Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6m3l; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.75 Å)
- Summary
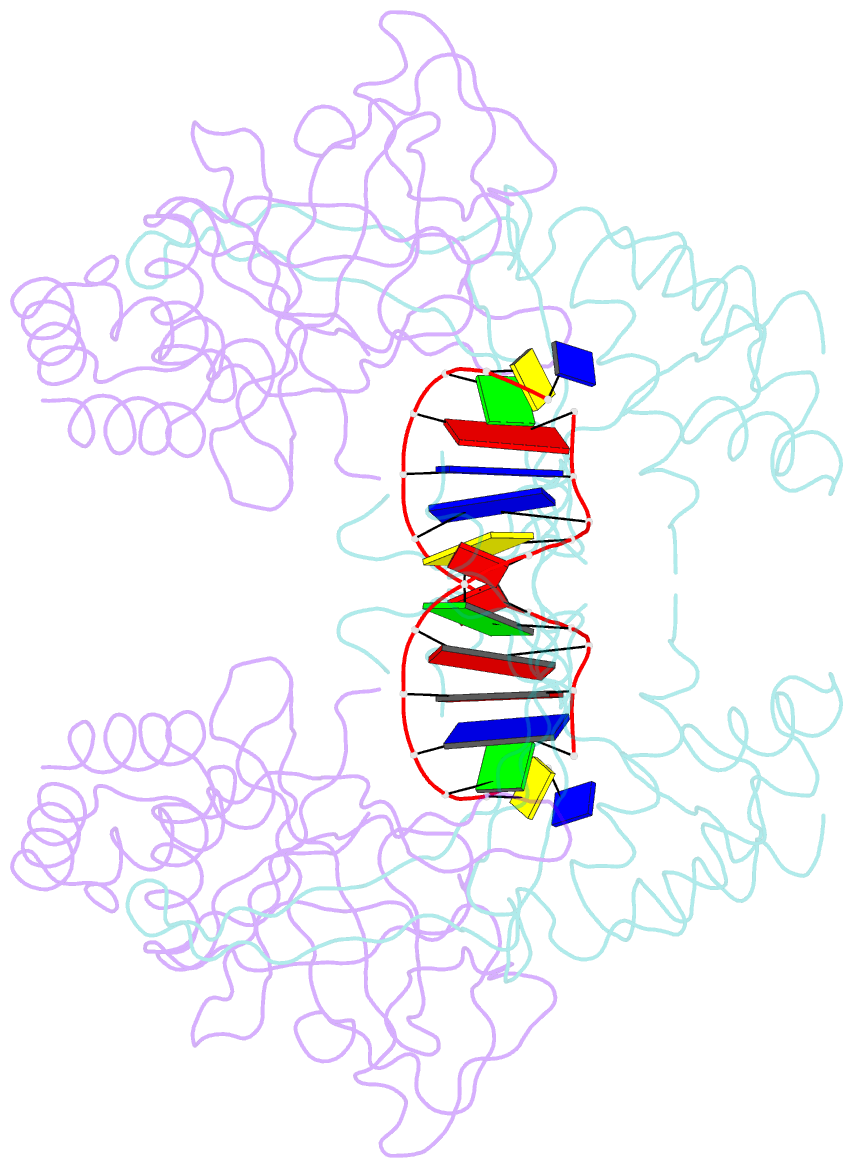
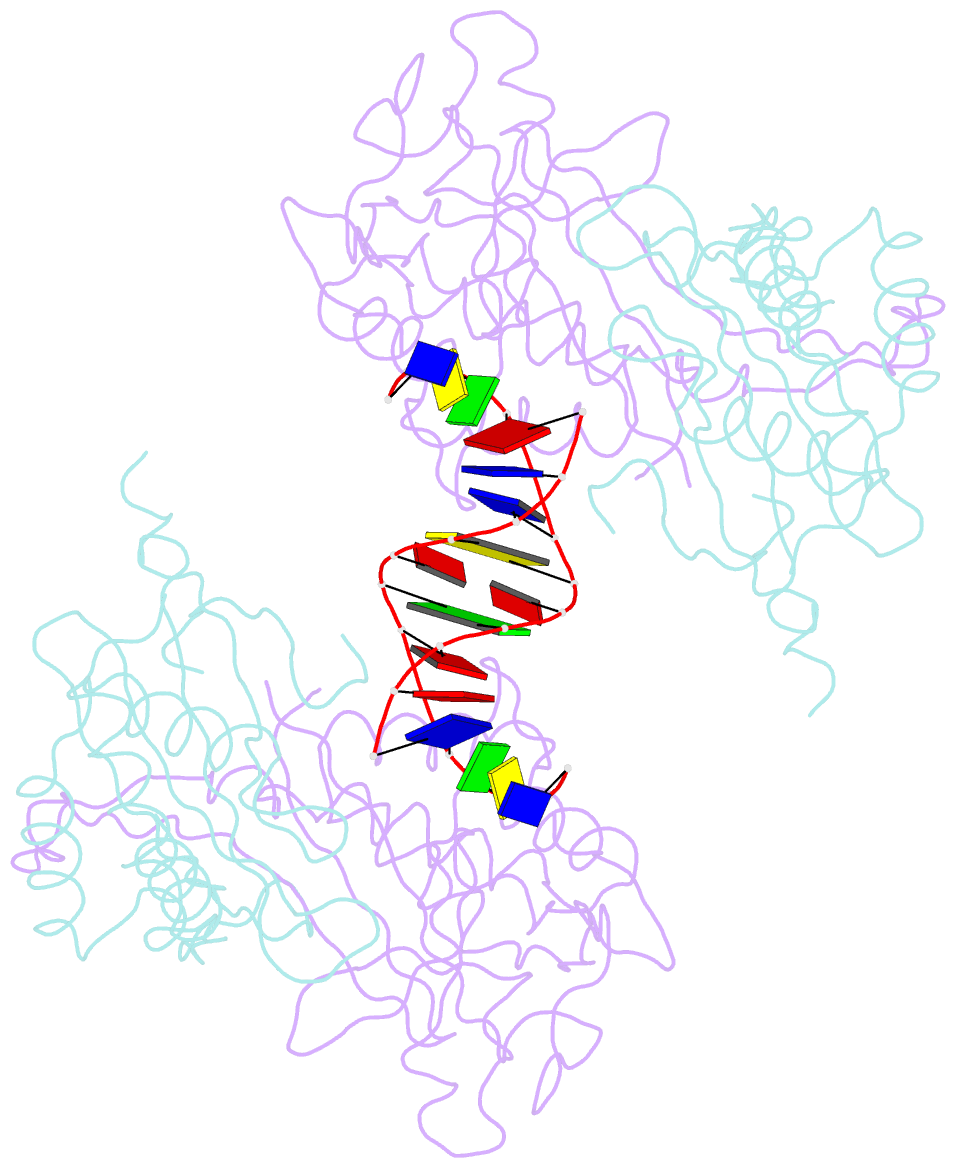
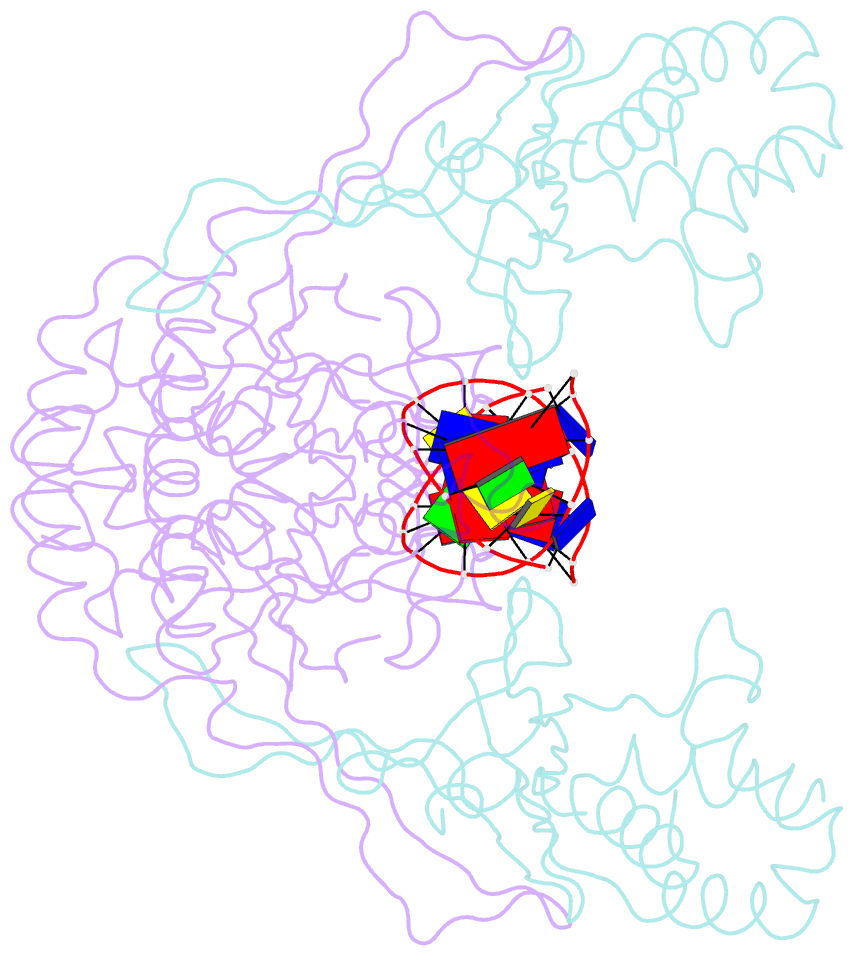
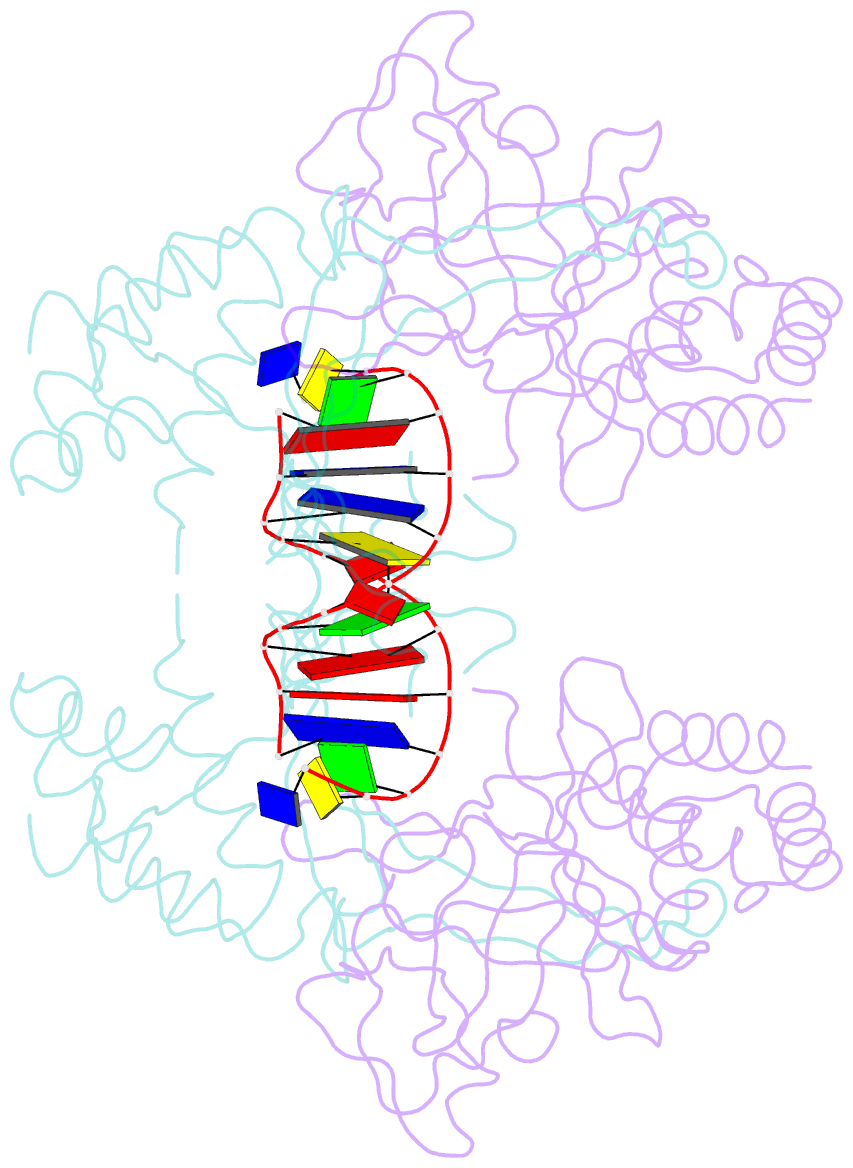
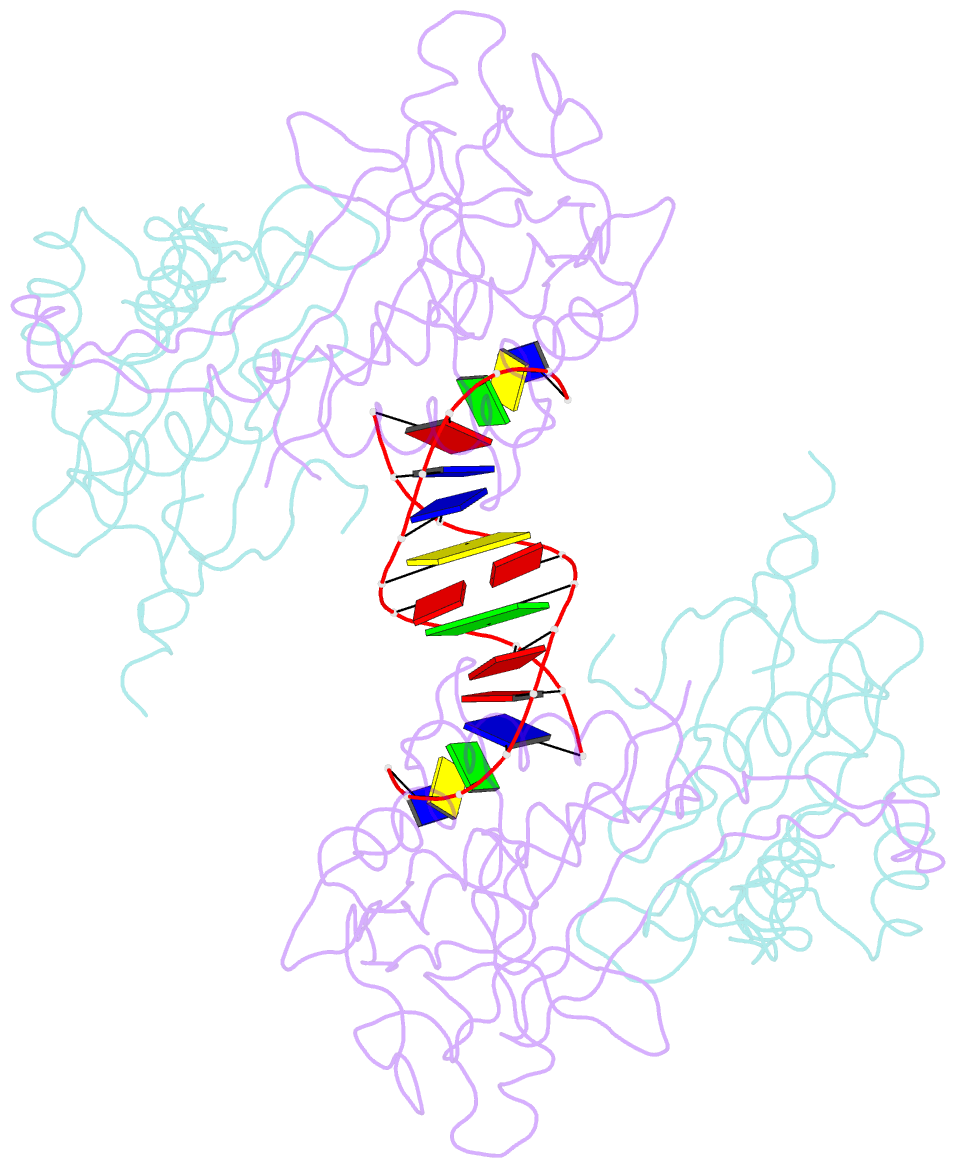
- Crystal structure of the r.pabi(y68f-k154a)-dsDNA(nonspecific) complex
- Reference
- Miyazono KI, Wang D, Ito T, Tanokura M (2020): "Distortion of double-stranded DNA structure by the binding of the restriction DNA glycosylase R.PabI." Nucleic Acids Res., 48, 5106-5118. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa184.
- Abstract
- R.PabI is a restriction DNA glycosylase that recognizes the sequence 5'-GTAC-3' and hydrolyses the N-glycosidic bond of adenine in the recognition sequence. R.PabI drastically bends and unwinds the recognition sequence of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) and flips the adenine and guanine bases in the recognition sequence into the catalytic and recognition sites on the protein surface. In this study, we determined the crystal structure of the R.PabI-dsDNA complex in which the dsDNA is drastically bent by the binding of R.PabI but the base pairs are not unwound. This structure is predicted to be important for the indirect readout of the recognition sequence by R.PabI. In the complex structure, wedge loops of the R.PabI dimer are inserted into the minor groove of dsDNA to stabilize the deformed dsDNA structure. A base stacking is distorted between the two wedge-inserted regions. R.PabI is predicted to utilize the distorted base stacking for the detection of the recognition sequence.