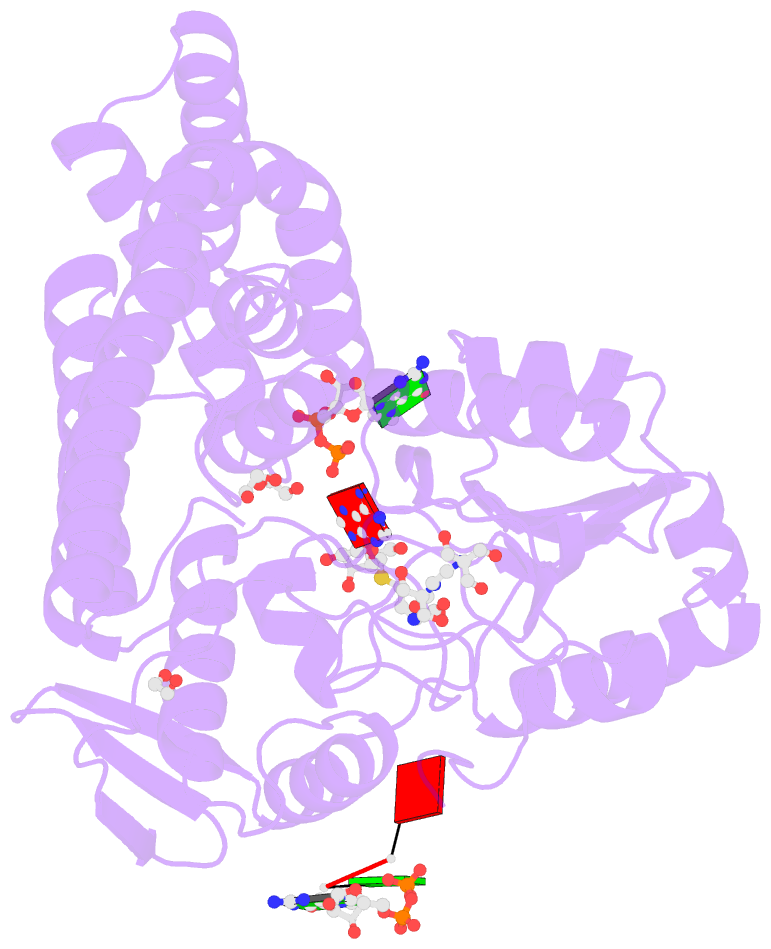
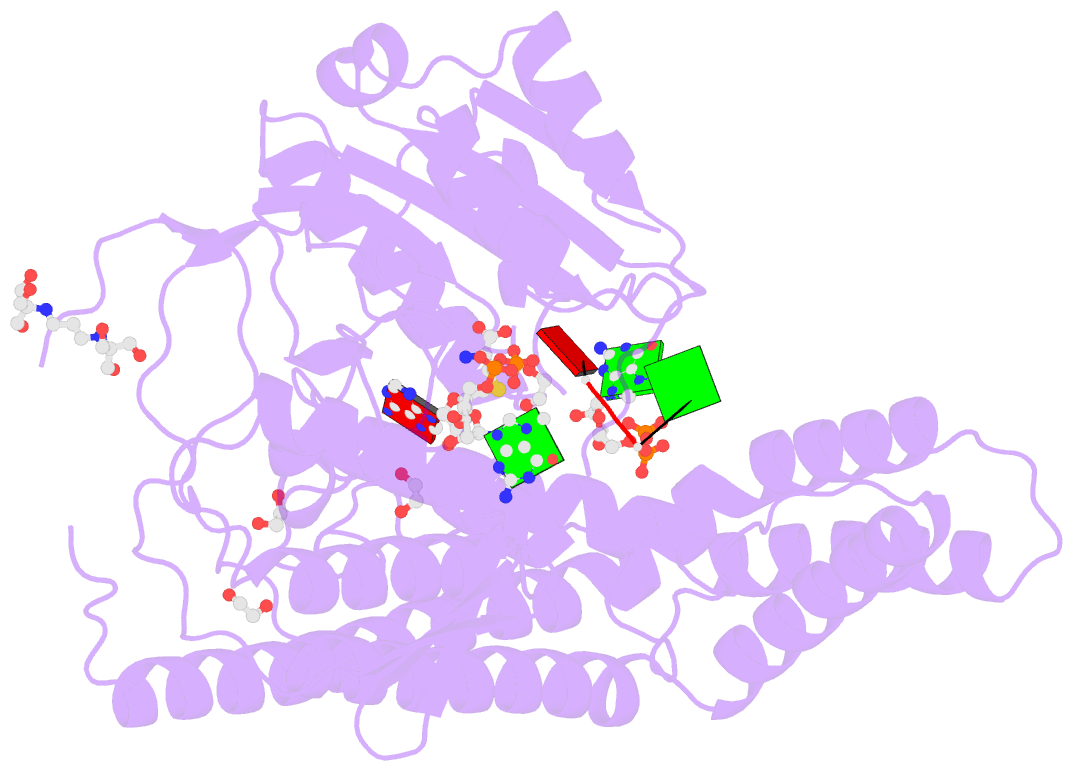
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6is0; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.8 Å)
- Summary
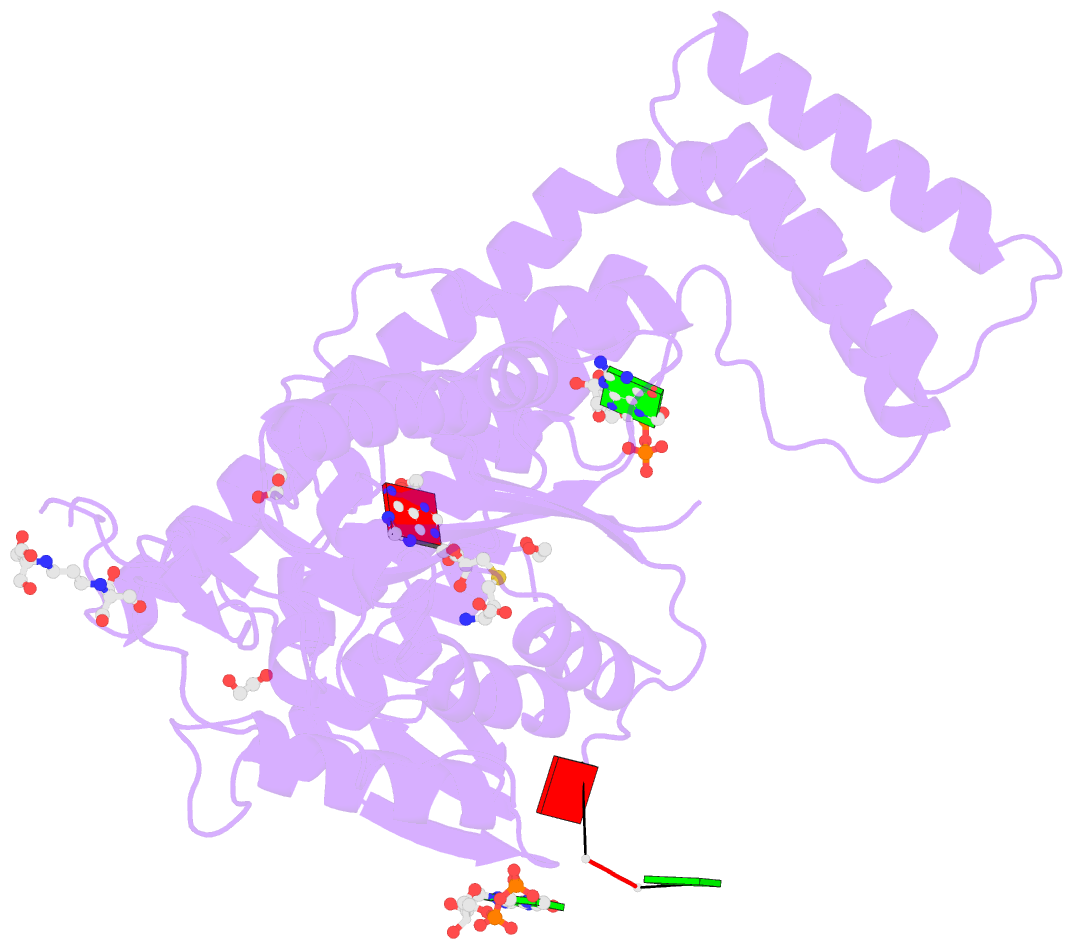
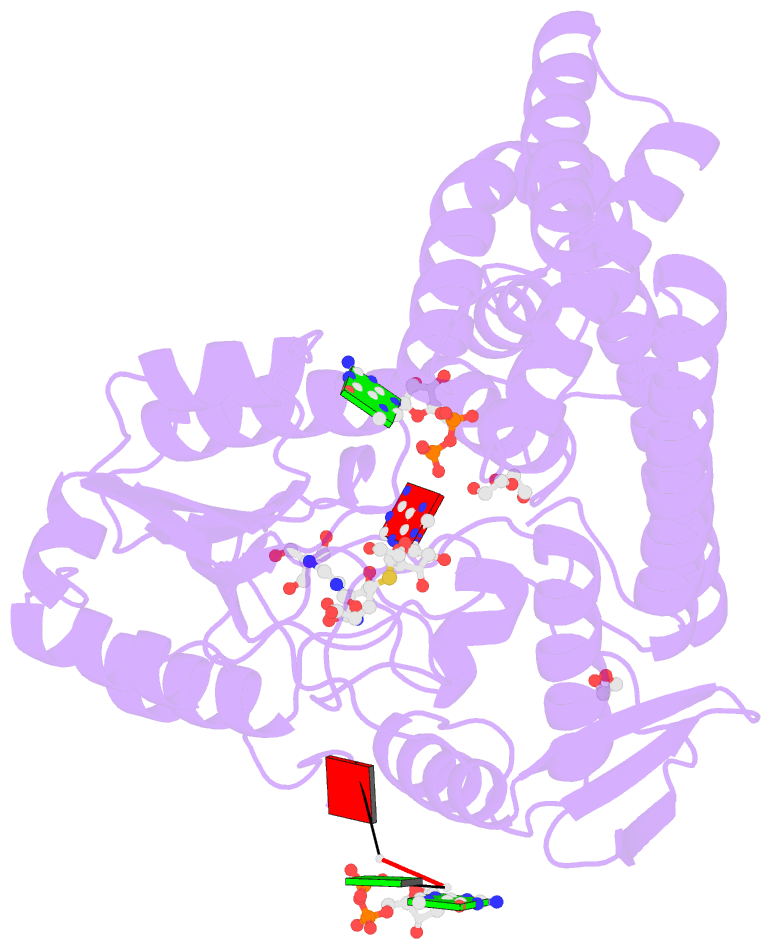
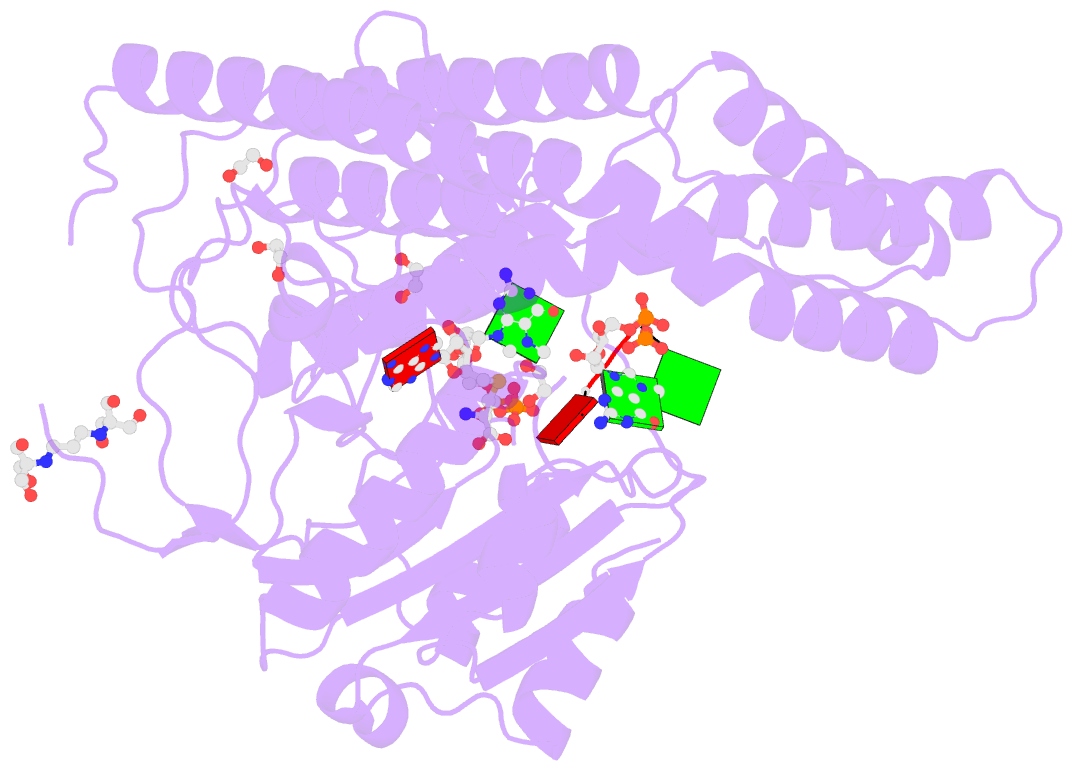
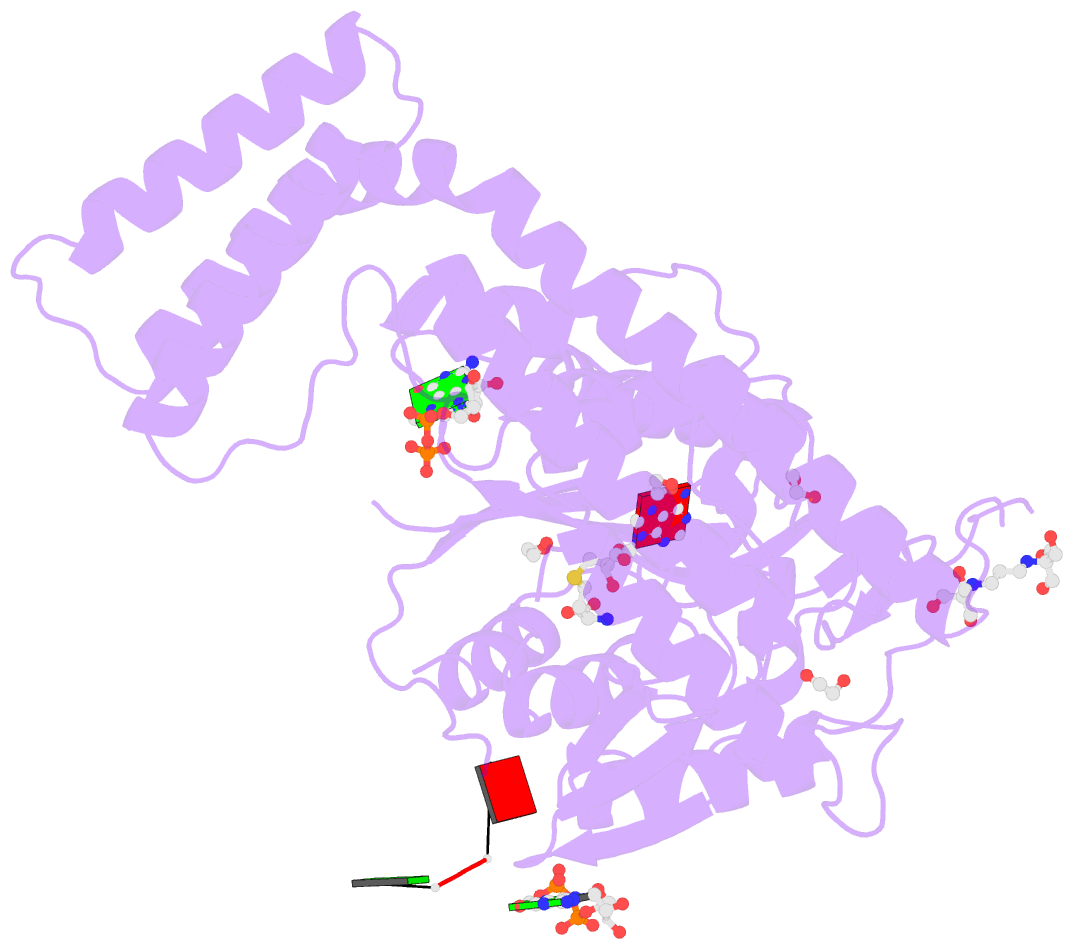
