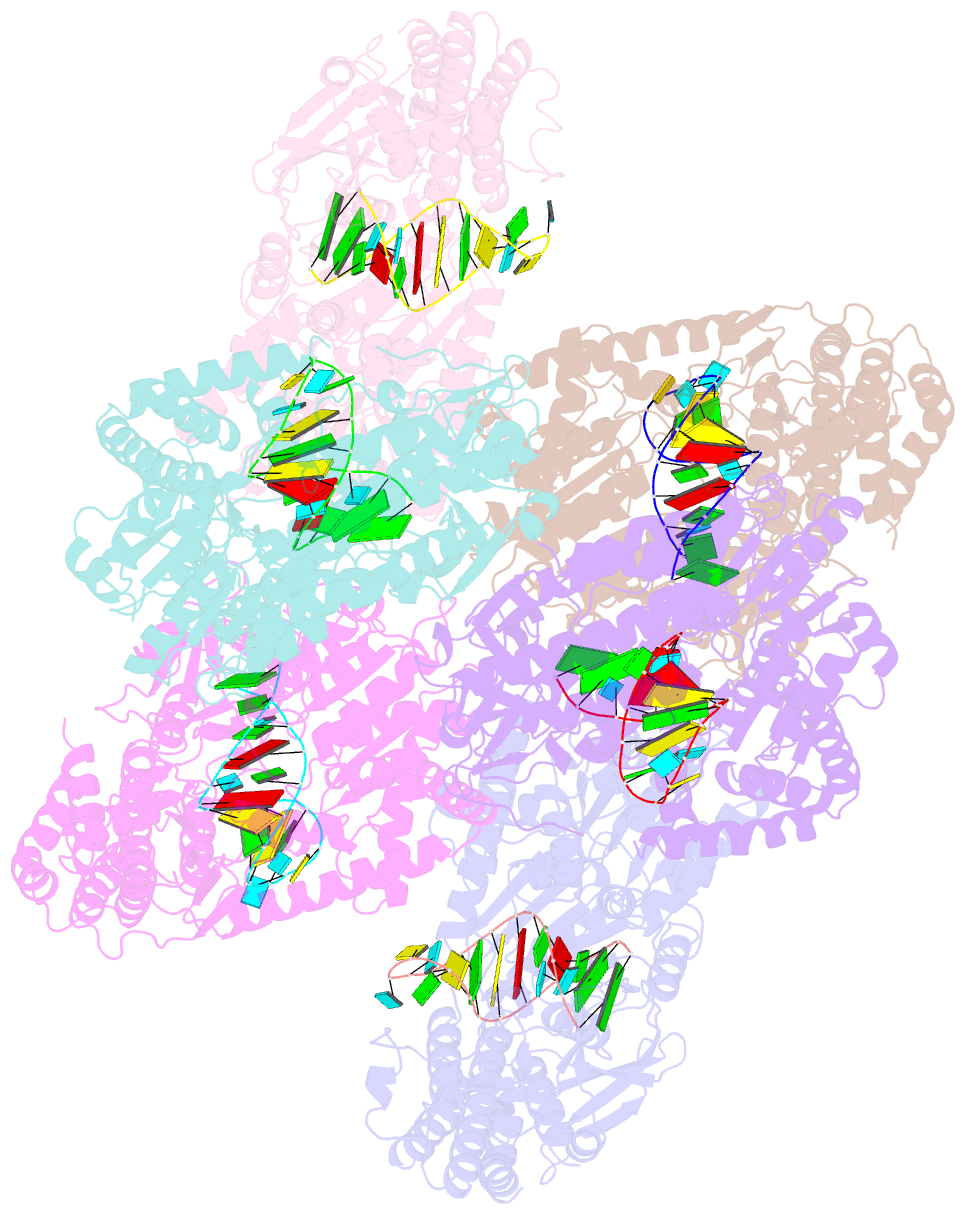
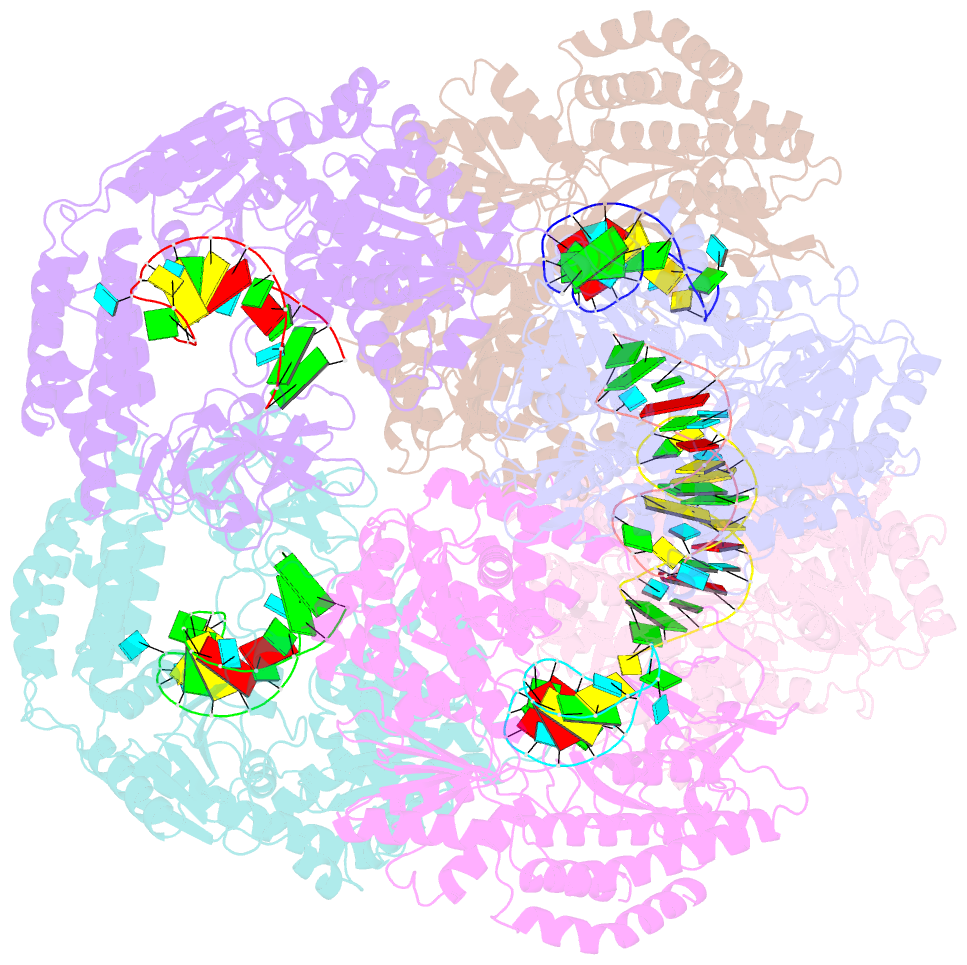
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6kyv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- immune system
- Method
- X-ray (3.0 Å)
- Summary
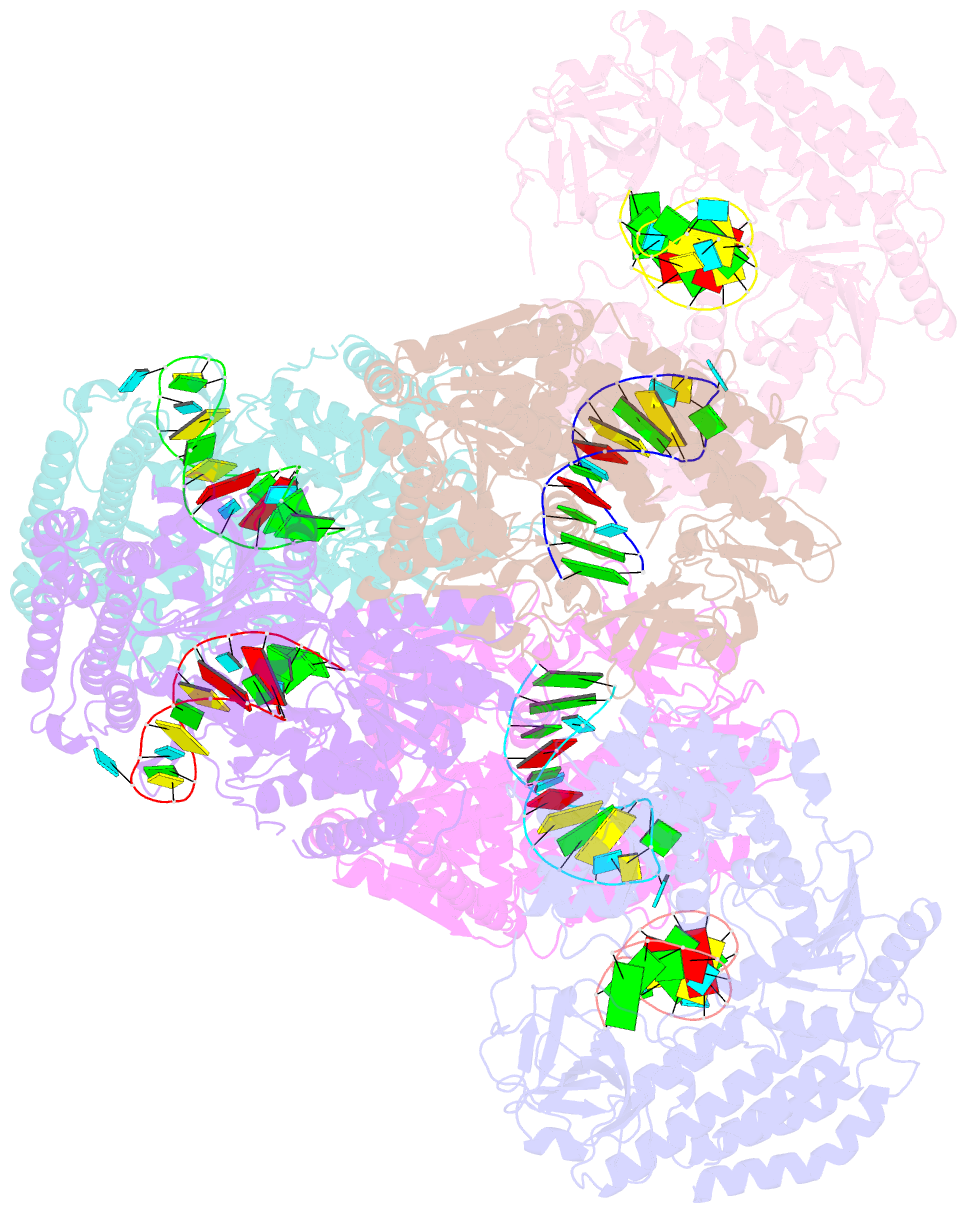
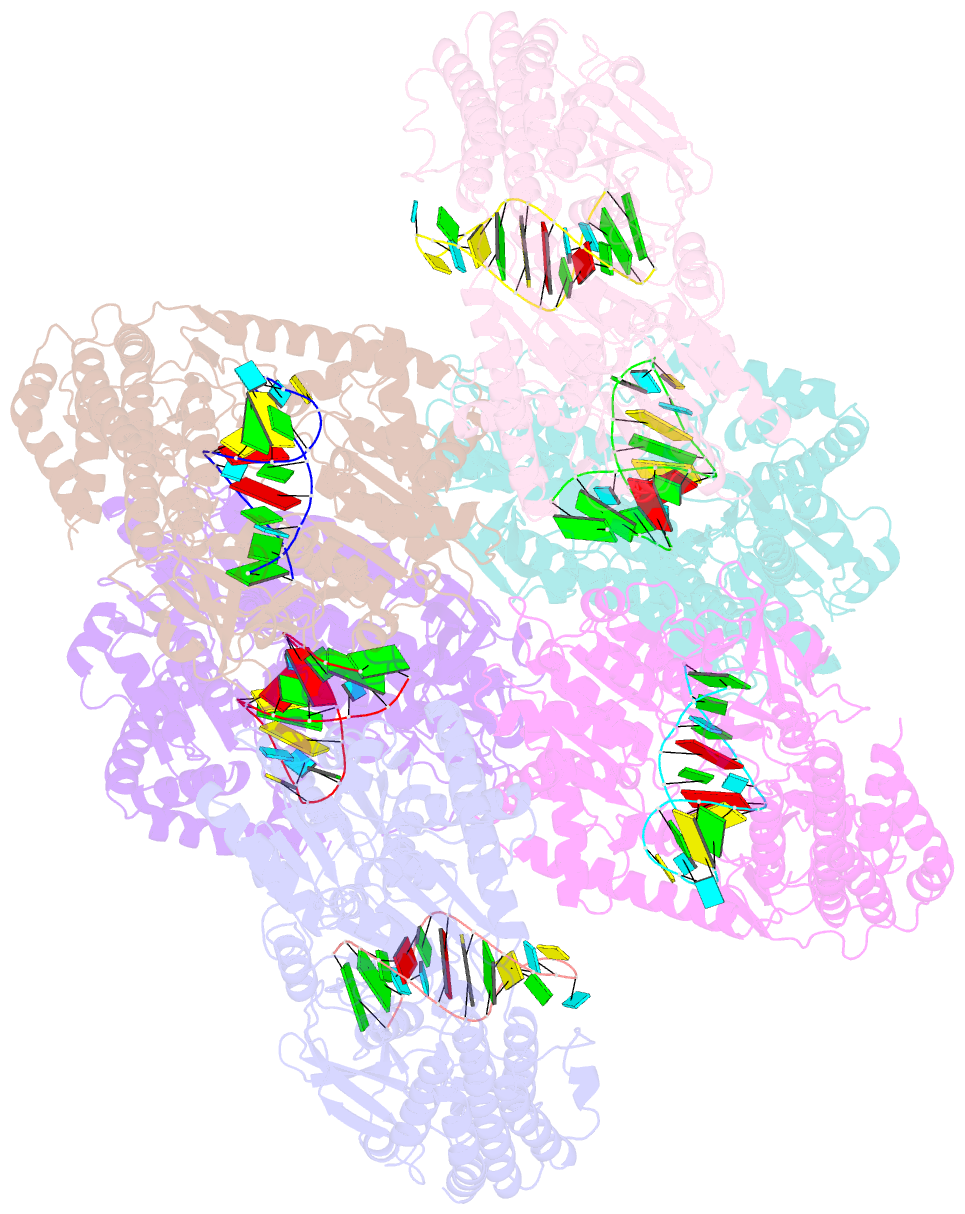
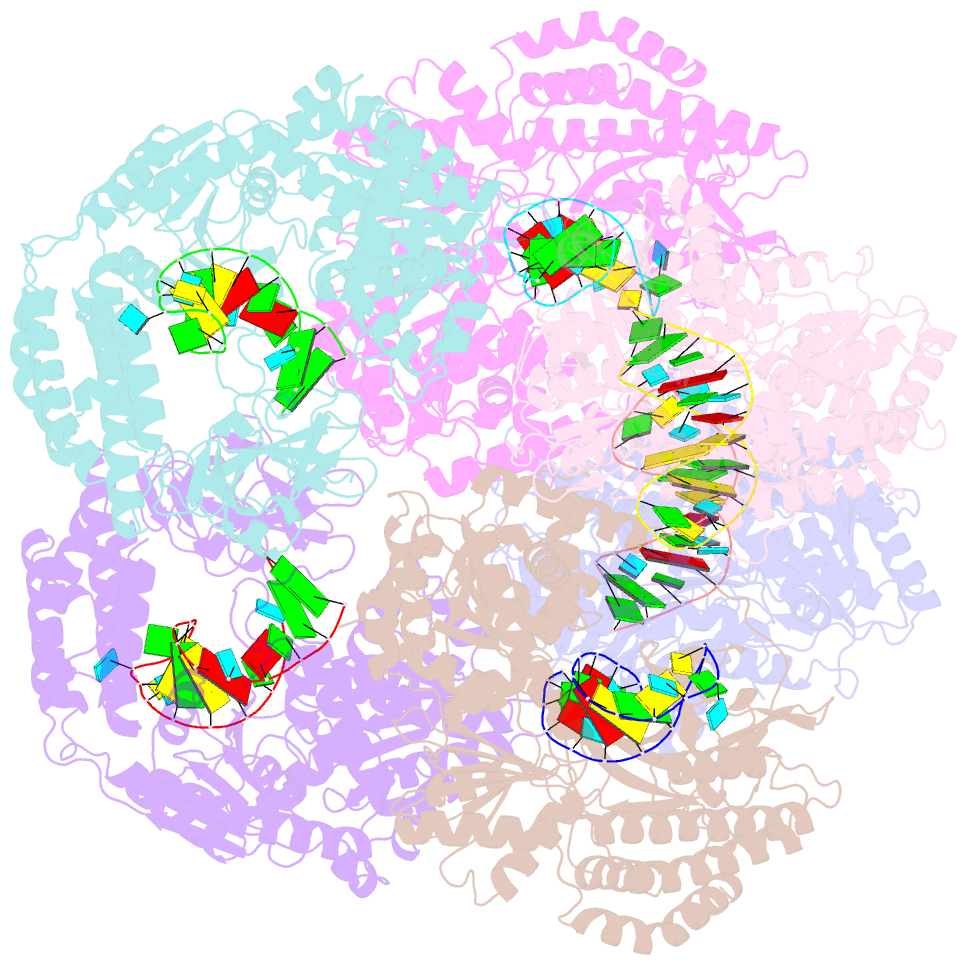
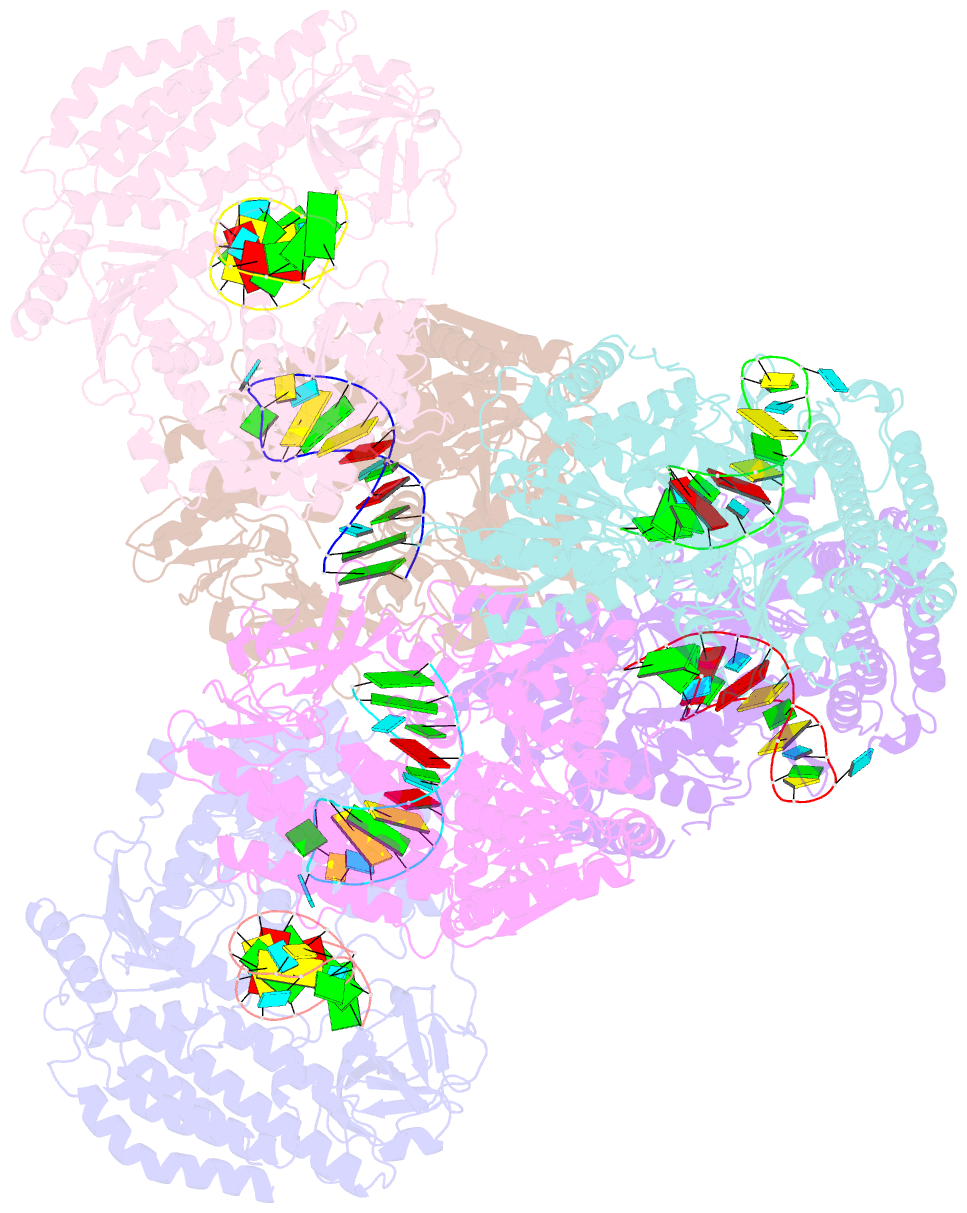
