Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6v93; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.1 Å)
- Summary
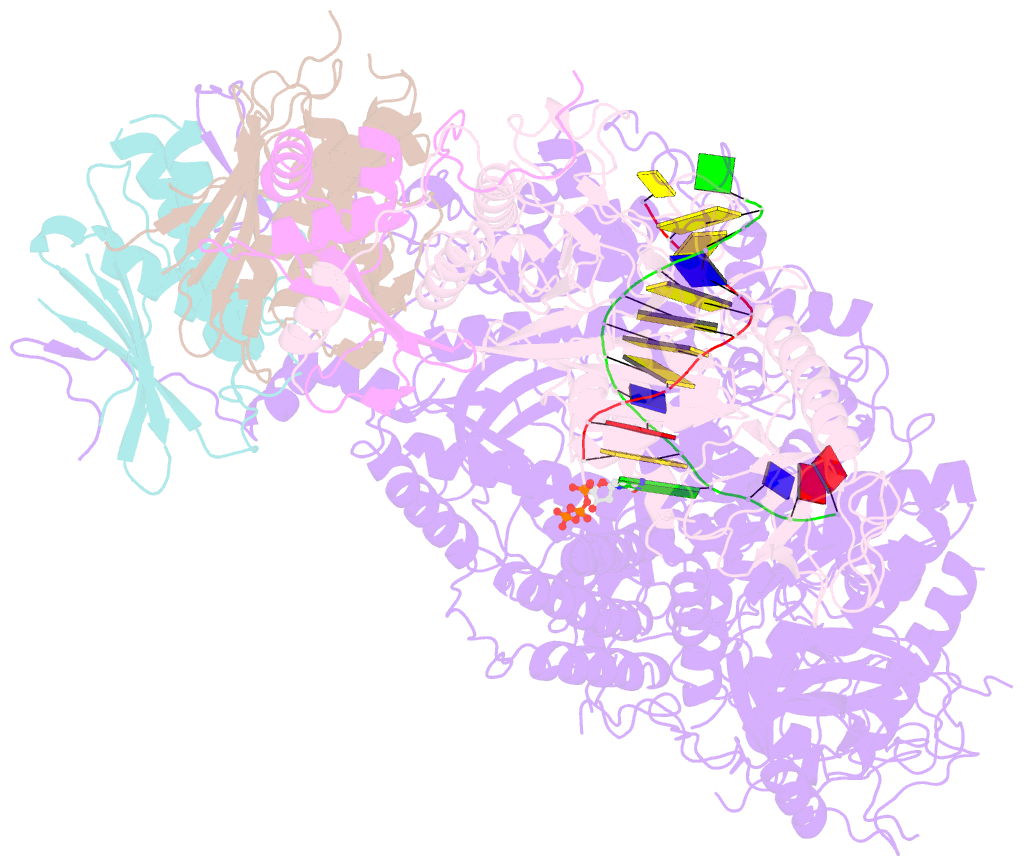
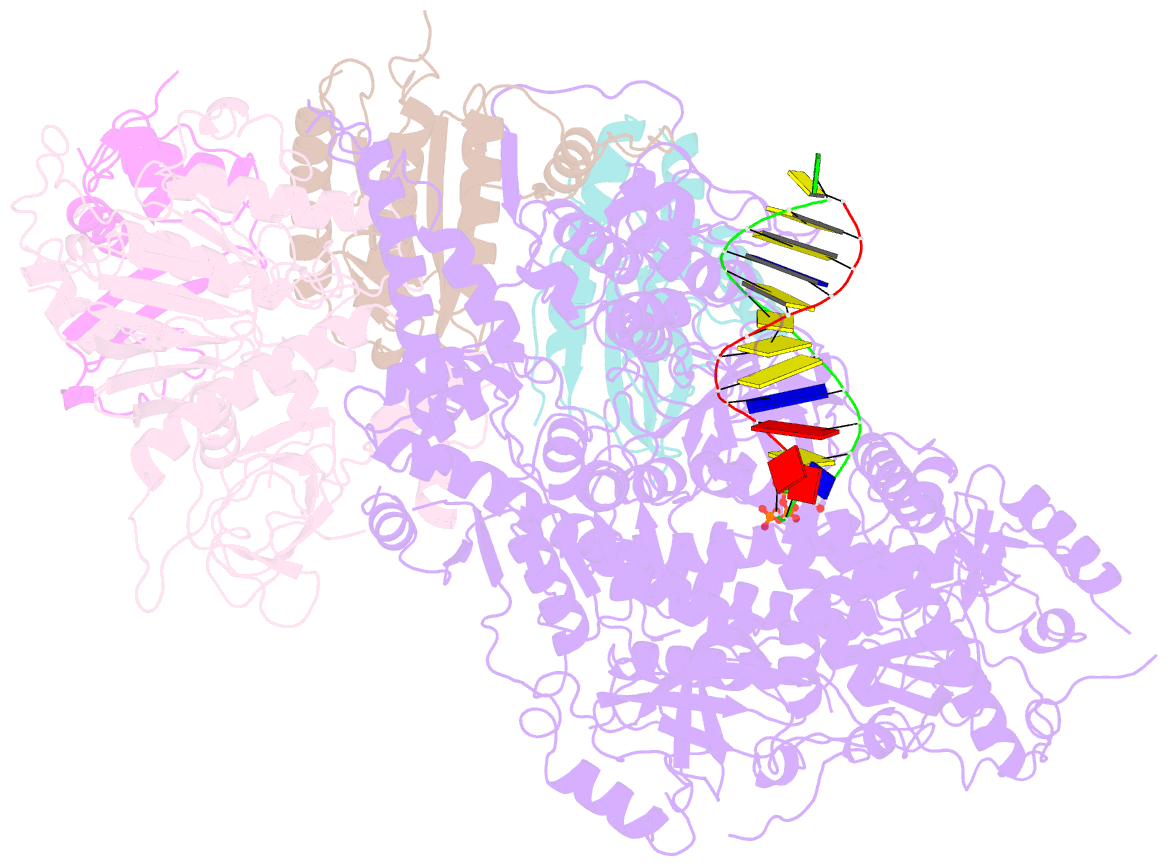
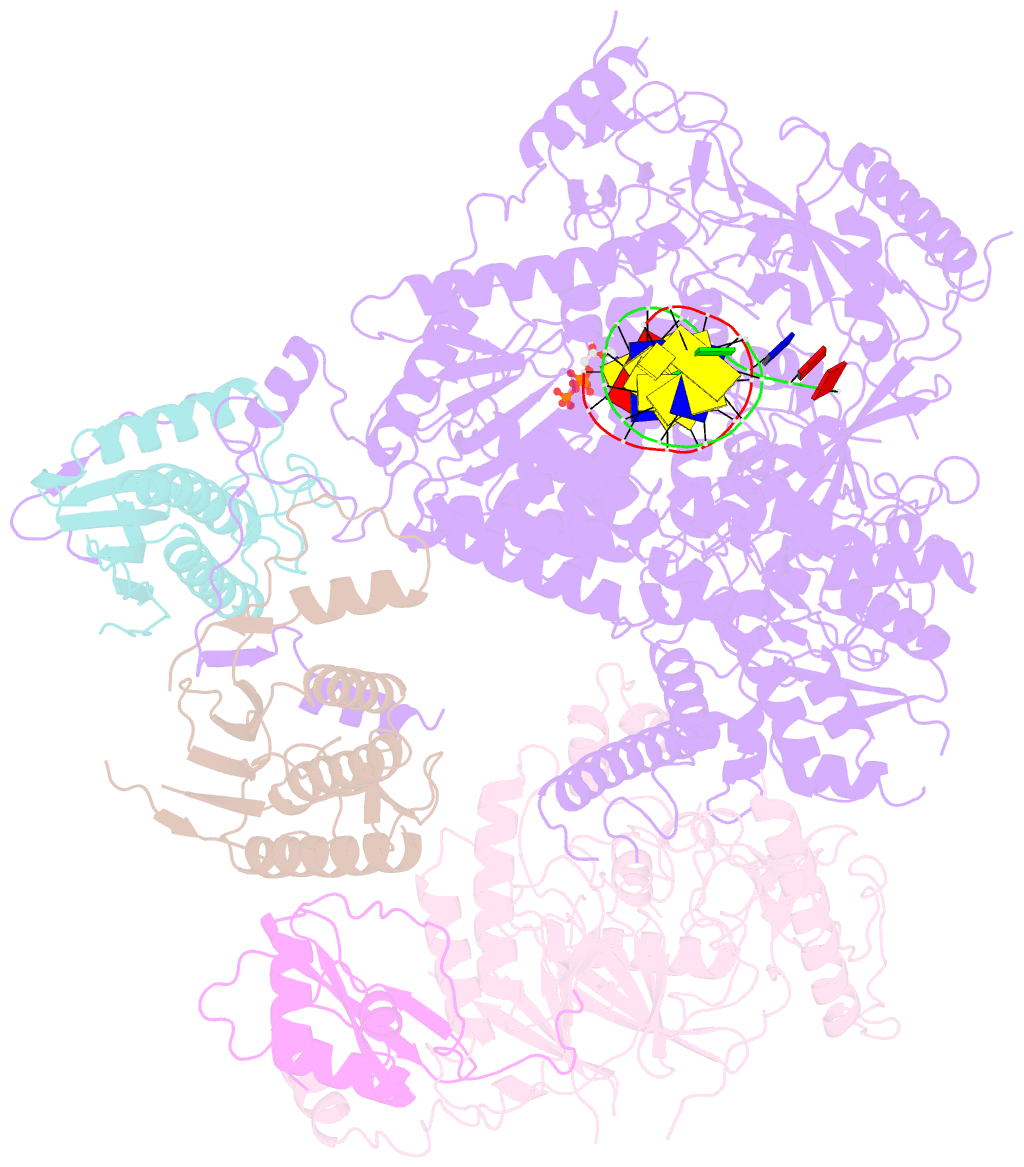
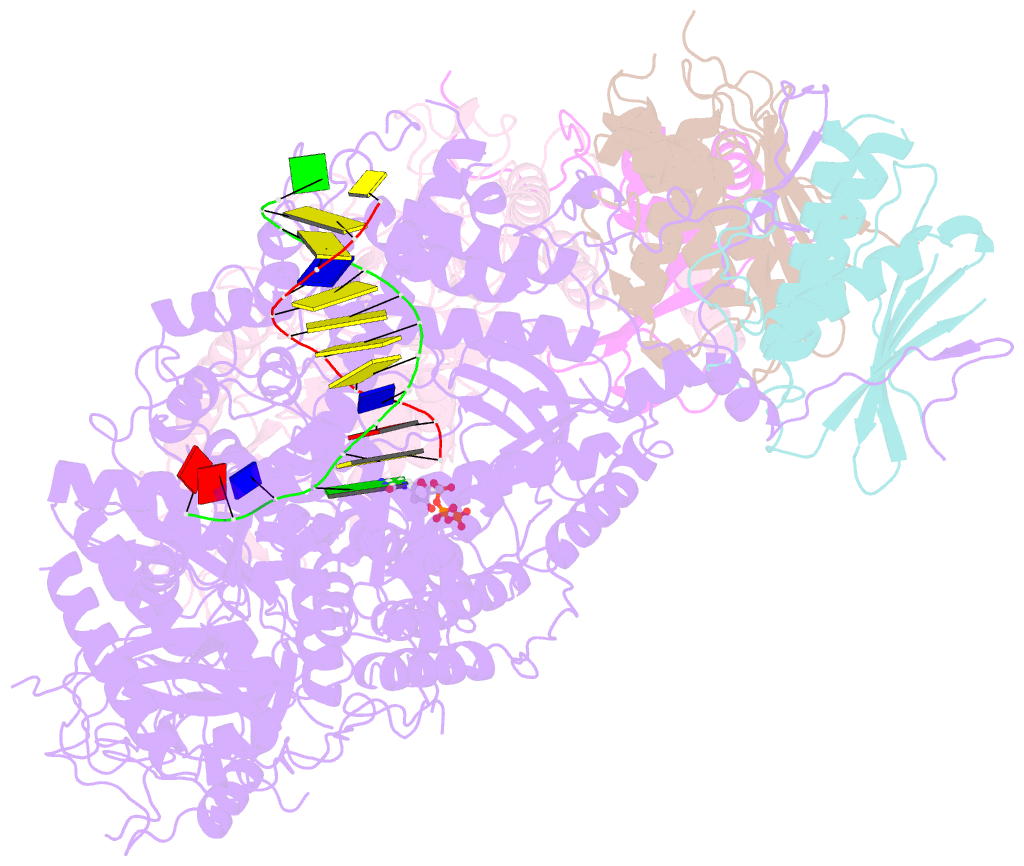
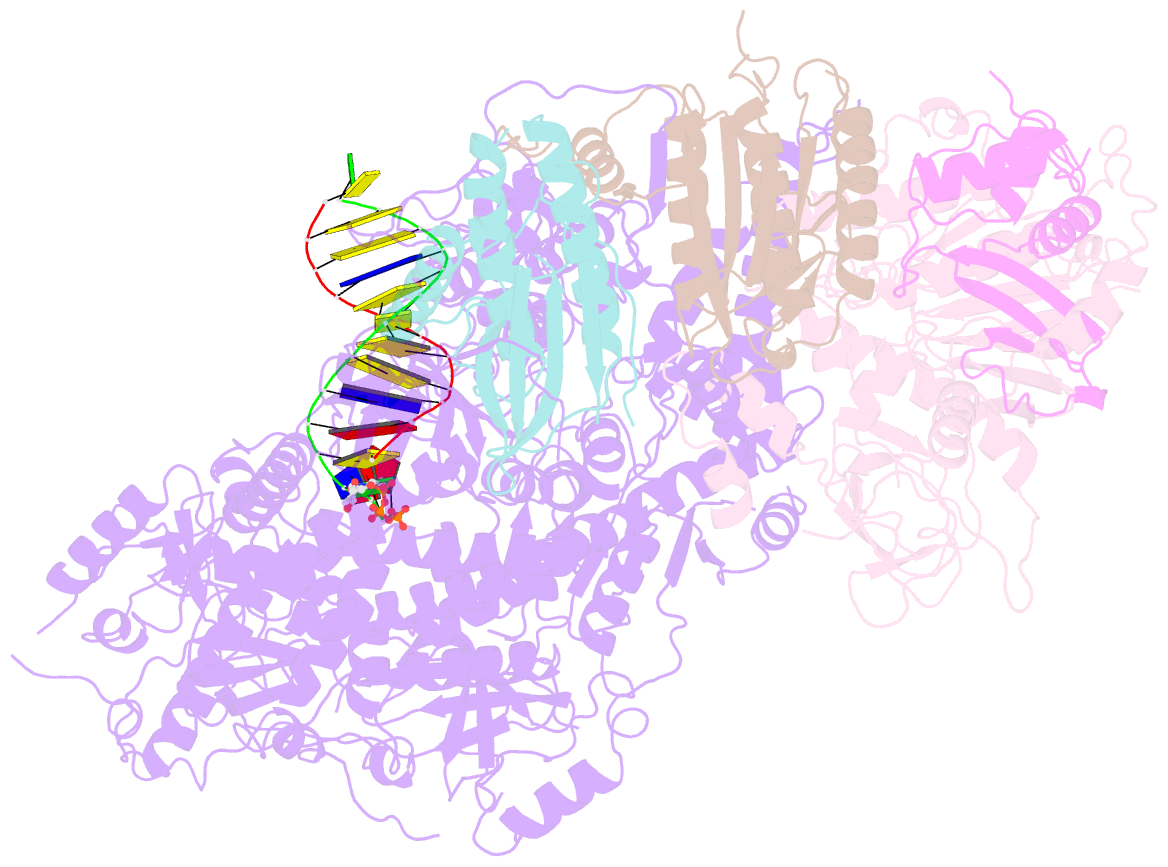
