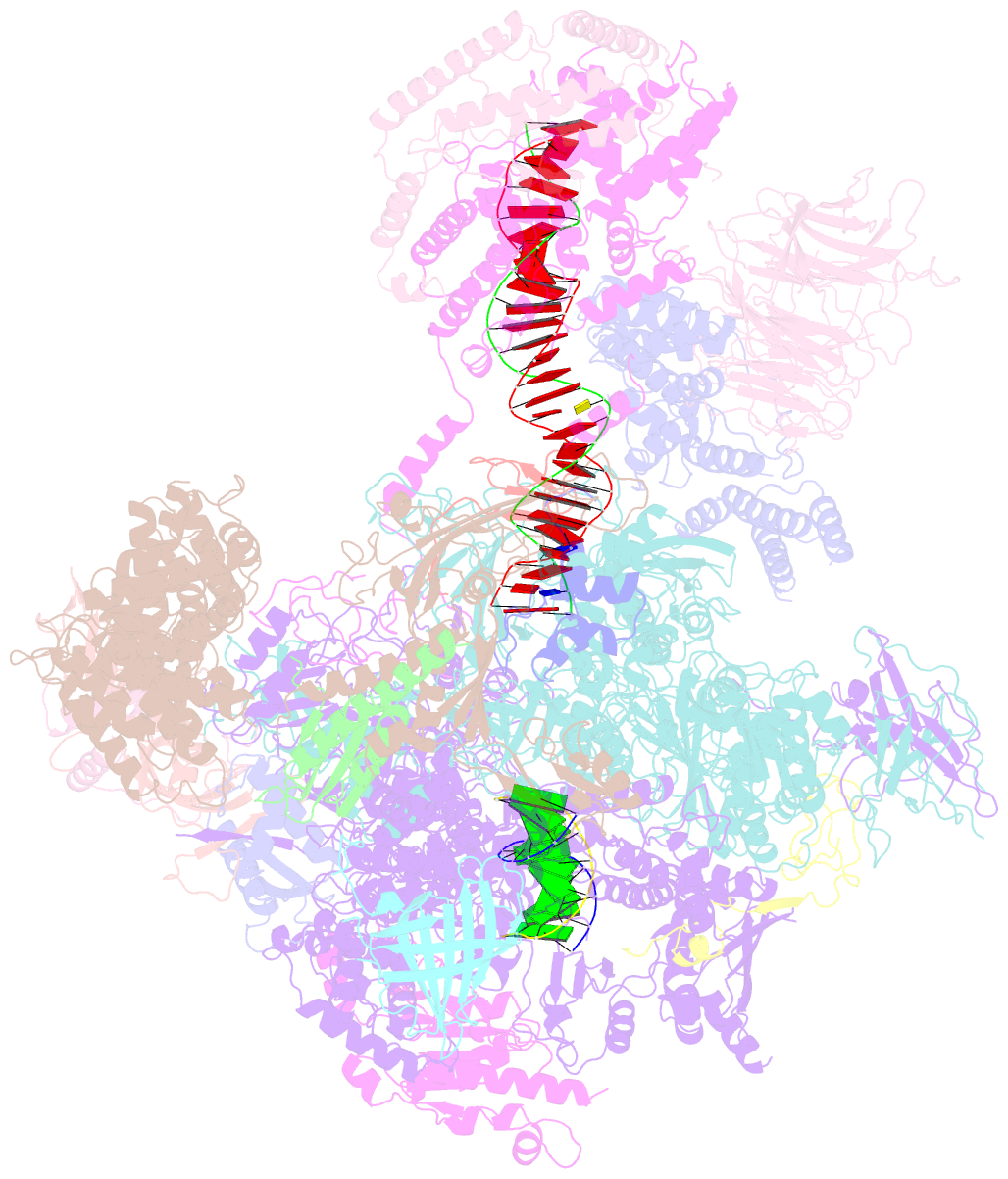
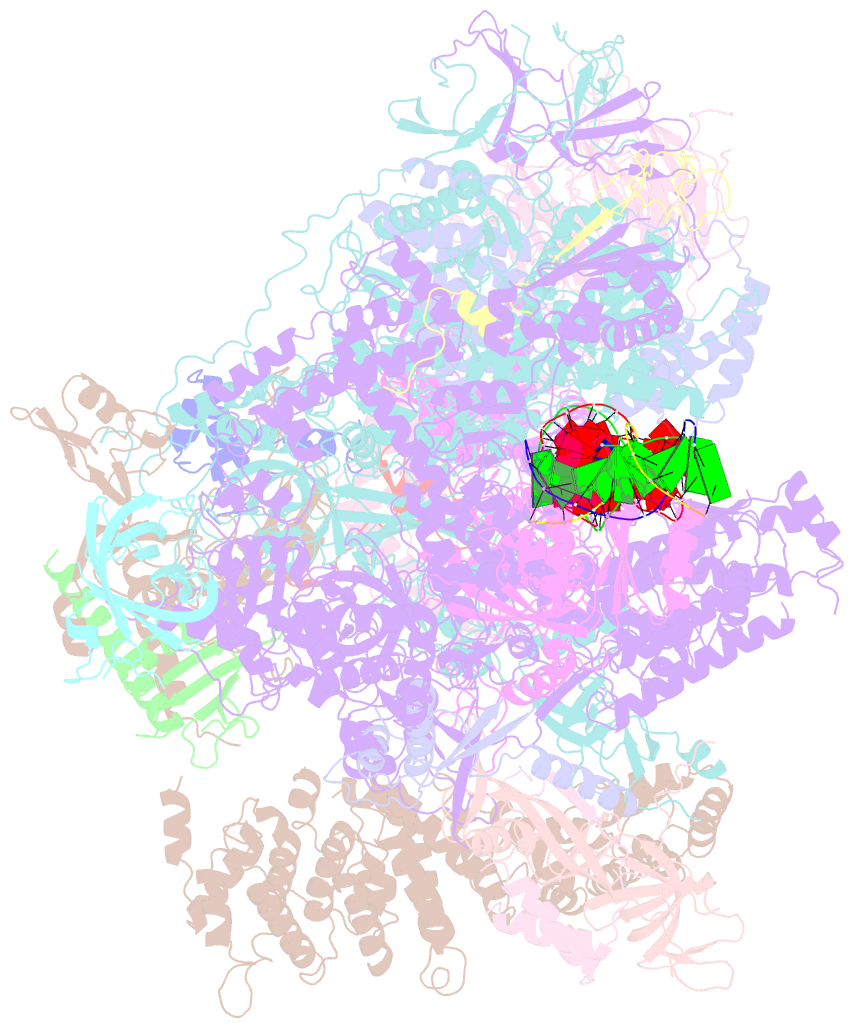
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6tps; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.54 Å)
- Summary
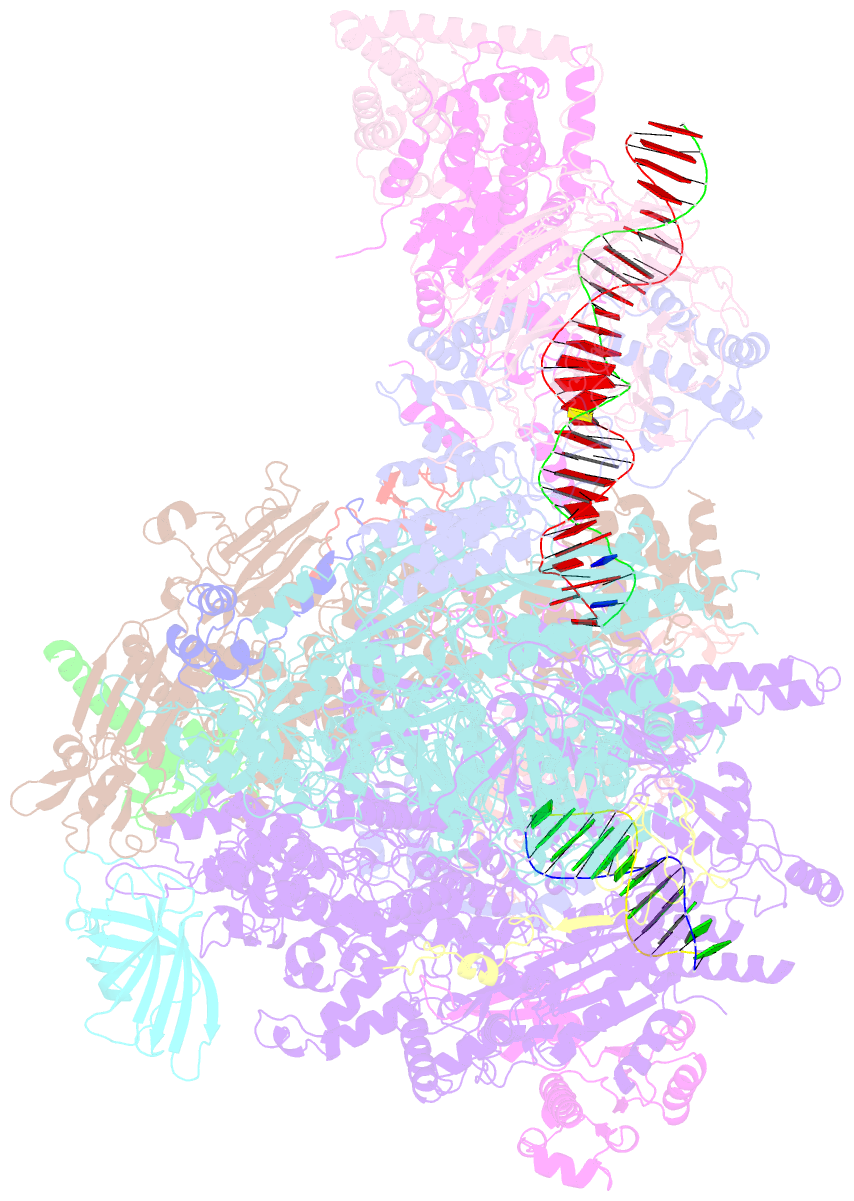
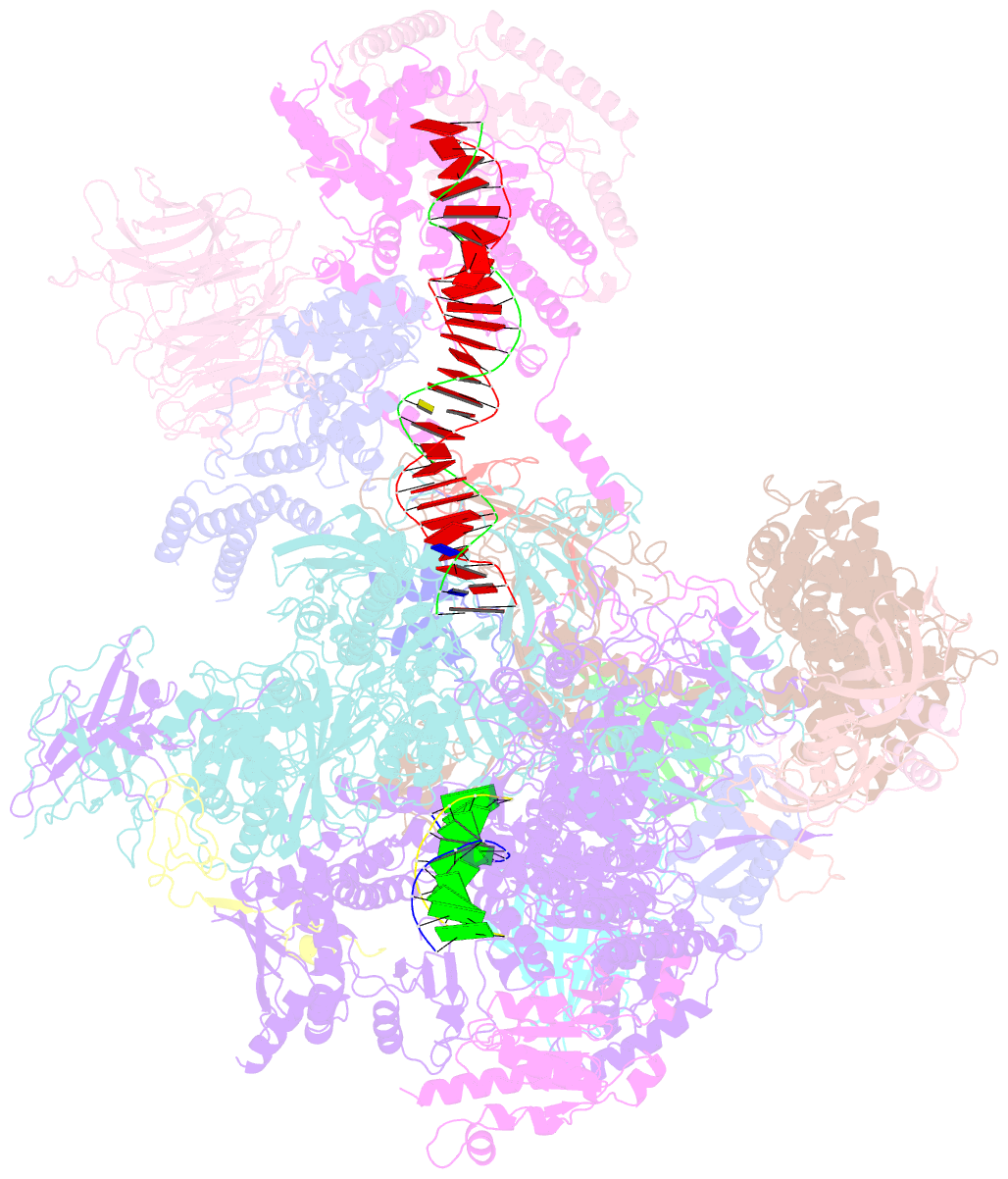
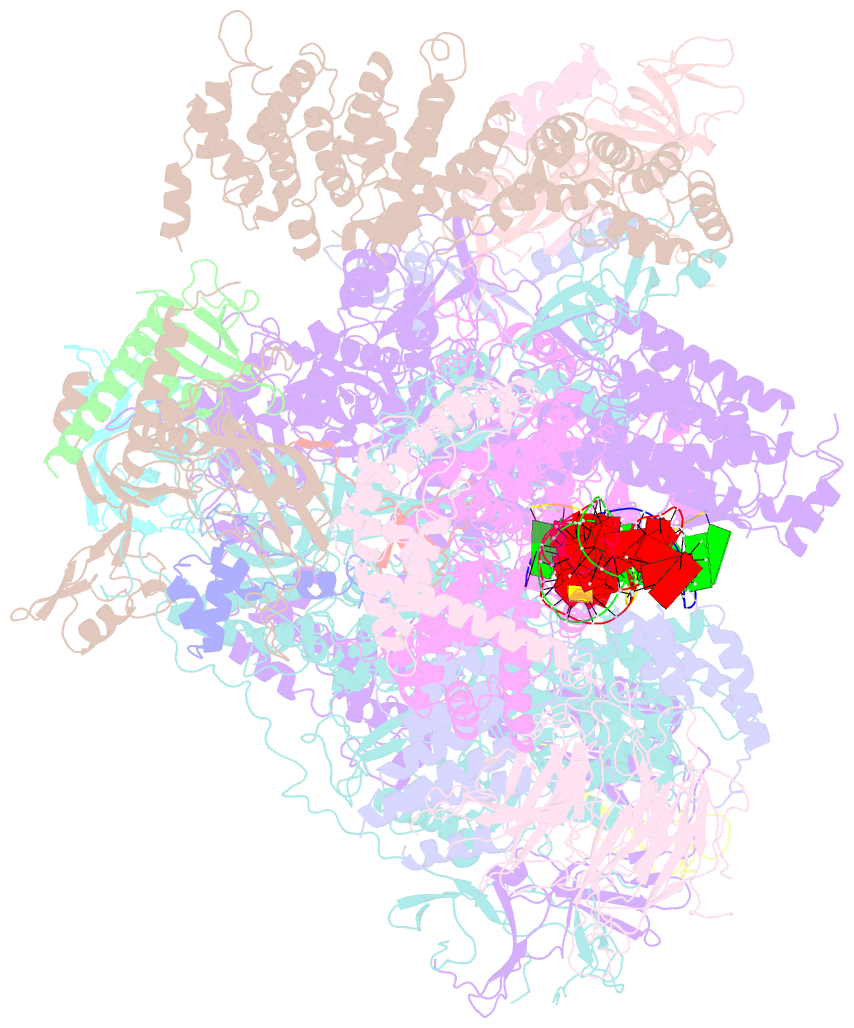
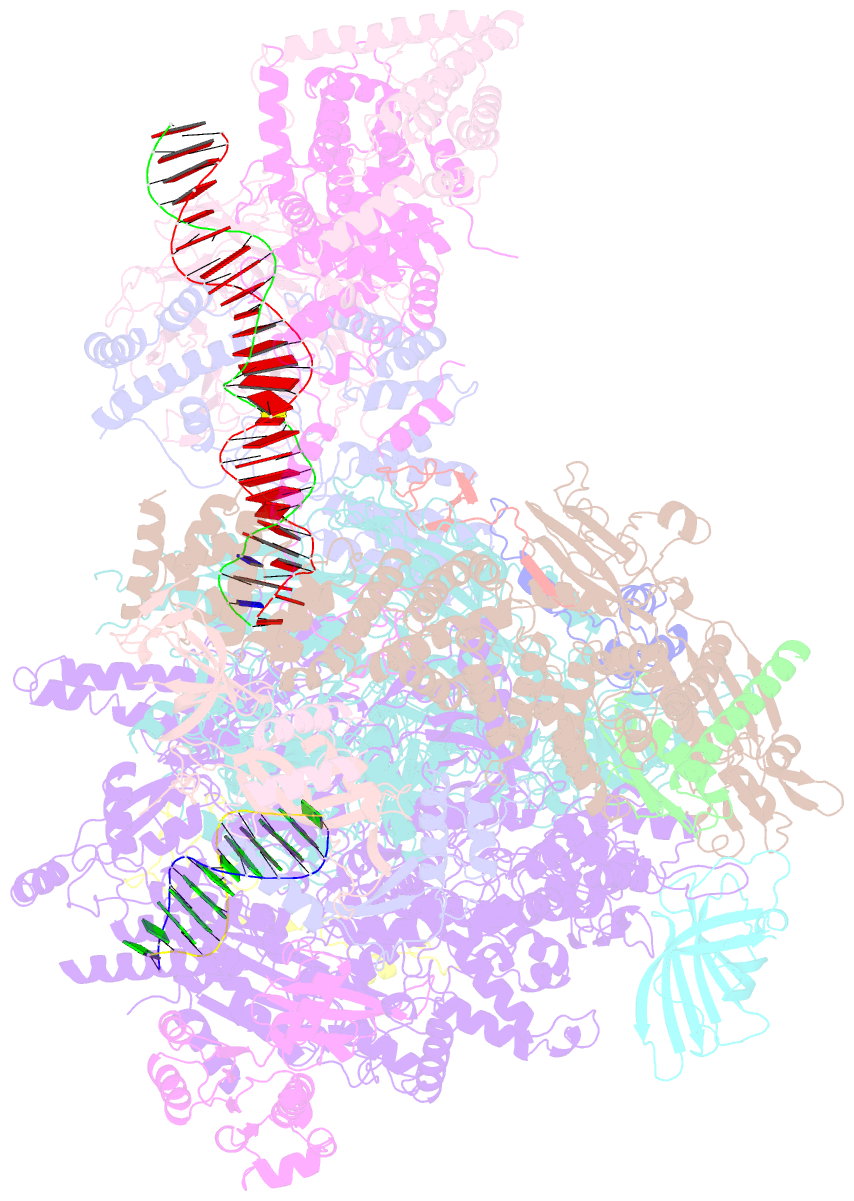
- Early intermediate RNA polymerase i pre-initiation complex - eipic
- Reference
- Pilsl M, Engel C (2020): "Structural basis of RNA polymerase I pre-initiation complex formation and promoter melting." Nat Commun, 11, 1206. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15052-y.
- Abstract
- Transcription of the ribosomal RNA precursor by RNA polymerase (Pol) I is a prerequisite for the biosynthesis of ribosomes in eukaryotes. Compared to Pols II and III, the mechanisms underlying promoter recognition, initiation complex formation and DNA melting by Pol I substantially diverge. Here, we report the high-resolution cryo-EM reconstruction of a Pol I early initiation intermediate assembled on a double-stranded promoter scaffold that prevents the establishment of downstream DNA contacts. Our analyses demonstrate how efficient promoter-backbone interaction is achieved by combined re-arrangements of flexible regions in the 'core factor' subunits Rrn7 and Rrn11. Furthermore, structure-function analysis illustrates how destabilization of the melted DNA region correlates with contraction of the polymerase cleft upon transcription activation, thereby combining promoter recruitment with DNA-melting. This suggests that molecular mechanisms and structural features of Pol I initiation have co-evolved to support the efficient melting, initial transcription and promoter clearance required for high-level rRNA synthesis.