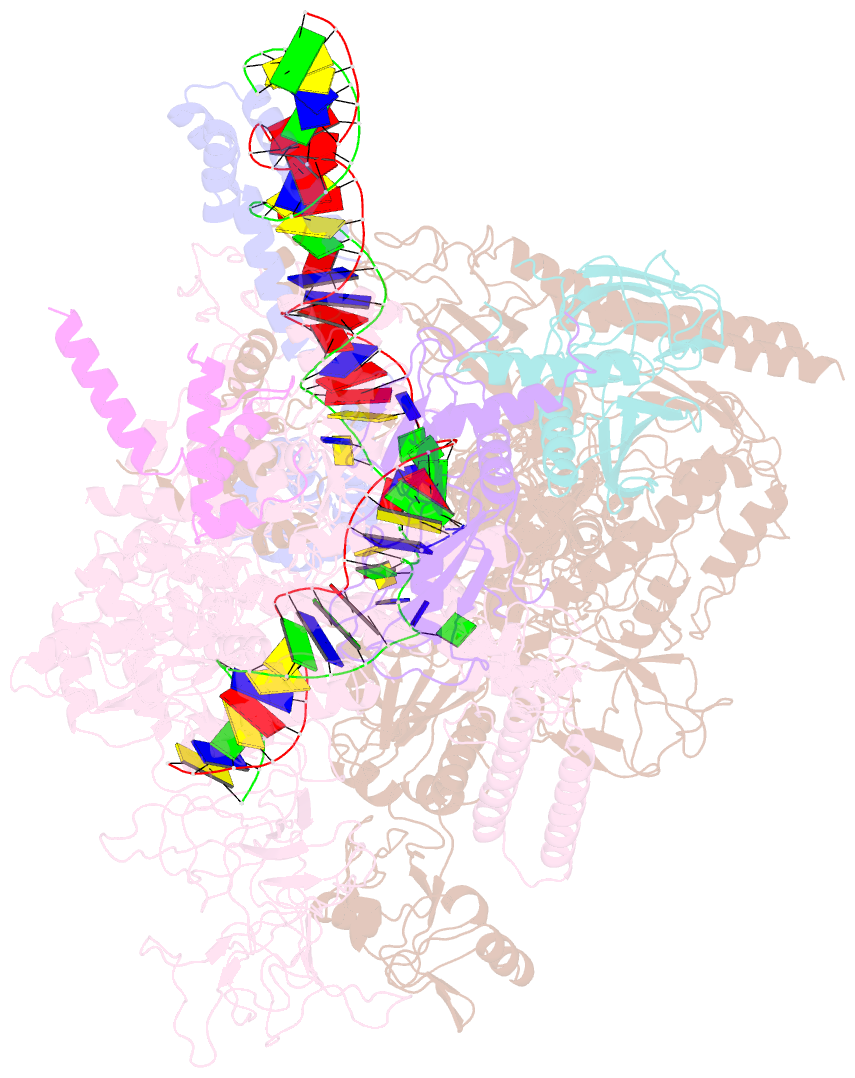
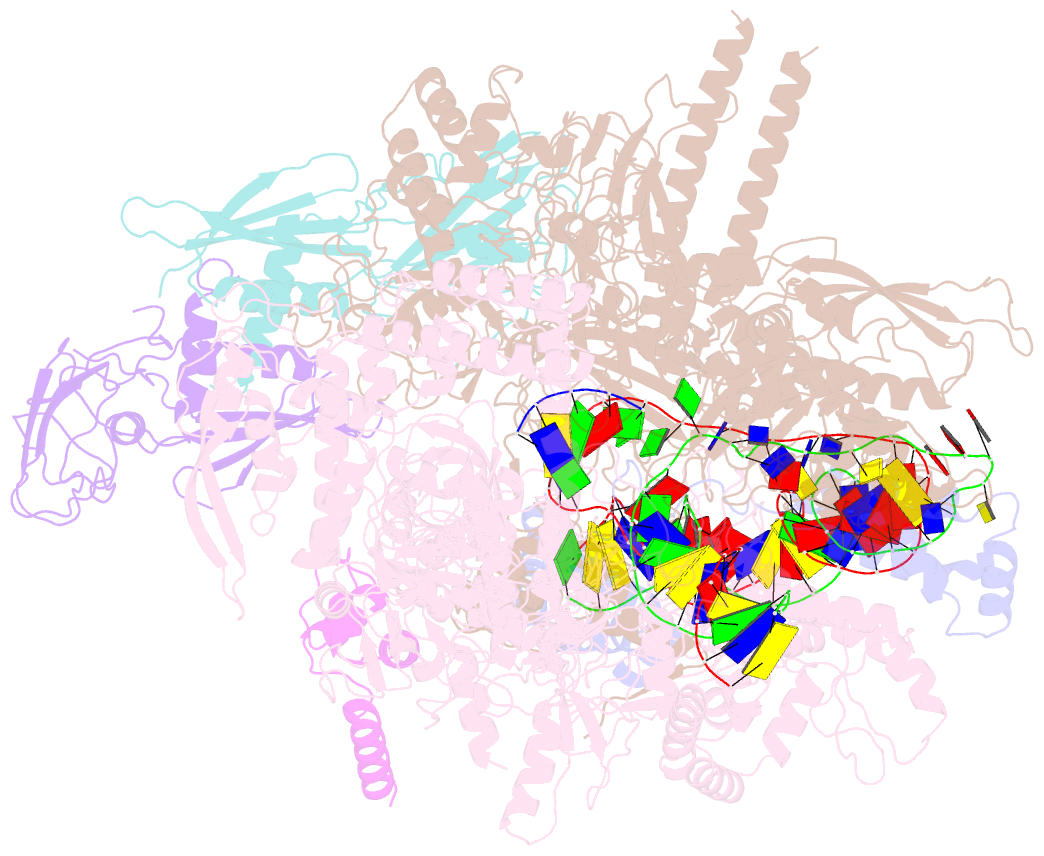
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6jbq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.02 Å)
- Summary
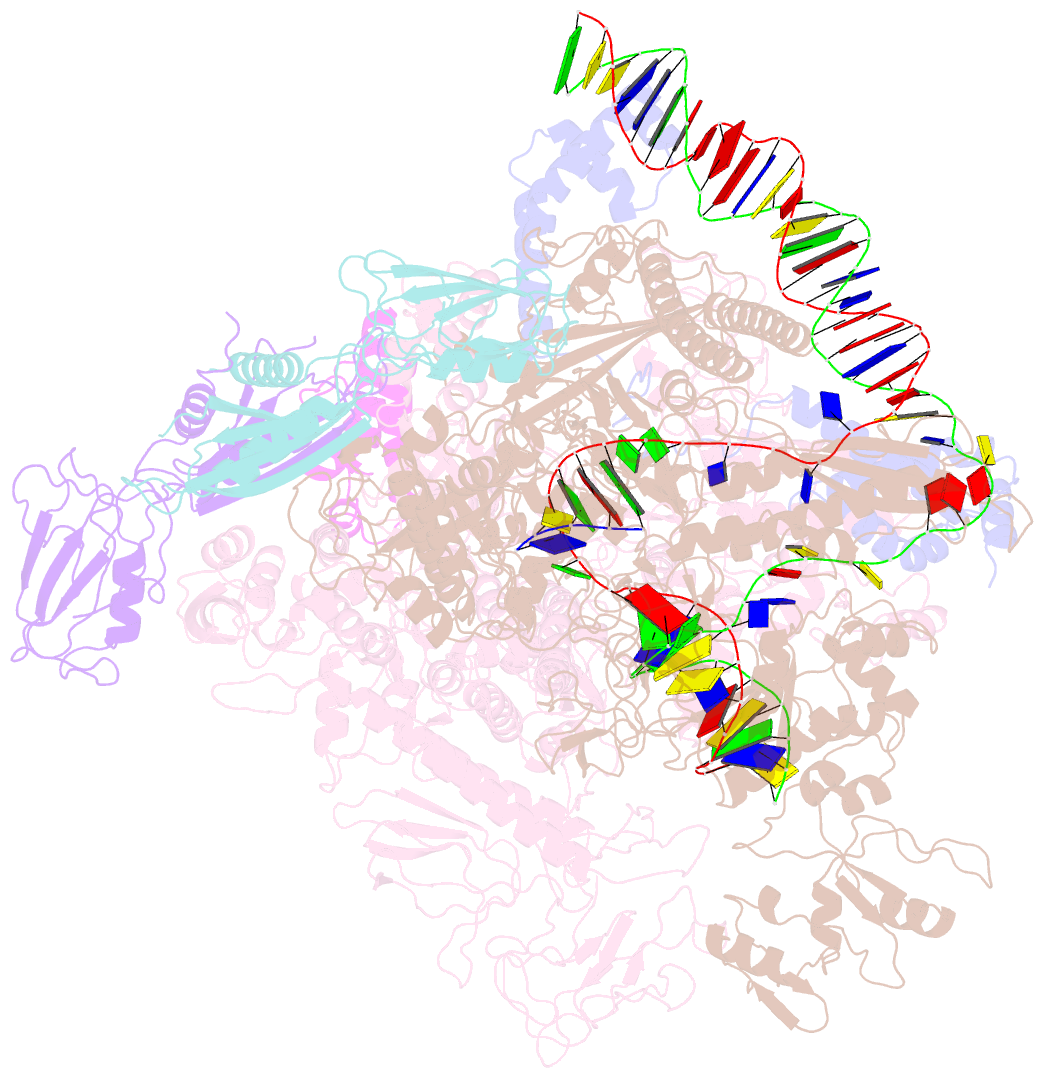
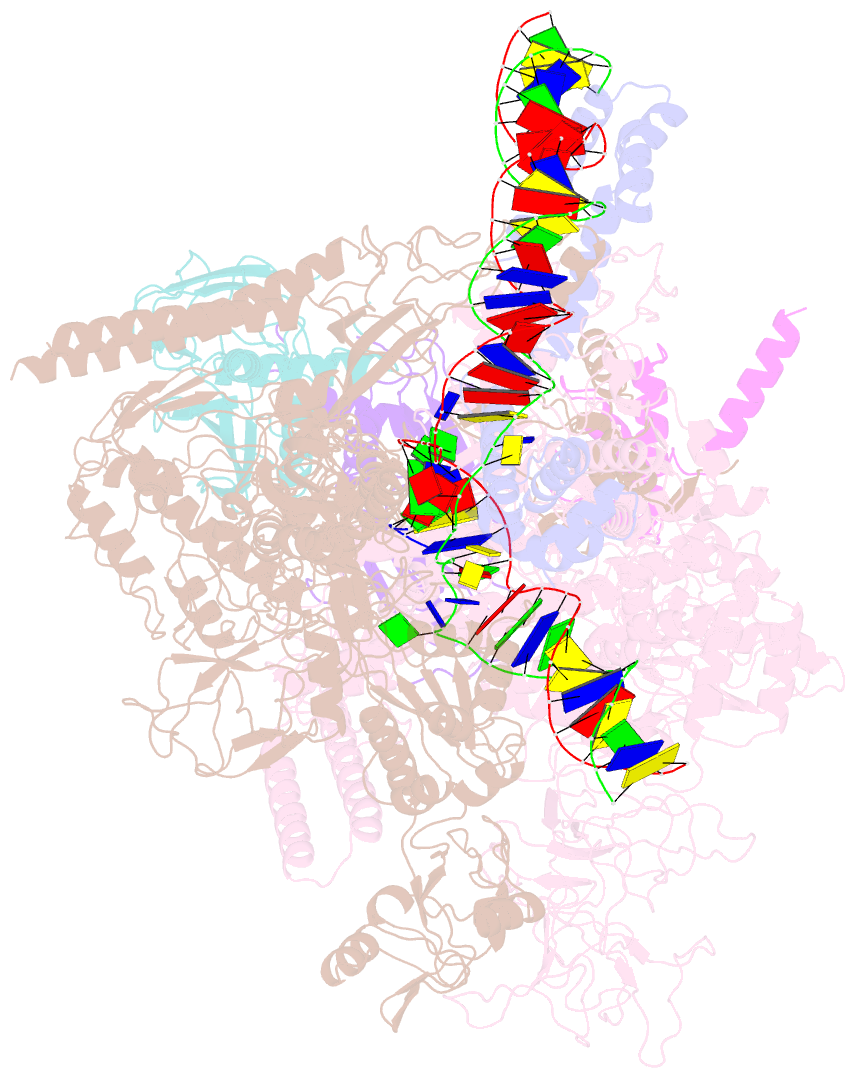
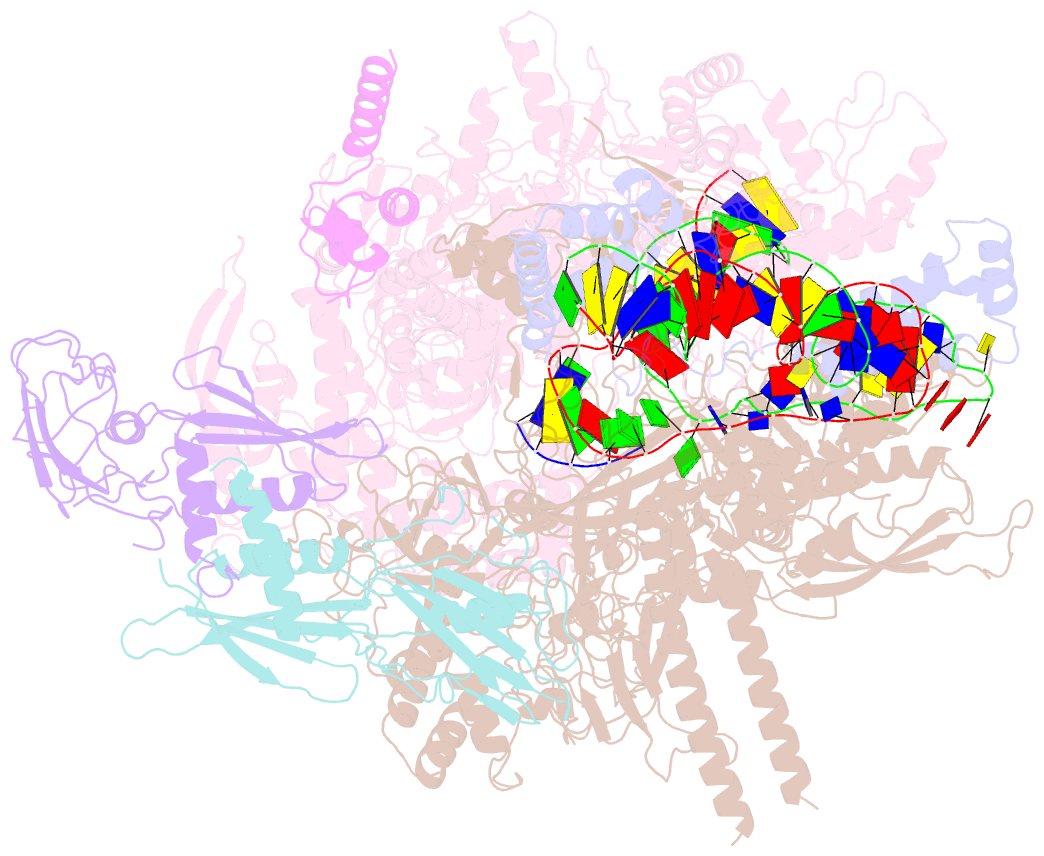
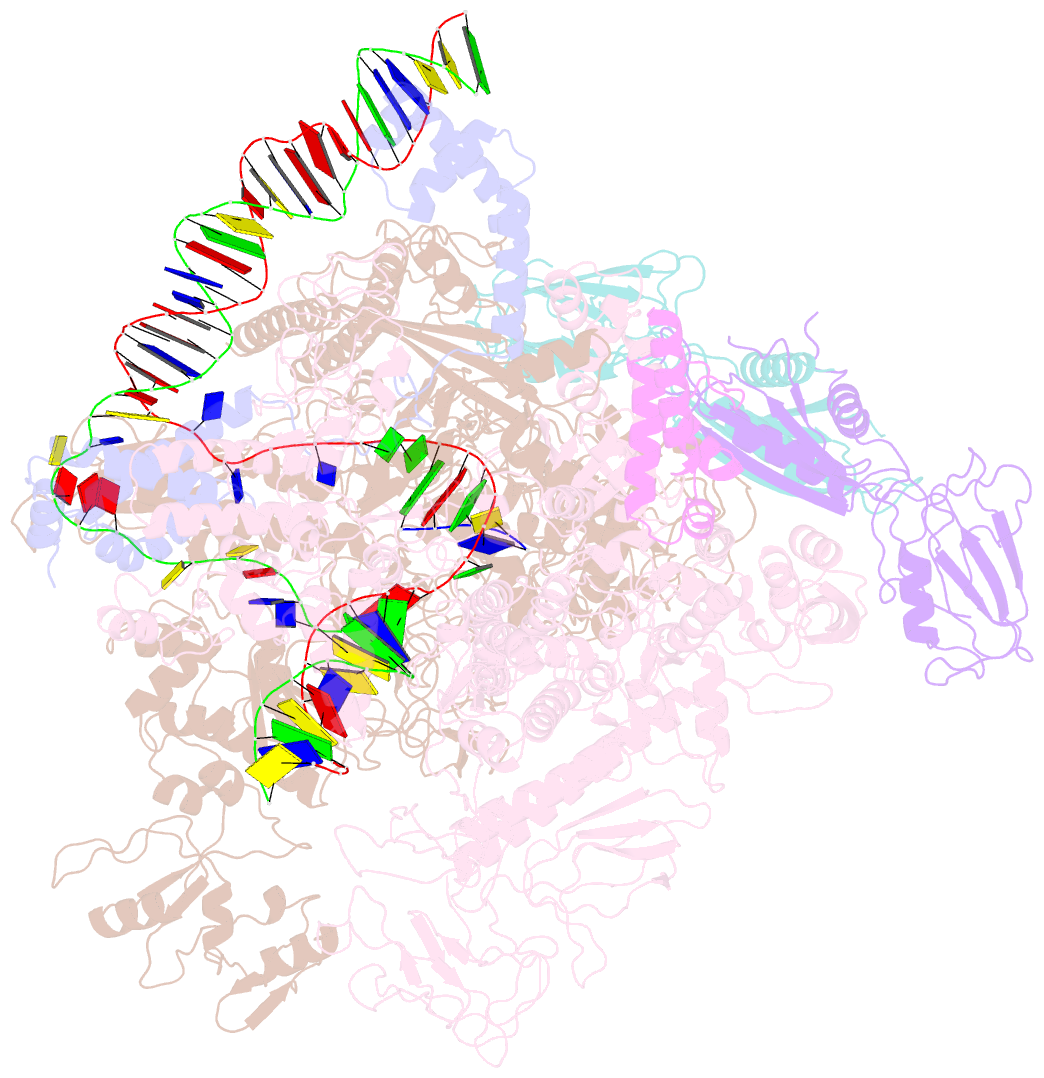
