Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6pbd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.343 Å)
- Summary
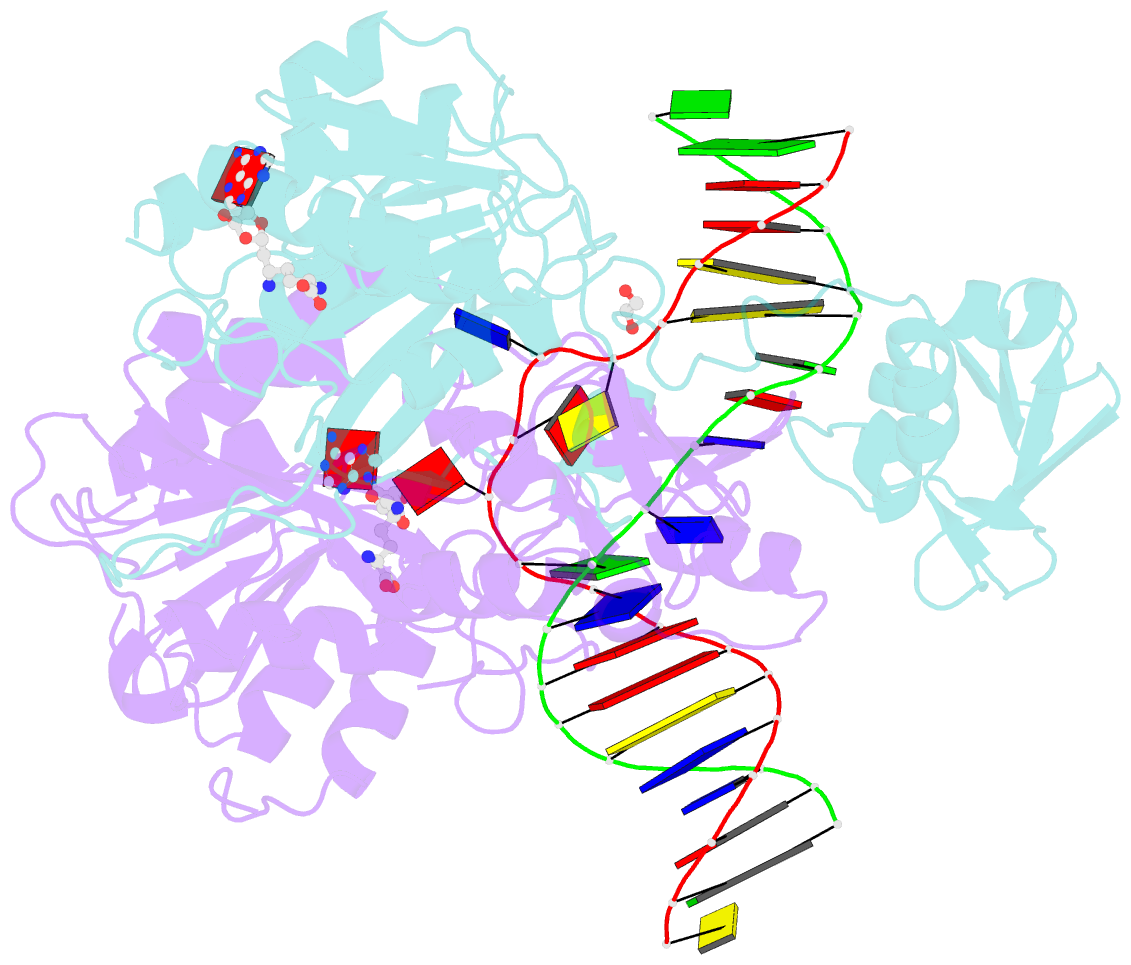
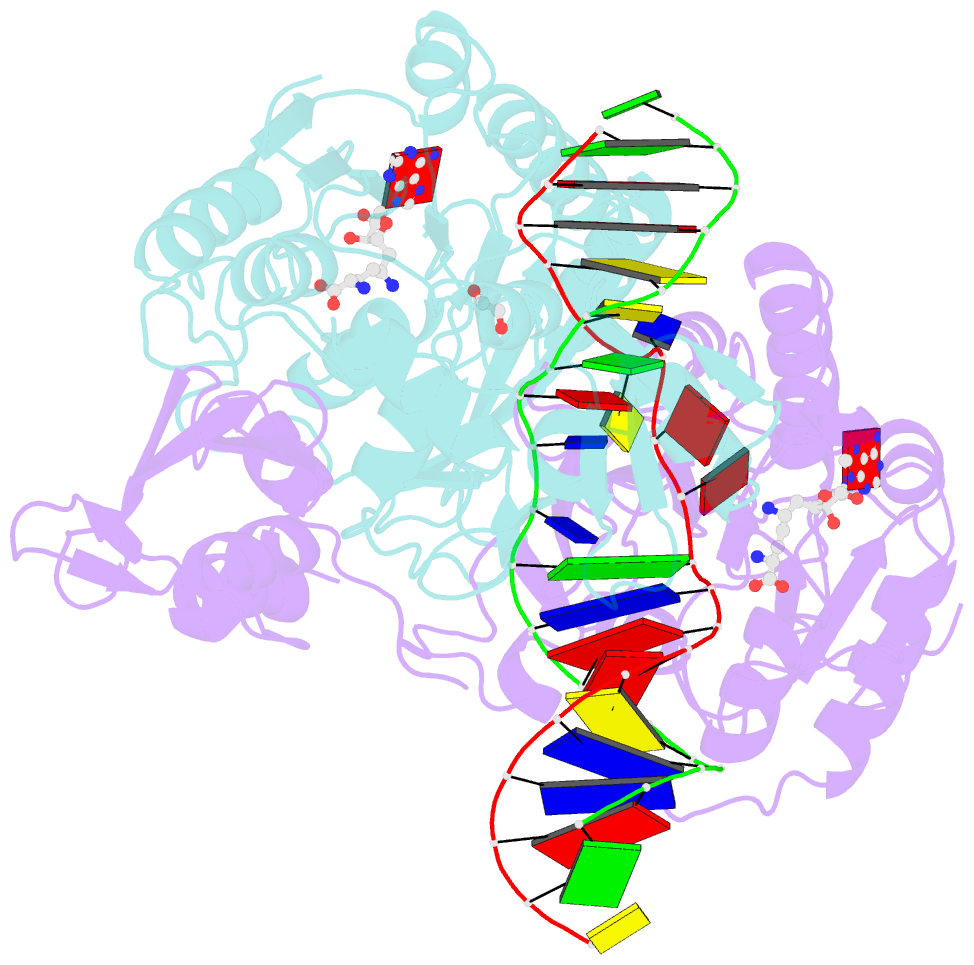
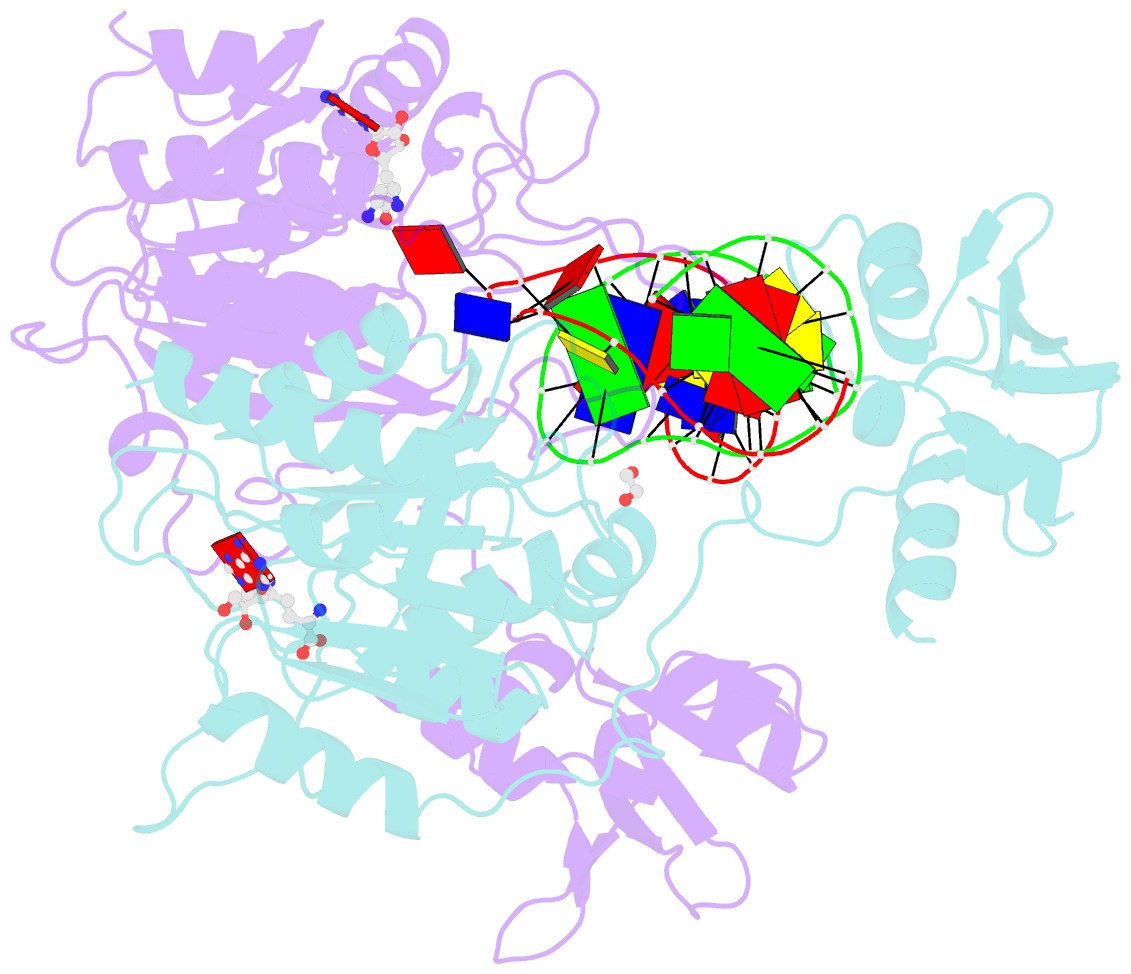
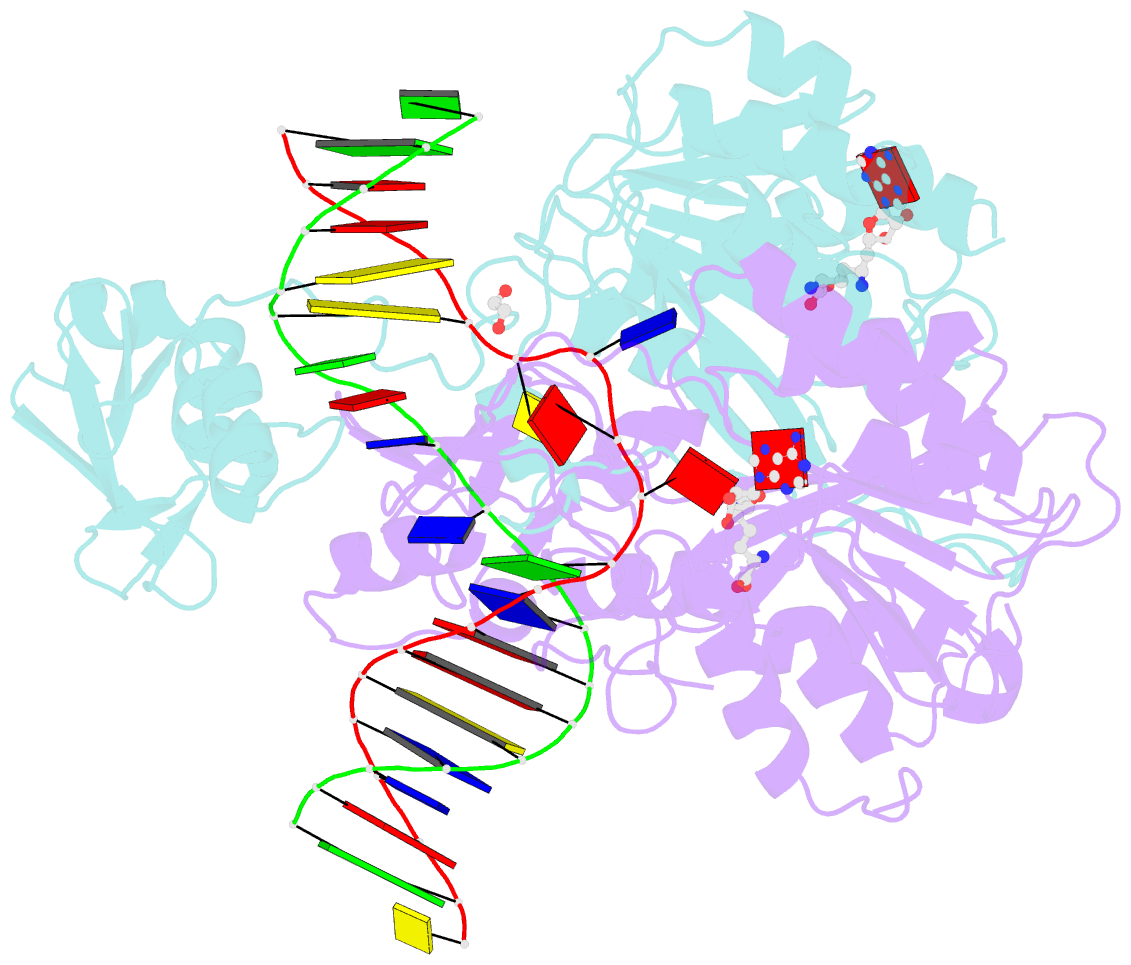
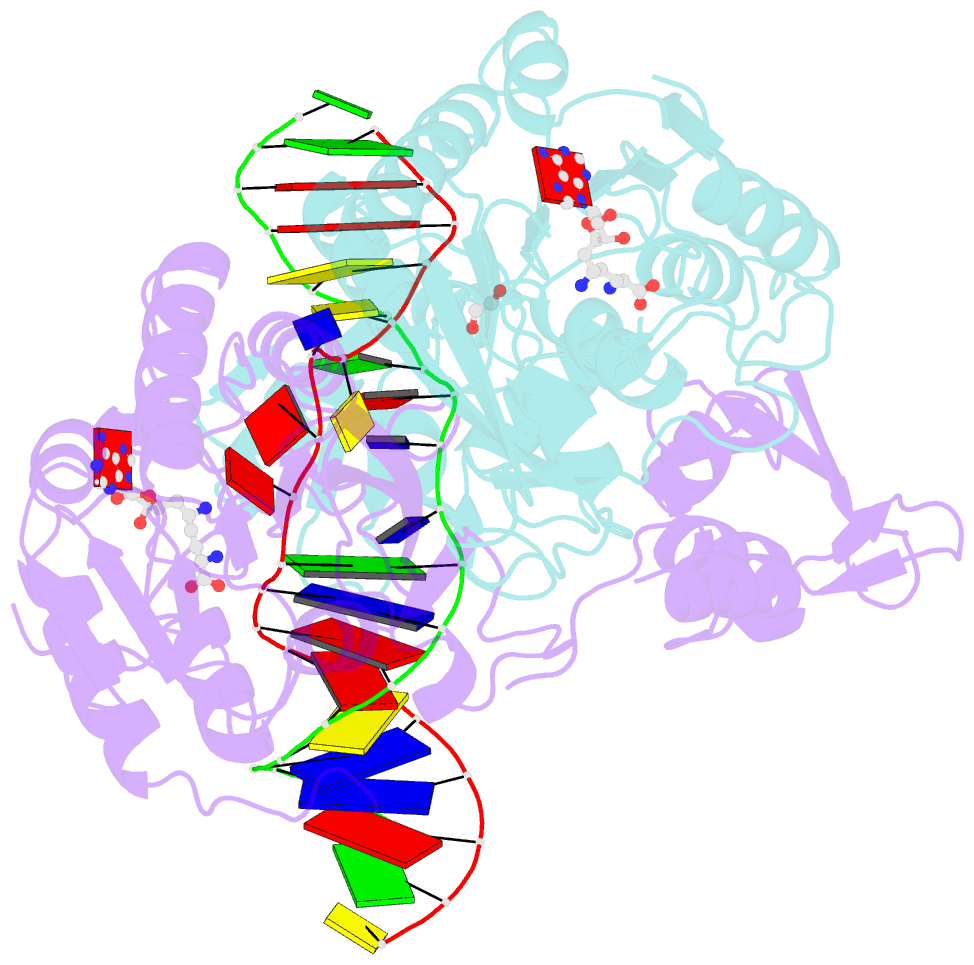
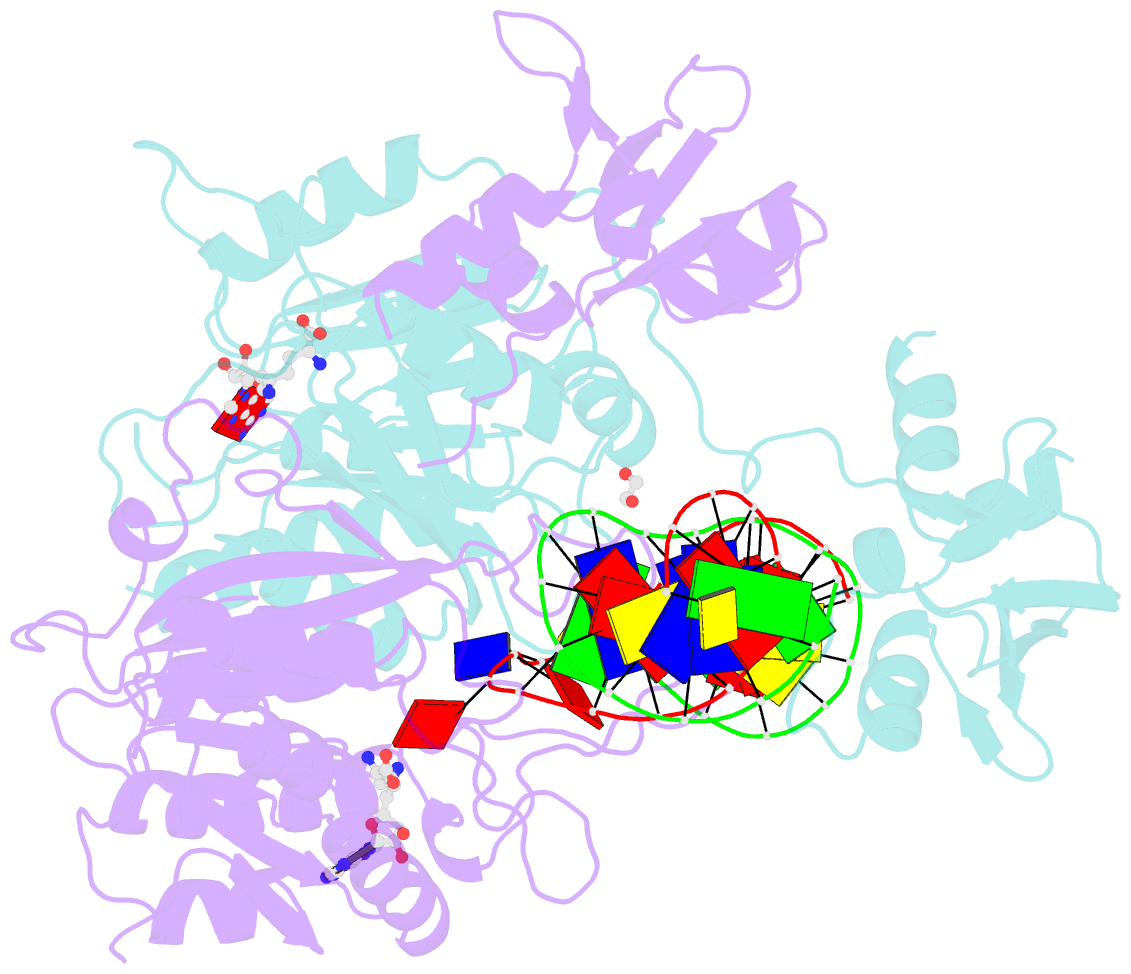
