Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6k3k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- NMR
- Summary
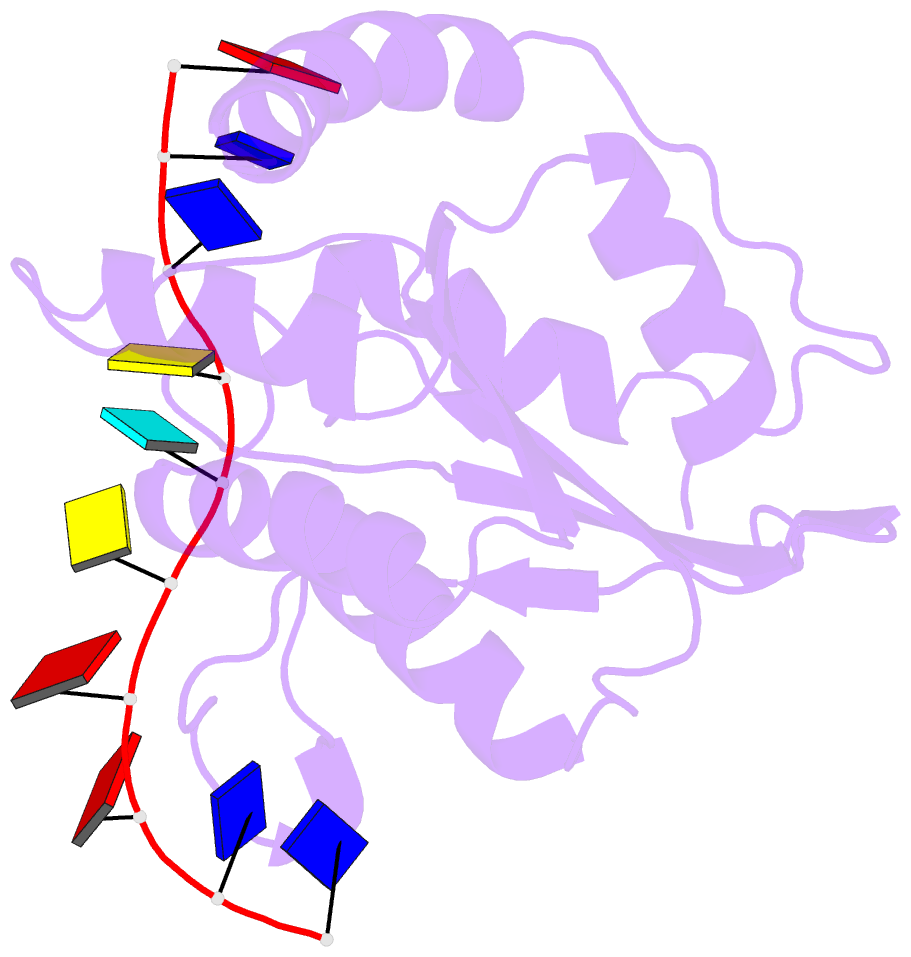
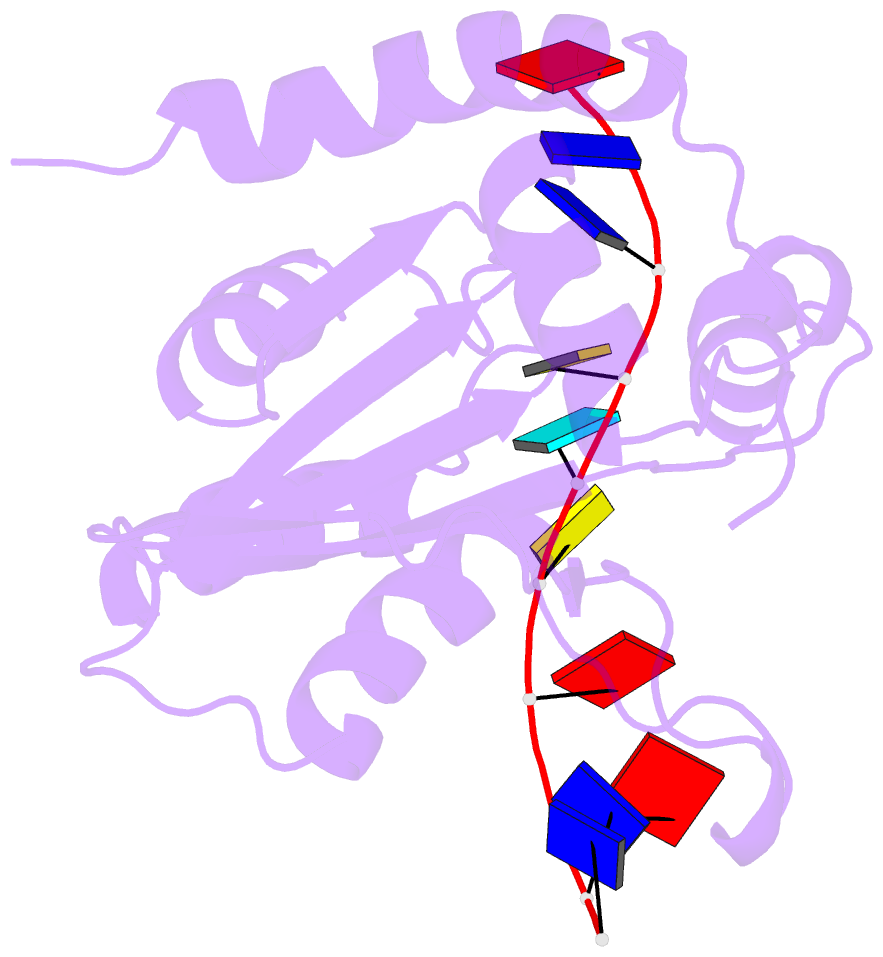
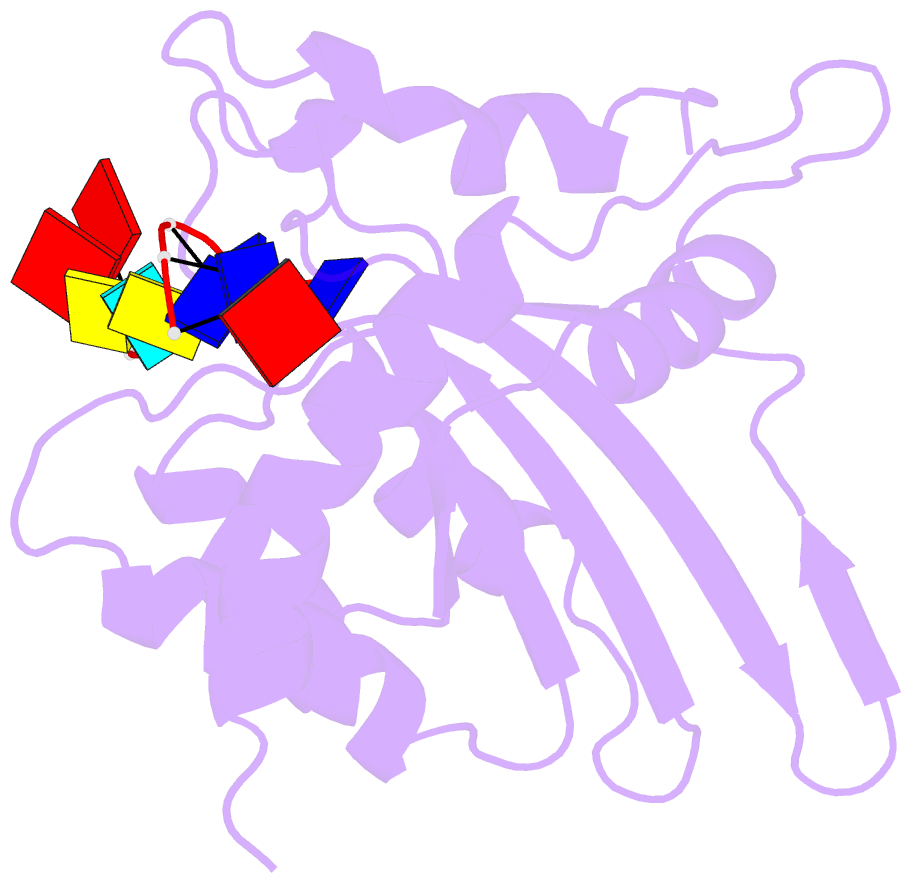
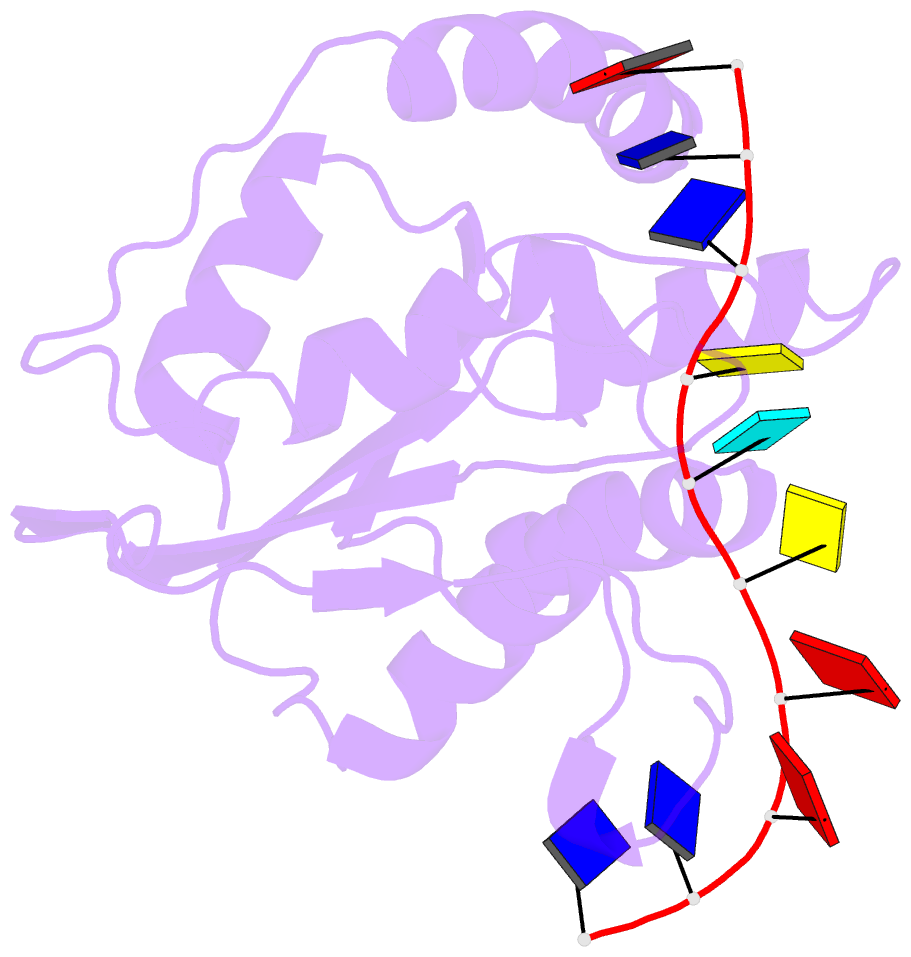
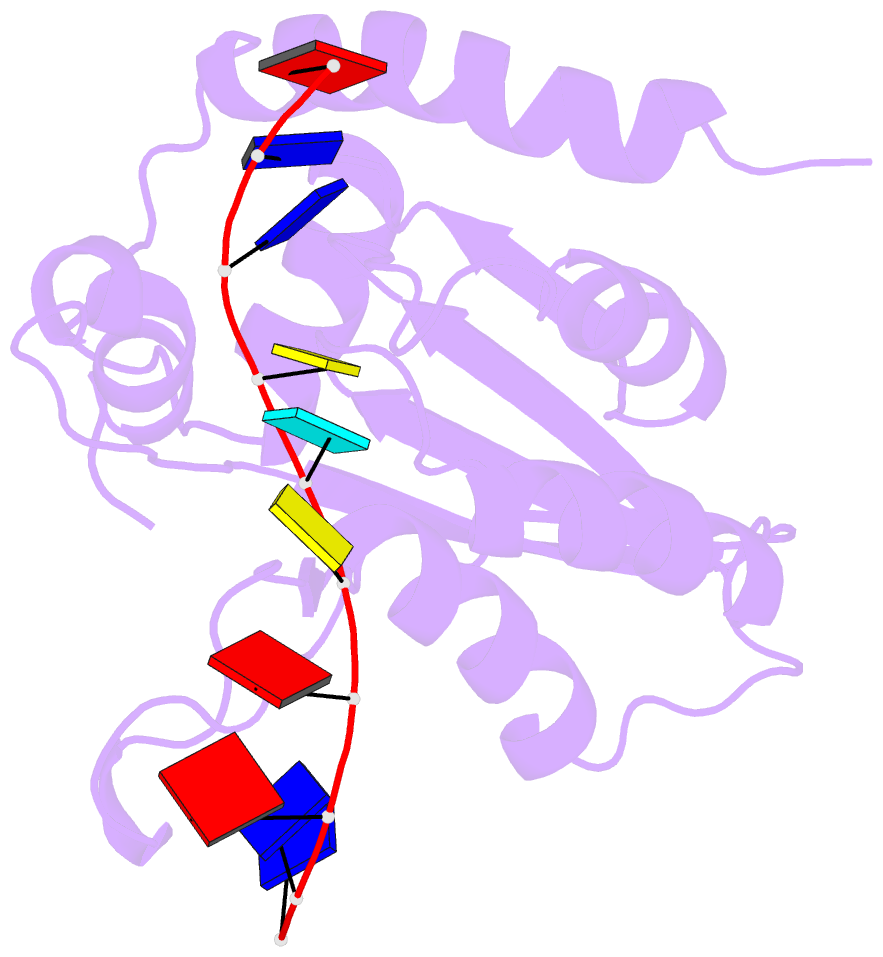
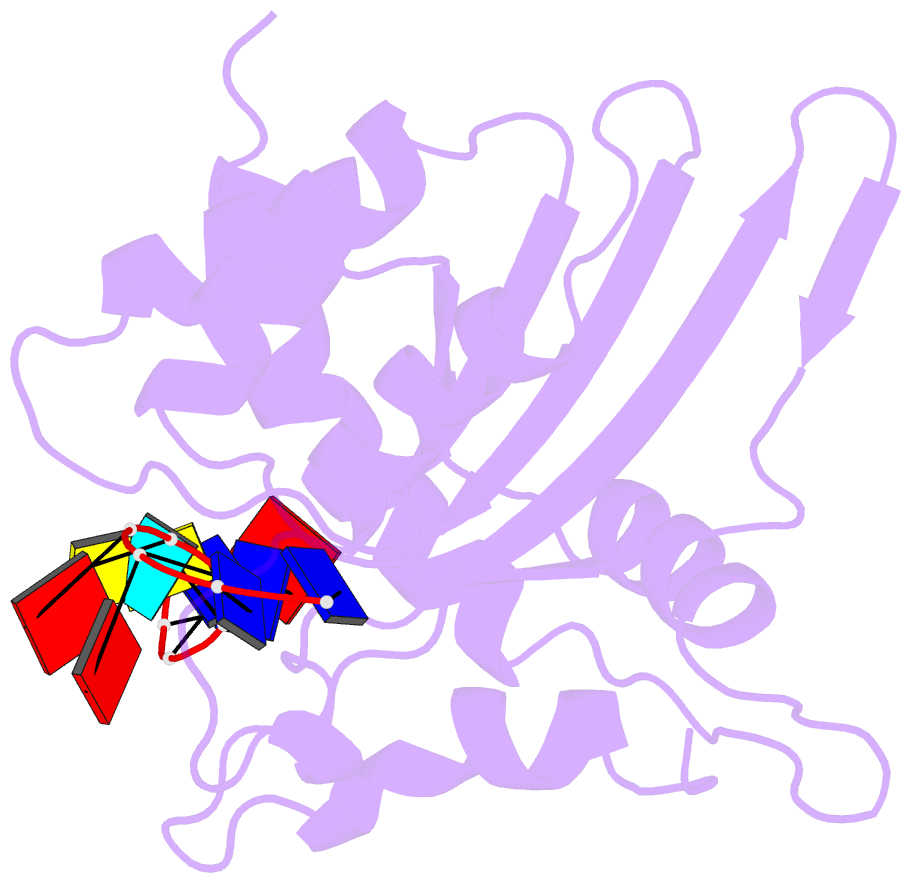
- Solution structure of apobec3g-cd2 with ssDNA, product b