- Crystal structure of rig-i and hairpin RNA with g-u wobble base pairs
- Reference
- Kim KH, Hwang J, Kim JH, Son KP, Jang Y, Kim M, Kang SJ, Lee JO, Kang JY, Choi BS (2020): "Structural and biophysical properties of RIG-I bound to dsRNA with G-U wobble base pairs." Rna Biol., 17, 325-334. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1700034.
- Abstract
- Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) is responsible for innate immunity via the recognition of short double-stranded RNAs in the cytosol. With the clue that G-U wobble base pairs in the influenza A virus's RNA promoter region are responsible for RIG-I activation, we determined the complex structure of RIG-I ΔCARD and a short hairpin RNA with G-U wobble base pairs by X-ray crystallography. Interestingly, the overall helical backbone trace was not affected by the presence of the wobble base pairs; however, the base pair inclination and helical axis angle changed upon RIG-I binding. NMR spectroscopy revealed that RIG-I binding renders the flexible base pair of the influenza A virus's RNA promoter region between the two G-U wobble base pairs even more flexible. Binding to RNA with wobble base pairs resulted in a more flexible RIG-I complex. This flexible complex formation correlates with the entropy-favoured binding of RIG-I and RNA, which results in tighter binding affinity and RIG-I activation. This study suggests that the structure and dynamics of RIG-I are tailored to the binding of specific RNA sequences with different flexibility.