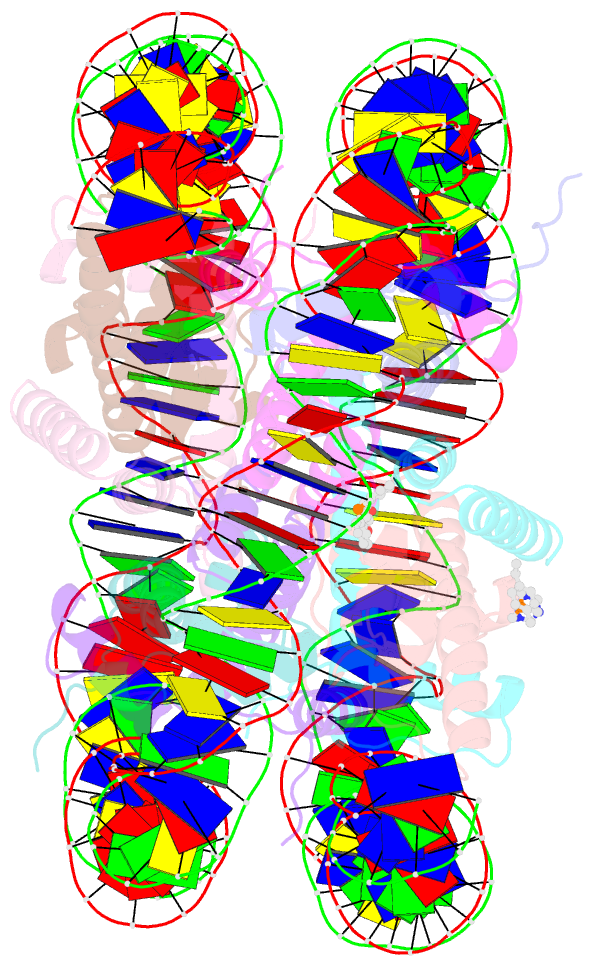
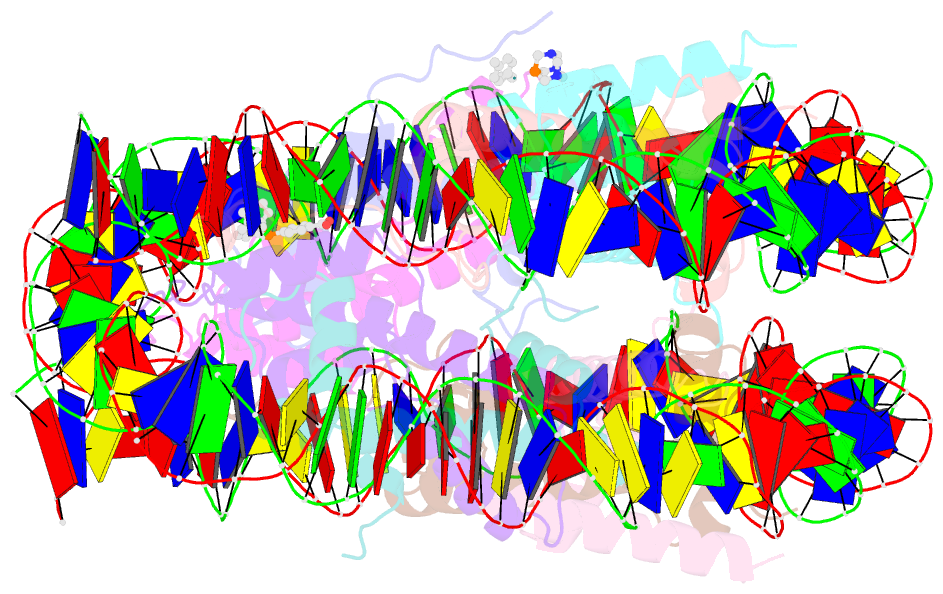
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6iq4; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.25 Å)
- Summary
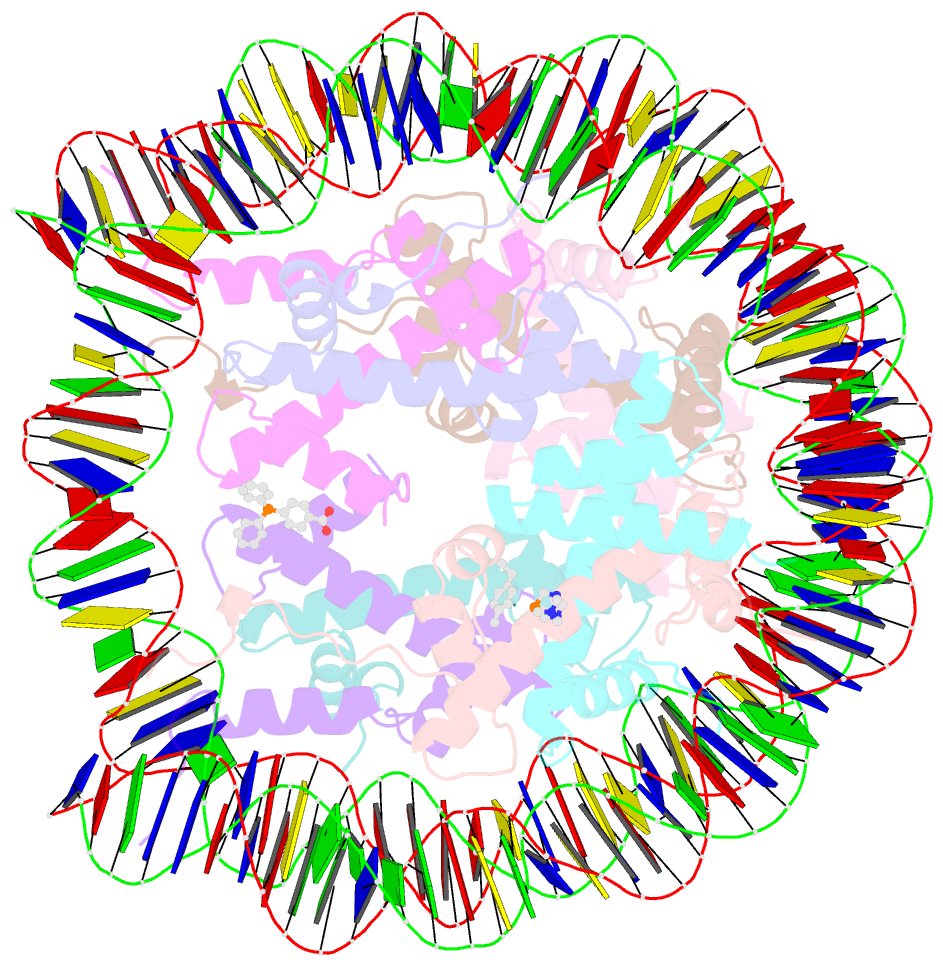
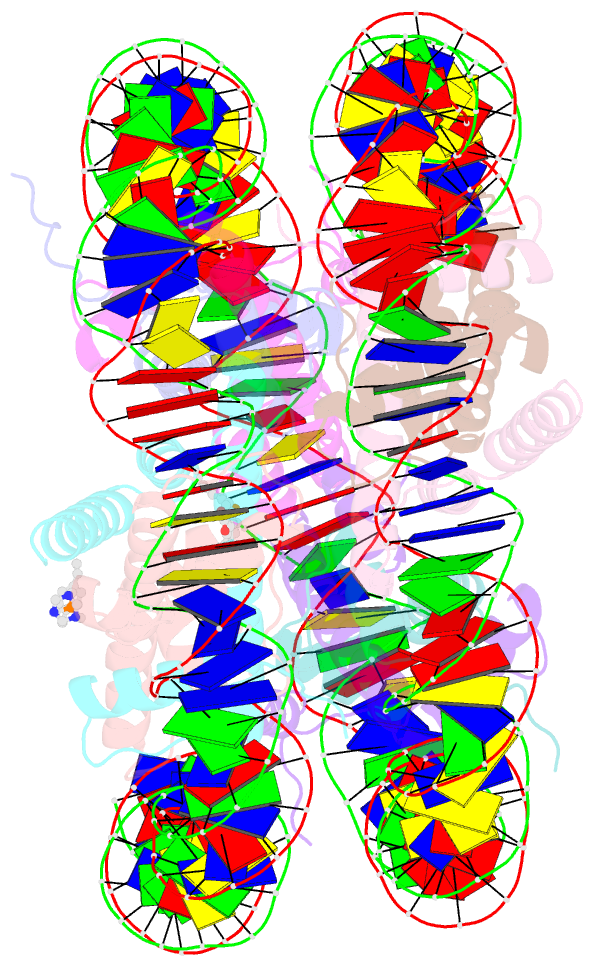
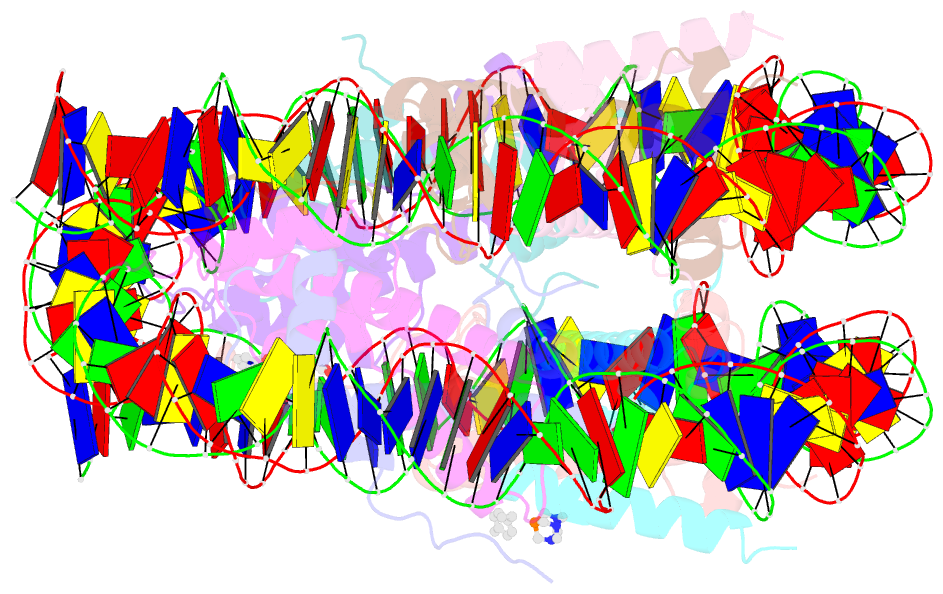
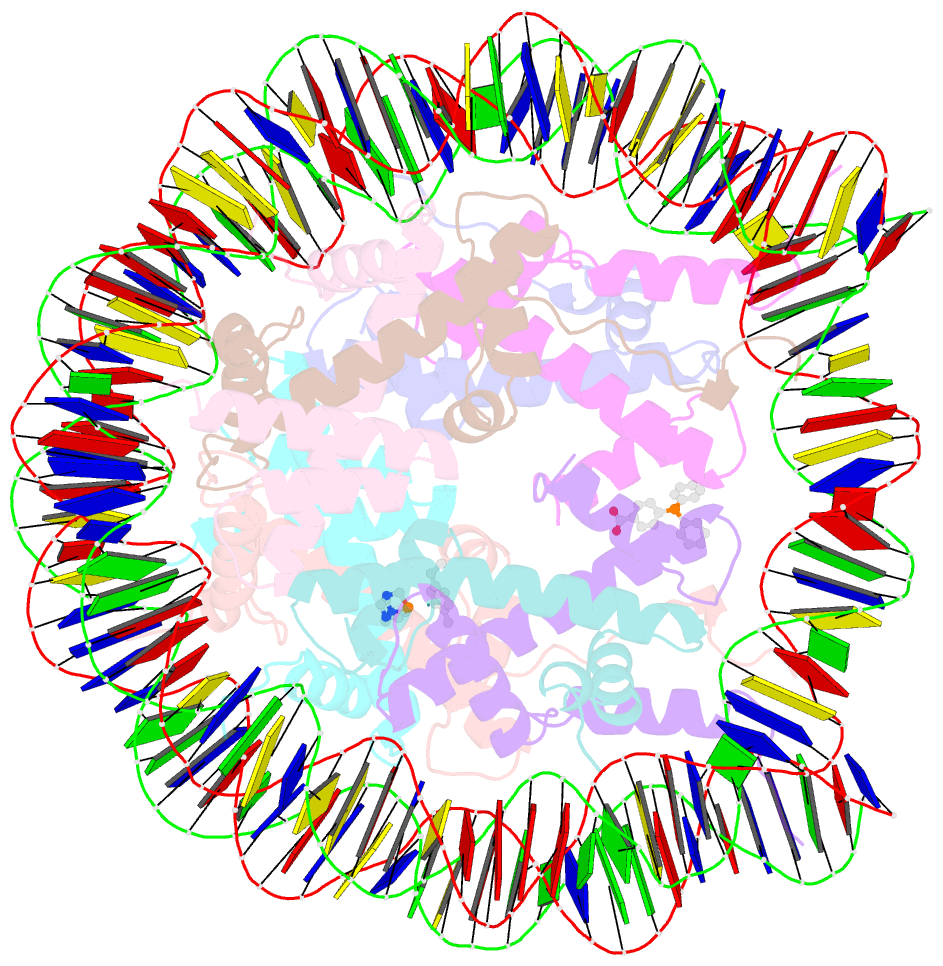
- Nucleosome core particle cross-linked with a hetero-binuclear molecule possessing rapta and gold(i) 4-(diphenylphosphino)benzoic acid groups.
- Reference
- Batchelor LK, De Falco L, von Erlach T, Sharma D, Adhireksan Z, Roethlisberger U, Davey CA, Dyson PJ (2019): "Crosslinking Allosteric Sites on the Nucleosome." Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.Engl., 58, 15660-15664. doi: 10.1002/anie.201906423.
- Abstract
- Targeting defined histone protein sites in chromatin is an emerging therapeutic approach that can potentially be enhanced by allosteric effects within the nucleosome. Here we characterized a novel hetero-bimetallic compound with a design based on a nucleosomal allostery effect observed earlier for two unrelated drugs-the RuII antimetastasis/antitumor RAPTA-T and the AuI anti-arthritic auranofin. The RuII moiety binds specifically to two H2A glutamate residues on the nucleosome acidic patch, allosterically triggering a cascade of structural changes that promote binding of the AuI moiety to selective histidine residues on H3, resulting in cross-linking sites that are over 35 Å distant. By tethering the H2A-H2B dimers to the H3-H4 tetramer, the hetero-bimetallic compound significantly increases stability of the nucleosome, illustrating its utility as a site-selective cross-linking agent.