Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6p1a; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation
- Method
- X-ray (2.837 Å)
- Summary
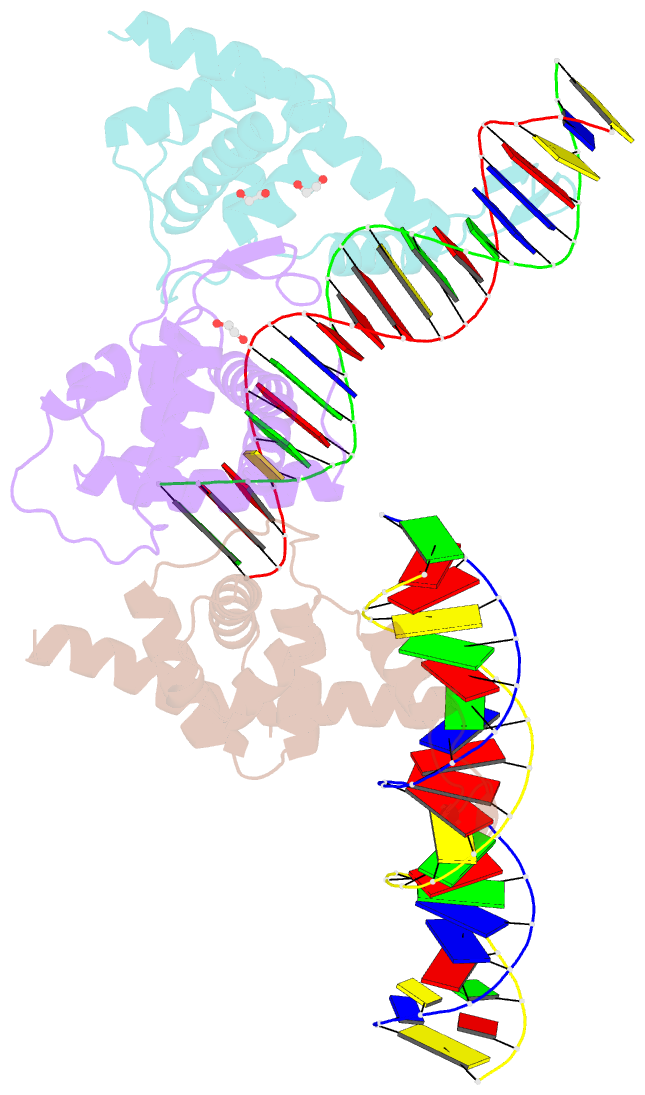
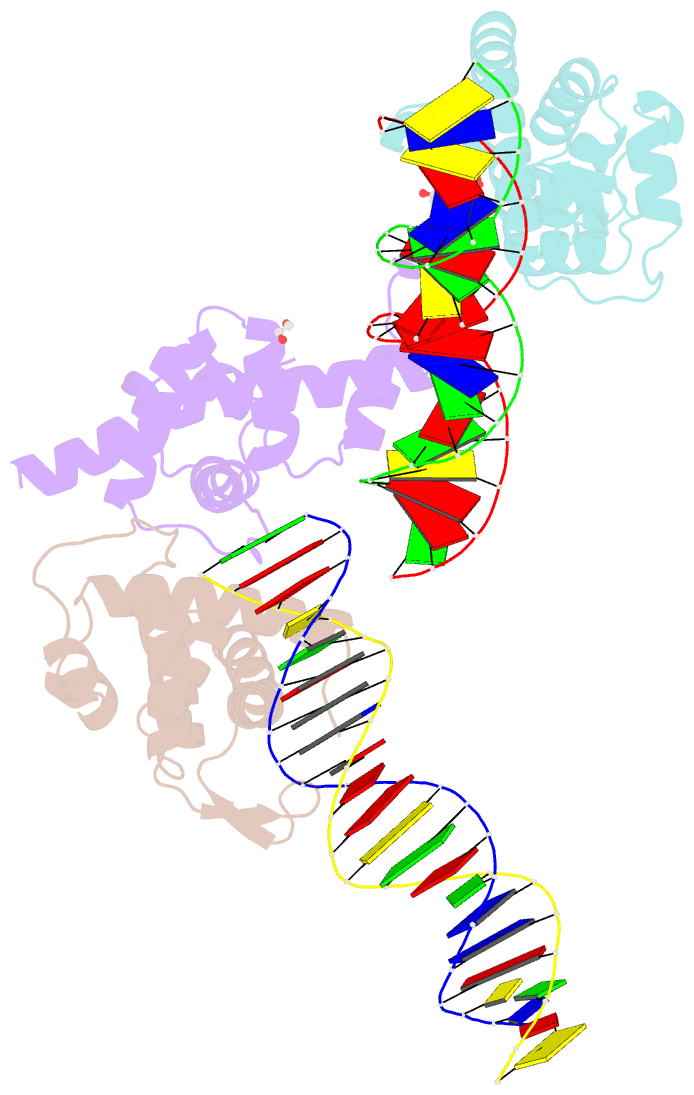
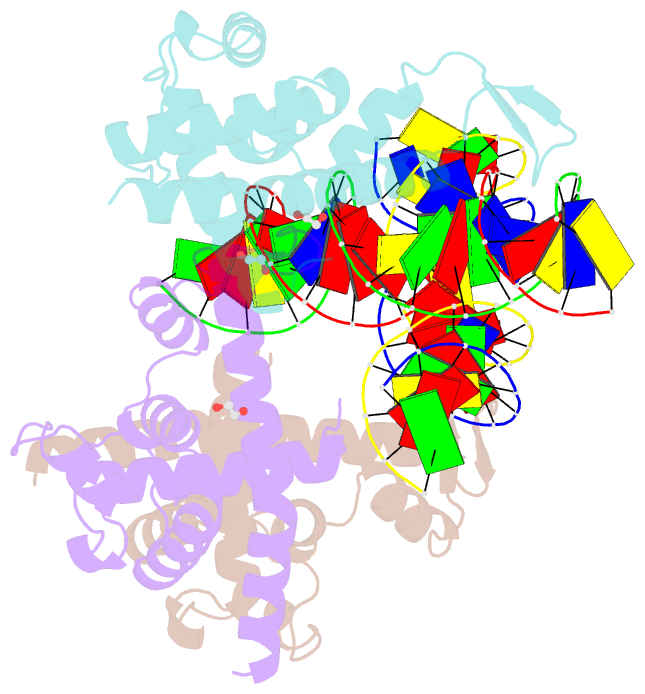
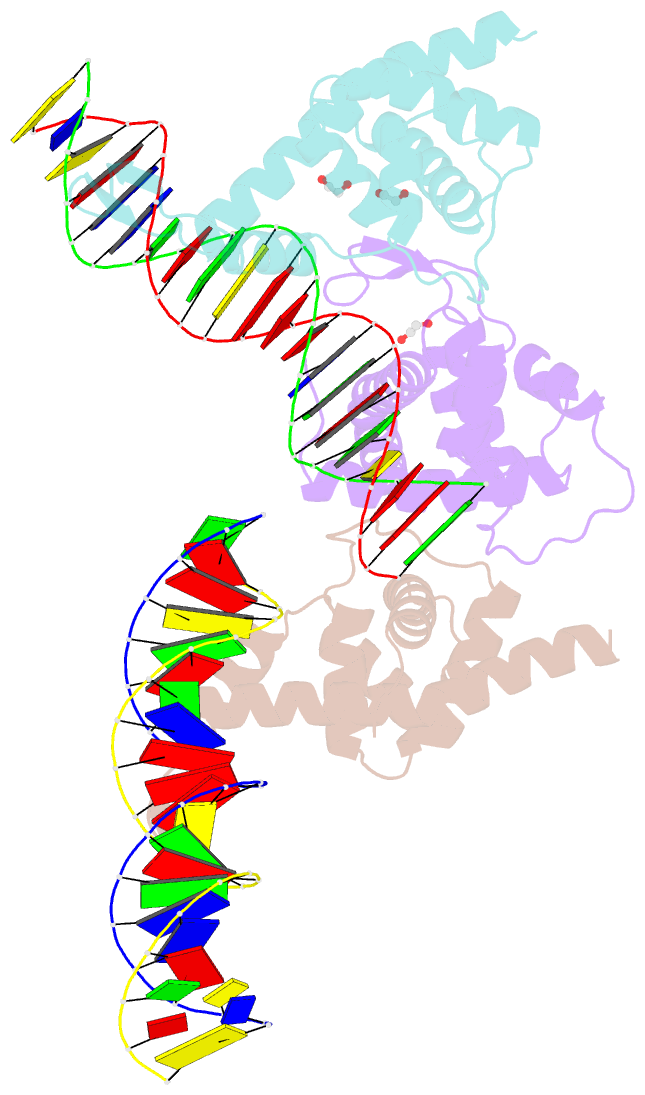
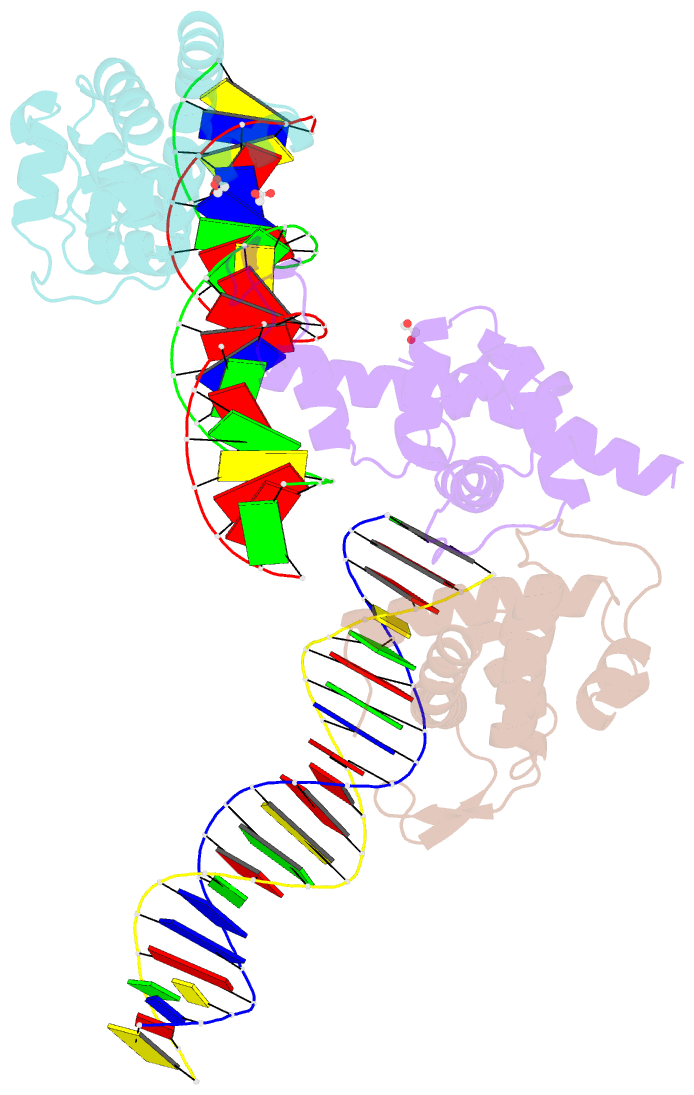
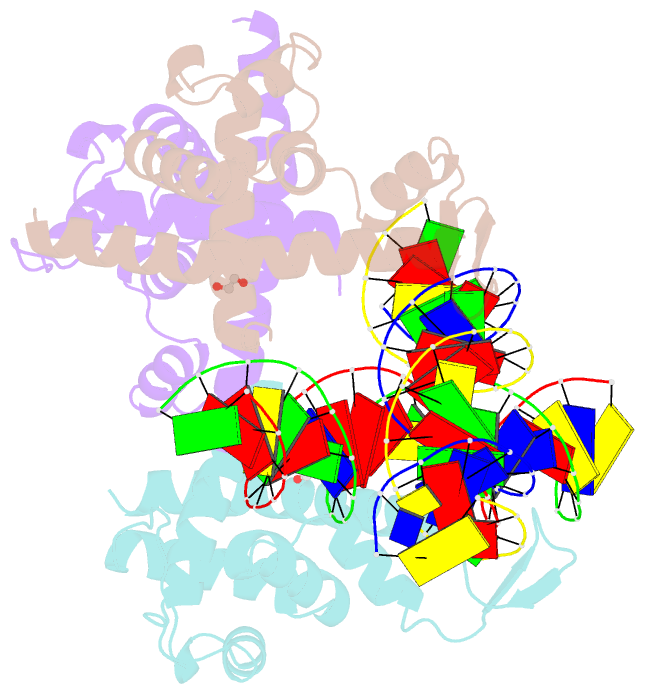
- Transcription antitermination factor q21 in complex with q21-binding-element DNA
- Reference
- Yin Z, Kaelber JT, Ebright RH (2019): "Structural basis of Q-dependent antitermination." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 116, 18384-18390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909801116.
- Abstract
- Lambdoid bacteriophage Q protein mediates the switch from middle to late bacteriophage gene expression by enabling RNA polymerase (RNAP) to read through transcription terminators preceding bacteriophage late genes. Q loads onto RNAP engaged in promoter-proximal pausing at a Q binding element (QBE) and adjacent sigma-dependent pause element (SDPE) to yield a Q-loading complex, and Q subsequently translocates with RNAP as a pausing-deficient, termination-deficient Q-loaded complex. Here, we report high-resolution structures of 4 states on the pathway of antitermination by Q from bacteriophage 21 (Q21): Q21, the Q21-QBE complex, the Q21-loading complex, and the Q21-loaded complex. The results show that Q21 forms a torus, a "nozzle," that narrows and extends the RNAP RNA-exit channel, extruding topologically linked single-stranded RNA and preventing the formation of pause and terminator hairpins.