Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6pzq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- metal binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.703 Å)
- Summary
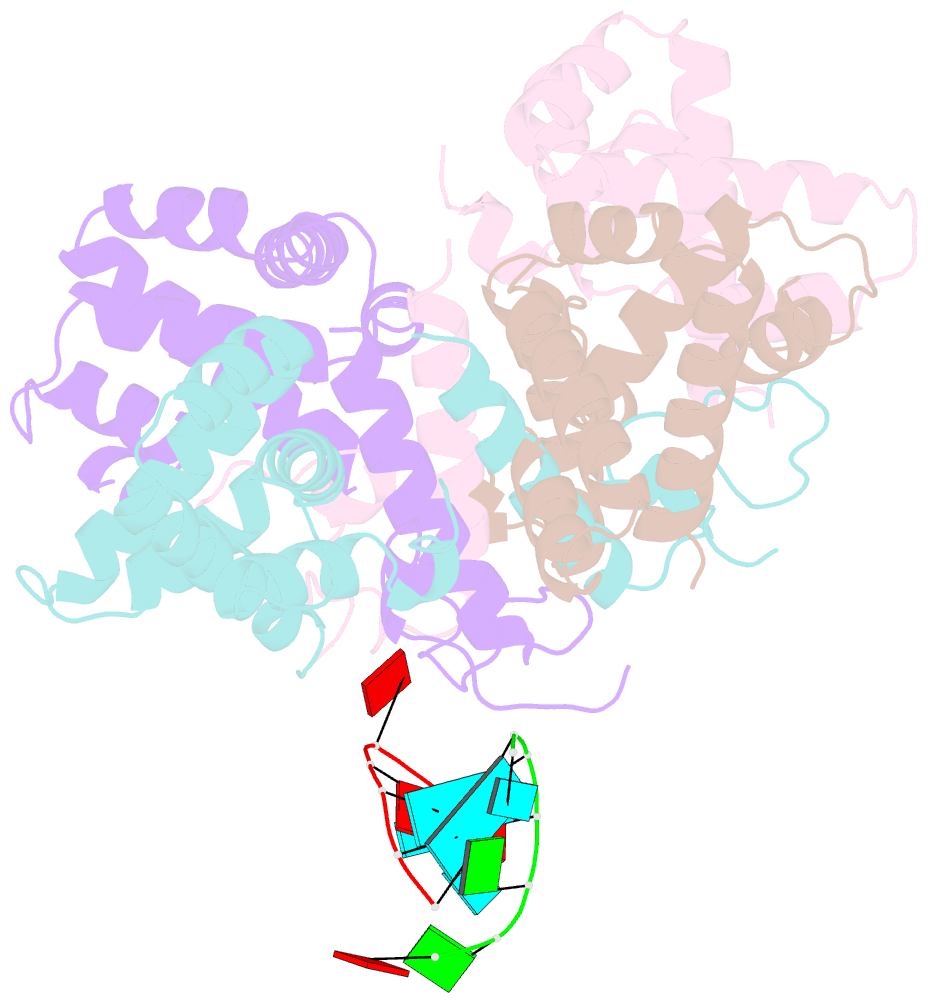
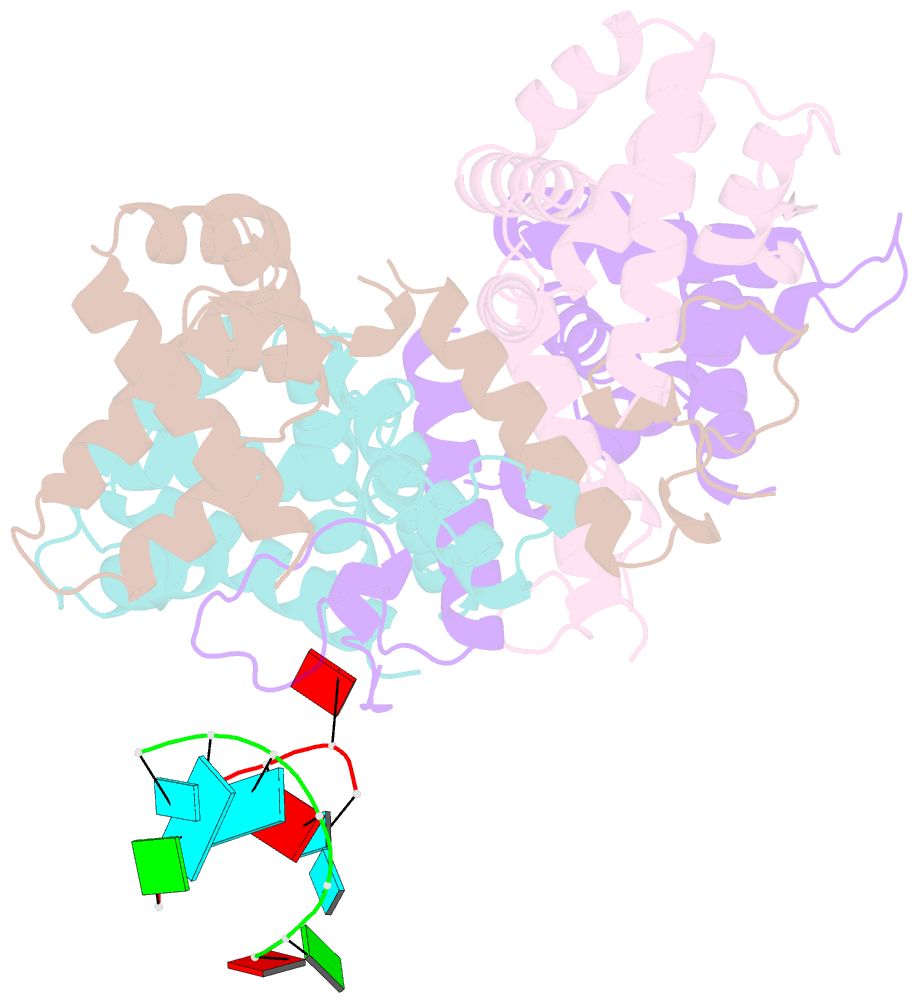
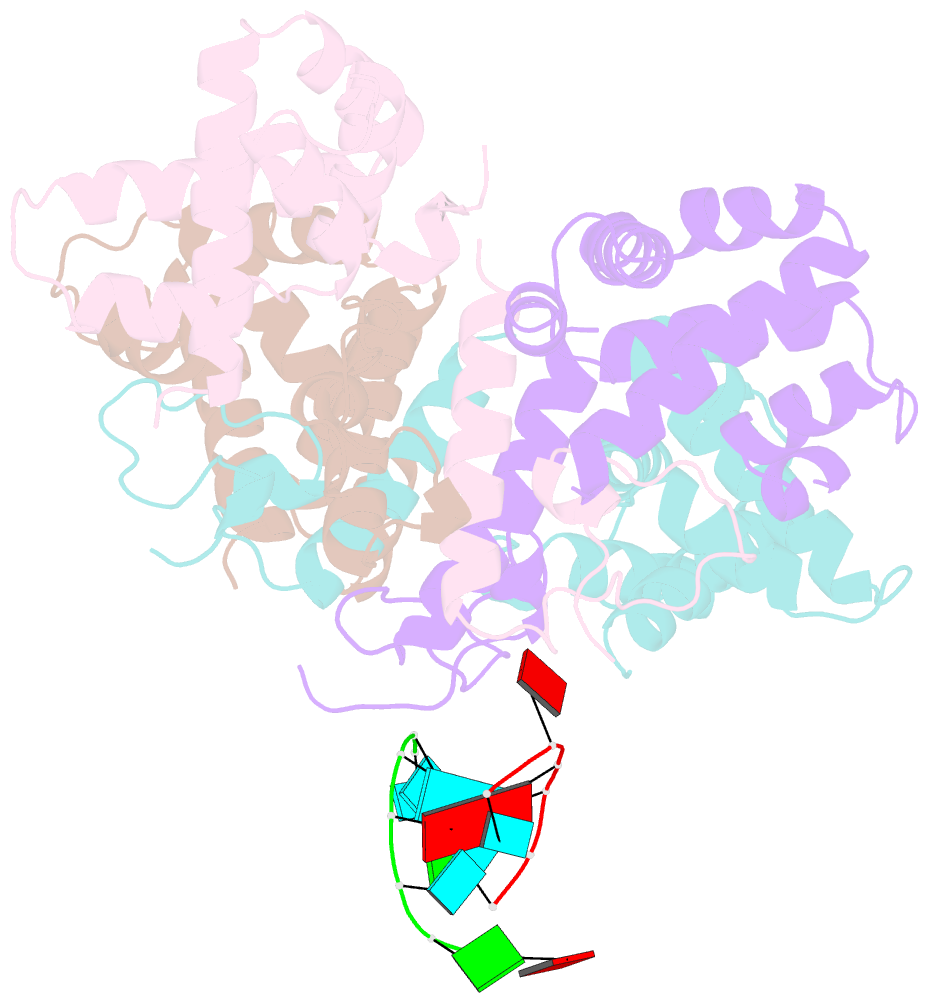
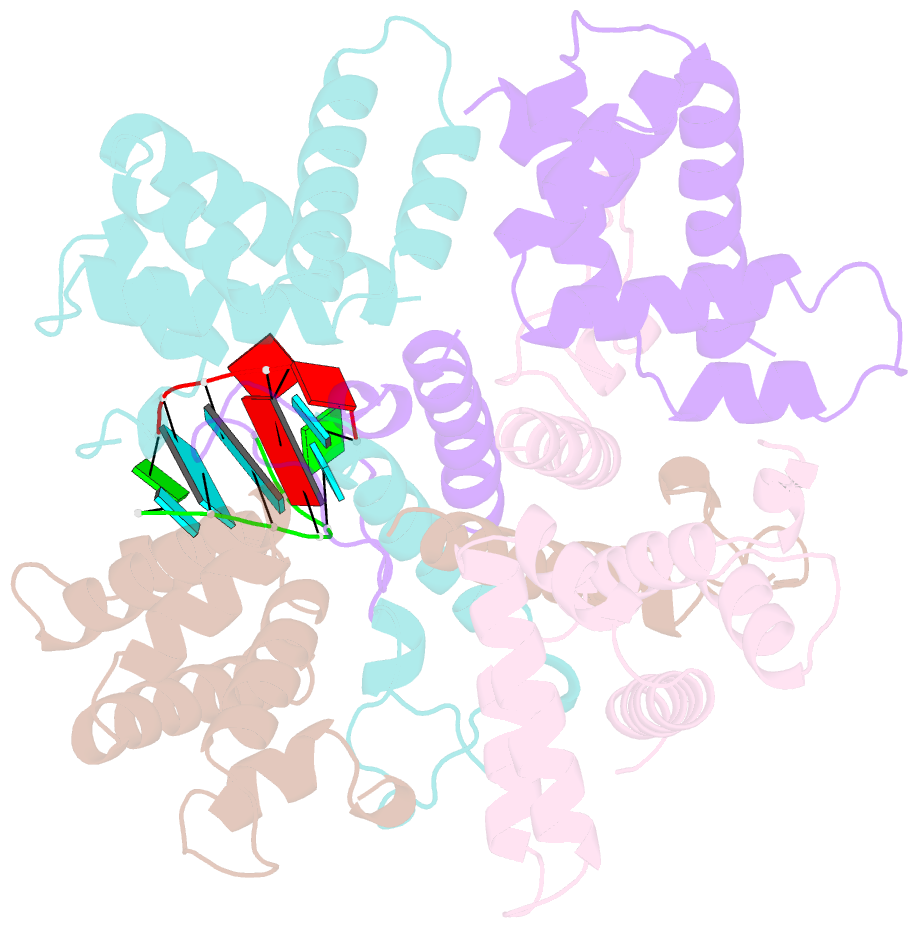
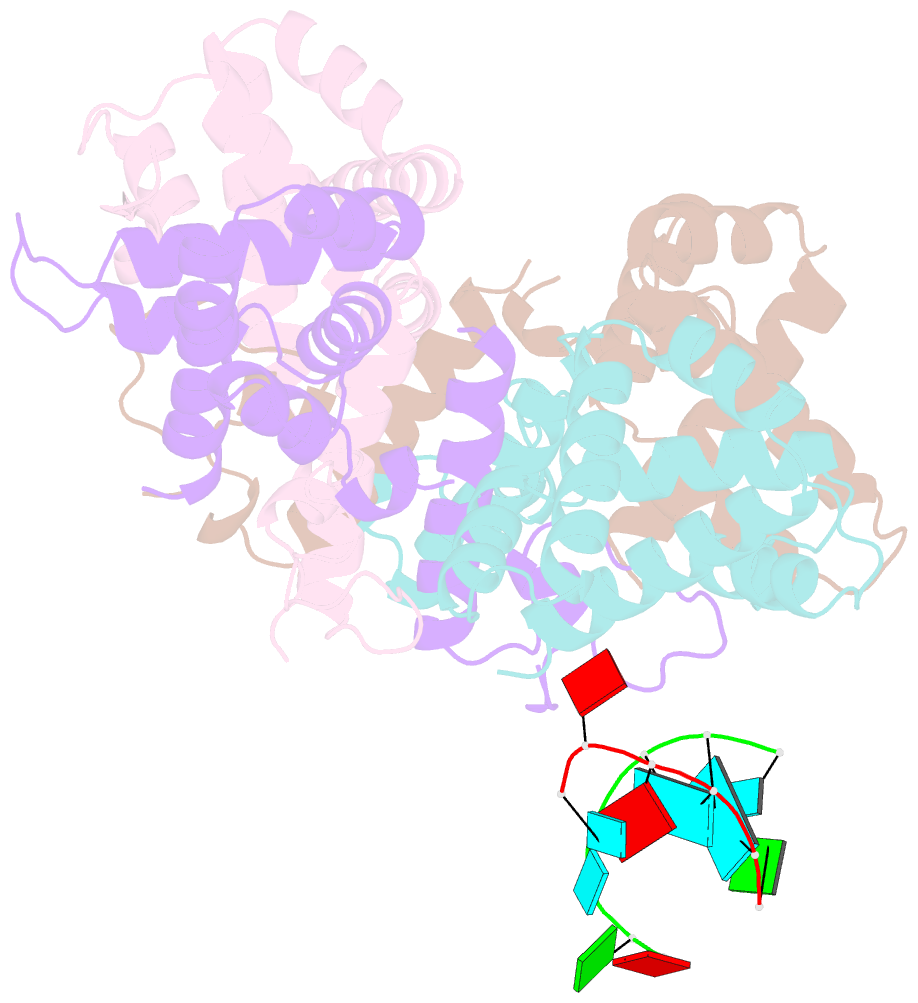
- Structure of the human respiratory syncytial virus m2-1 protein in complex with a short positive-sense gene-end RNA
- Reference
- Gao Y, Cao D, Pawnikar S, John KP, Ahn HM, Hill S, Ha JM, Parikh P, Ogilvie C, Swain A, Yang A, Bell A, Salazar A, Miao Y, Liang B (2020): "Structure of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus M2-1 Protein in Complex with a Short Positive-Sense Gene-End RNA." Structure, 28, 979. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2020.07.001.
- Abstract
- The M2-1 protein of human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a transcription anti-terminator that regulates the processivity of the HRSV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP). Here, we report a crystal structure of HRSV M2-1 bound to a short positive-sense gene-end RNA (SH7) at 2.7 Å resolution. We identified multiple critical residues of M2-1 involved in RNA interaction and examined their roles using mutagenesis and MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) assay. We found that hydrophobic residue Phe23 is indispensable for M2-1 to recognize the base of RNA. We also captured spontaneous binding of RNA (SH7) to M2-1 in all-atom simulations using a robust Gaussian accelerated molecular dynamics (GaMD) method. Both experiments and simulations revealed that the interactions of RNA with two separate domains of M2-1, the zinc-binding domain (ZBD) and the core domain (CD), are independent of each other. Collectively, our results provided a structural basis for RNA recognition by HRSV M2-1.