Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6qy3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (9.1 Å)
- Summary
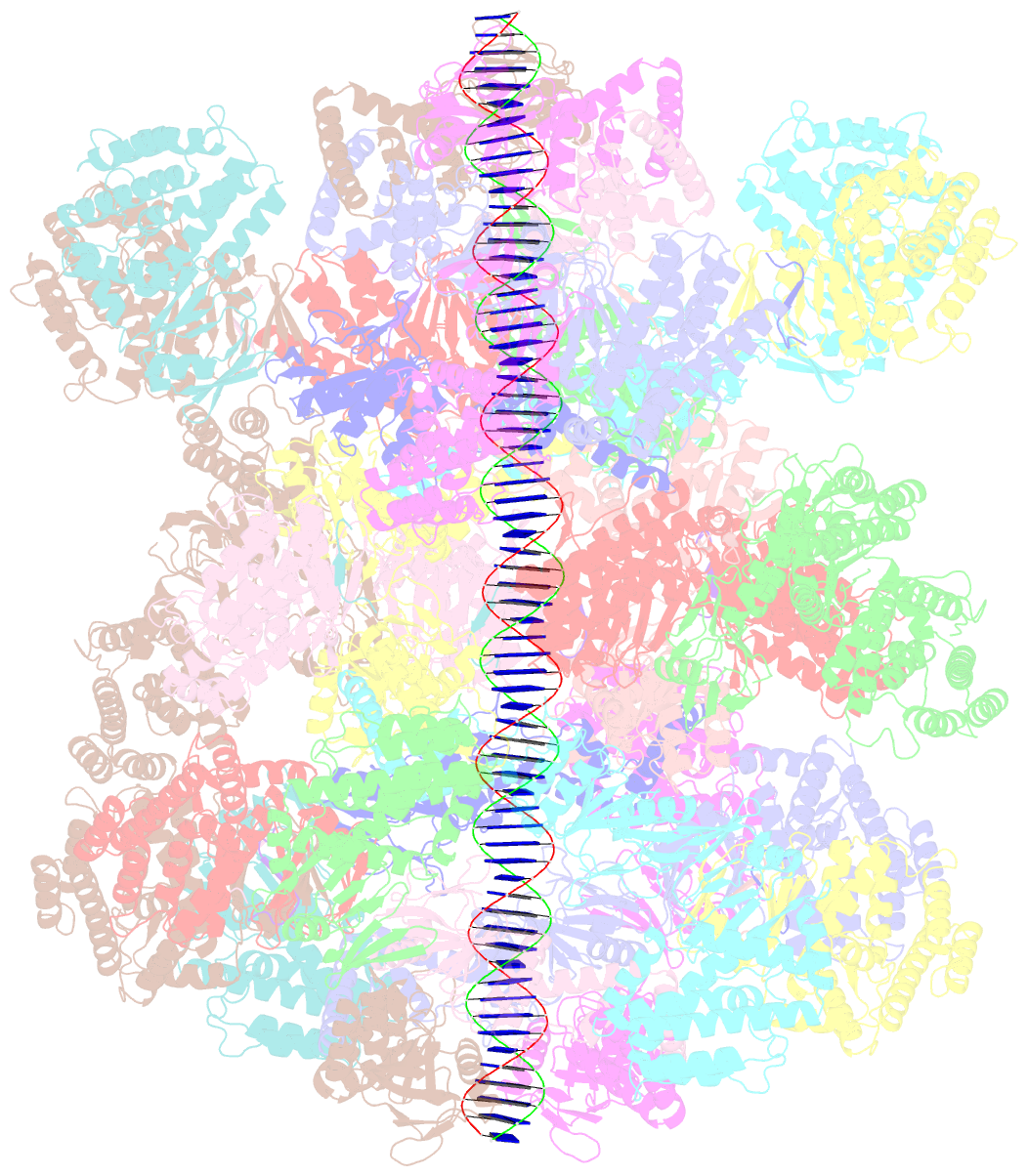
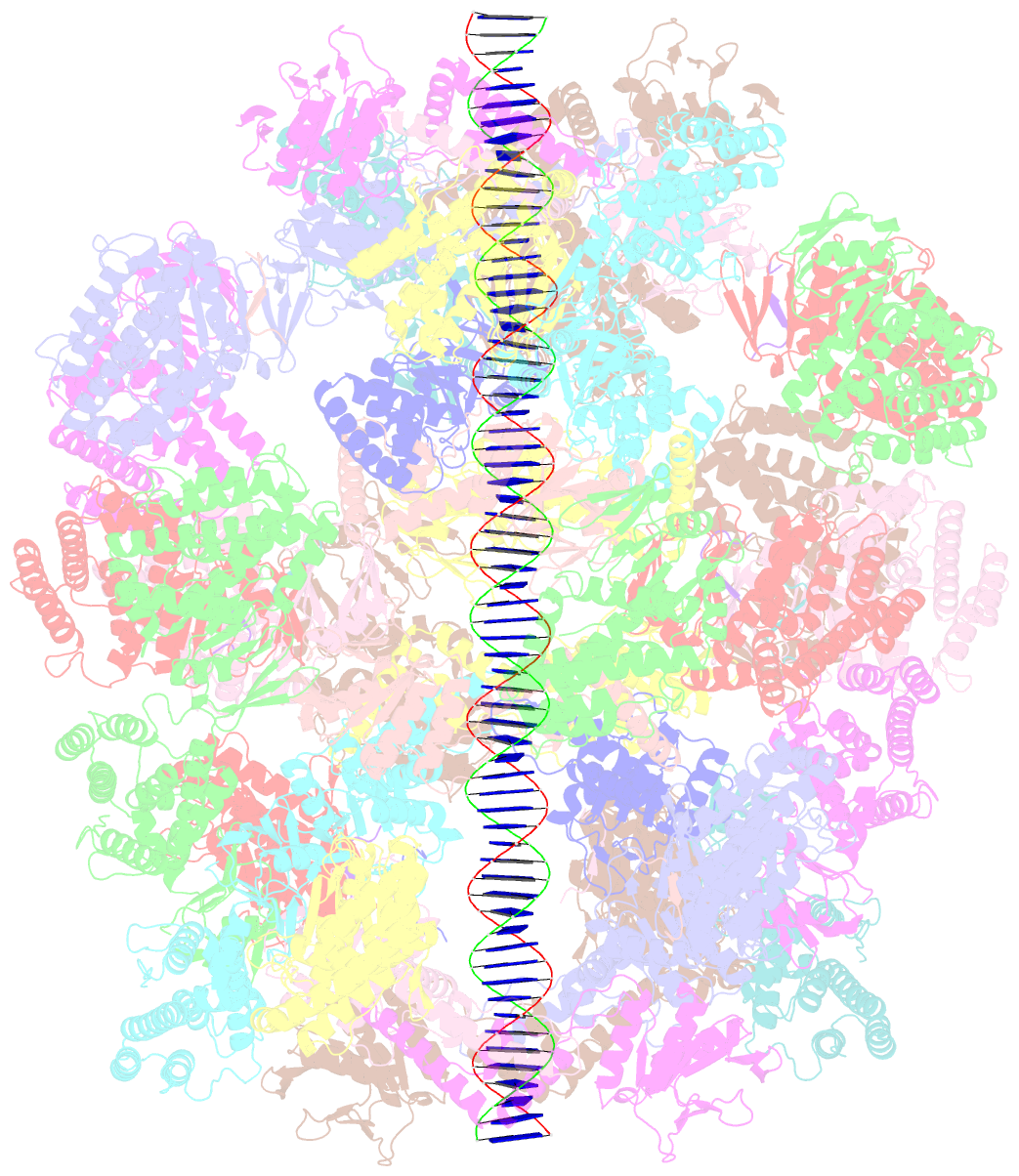
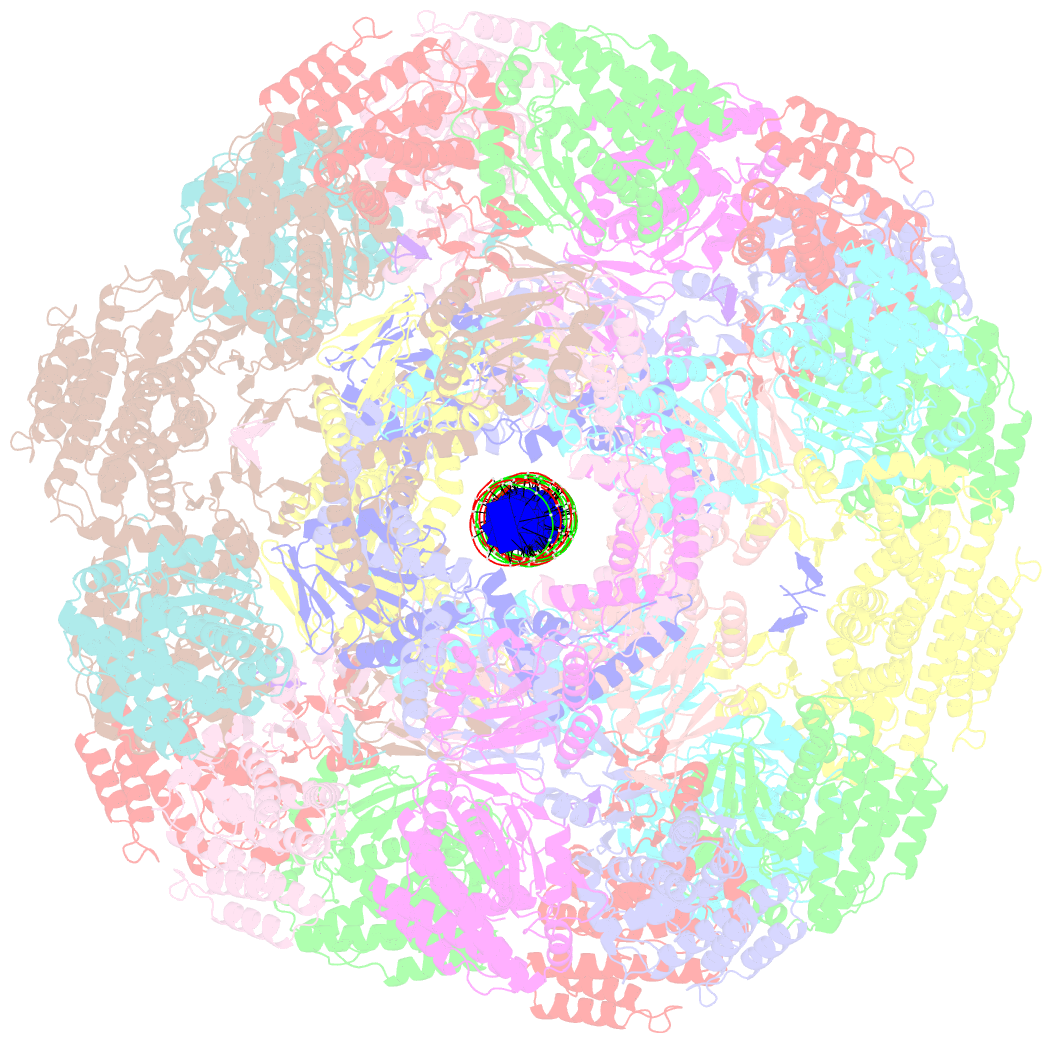
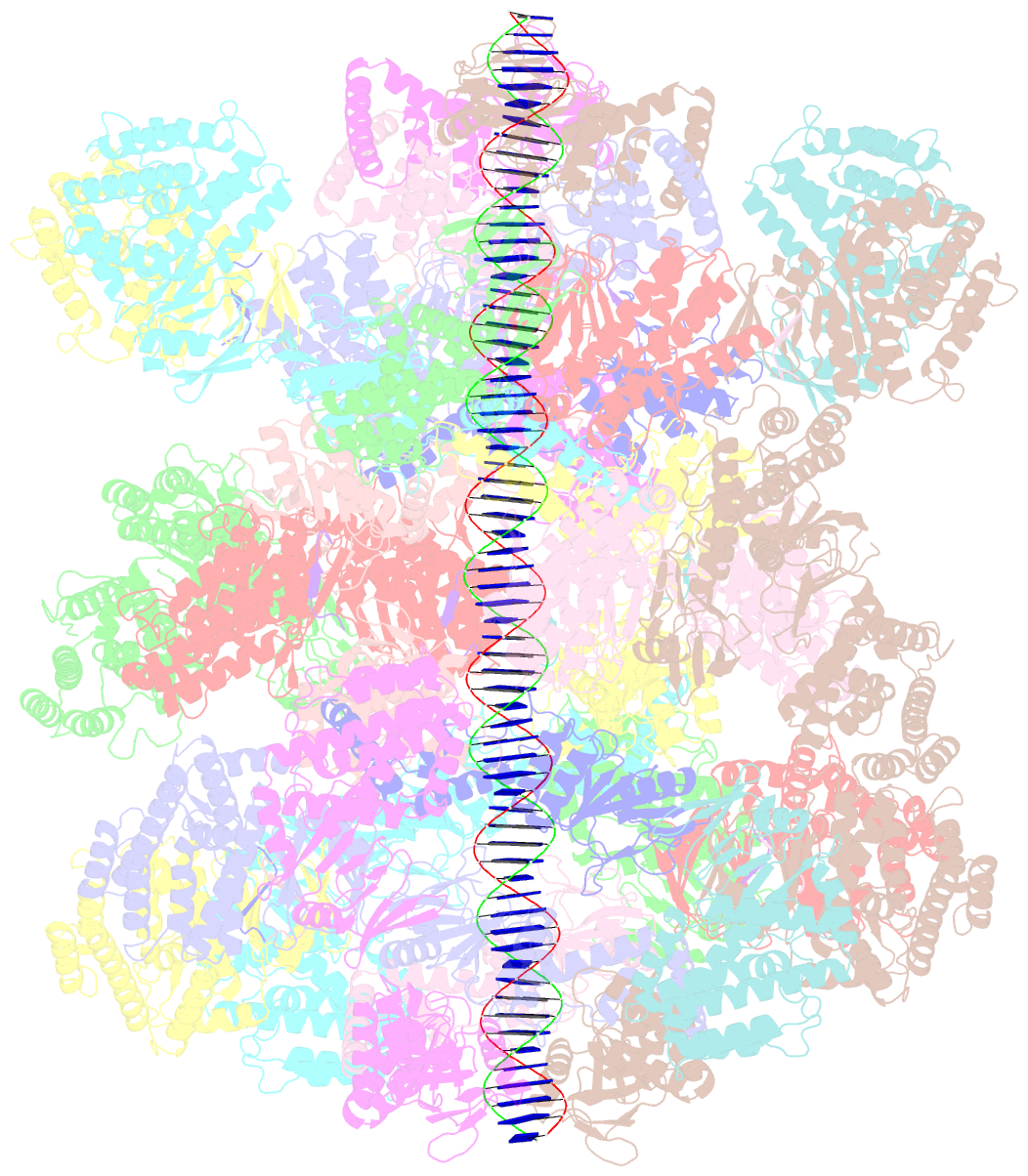
