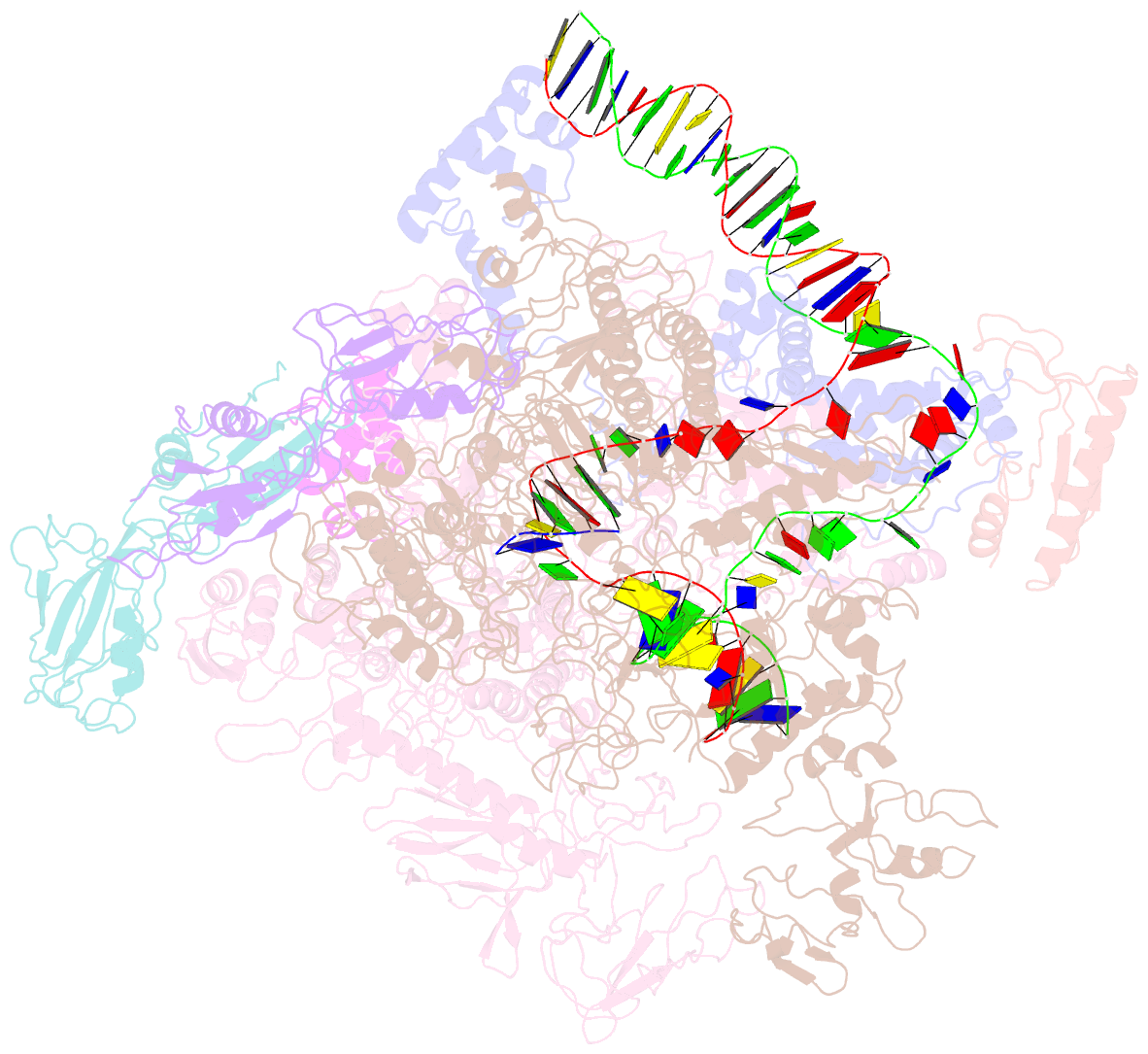
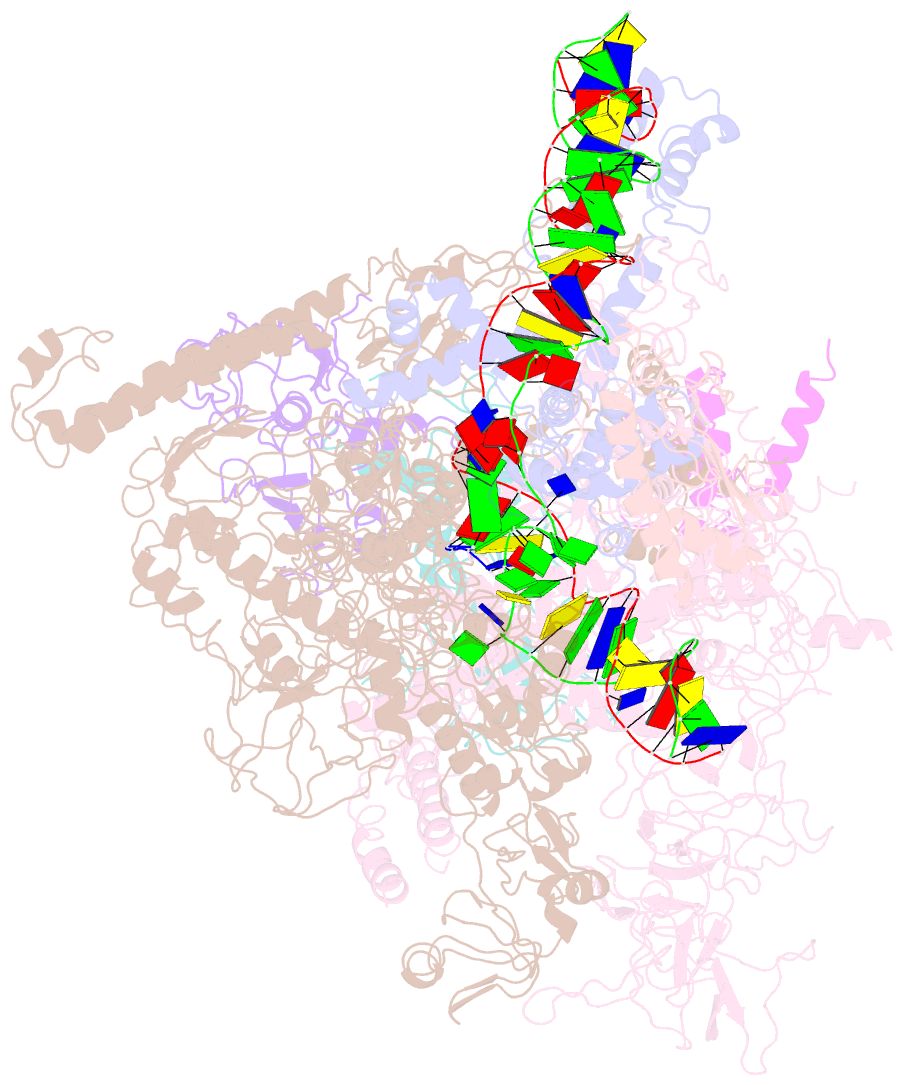
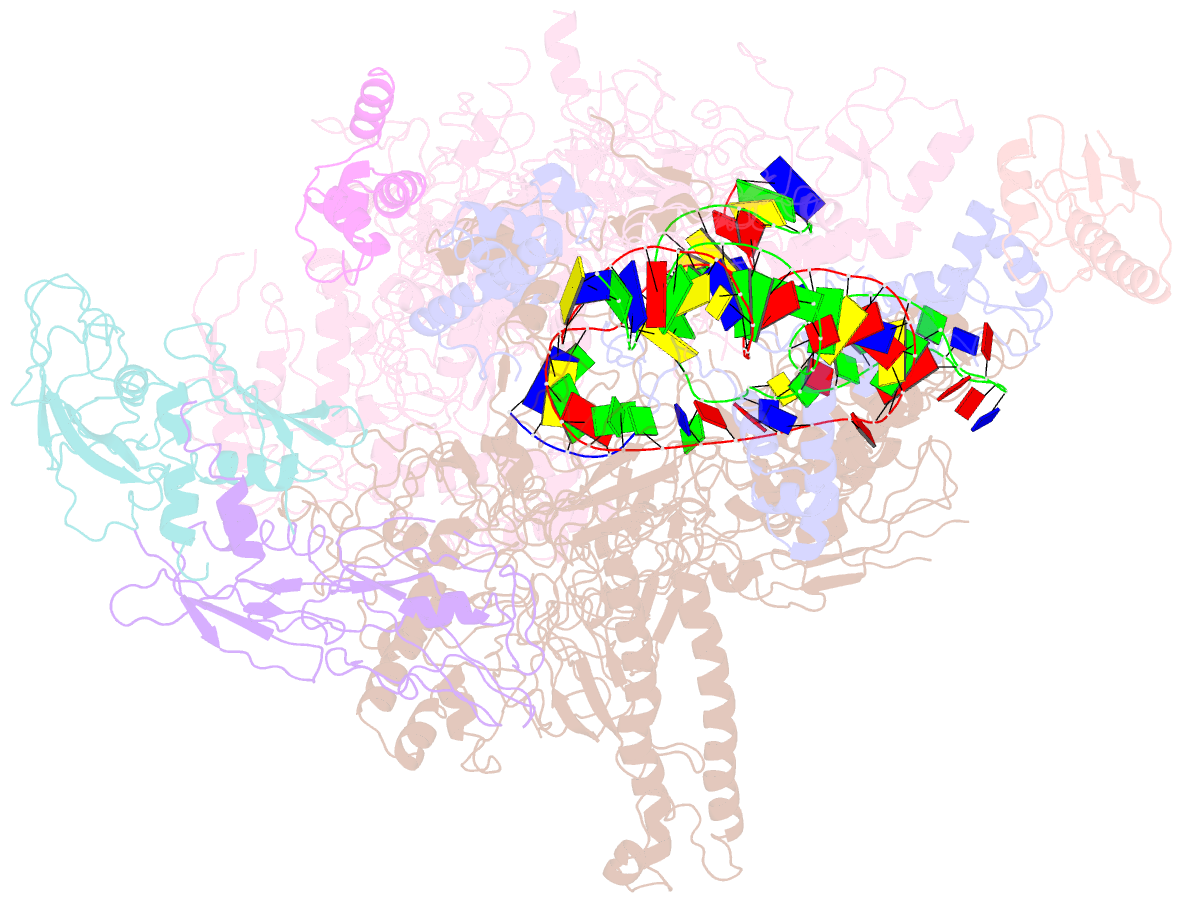
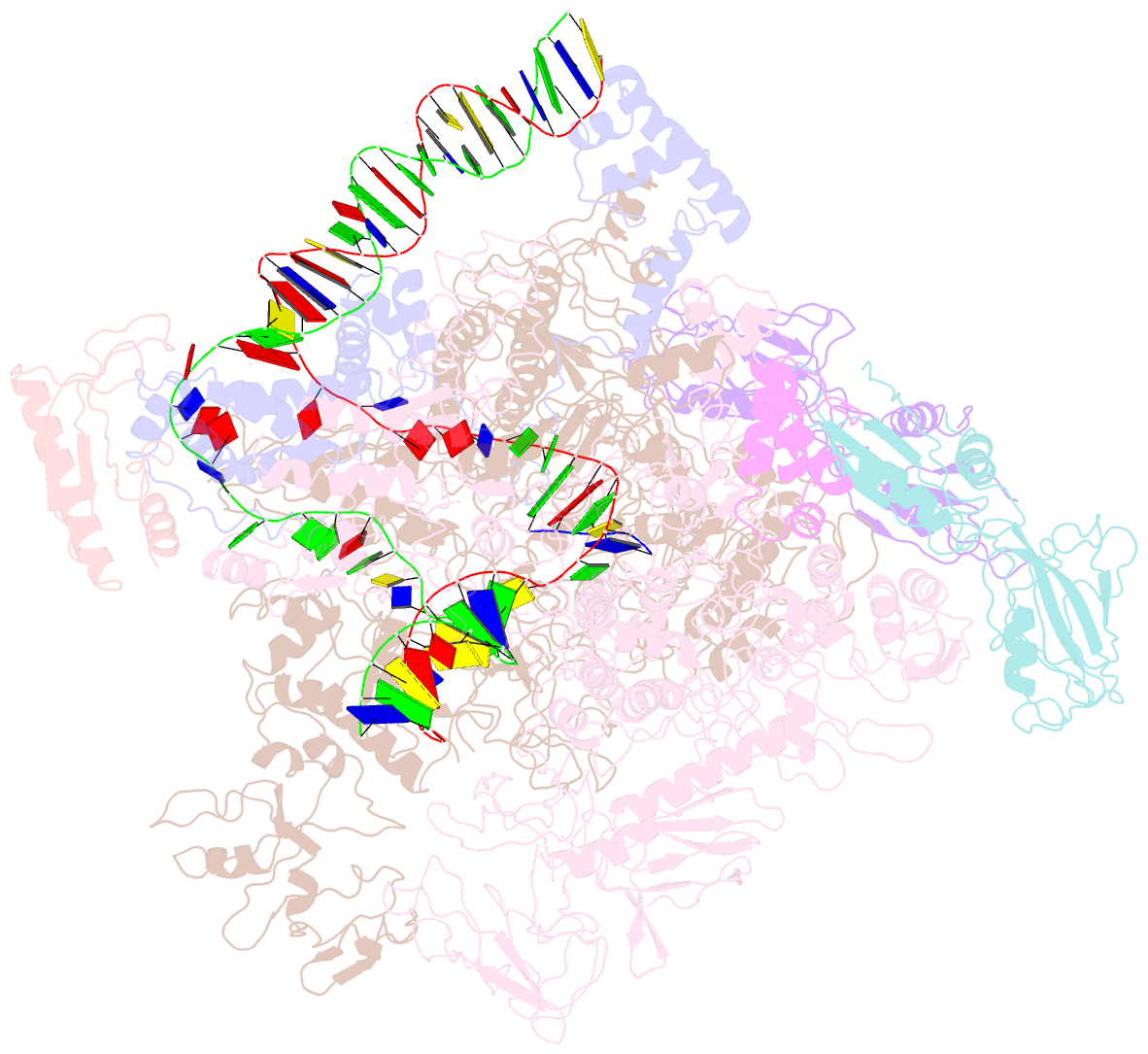
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6kj6; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.8 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of escherichia coli crl transcription activation complex
- Reference
- Xu J, Cui K, Shen L, Shi J, Li L, You L, Fang C, Zhao G, Feng Y, Yang B, Zhang Y (2019): "Crl activates transcription by stabilizing active conformation of the master stress transcription initiation factor." Elife, 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50928.
- Abstract
- σS is a master transcription initiation factor that protects bacterial cells from various harmful environmental stresses including antibiotic pressure. Although its mechanism remains unclear, it is known that full activation of σS-mediated transcription requires a σS-specific activator, Crl. In this study, we determined a 3.80 Å cryo-EM structure of an Escherichia coli transcription activation complex (E. coli Crl-TAC) comprising E. coli σS-RNA polymerase (σS-RNAP) holoenzyme, Crl, and a nucleic-acid scaffold. The structure reveals that Crl interacts with domain 2 of σS (σS2) and the RNAP core enzyme, but does not contact promoter DNA. Results from subsequent hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS) indicate that Crl stabilizes key structural motifs within σS2 to promote the assembly of the σS-RNAP holoenzyme and also to facilitate formation of an RNA polymerase-promoter DNA open complex (RPo). Our study demonstrates a unique DNA contact-independent mechanism of transcription activation, thereby defining a previously unrecognized mode of transcription activation in cells.