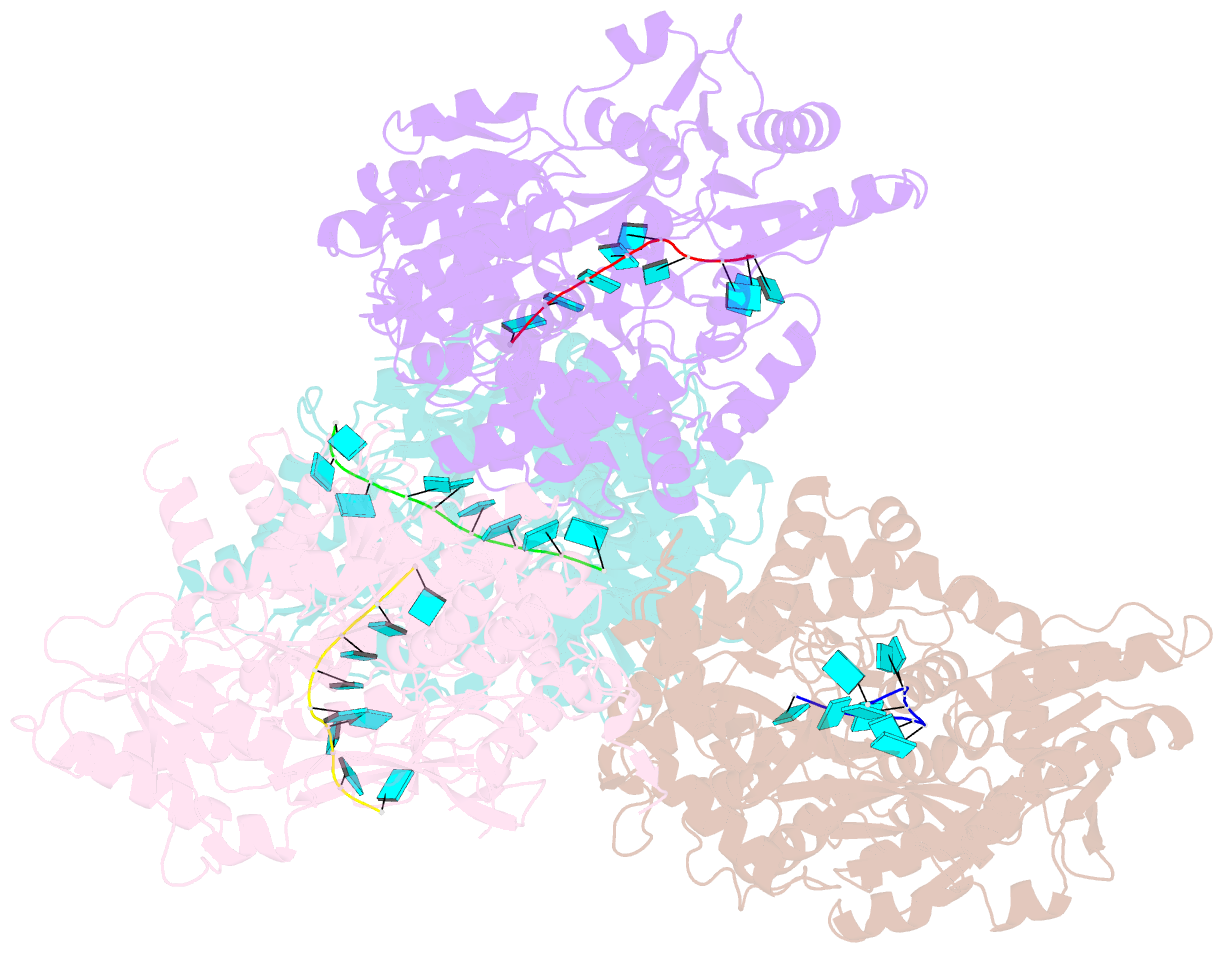
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6i3p; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase
- Method
- X-ray (2.75 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of deah-box atpase prp22 with bound ssrna
- Reference
- Hamann F, Enders M, Ficner R (2019): "Structural basis for RNA translocation by DEAH-box ATPases." Nucleic Acids Res., 47, 4349-4362. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz150.
- Abstract
- DEAH-box adenosine triphosphatases (ATPases) play a crucial role in the spliceosome-mediated excision of pre-mRNA introns. Recent spliceosomal cryo-EM structures suggest that these proteins utilize translocation to apply forces on ssRNAs rather than direct RNA duplex unwinding to ensure global rearrangements. By solving the crystal structure of Prp22 in different adenosine nucleotide-free states, we identified two missing conformational snapshots of genuine DEAH-box ATPases that help to unravel the molecular mechanism of translocation for this protein family. The intrinsic mobility of the RecA2 domain in the absence of adenosine di- or triphosphate (ADP/ATP) and RNA enables DEAH-box ATPases to adopt different open conformations of the helicase core. The presence of RNA suppresses this mobility and stabilizes one defined open conformation when no adenosine nucleotide is bound. A comparison of this novel conformation with the ATP-bound state of Prp43 reveals that these ATPases cycle between closed and open conformations of the helicase core, which accommodate either a four- or five-nucleotide stack in the RNA-binding tunnel, respectively. The continuous repetition of these states enables these proteins to translocate in 3'-5' direction along an ssRNA with a step-size of one RNA nucleotide per hydrolyzed ATP. This ATP-driven motor function is maintained by a serine in the conserved motif V that senses the catalytic state and accordingly positions the RecA2 domain.