- DNA n6-adenine methyltransferase ccrm in complex with double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide containing its recognition sequence gaatc
- Reference
- Horton JR, Woodcock CB, Opot SB, Reich NO, Zhang X, Cheng X (2019): "The cell cycle-regulated DNA adenine methyltransferase CcrM opens a bubble at its DNA recognition site." Nat Commun, 10, 4600. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12498-7.
- Abstract
- The Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle-regulated DNA methyltransferase (CcrM) methylates the adenine of hemimethylated GANTC after replication. Here we present the structure of CcrM in complex with double-stranded DNA containing the recognition sequence. CcrM contains an N-terminal methyltransferase domain and a C-terminal nonspecific DNA-binding domain. CcrM is a dimer, with each monomer contacting primarily one DNA strand: the methyltransferase domain of one molecule binds the target strand, recognizes the target sequence, and catalyzes methyl transfer, while the C-terminal domain of the second molecule binds the non-target strand. The DNA contacts at the 5-base pair recognition site results in dramatic DNA distortions including bending, unwinding and base flipping. The two DNA strands are pulled apart, creating a bubble comprising four recognized base pairs. The five bases of the target strand are recognized meticulously by stacking contacts, van der Waals interactions and specific Watson-Crick polar hydrogen bonds to ensure high enzymatic specificity.