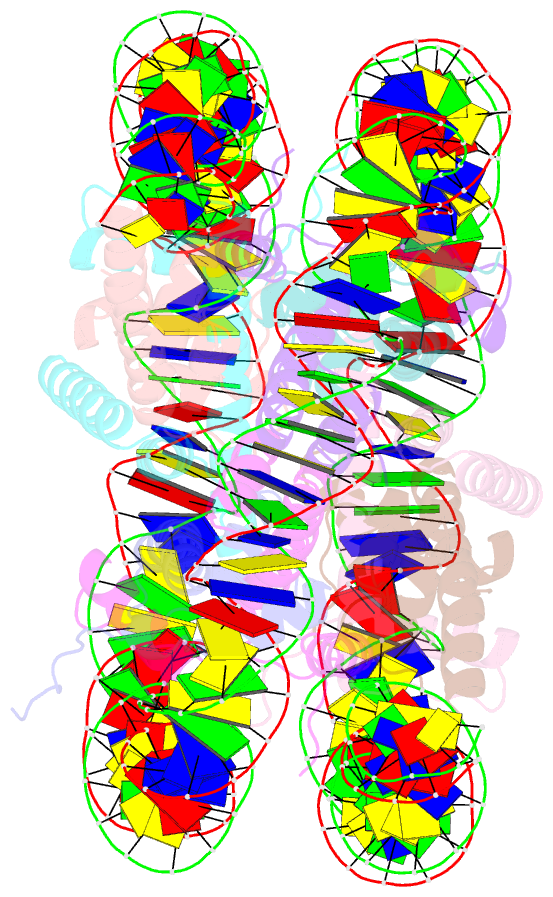
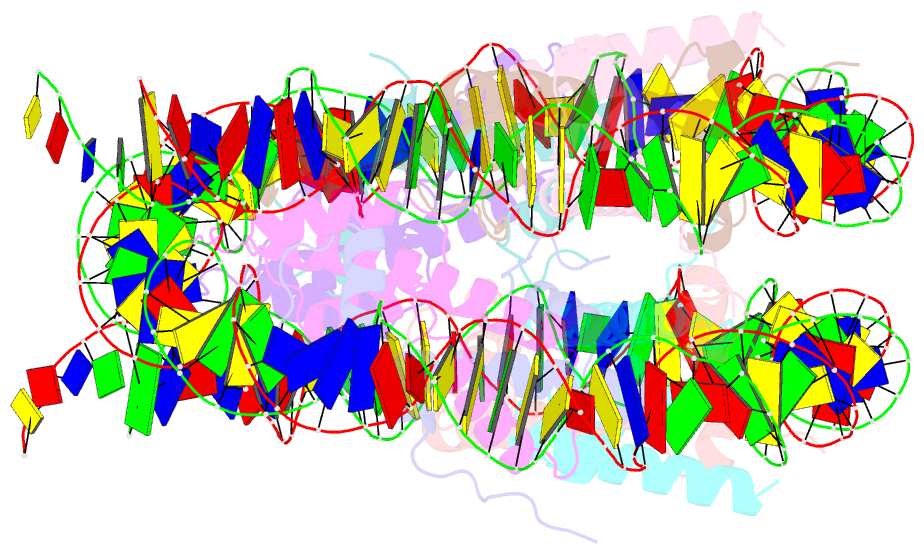
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6jxd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.25 Å)
- Summary
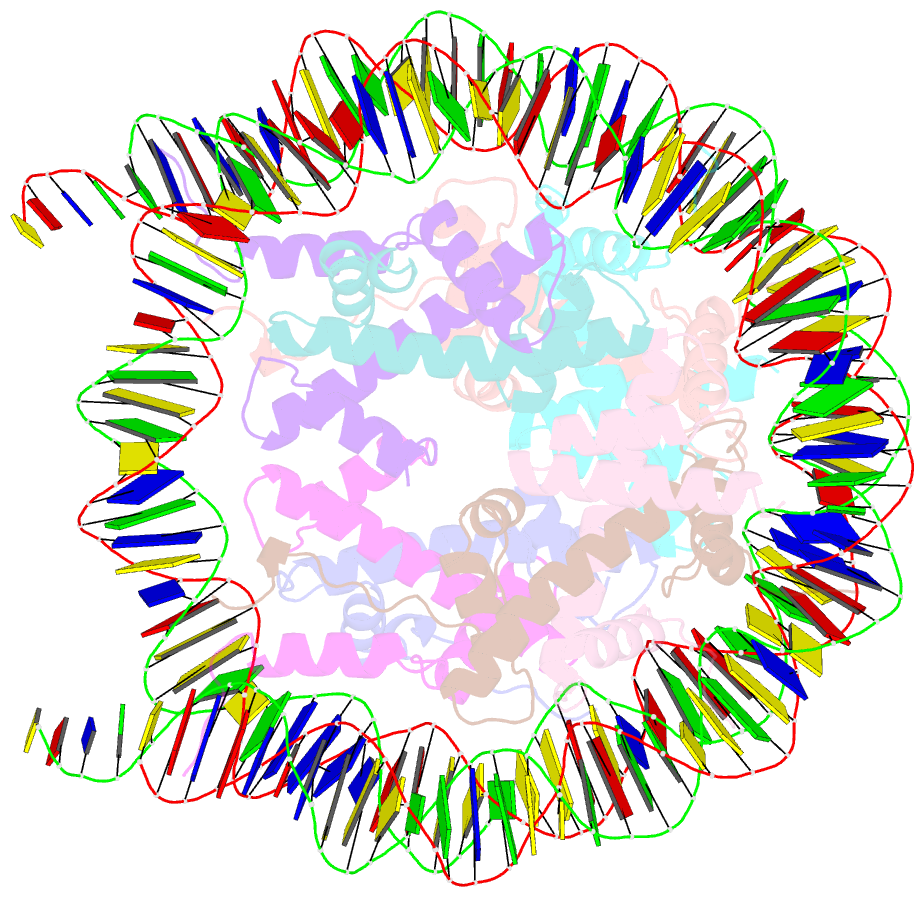
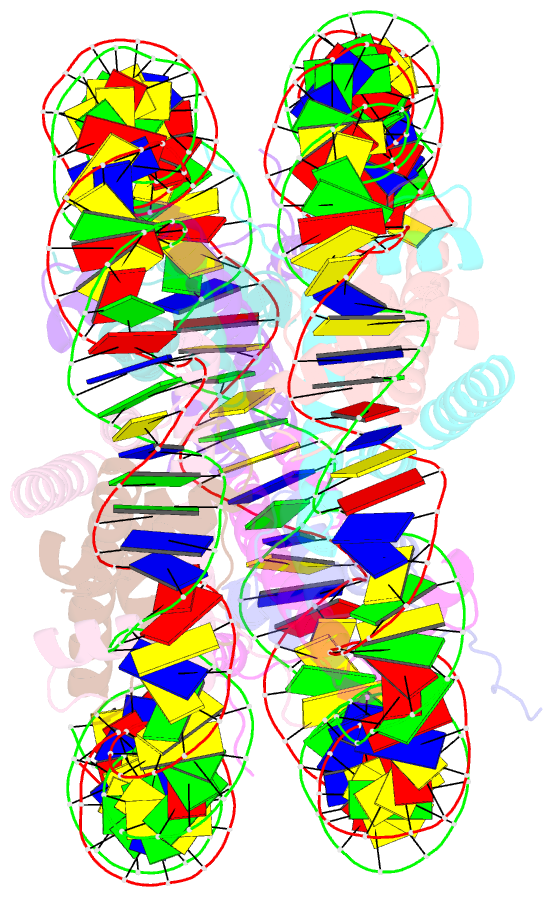
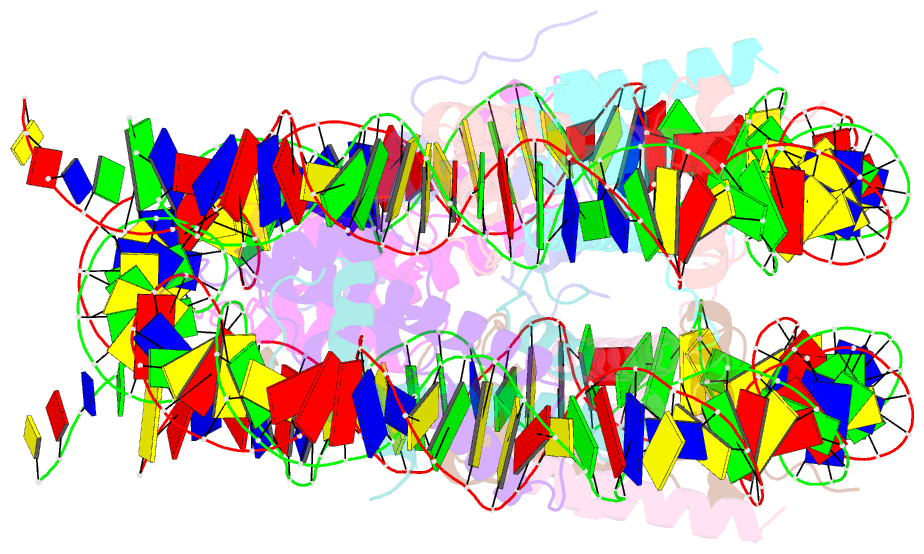
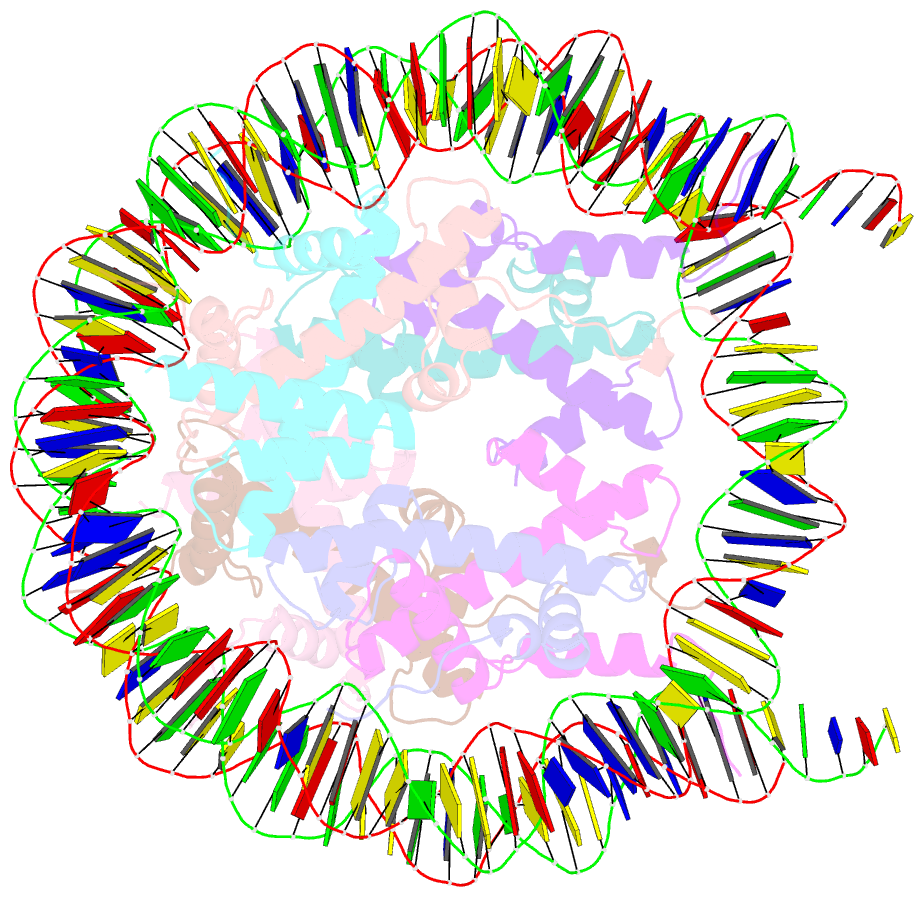
- Human nucleosome core particle with cohesive end DNA termini
- Reference
- Sharma D, De Falco L, Padavattan S, Rao C, Geifman-Shochat S, Liu CF, Davey CA (2019): "PARP1 exhibits enhanced association and catalytic efficiency with gamma H2A.X-nucleosome." Nat Commun, 10, 5751. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13641-0.
- Abstract
- The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, PARP1, plays a key role in maintaining genomic integrity by detecting DNA damage and mediating repair. γH2A.X is the primary histone marker for DNA double-strand breaks and PARP1 localizes to H2A.X-enriched chromatin damage sites, but the basis for this association is not clear. We characterize the kinetics of PARP1 binding to a variety of nucleosomes harbouring DNA double-strand breaks, which reveal that PARP1 associates faster with (γ)H2A.X- versus H2A-nucleosomes, resulting in a higher affinity for the former, which is maximal for γH2A.X-nucleosome that is also the activator eliciting the greatest poly-ADP-ribosylation catalytic efficiency. The enhanced activities with γH2A.X-nucleosome coincide with increased accessibility of the DNA termini resulting from the H2A.X-Ser139 phosphorylation. Indeed, H2A- and (γ)H2A.X-nucleosomes have distinct stability characteristics, which are rationalized by mutational analysis and (γ)H2A.X-nucleosome core crystal structures. This suggests that the γH2A.X epigenetic marker directly facilitates DNA repair by stabilizing PARP1 association and promoting catalysis.