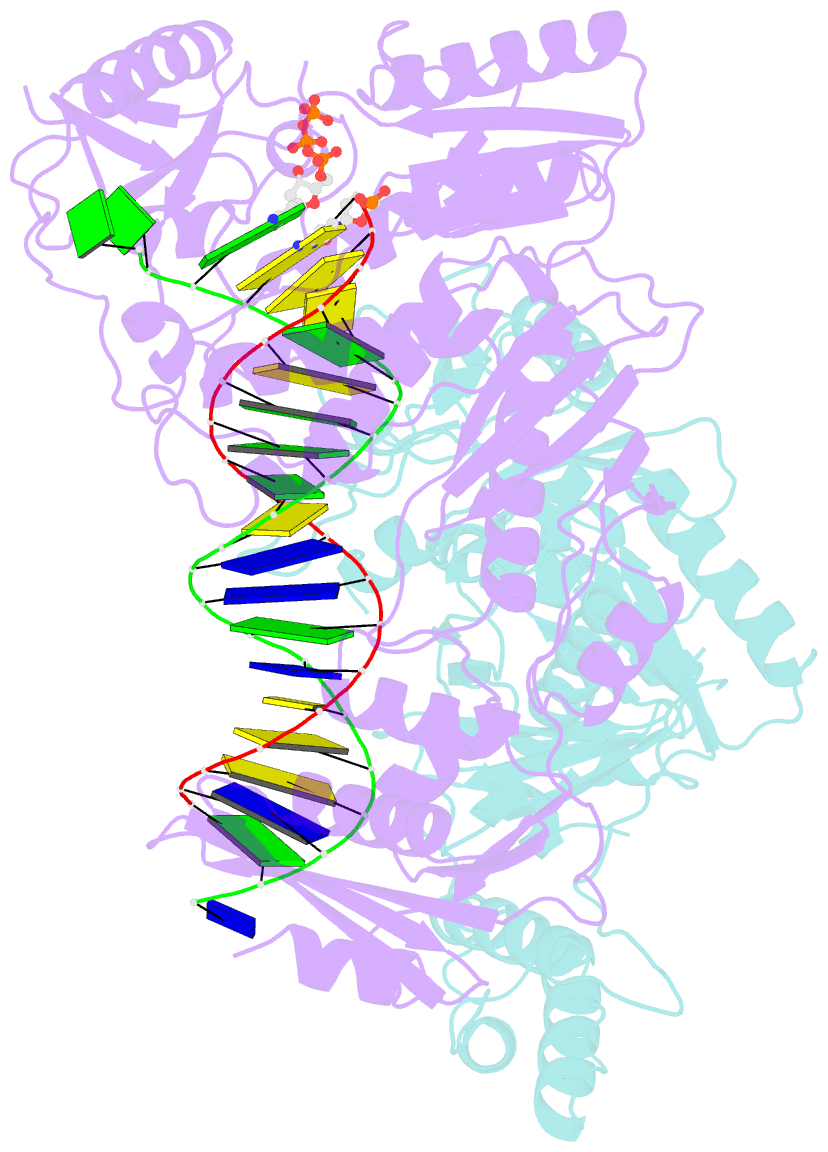
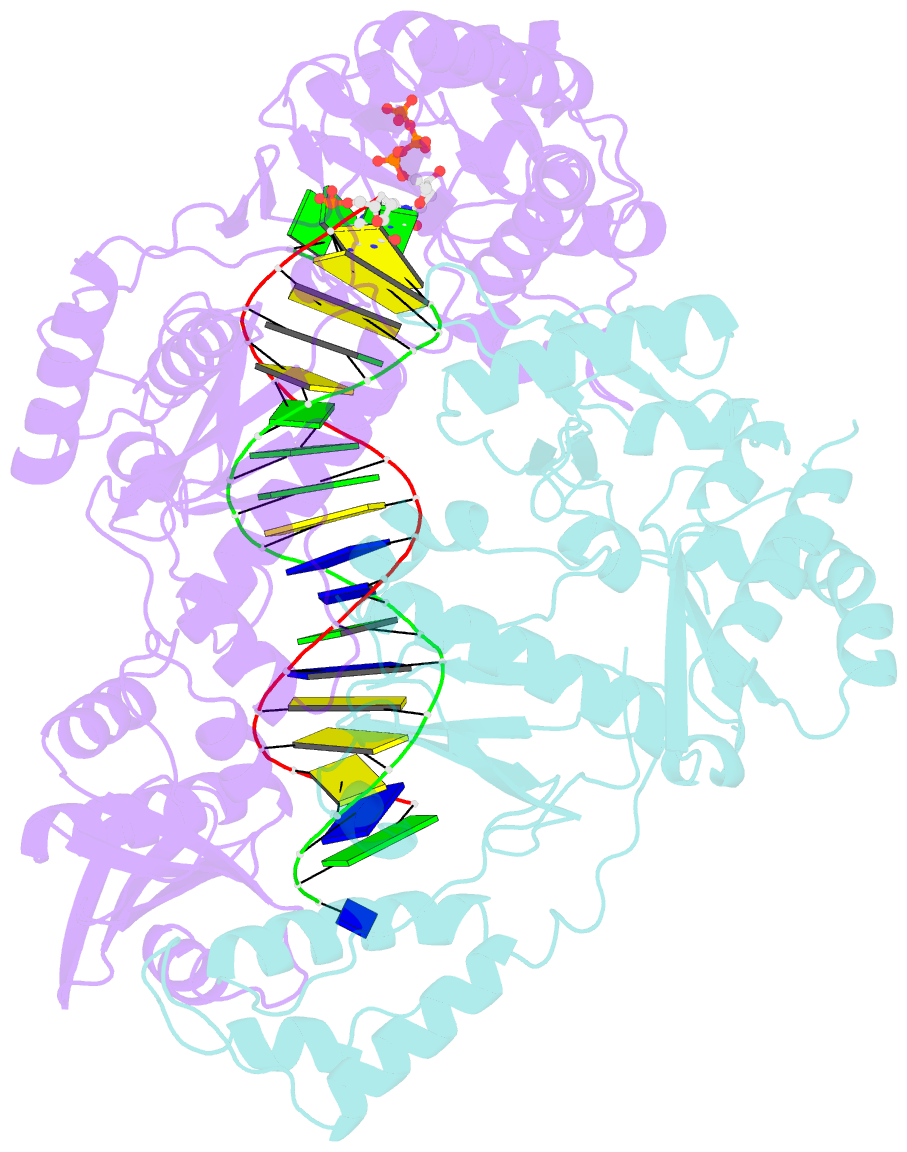
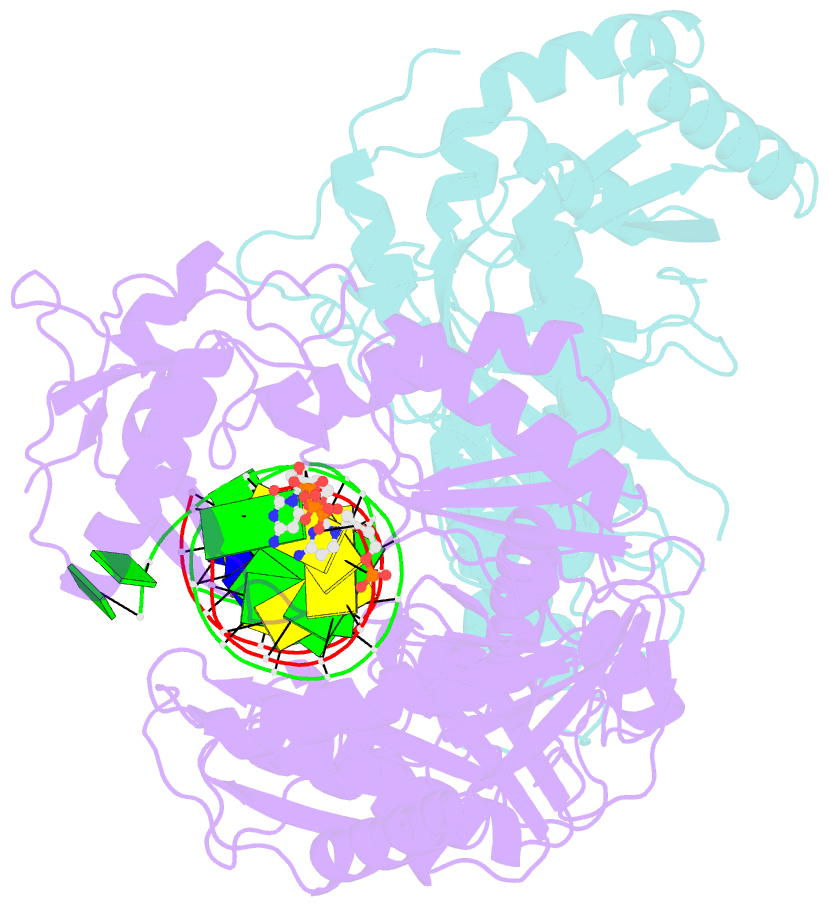
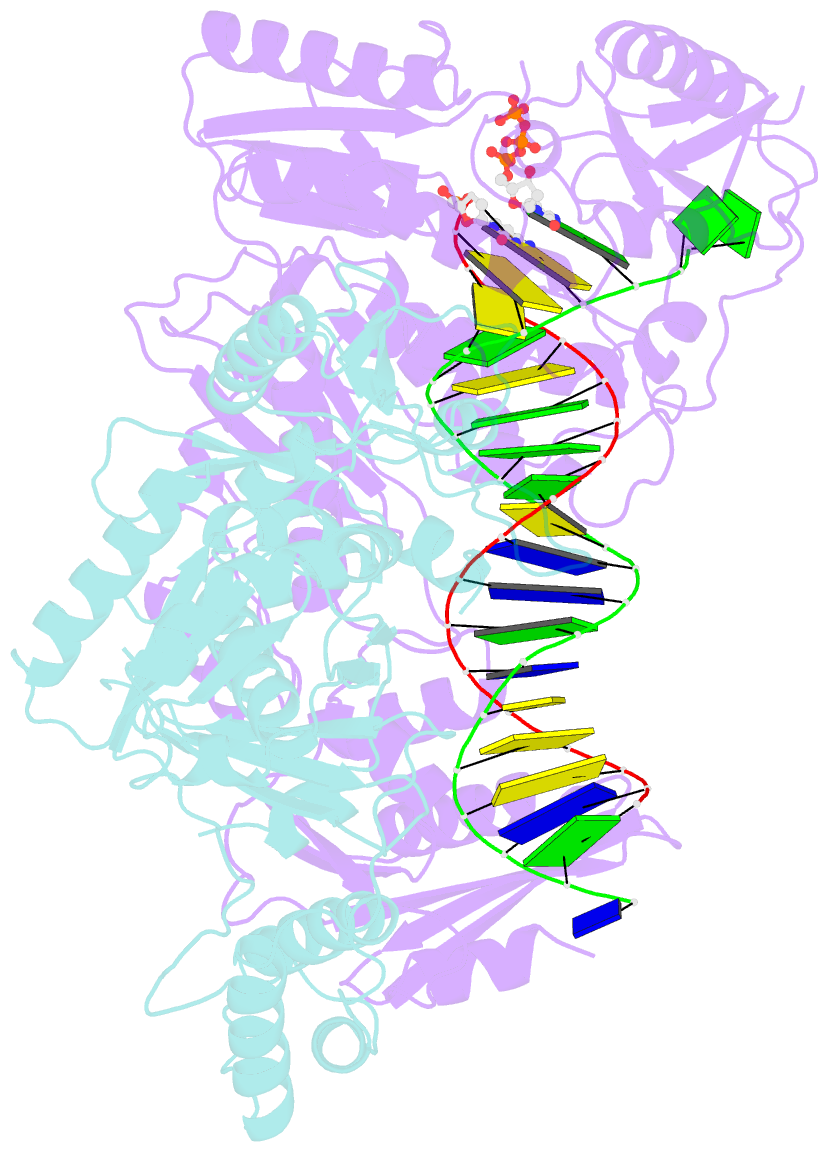
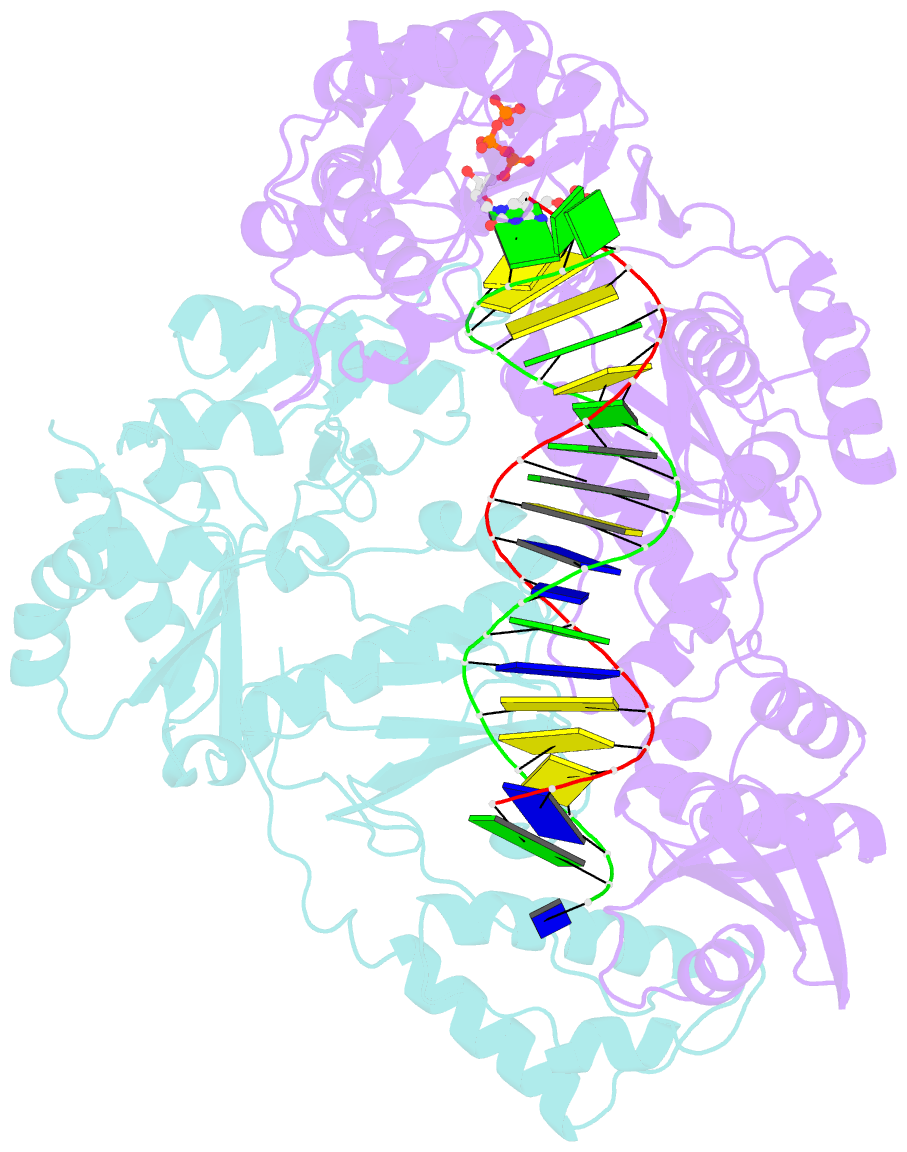
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6uis; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.75 Å)
- Summary
- Hiv-1 m184v reverse transcriptase-DNA complex with dctp
- Reference
