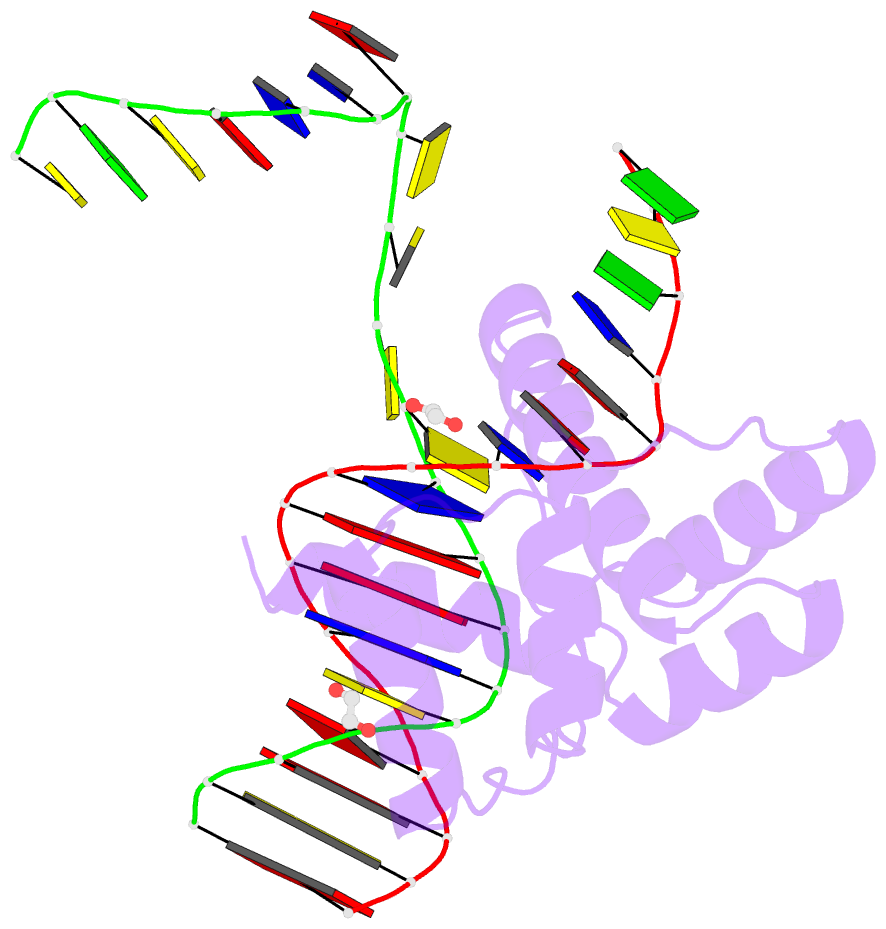
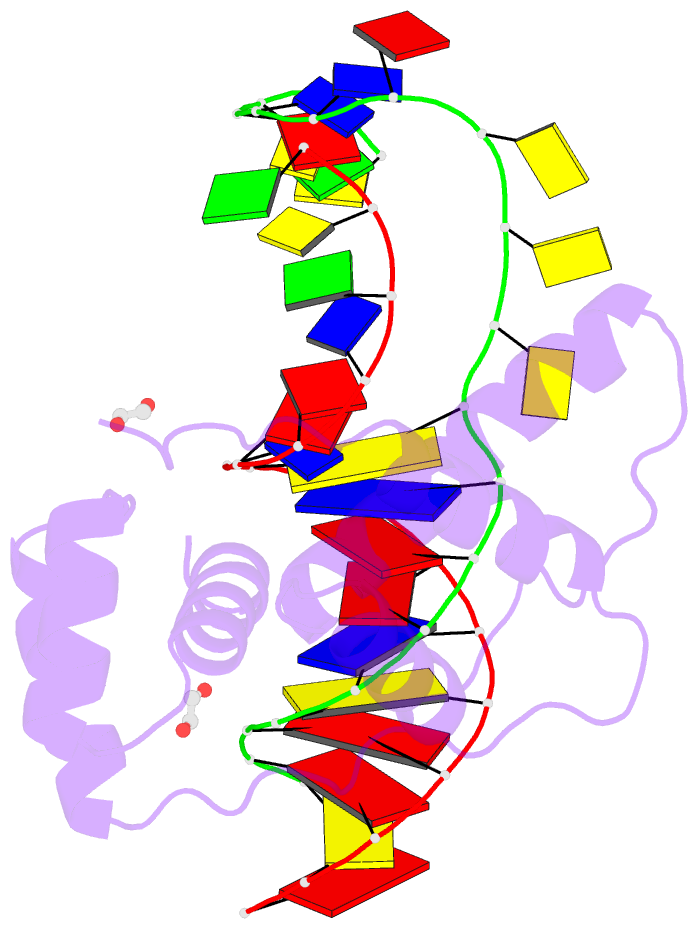
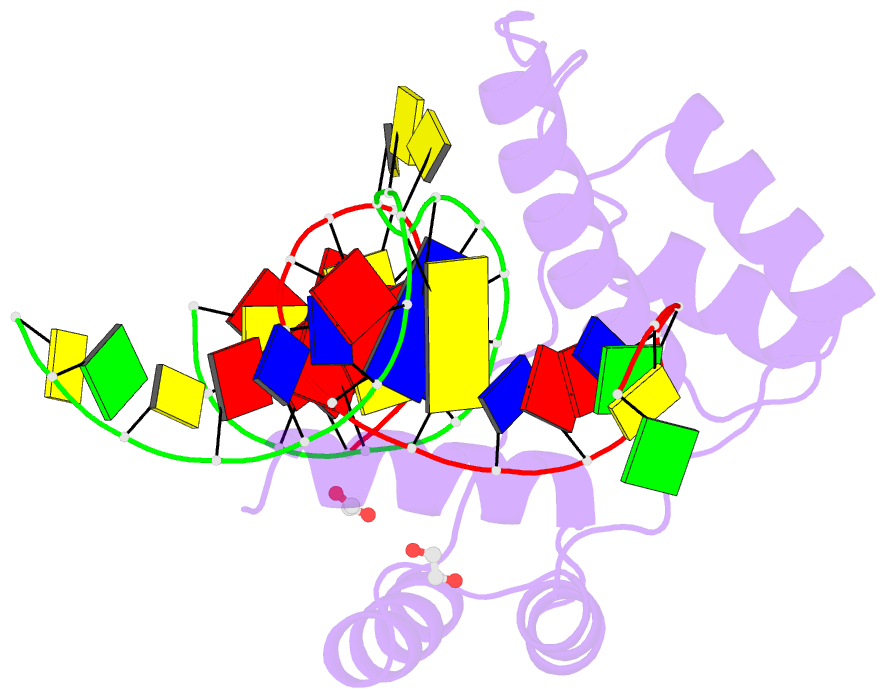
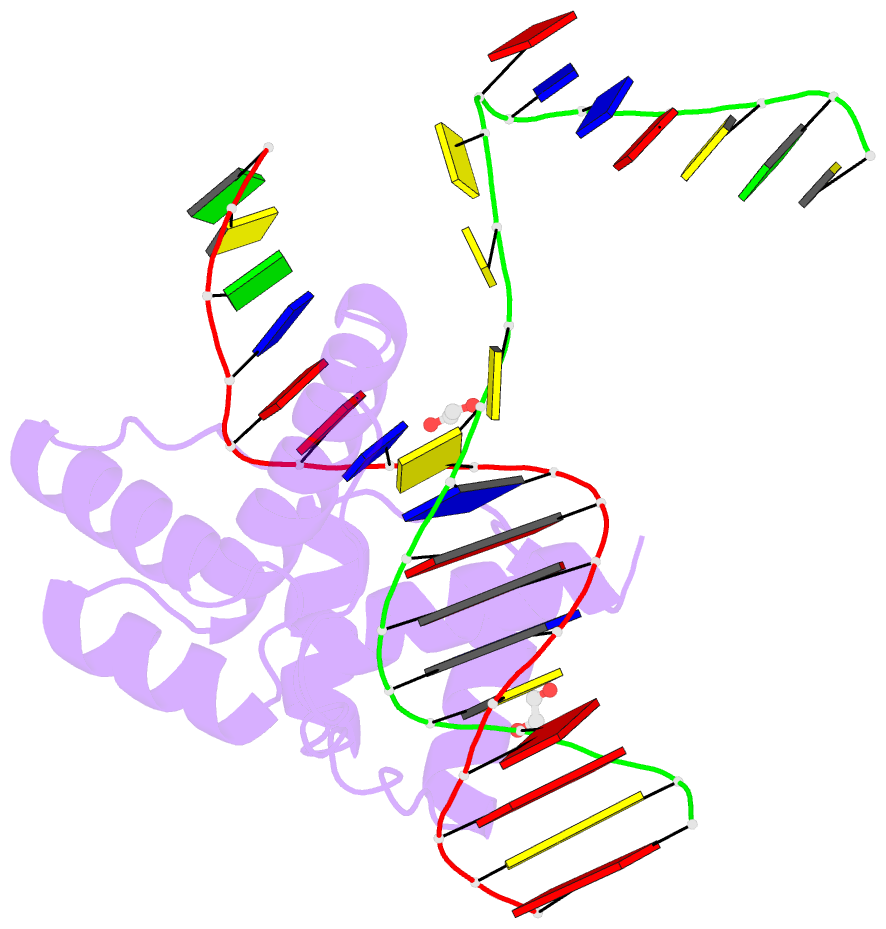
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6u81; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.34 Å)
- Summary
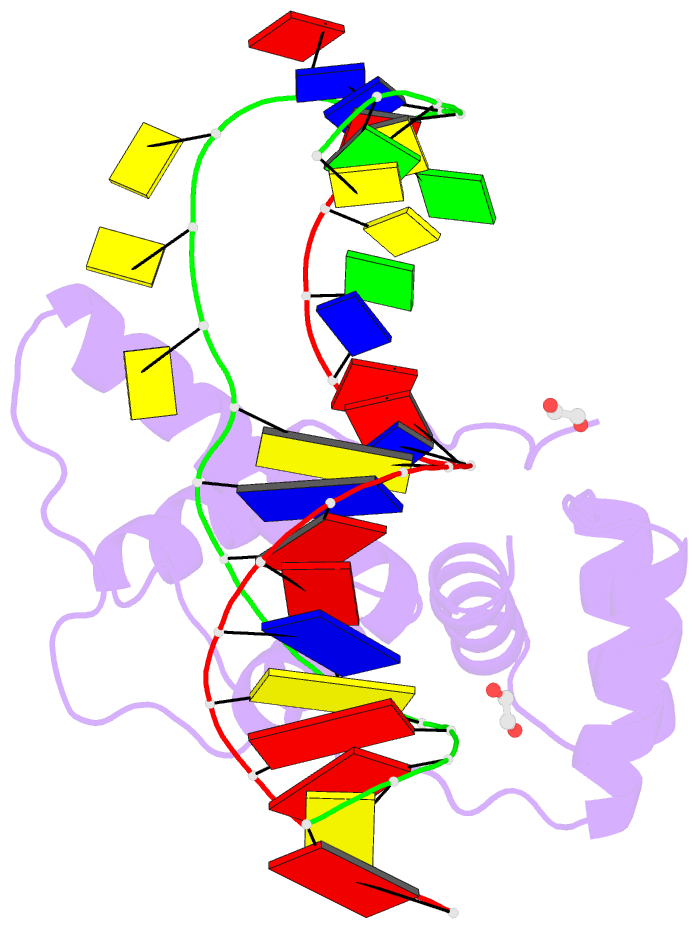
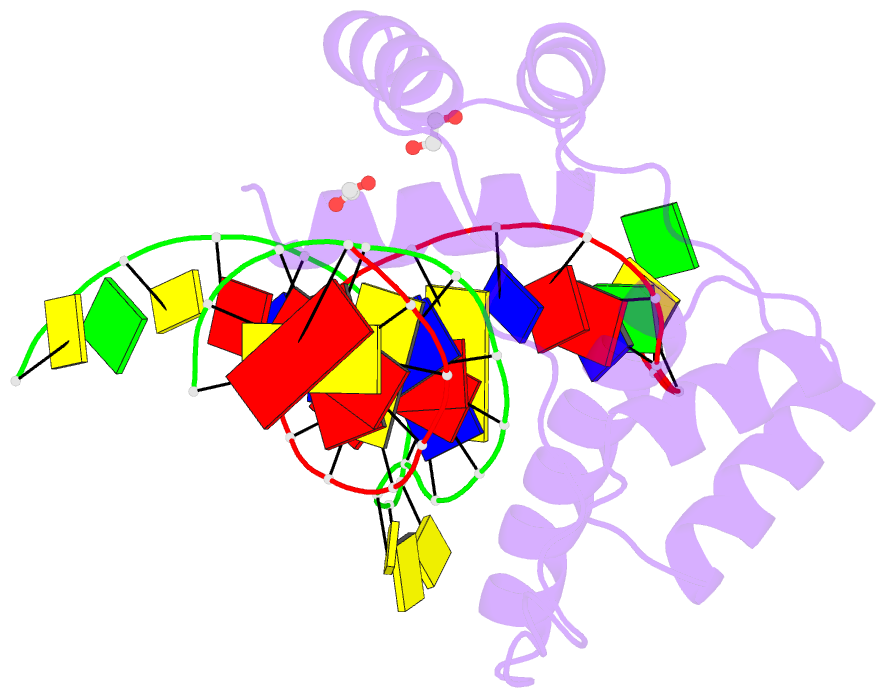
- Crystal structure of the double homeodomain of dux4 in complex with a DNA aptamer
- Reference
- Klingler C, Ashley J, Shi K, Stiefvater A, Kyba M, Sinnreich M, Aihara H, Kinter J (2020): "DNA aptamers against the DUX4 protein reveal novel therapeutic implications for FSHD." Faseb J., 34, 4573-4590. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902696.
- Abstract
- Aberrant expression of the transcription factor double homeobox protein 4 (DUX4) can lead to a number of diseases including facio-scapulo-humeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and sarcomas. Inhibition of DUX4 may represent a therapeutic strategy for these diseases. By applying Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential Enrichment (SELEX), we identified aptamers against DUX4 with specific secondary structural elements conveying high affinity to DUX4 as assessed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer and fluorescence polarization techniques. Sequences analysis of these aptamers revealed the presence of two consensus DUX4 motifs in a reverse complementary fashion forming hairpins interspersed with bulge loops at distinct positions that enlarged the binding surface with the DUX4 protein, as determined by crystal structure analysis. We demonstrate that insertion of specific structural elements into transcription factor binding oligonucleotides can enhance specificity and affinity.