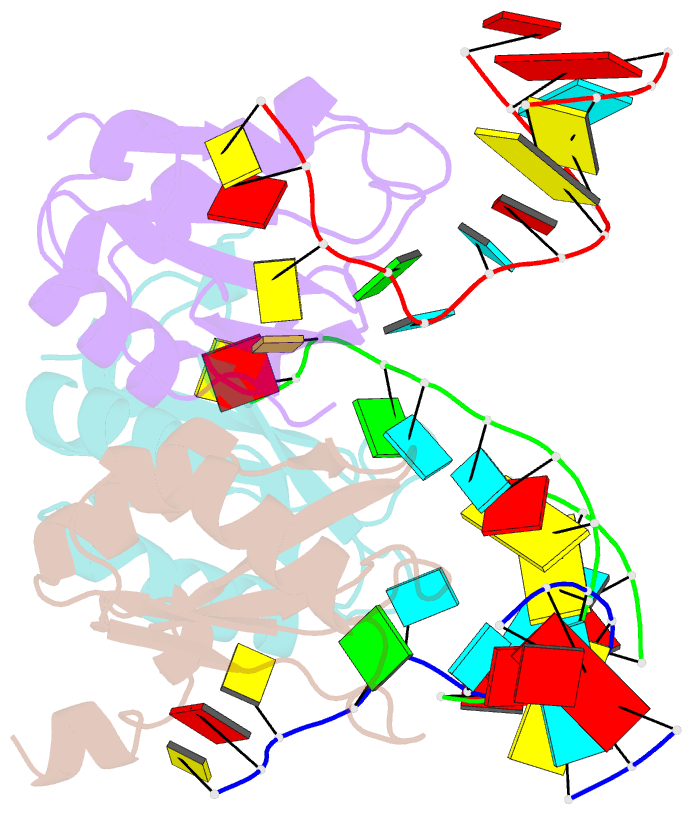
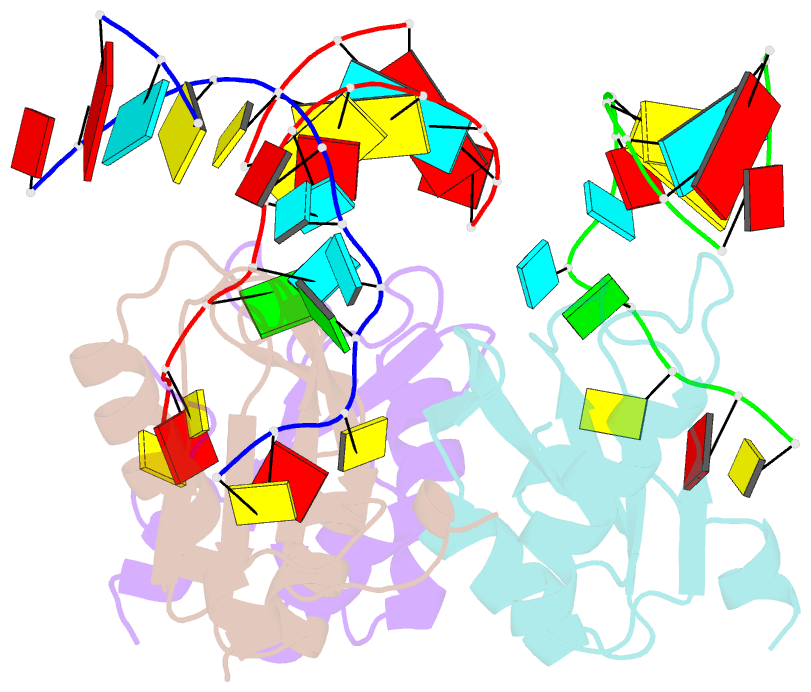
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6sqn; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.05 Å)
- Summary
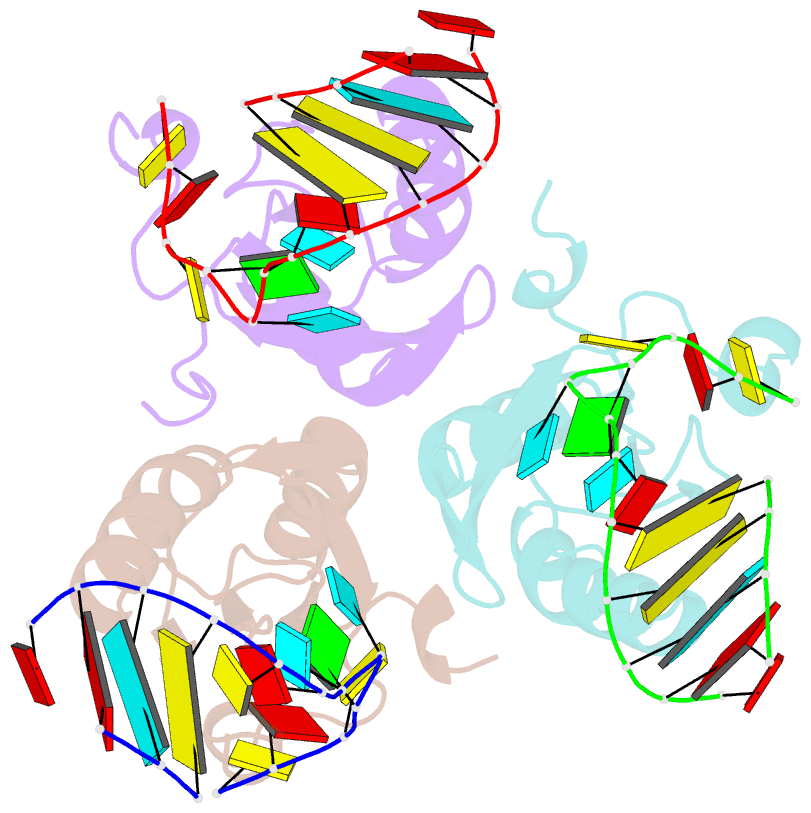
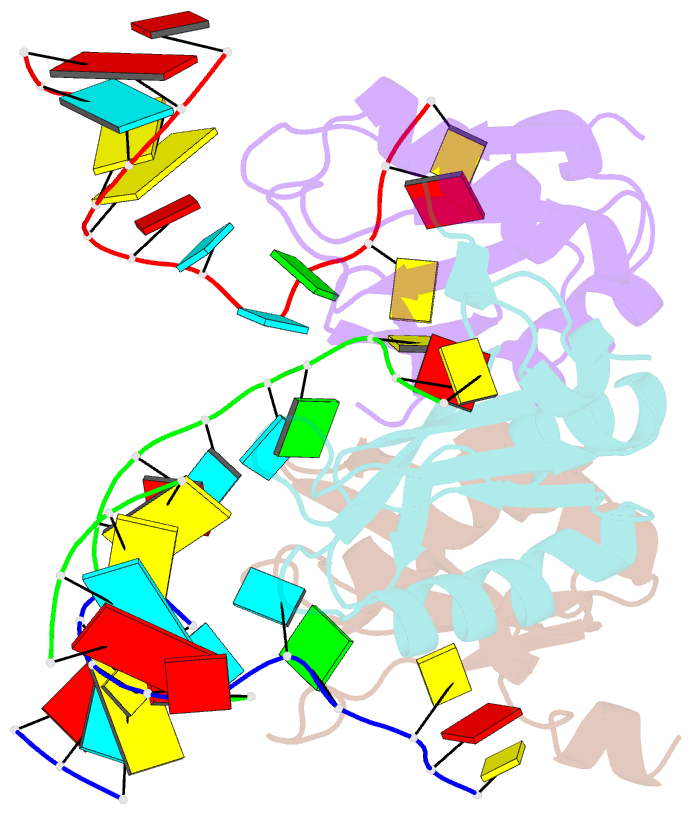
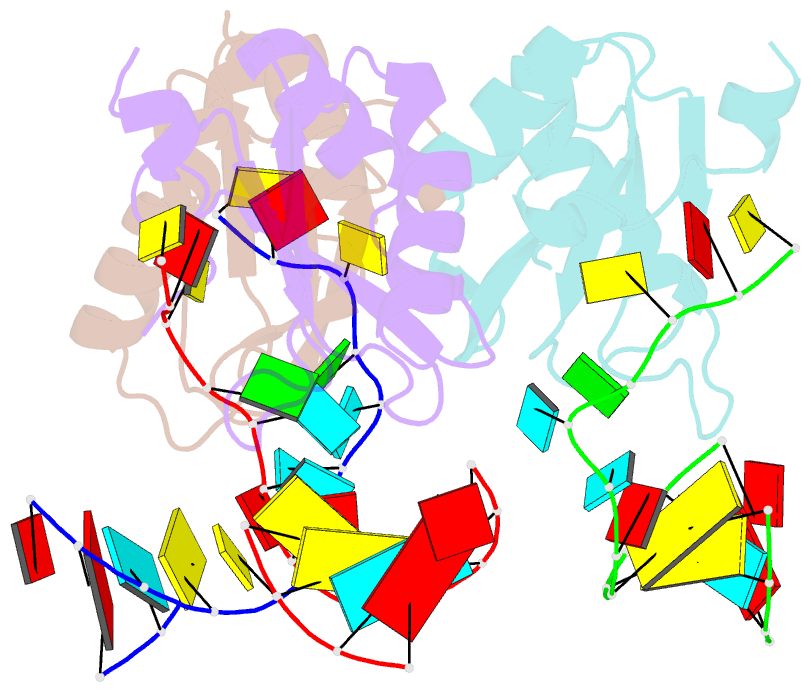
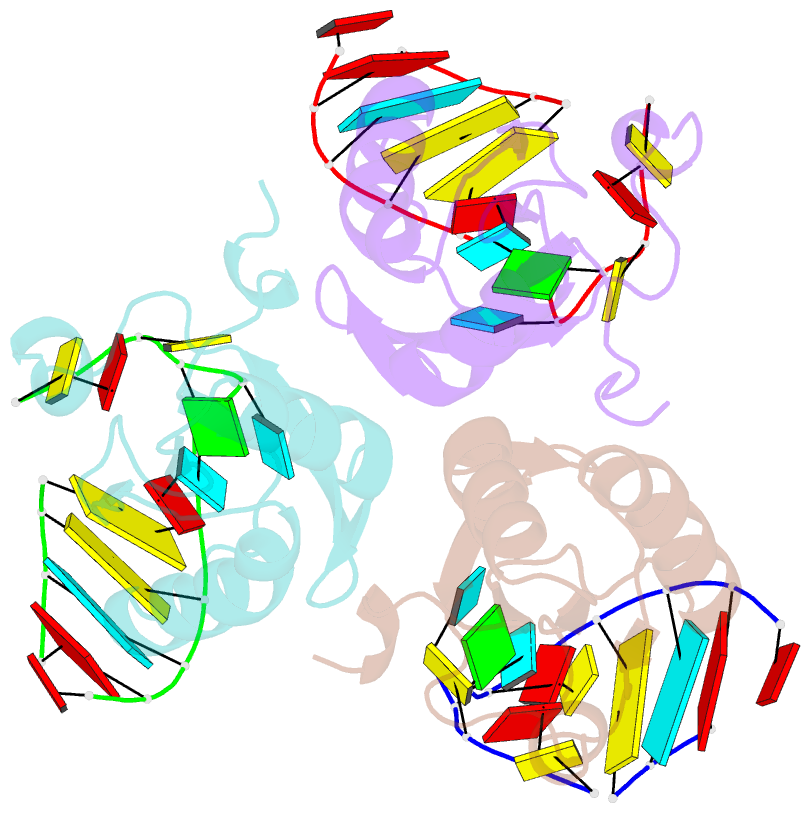
- Structure of the u1a variant a1-98 y31h-q36r-f56w triple mutant co-crystallized with RNA
- Reference
- Rosenbach H, Victor J, Borggrafe J, Biehl R, Steger G, Etzkorn M, Span I (2020): "Expanding crystallization tools for nucleic acid complexes using U1A protein variants." J.Struct.Biol., 210, 107480. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2020.107480.
- Abstract
- The major bottlenecks in structure elucidation of nucleic acids are crystallization and phasing. Co-crystallization with proteins is a straight forward approach to overcome these challenges. The human RNA-binding protein U1A has previously been established as crystallization module, however, the absence of UV-active residues and the predetermined architecture in the asymmetric unit constitute clear limitations of the U1A system. Here, we report three crystal structures of tryptophan-containing U1A variants, which expand the crystallization toolbox for nucleic acids. Analysis of the structures complemented by SAXS, NMR spectroscopy, and optical spectroscopy allow for insights into the potential of the U1A variants to serve as crystallization modules for nucleic acids. In addition, we report a fast and efficient protocol for crystallization of RNA by soaking and present a fluorescence-based approach for detecting RNA-binding in crystallo. Our results provide a new tool set for the crystallization of RNA and RNA:DNA complexes.