Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6sa1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase
- Method
- X-ray (2.01 Å)
- Summary
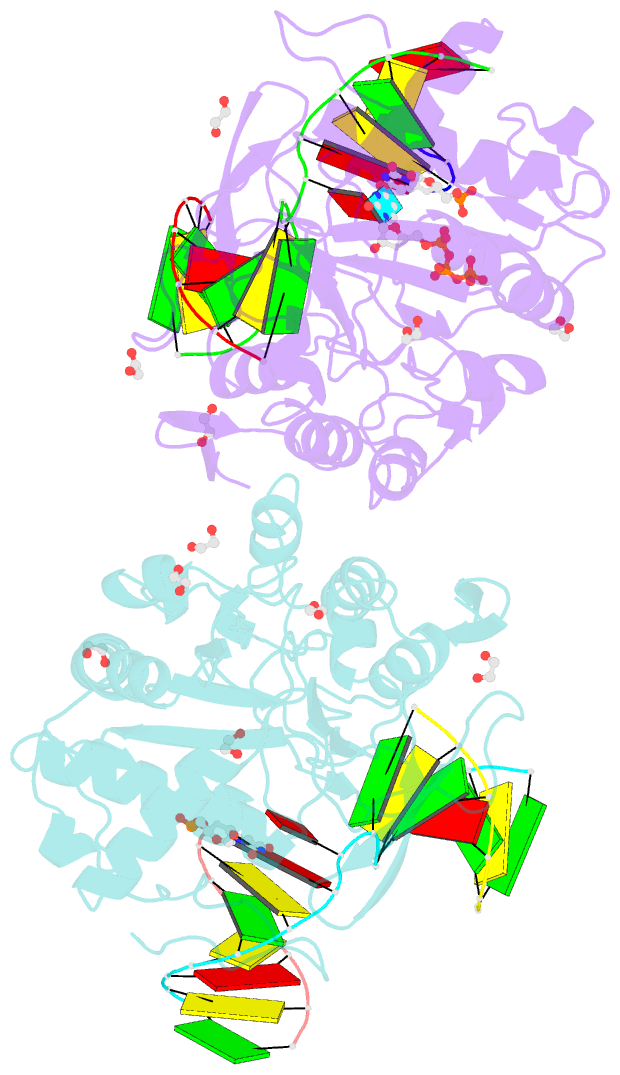
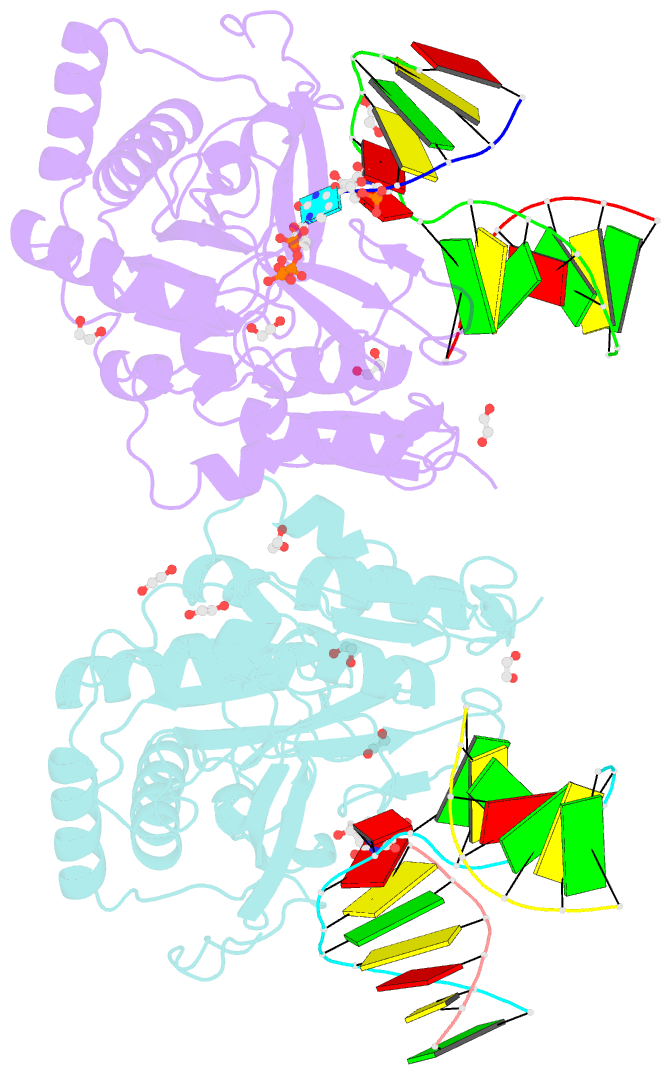
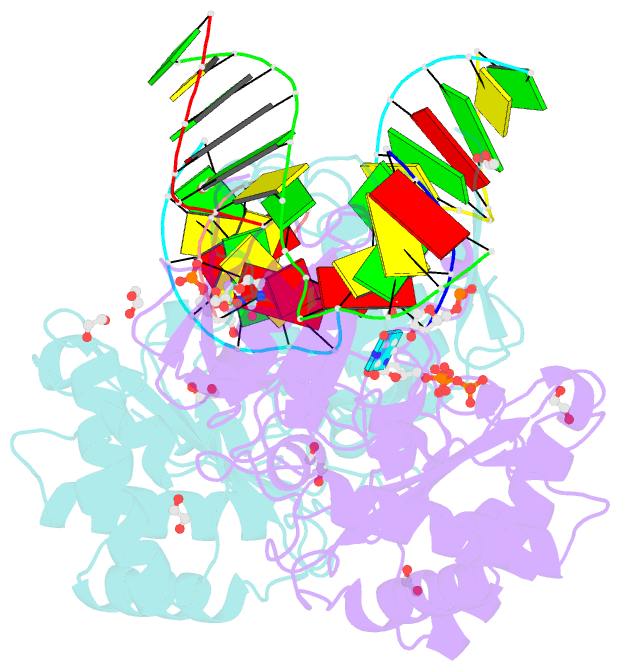
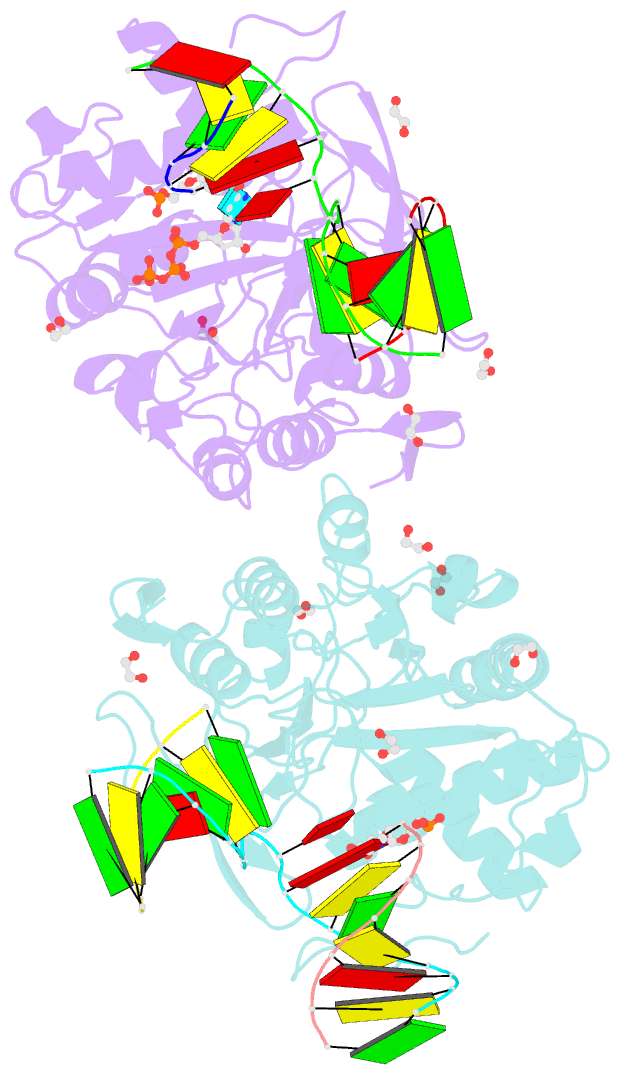
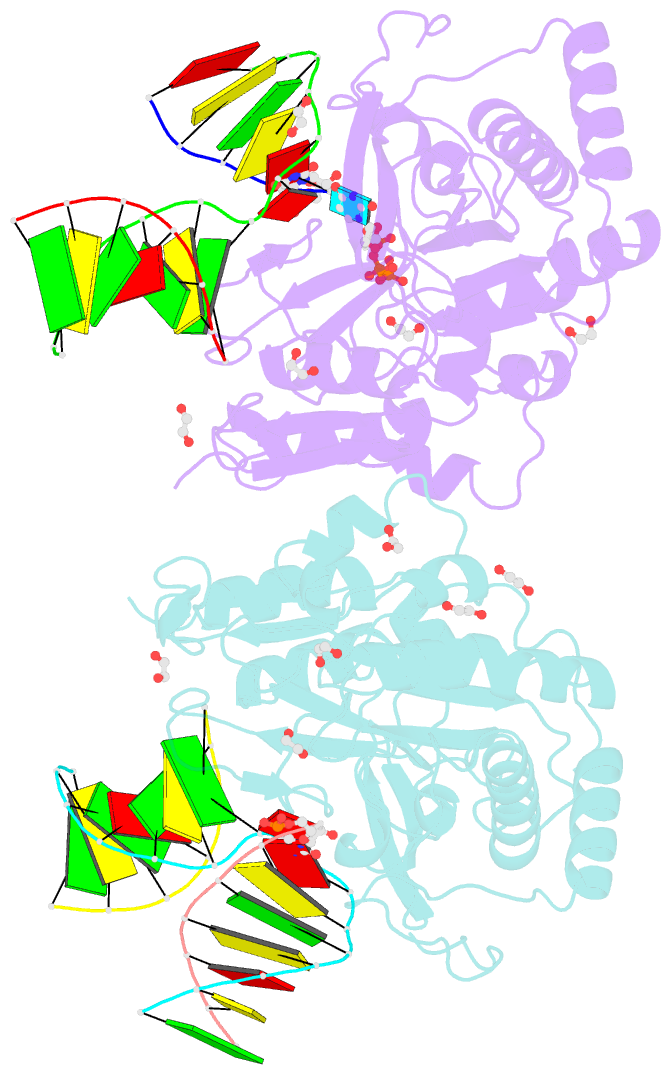
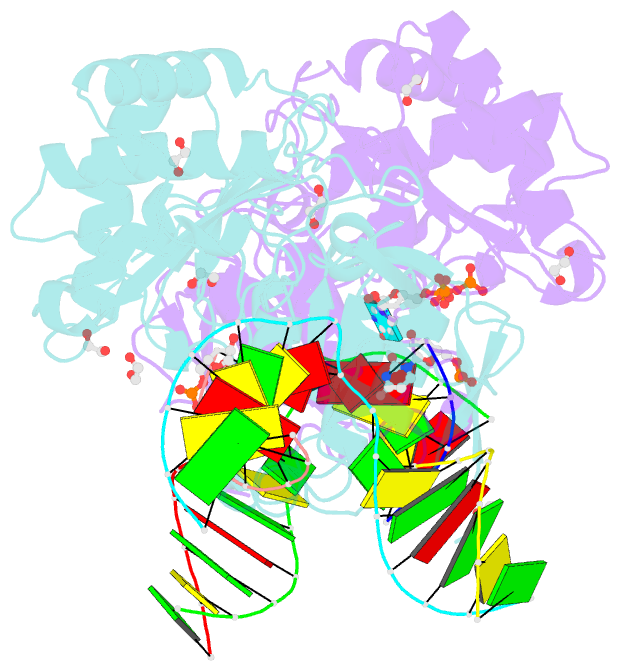
- Post catalytic complex of prim-polc from mycobacterium smegmatis with gapped DNA and 3'-dutp
- Reference
- Brissett NC, Zabrady K, Plocinski P, Bianchi J, Korycka-Machala M, Brzostek A, Dziadek J, Doherty AJ (2020): "Molecular basis for DNA repair synthesis on short gaps by mycobacterial Primase-Polymerase C." Nat Commun, 11, 4196. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18012-8.
- Abstract
- Cells utilise specialized polymerases from the Primase-Polymerase (Prim-Pol) superfamily to maintain genome stability. Prim-Pol's function in genome maintenance pathways including replication, repair and damage tolerance. Mycobacteria contain multiple Prim-Pols required for lesion repair, including Prim-PolC that performs short gap repair synthesis during excision repair. To understand the molecular basis of Prim-PolC's gap recognition and synthesis activities, we elucidated crystal structures of pre- and post-catalytic complexes bound to gapped DNA substrates. These intermediates explain its binding preference for short gaps and reveal a distinctive modus operandi called Synthesis-dependent Template Displacement (STD). This mechanism enables Prim-PolC to couple primer extension with template base dislocation, ensuring that the unpaired templating bases in the gap are ushered into the active site in an ordered manner. Insights provided by these structures establishes the molecular basis of Prim-PolC's gap recognition and extension activities, while also illuminating the mechanisms of primer extension utilised by closely related Prim-Pols.