Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6ny3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.7 Å)
- Summary
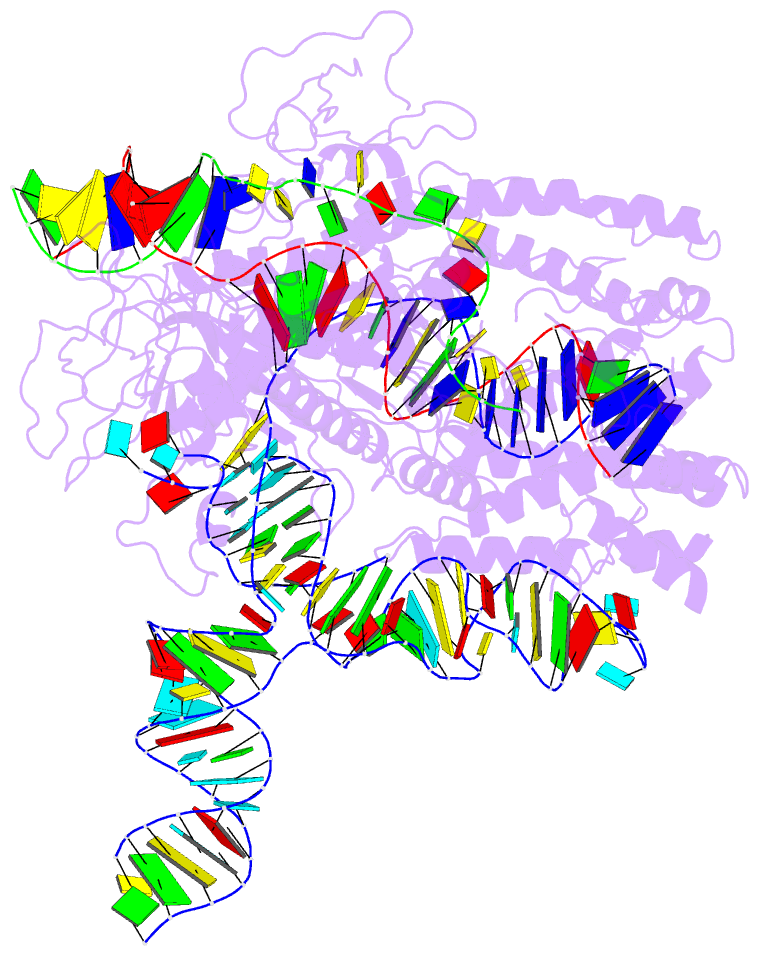
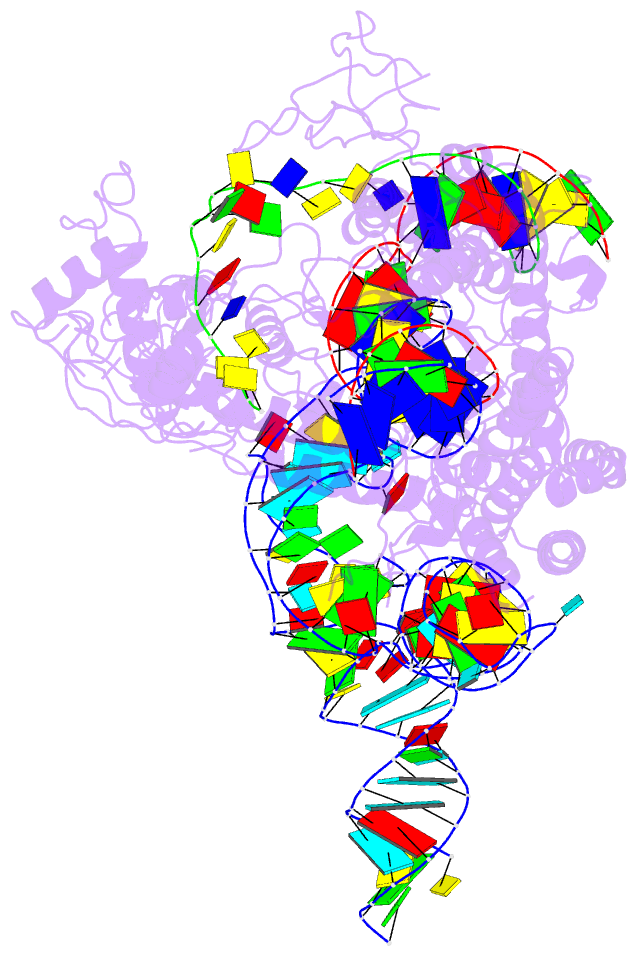
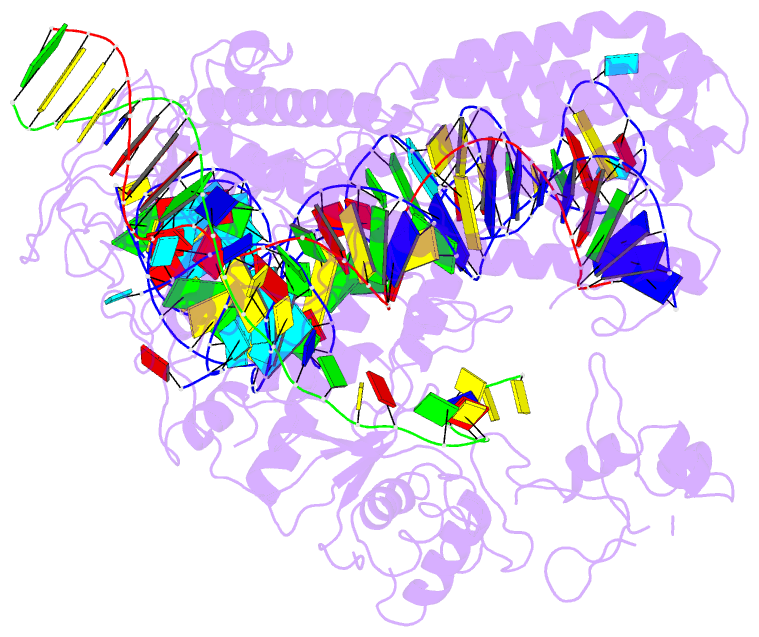
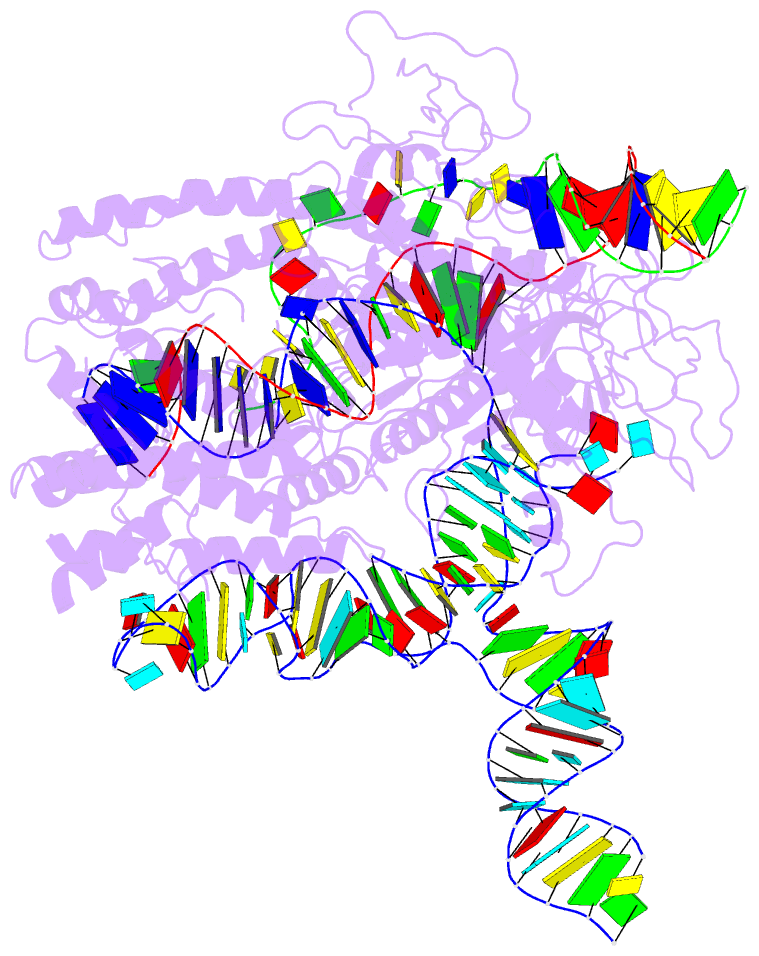
- Casx ternary complex with 30bp target DNA
- Reference
- Liu JJ, Orlova N, Oakes BL, Ma E, Spinner HB, Baney KLM, Chuck J, Tan D, Knott GJ, Harrington LB, Al-Shayeb B, Wagner A, Brotzmann J, Staahl BT, Taylor KL, Desmarais J, Nogales E, Doudna JA (2019): "CasX enzymes comprise a distinct family of RNA-guided genome editors." Nature, 566, 218-223. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0908-x.
- Abstract
- The RNA-guided CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins Cas9 and Cas12a provide adaptive immunity against invading nucleic acids, and function as powerful tools for genome editing in a wide range of organisms. Here we reveal the underlying mechanisms of a third, fundamentally distinct RNA-guided genome-editing platform named CRISPR-CasX, which uses unique structures for programmable double-stranded DNA binding and cleavage. Biochemical and in vivo data demonstrate that CasX is active for Escherichia coli and human genome modification. Eight cryo-electron microscopy structures of CasX in different states of assembly with its guide RNA and double-stranded DNA substrates reveal an extensive RNA scaffold and a domain required for DNA unwinding. These data demonstrate how CasX activity arose through convergent evolution to establish an enzyme family that is functionally separate from both Cas9 and Cas12a.