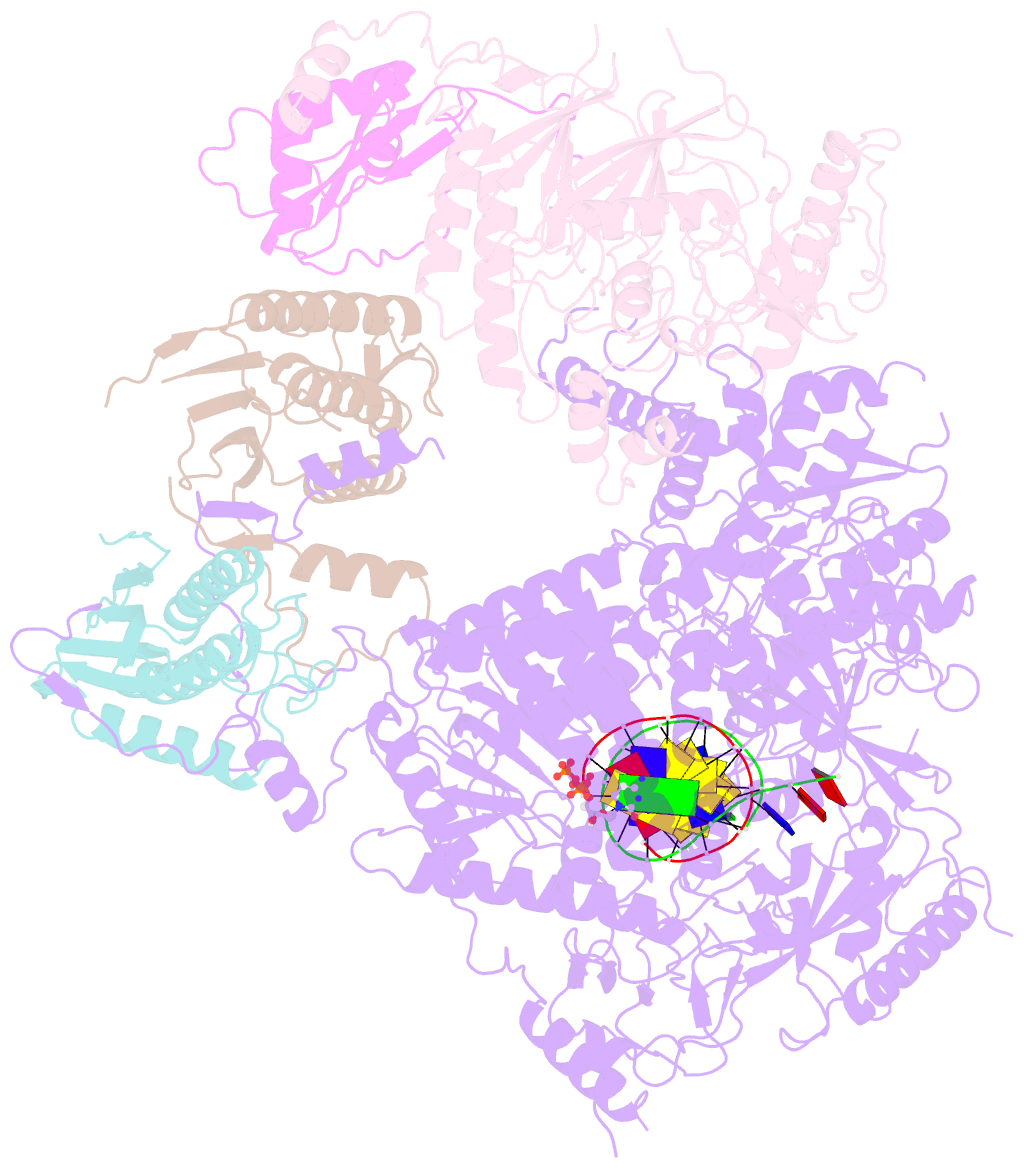
- Structure of DNA polymerase zeta-DNA-dntp ternary complex
- Reference
- Malik R, Kopylov M, Gomez-Llorente Y, Jain R, Johnson RE, Prakash L, Prakash S, Ubarretxena-Belandia I, Aggarwal AK (2020): "Structure and mechanism of B-family DNA polymerase zeta specialized for translesion DNA synthesis." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 27, 913-924. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-0476-7.
- Abstract
- DNA polymerase ζ (Polζ) belongs to the same B-family as high-fidelity replicative polymerases, yet is specialized for the extension reaction in translesion DNA synthesis (TLS). Despite its importance in TLS, the structure of Polζ is unknown. We present cryo-EM structures of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Polζ holoenzyme in the act of DNA synthesis (3.1 Å) and without DNA (4.1 Å). Polζ displays a pentameric ring-like architecture, with catalytic Rev3, accessory Pol31' Pol32 and two Rev7 subunits forming an uninterrupted daisy chain of protein-protein interactions. We also uncover the features that impose high fidelity during the nucleotide-incorporation step and those that accommodate mismatches and lesions during the extension reaction. Collectively, we decrypt the molecular underpinnings of Polζ's role in TLS and provide a framework for new cancer therapeutics.