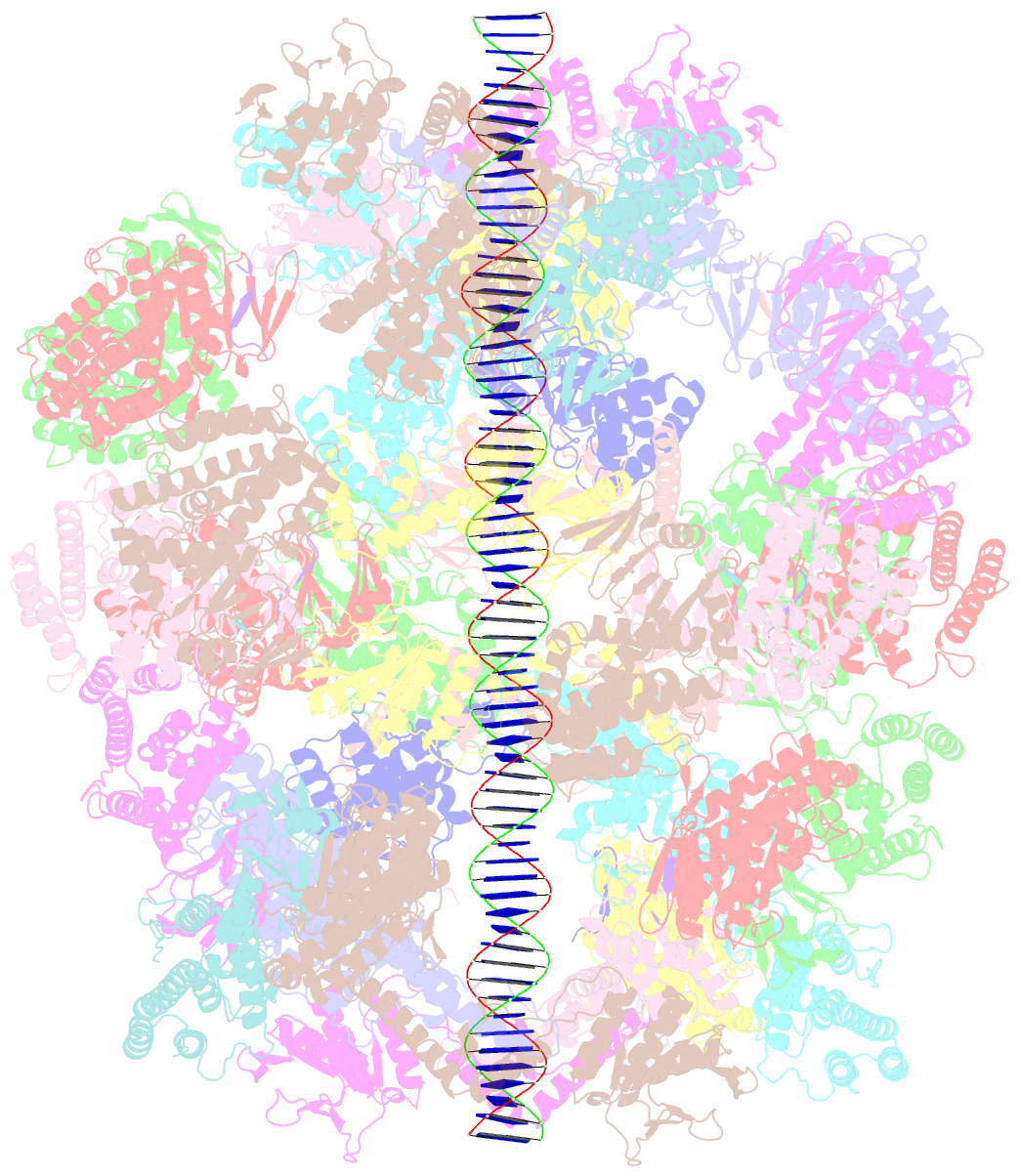
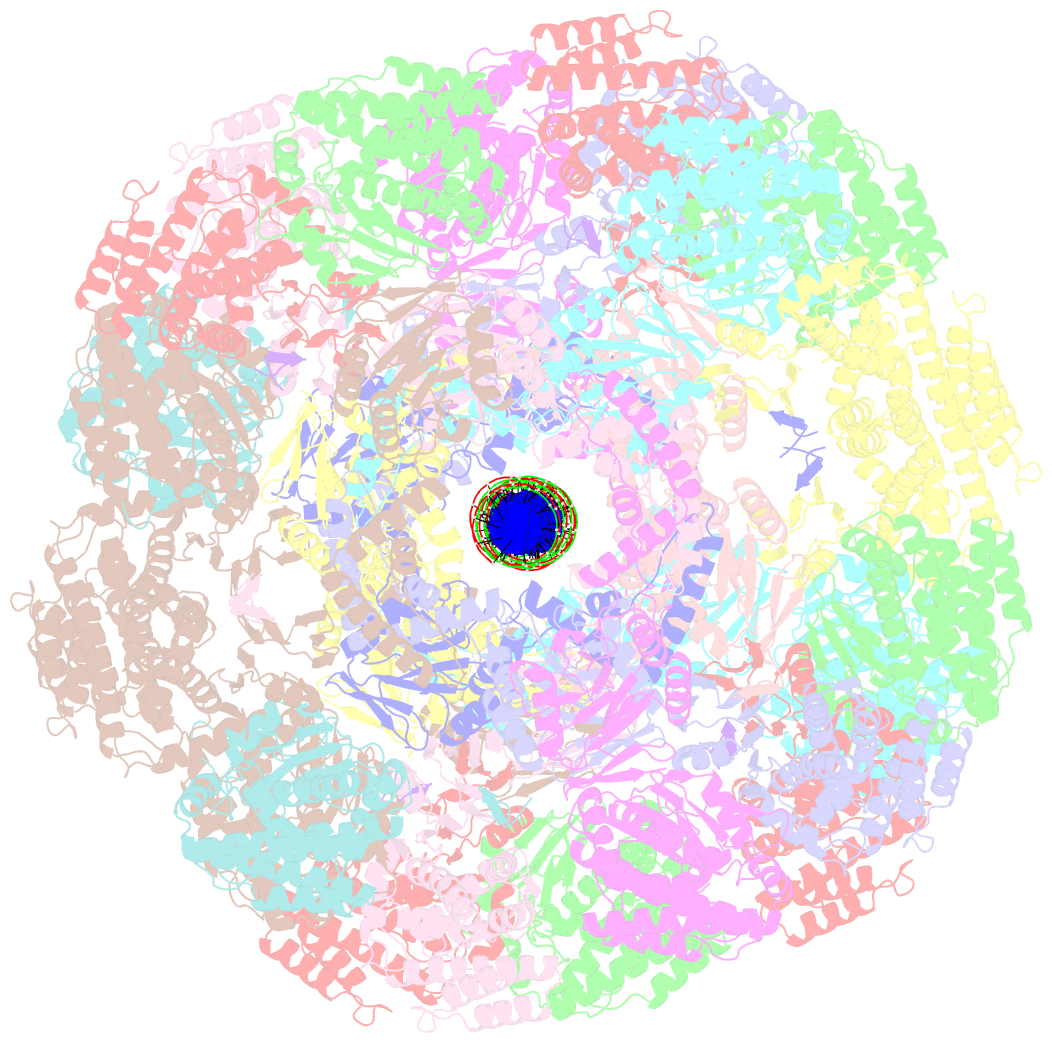
- Segment of the cas1-cas2-csn2-DNA filament complex from the type ii-a crispr-cas system
- Reference
- Wilkinson M, Drabavicius G, Silanskas A, Gasiunas G, Siksnys V, Wigley DB (2019): "Structure of the DNA-Bound Spacer Capture Complex of a Type II CRISPR-Cas System." Mol.Cell, 75, 90-101.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.020.
- Abstract
- CRISPR and associated Cas proteins function as an adaptive immune system in prokaryotes to combat bacteriophage infection. During the immunization step, new spacers are acquired by the CRISPR machinery, but the molecular mechanism of spacer capture remains enigmatic. We show that the Cas9, Cas1, Cas2, and Csn2 proteins of a Streptococcus thermophilus type II-A CRISPR-Cas system form a complex and provide cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of three different assemblies. The predominant form, with the stoichiometry Cas18-Cas24-Csn28, referred to as monomer, contains ∼30 bp duplex DNA bound along a central channel. A minor species, termed a dimer, comprises two monomers that sandwich a further eight Cas1 and four Cas2 subunits and contains two DNA ∼30-bp duplexes within the channel. A filamentous form also comprises Cas18-Cas24-Csn28 units (typically 2-6) but with a different Cas1-Cas2 interface between them and a continuous DNA duplex running along a central channel.