- Hung M, Tokarsky EJ, Lagpacan L, Zhang L, Suo Z, Lansdon EB (2019): "Elucidating molecular interactions ofL-nucleotides with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and mechanism of M184V-caused drug resistance." Commun Biol, 2, 469. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0706-x.
- Abstract
- Emtricitabine (FTC) and lamivudine (3TC), containing an oxathiolane ring with unnatural (-)-stereochemistry, are widely used nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) in anti-HIV therapy. Treatment with FTC or 3TC primarily selects for the HIV-1 RT M184V/I resistance mutations. Here we provide a comprehensive kinetic and structural basis for inhibiting HIV-1 RT by (-)-FTC-TP and (-)-3TC-TP and drug resistance by M184V. (-)-FTC-TP and (-)-3TC-TP have higher binding affinities (1/K d) for wild-type RT but slower incorporation rates than dCTP. HIV-1 RT ternary crystal structures with (-)-FTC-TP and (-)-3TC-TP corroborate kinetic results demonstrating that their oxathiolane sulfur orients toward the DNA primer 3'-terminus and their triphosphate exists in two different binding conformations. M184V RT displays greater (>200-fold) K d for the L-nucleotides and moderately higher (>9-fold) K d for the D-isomers compared to dCTP. The M184V RT structure illustrates how the mutation repositions the oxathiolane of (-)-FTC-TP and shifts its triphosphate into a non-productive conformation.