- Reference
- Yan X, Lan W, Wang C, Cao C (2019): "Structural Investigations on the Interactions between Cytidine Deaminase Human APOBEC3G and DNA." Chem Asian J, 14, 2235-2241. doi: 10.1002/asia.201900480.
- Abstract
- Human APOBEC3G (A3G) inhibits the replication of human immunodeficiency virus-1 by deaminating cytidine at the 3'-end in the target motif 5'-CCC-3' in viral cDNA during reverse transcription. It in vitro deaminates two consecutive cytidines in a 3'->5' order. Although a crystal structure of the A3G catalytic domain (A3G-CD2) with DNA was reported, it is unknown why residues involved in enzymatic reaction are distributed widely. Here, we introduced an iodine atom into the C-5 position of cytidine (dC6 I ) in DNA 5'-ATTC4 C5 C6 I A7 ATT-3' (TCCC6 I ). It switches the deamination sequence preference from CCC to TCC, although small dC6 I deamination was observed. Solution structures of A3G-CD2 in complexes with products DNA TCUC6 I and TCUU6 I indicate that the substrate DNA binds A3G-CD2 in TCC and CCC modes. The dC6 deamination correlates with the 4th base type. The CCC mode favours dC6 deamination, while the TCC mode results in dC5 deamination. These studies present an extensive basis to design inhibitors to impede viral evolvability.