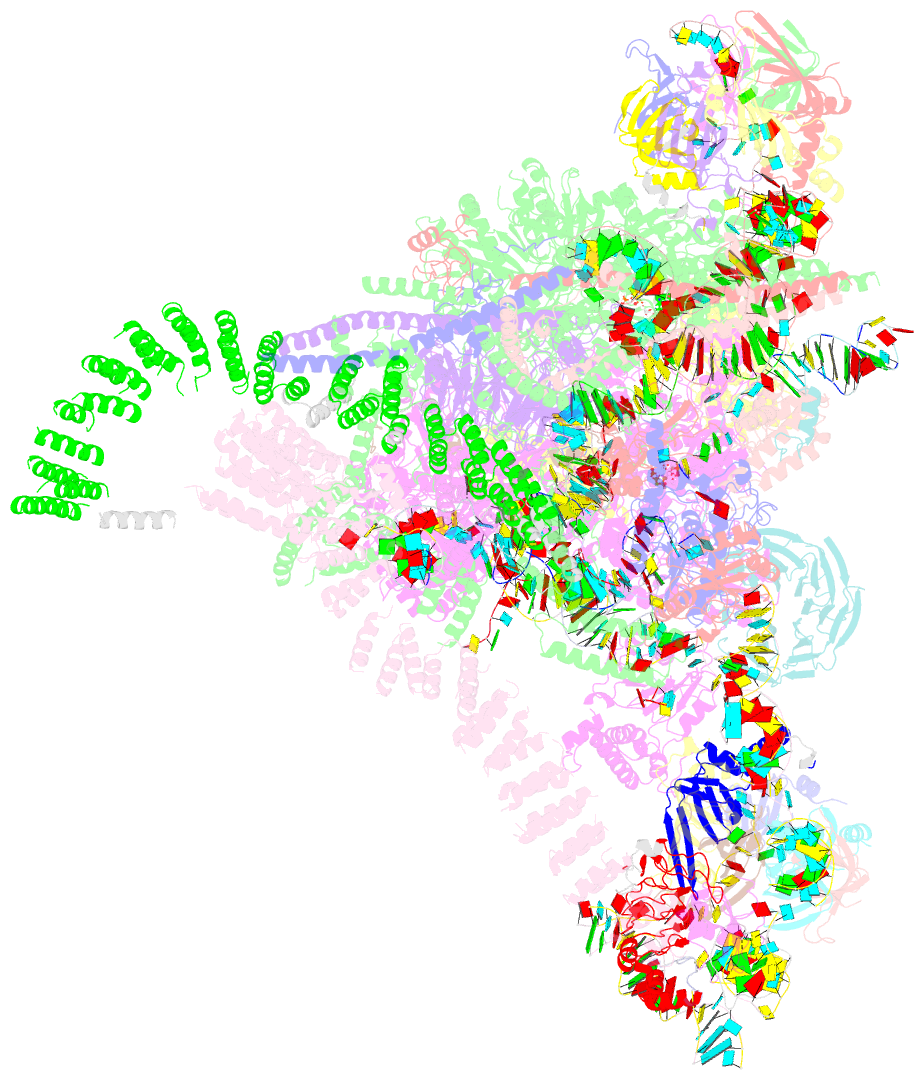
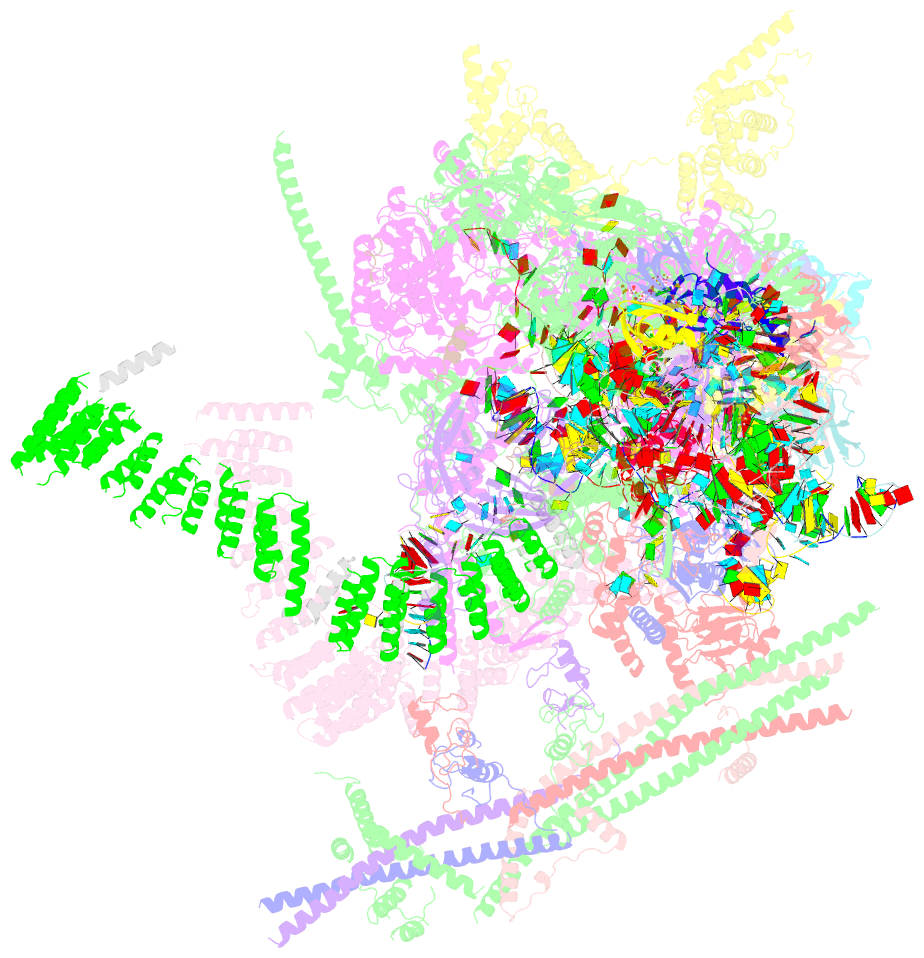
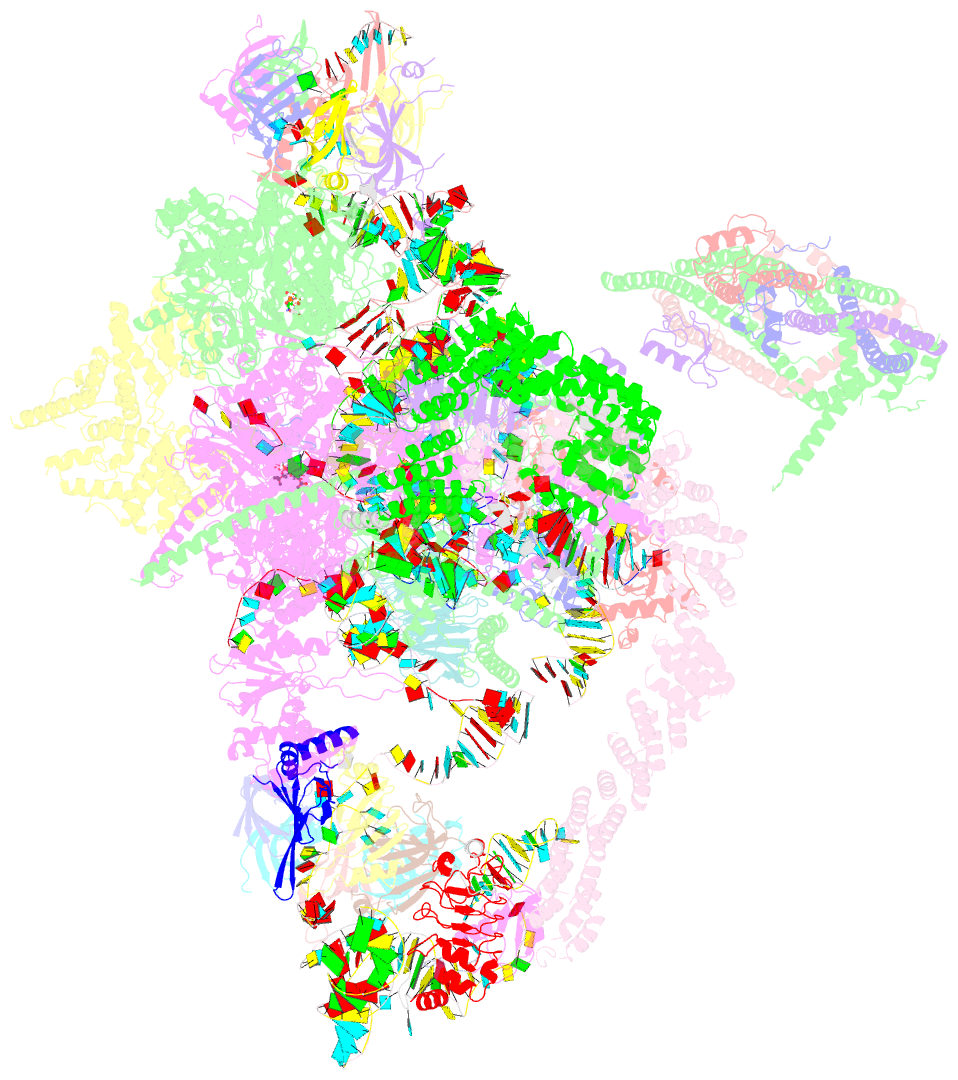
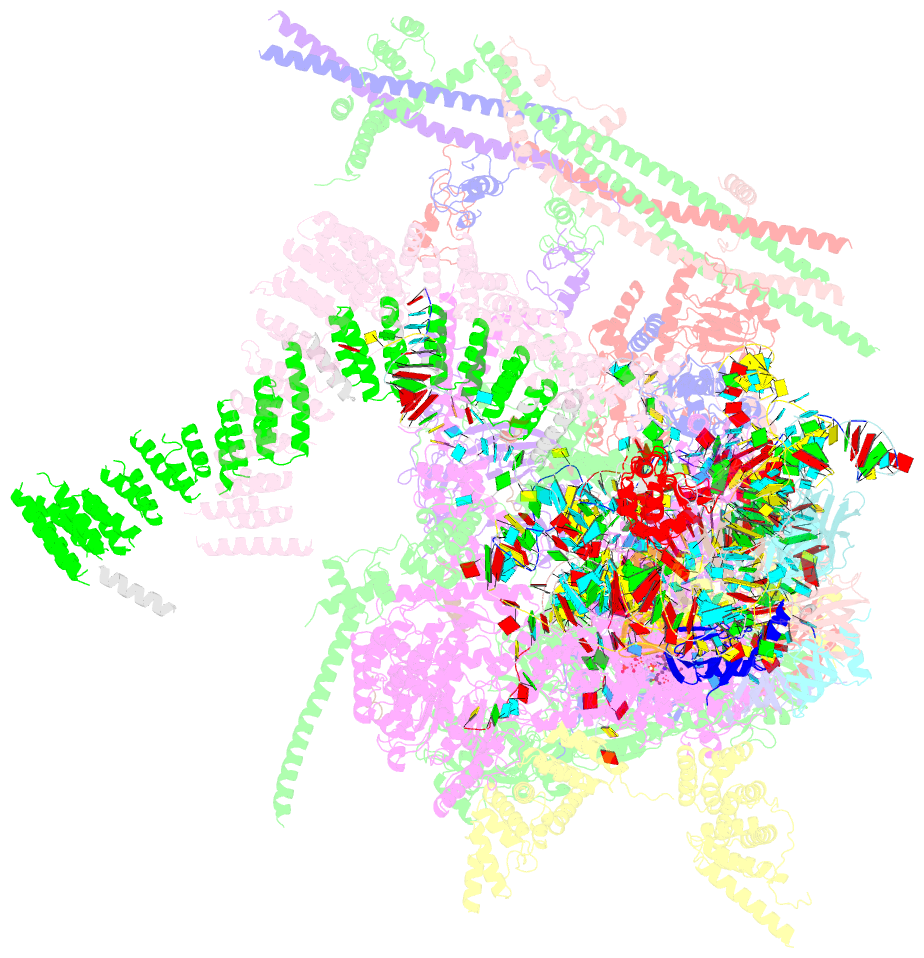
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6j6g; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- splicing
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of the yeast b*-a2 complex at an average resolution of 3.2 angstrom
- Reference
- Wan R, Bai R, Yan C, Lei J, Shi Y (2019): "Structures of the Catalytically Activated Yeast Spliceosome Reveal the Mechanism of Branching." Cell, 177, 339-351.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.006.
- Abstract
- Pre-mRNA splicing is executed by the spliceosome. Structural characterization of the catalytically activated complex (B∗) is pivotal for understanding the branching reaction. In this study, we assembled the B∗ complexes on two different pre-mRNAs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and determined the cryo-EM structures of four distinct B∗ complexes at overall resolutions of 2.9-3.8 Å. The duplex between U2 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and the branch point sequence (BPS) is discretely away from the 5'-splice site (5'SS) in the three B∗ complexes that are devoid of the step I splicing factors Yju2 and Cwc25. Recruitment of Yju2 into the active site brings the U2/BPS duplex into the vicinity of 5'SS, with the BPS nucleophile positioned 4 Å away from the catalytic metal M2. This analysis reveals the functional mechanism of Yju2 and Cwc25 in branching. These structures on different pre-mRNAs reveal substrate-specific conformations of the spliceosome in a major functional state.