- Cryoem structure of escherichia coli sigmae transcription initiation complex containing 5nt of RNA
- Reference
- Fang C, Li L, Shen L, Shi J, Wang S, Feng Y, Zhang Y (2019): "Structures and mechanism of transcription initiation by bacterial ECF factors." Nucleic Acids Res., 47, 7094-7104. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz470.
- Abstract
- Bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP) forms distinct holoenzymes with extra-cytoplasmic function (ECF) σ factors to initiate specific gene expression programs. In this study, we report a cryo-EM structure at 4.0 Å of Escherichia coli transcription initiation complex comprising σE-the most-studied bacterial ECF σ factor (Ec σE-RPo), and a crystal structure at 3.1 Å of Mycobacterium tuberculosis transcription initiation complex with a chimeric σH/E (Mtb σH/E-RPo). The structure of Ec σE-RPo reveals key interactions essential for assembly of E. coli σE-RNAP holoenzyme and for promoter recognition and unwinding by E. coli σE. Moreover, both structures show that the non-conserved linkers (σ2/σ4 linker) of the two ECF σ factors are inserted into the active-center cleft and exit through the RNA-exit channel. We performed secondary-structure prediction of 27,670 ECF σ factors and find that their non-conserved linkers probably reach into and exit from RNAP active-center cleft in a similar manner. Further biochemical results suggest that such σ2/σ4 linker plays an important role in RPo formation, abortive production and promoter escape during ECF σ factors-mediated transcription initiation.