Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6o1k; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA-hydrolase
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.13 Å)
- Summary
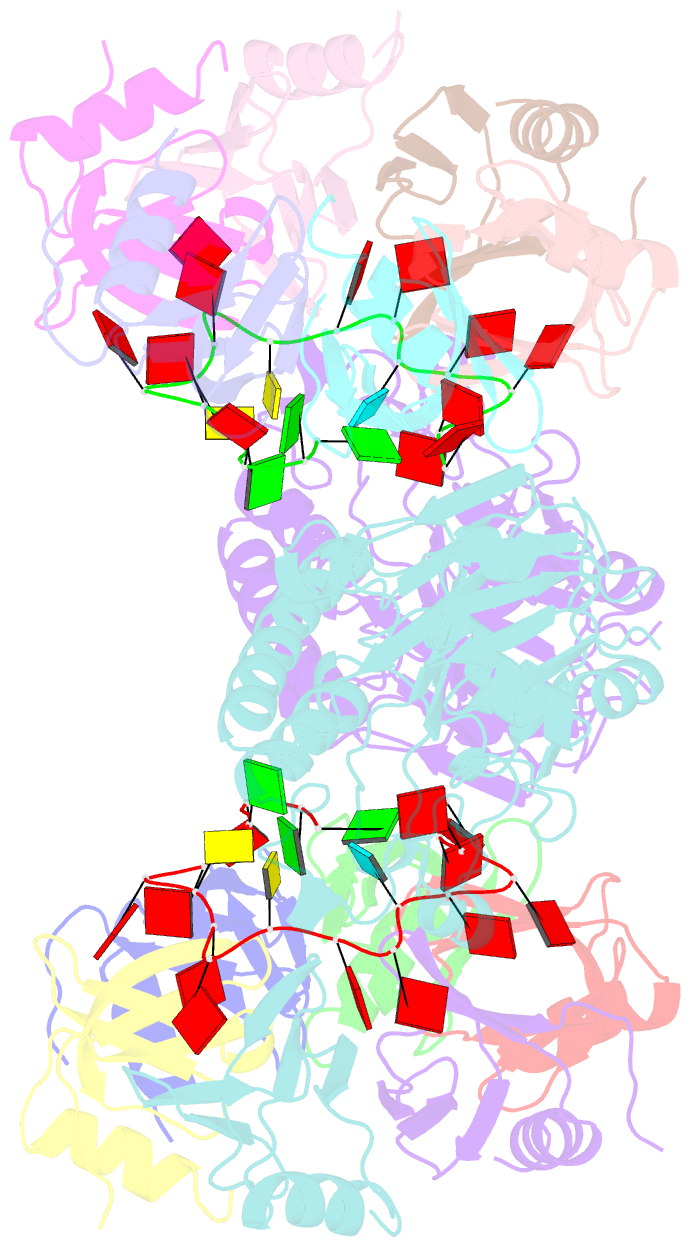
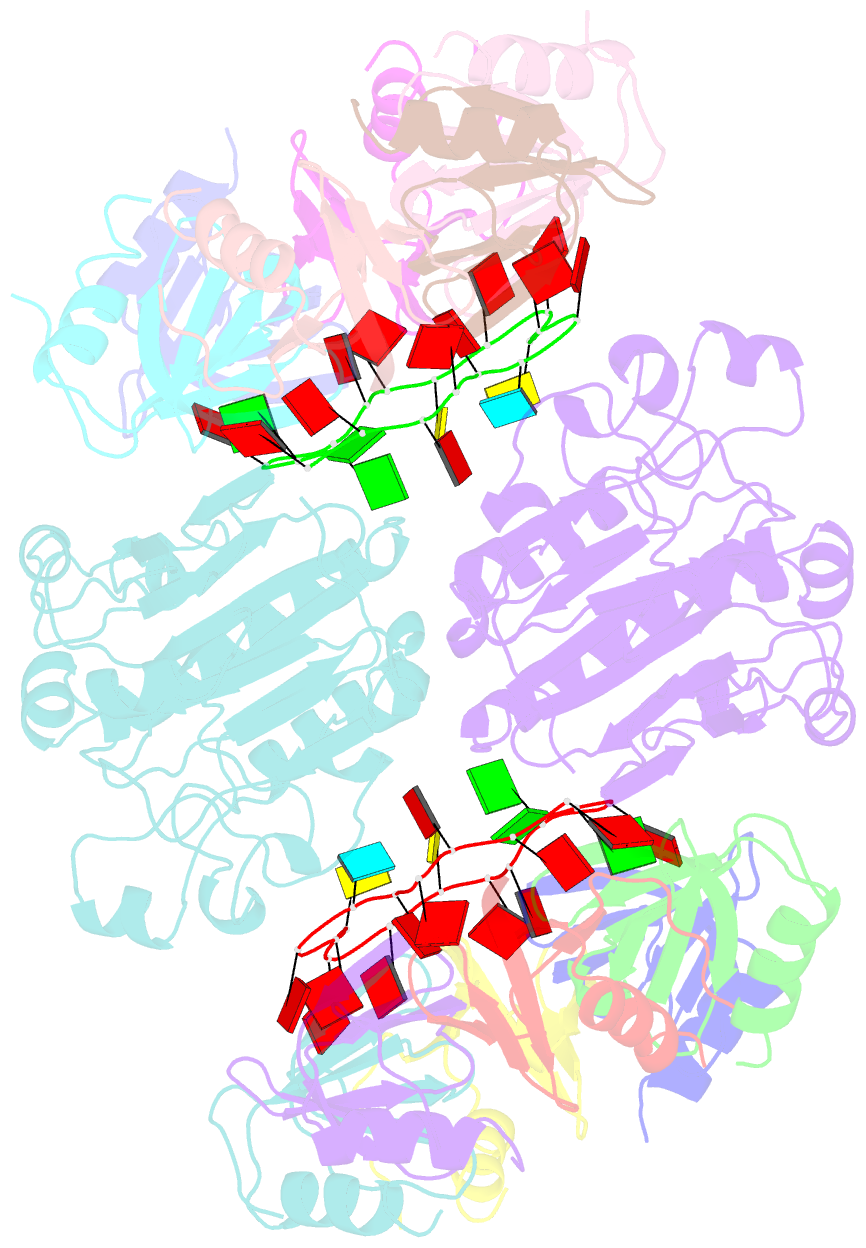
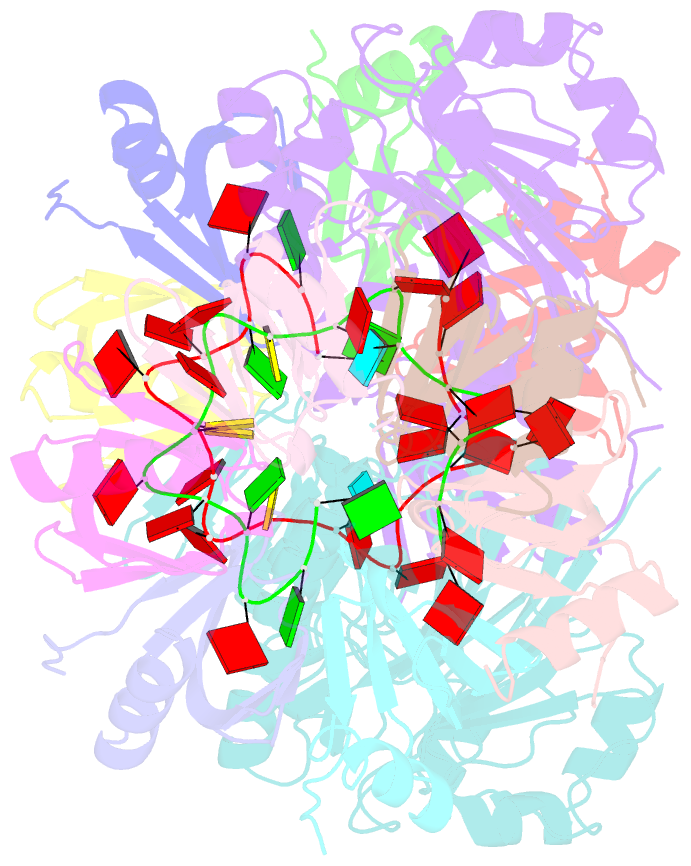
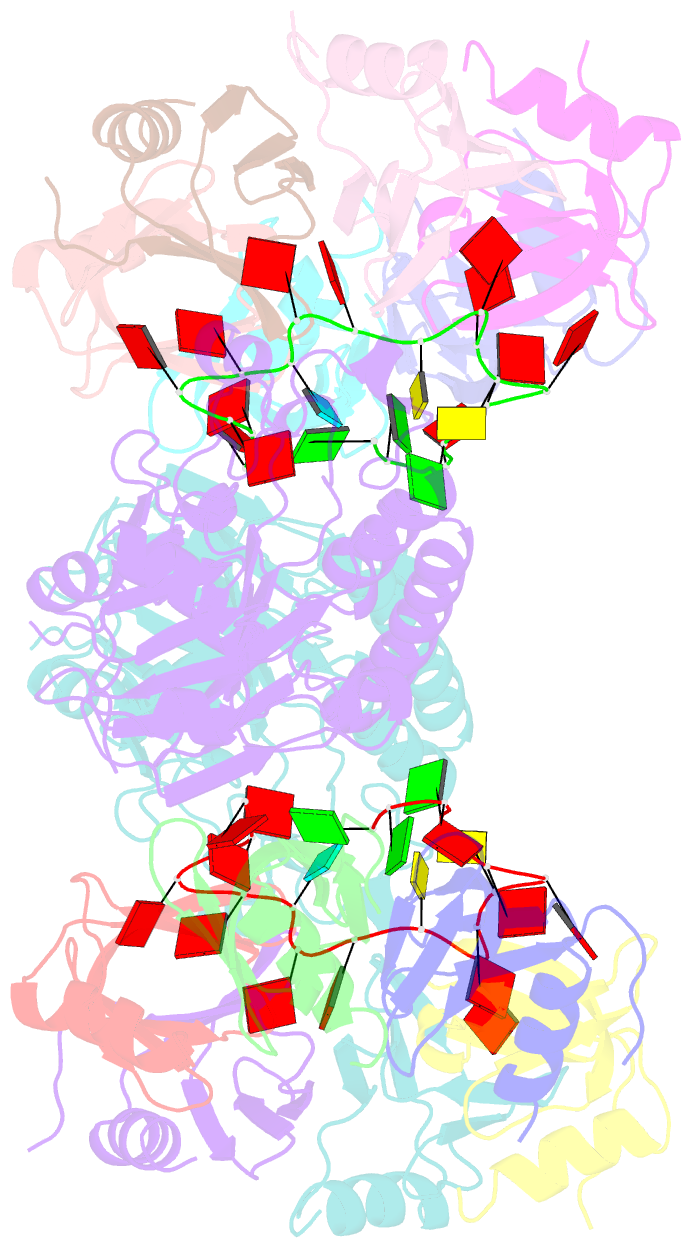
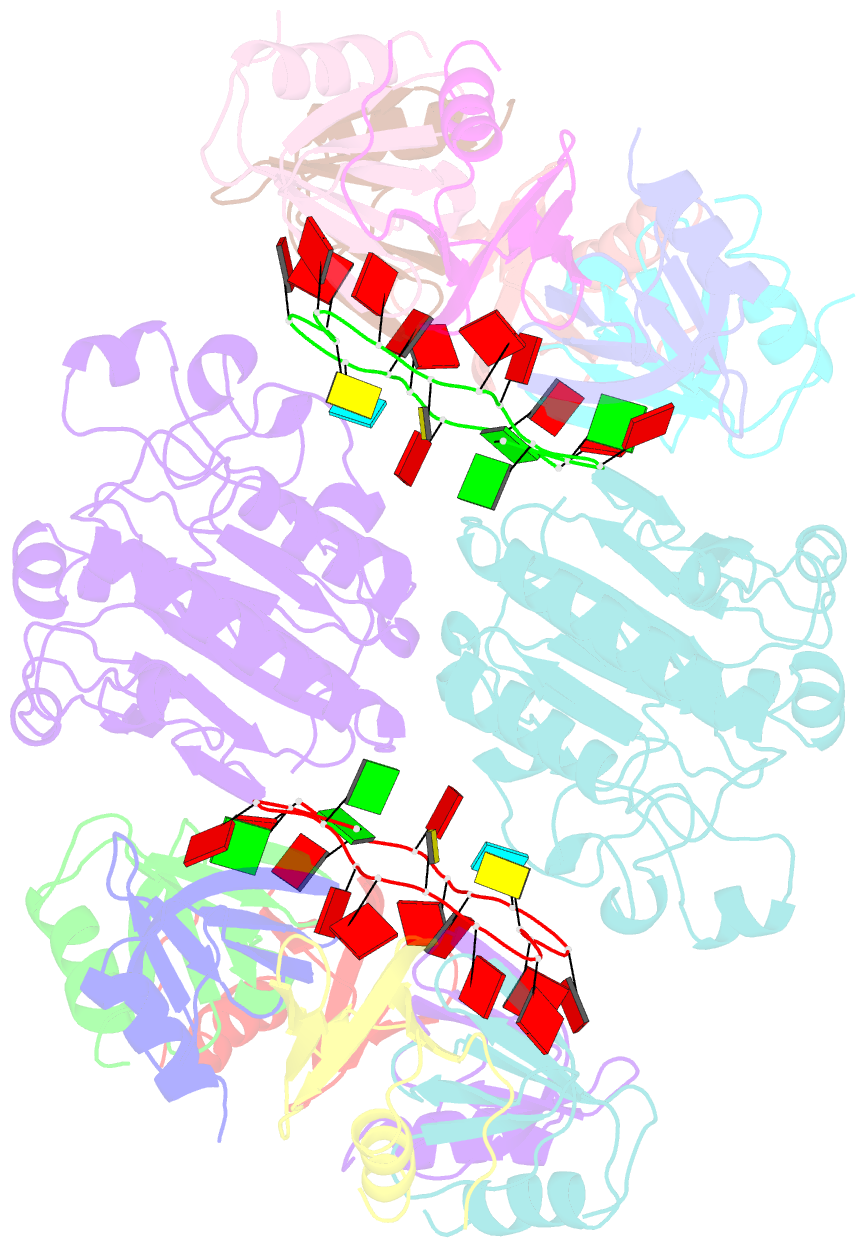
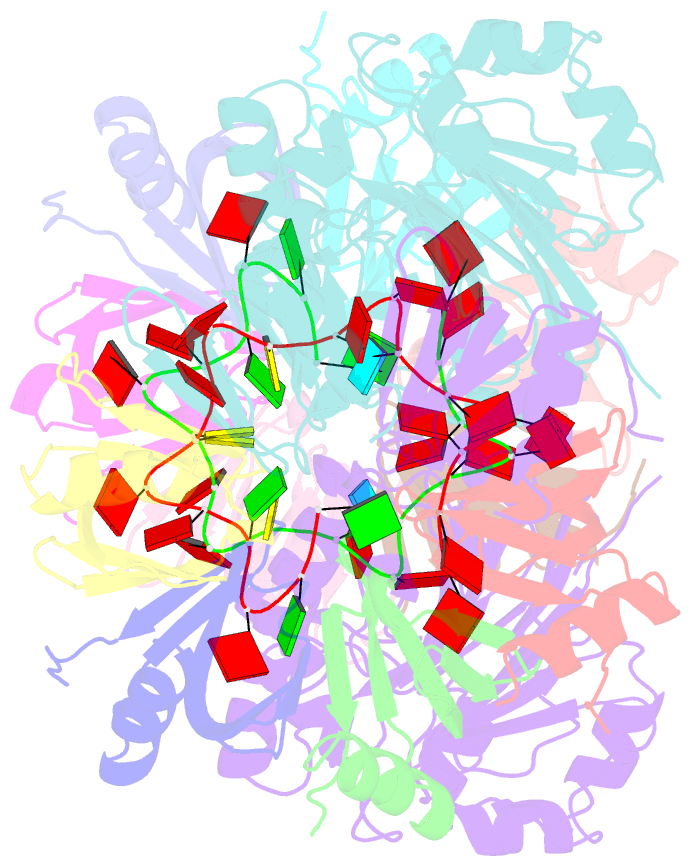
- Architectural principles for hfq-crc-mediated regulation of gene expression. hfq-crc-amie 2:2:2 complex (core complex)
- Reference
- Pei XY, Dendooven T, Sonnleitner E, Chen S, Blasi U, Luisi BF (2019): "Architectural principles for Hfq/Crc-mediated regulation of gene expression." Elife, 8. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43158.
- Abstract
- In diverse bacterial species, the global regulator Hfq contributes to post-transcriptional networks that control expression of numerous genes. Hfq of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits translation of target transcripts by forming a regulatory complex with the catabolite repression protein Crc. This repressive complex acts as part of an intricate mechanism of preferred nutrient utilisation. We describe high-resolution cryo-EM structures of the assembly of Hfq and Crc bound to the translation initiation site of a target mRNA. The core of the assembly is formed through interactions of two cognate RNAs, two Hfq hexamers and a Crc pair. Additional Crc protomers are recruited to the core to generate higher-order assemblies with demonstrated regulatory activity in vivo. This study reveals how Hfq cooperates with a partner protein to regulate translation, and provides a structural basis for an RNA code that guides global regulators to interact cooperatively and regulate different RNA targets.