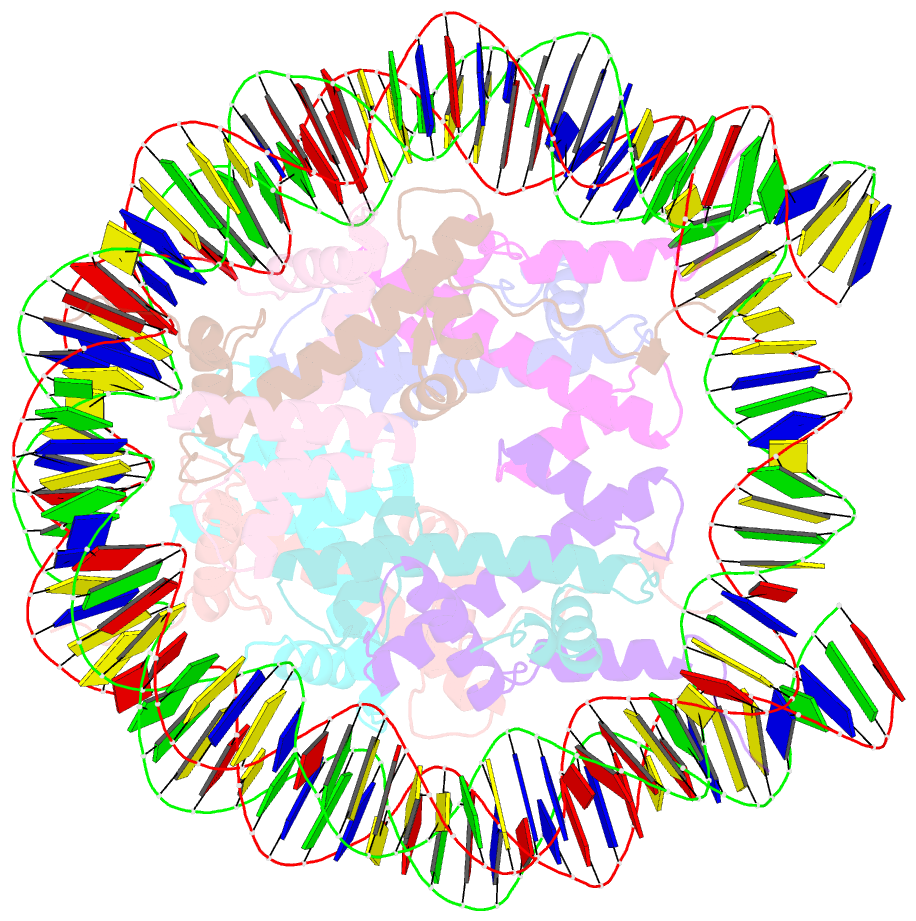
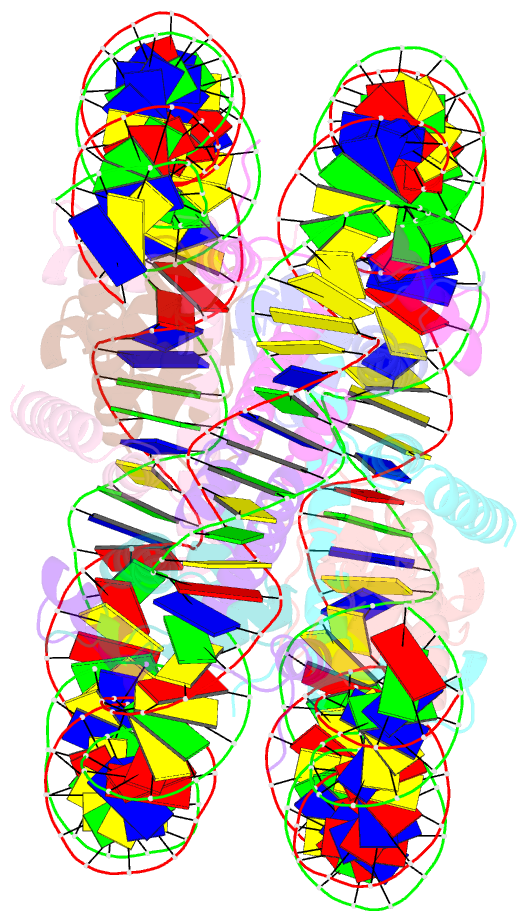
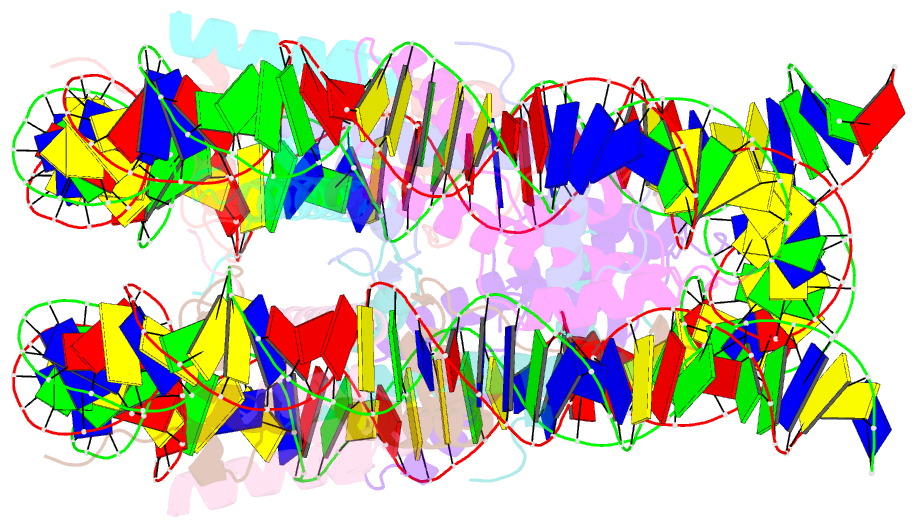
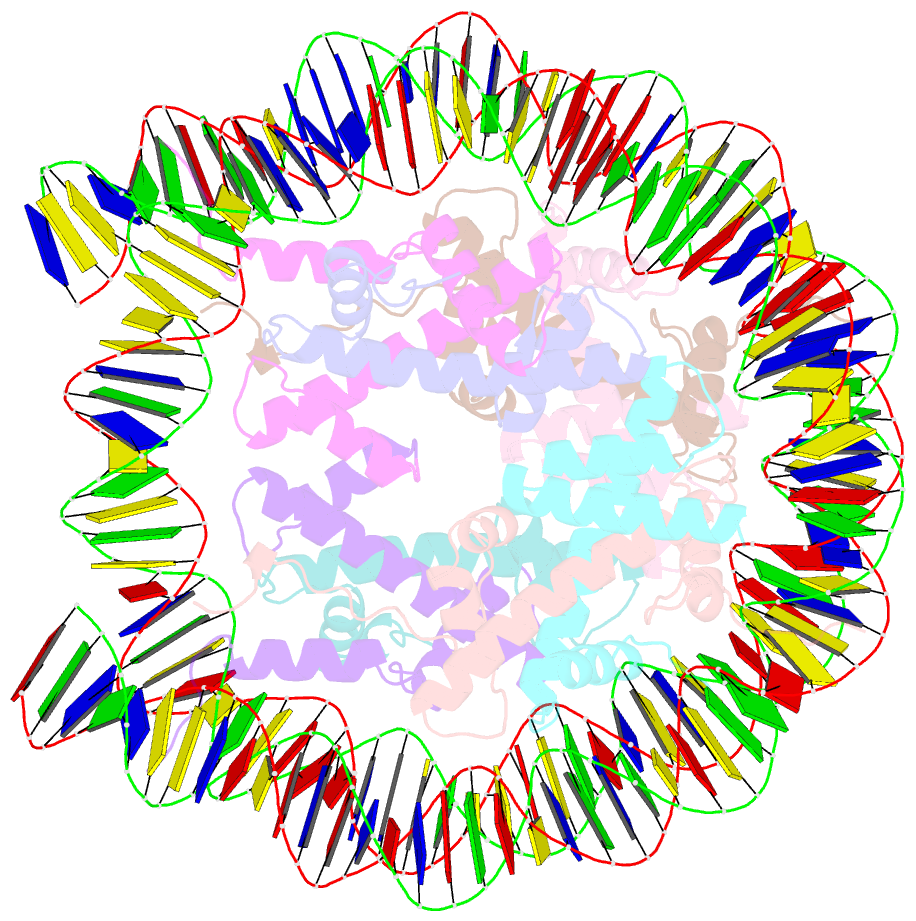
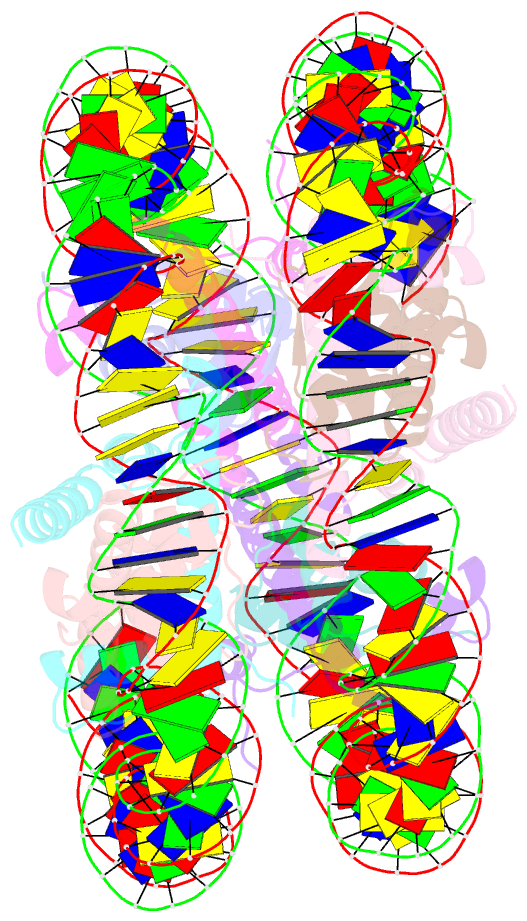
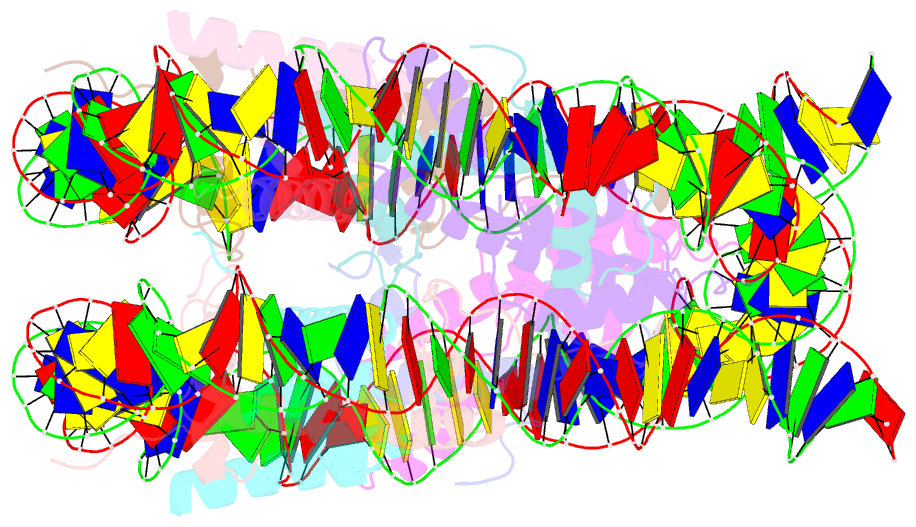
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6t93; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.49 Å)
- Summary
- Nucleosome with oct4-sox2 motif at shl-6
- Reference
- Michael AK, Grand RS, Isbel L, Cavadini S, Kozicka Z, Kempf G, Bunker RD, Schenk AD, Graff-Meyer A, Pathare GR, Weiss J, Matsumoto S, Burger L, Schubeler D, Thoma NH (2020): "Mechanisms of OCT4-SOX2 motif readout on nucleosomes." Science, 368, 1460-1465. doi: 10.1126/science.abb0074.
- Abstract
- Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression through chromatin where nucleosomes restrict DNA access. To study how TFs bind nucleosome-occupied motifs, we focused on the reprogramming factors OCT4 and SOX2 in mouse embryonic stem cells. We determined TF engagement throughout a nucleosome at base-pair resolution in vitro, enabling structure determination by cryo-electron microscopy at two preferred positions. Depending on motif location, OCT4 and SOX2 differentially distort nucleosomal DNA. At one position, OCT4-SOX2 removes DNA from histone H2A and histone H3; however, at an inverted motif, the TFs only induce local DNA distortions. OCT4 uses one of its two DNA-binding domains to engage DNA in both structures, reading out a partial motif. These findings explain site-specific nucleosome engagement by the pluripotency factors OCT4 and SOX2, and they reveal how TFs distort nucleosomes to access chromatinized motifs.