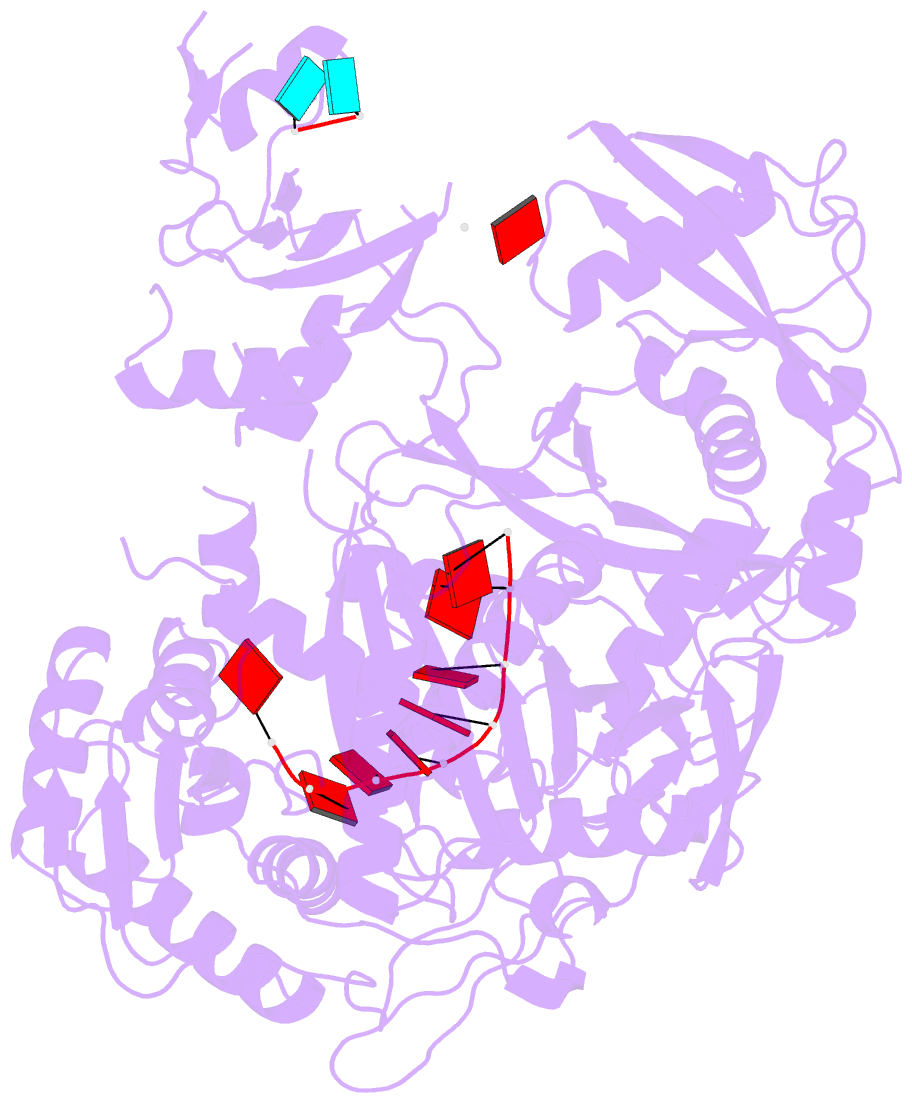
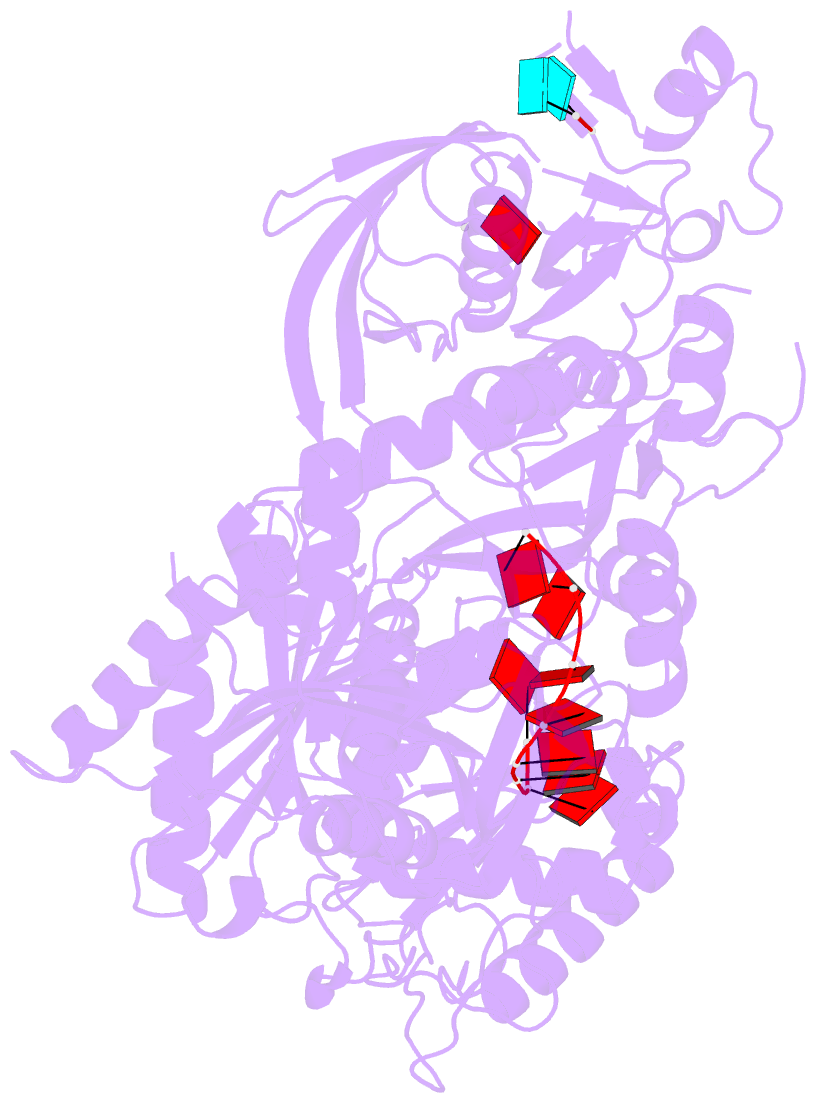
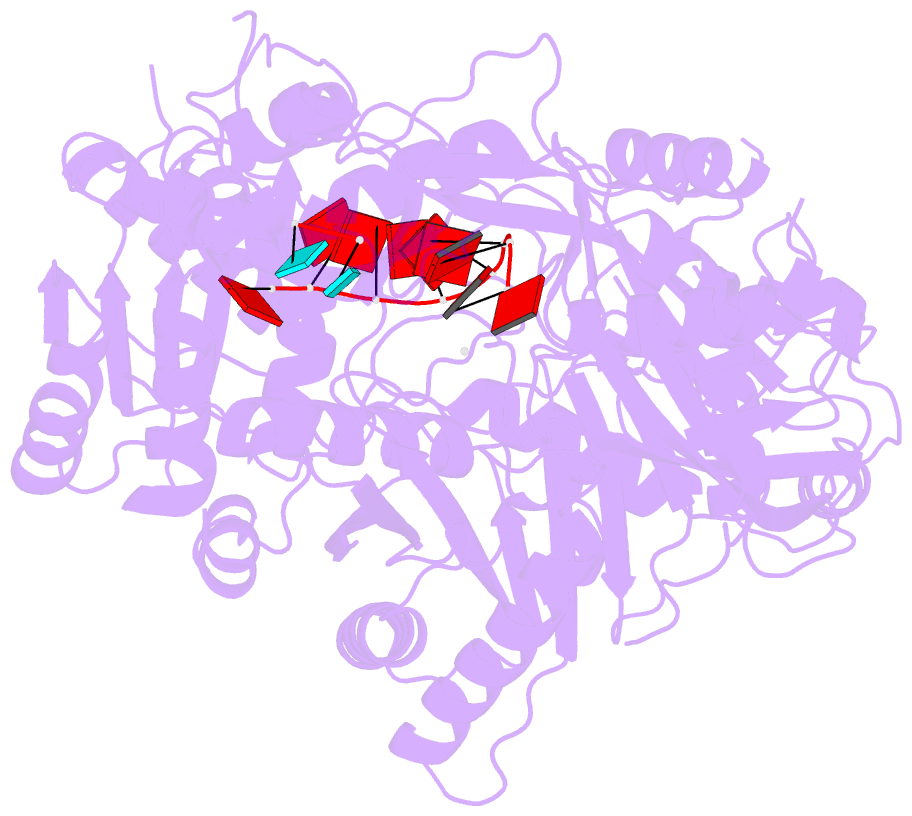
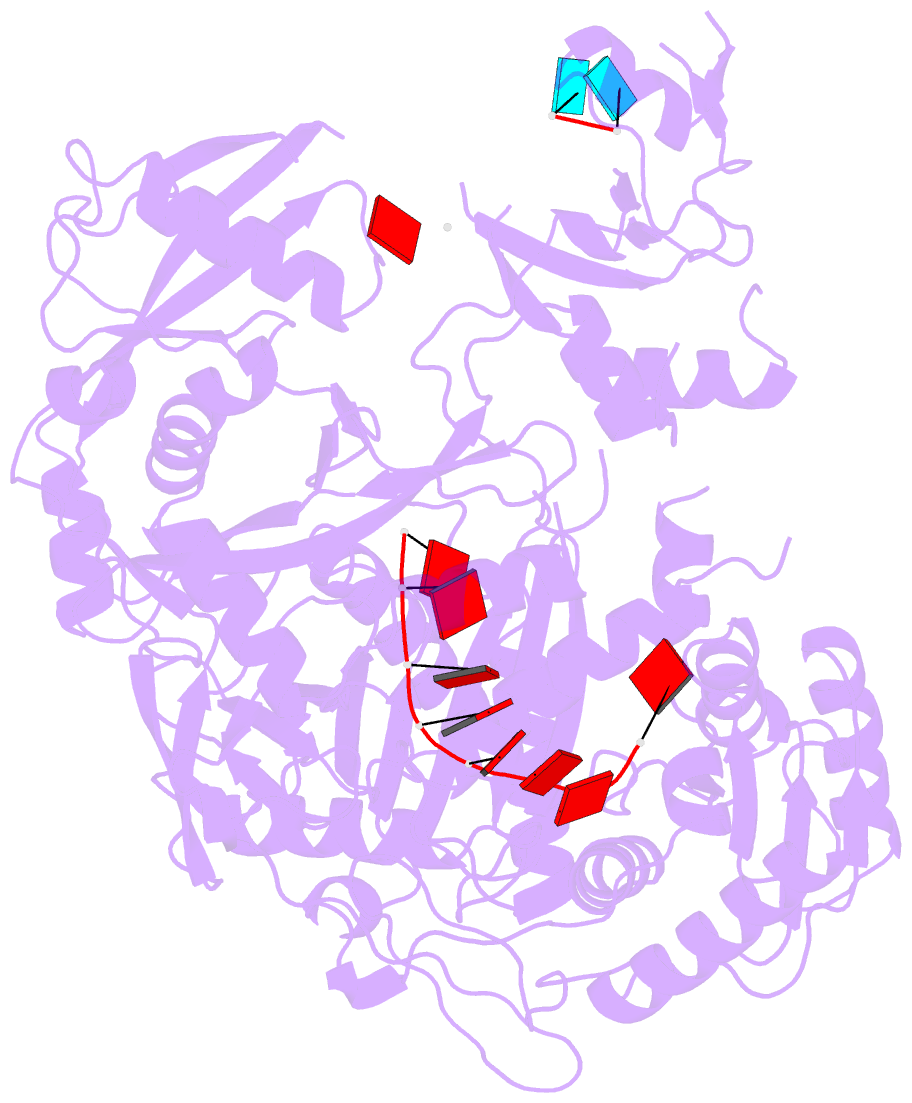
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6oon; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.9 Å)
- Summary
- Human argonaute4 bound to guide RNA
- Reference
- Park MS, Araya-Secchi R, Brackbill JA, Phan HD, Kehling AC, Abd El-Wahab EW, Dayeh DM, Sotomayor M, Nakanishi K (2019): "Multidomain Convergence of Argonaute during RISC Assembly Correlates with the Formation of Internal Water Clusters." Mol.Cell, 75, 725-740.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.011.
- Abstract
- Despite the relevance of Argonaute proteins in RNA silencing, little is known about the structural steps of small RNA loading to form RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs). We report the 1.9 Å crystal structure of human Argonaute4 with guide RNA. Comparison with the previously determined apo structure of Neurospora crassa QDE2 revealed that the PIWI domain has two subdomains. Binding of guide RNA fastens the subdomains, thereby rearranging the active-site residues and increasing the affinity for TNRC6 proteins. We also identified two water pockets beneath the nucleic acid-binding channel that appeared to stabilize the mature RISC. Indeed, mutating the water-pocket residues of Argonaute2 and Argonaute4 compromised RISC assembly. Simulations predict that internal water molecules are exchangeable with the bulk solvent but always occupy specific positions at the domain interfaces. These results suggest that after guide RNA-driven conformational changes, water-mediated hydrogen-bonding networks tie together the converged domains to complete the functional RISC structure.