- Crystal structure of the zebrafish cap-specific adenosine methyltransferase bound to sah and m7g-capped RNA
- Reference
- Akichika S, Hirano S, Shichino Y, Suzuki T, Nishimasu H, Ishitani R, Sugita A, Hirose Y, Iwasaki S, Nureki O, Suzuki T (2019): "Cap-specific terminal N 6 -methylation of RNA by an RNA polymerase II-associated methyltransferase." Science, 363. doi: 10.1126/science.aav0080.
- Abstract
- N 6-methyladenosine (m6A), a major modification of messenger RNAs (mRNAs), plays critical roles in RNA metabolism and function. In addition to the internal m6A, N 6, 2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) is present at the transcription start nucleotide of capped mRNAs in vertebrates. However, its biogenesis and functional role remain elusive. Using a reverse genetics approach, we identified PCIF1, a factor that interacts with the serine-5-phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, as a cap-specific adenosine methyltransferase (CAPAM) responsible for N 6-methylation of m6Am. The crystal structure of CAPAM in complex with substrates revealed the molecular basis of cap-specific m6A formation. A transcriptome-wide analysis revealed that N 6-methylation of m6Am promotes the translation of capped mRNAs. Thus, a cap-specific m6A writer promotes translation of mRNAs starting from m6Am.