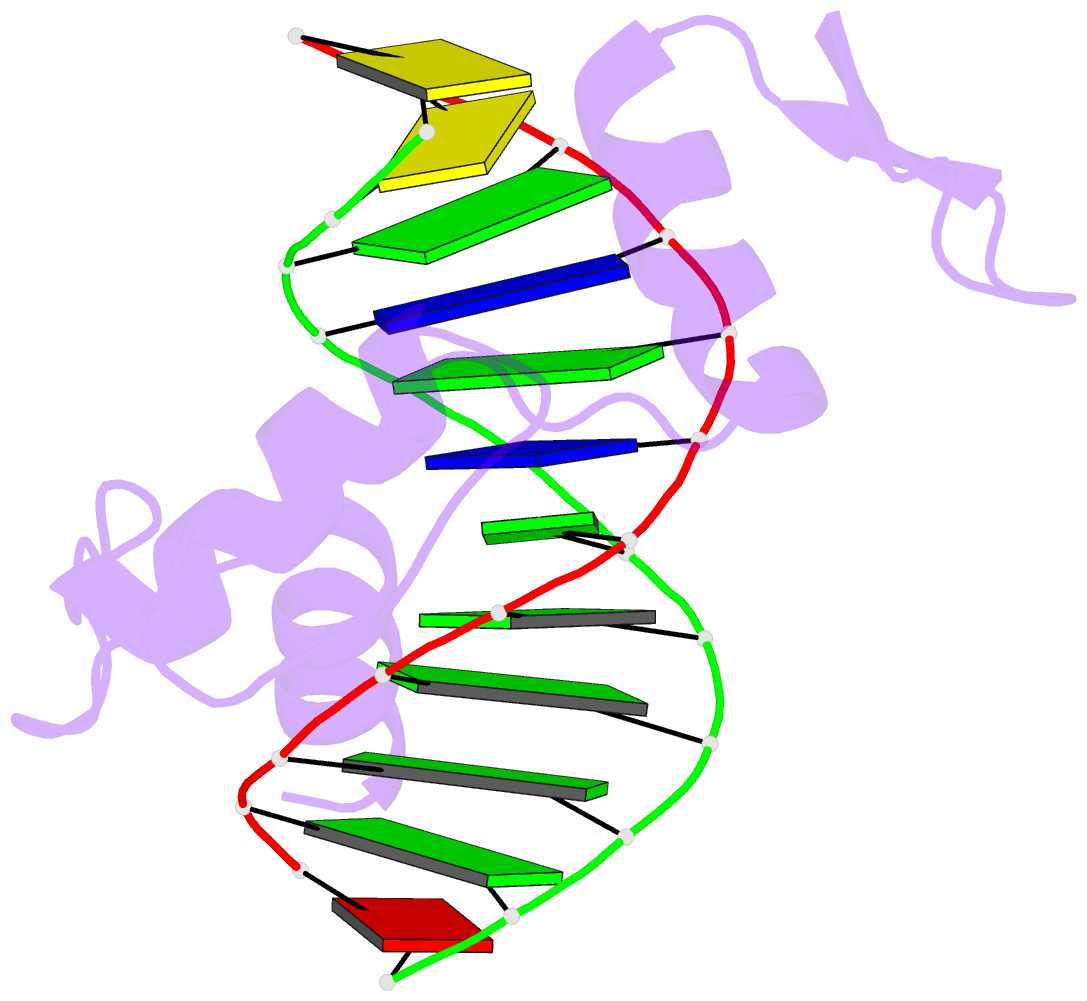
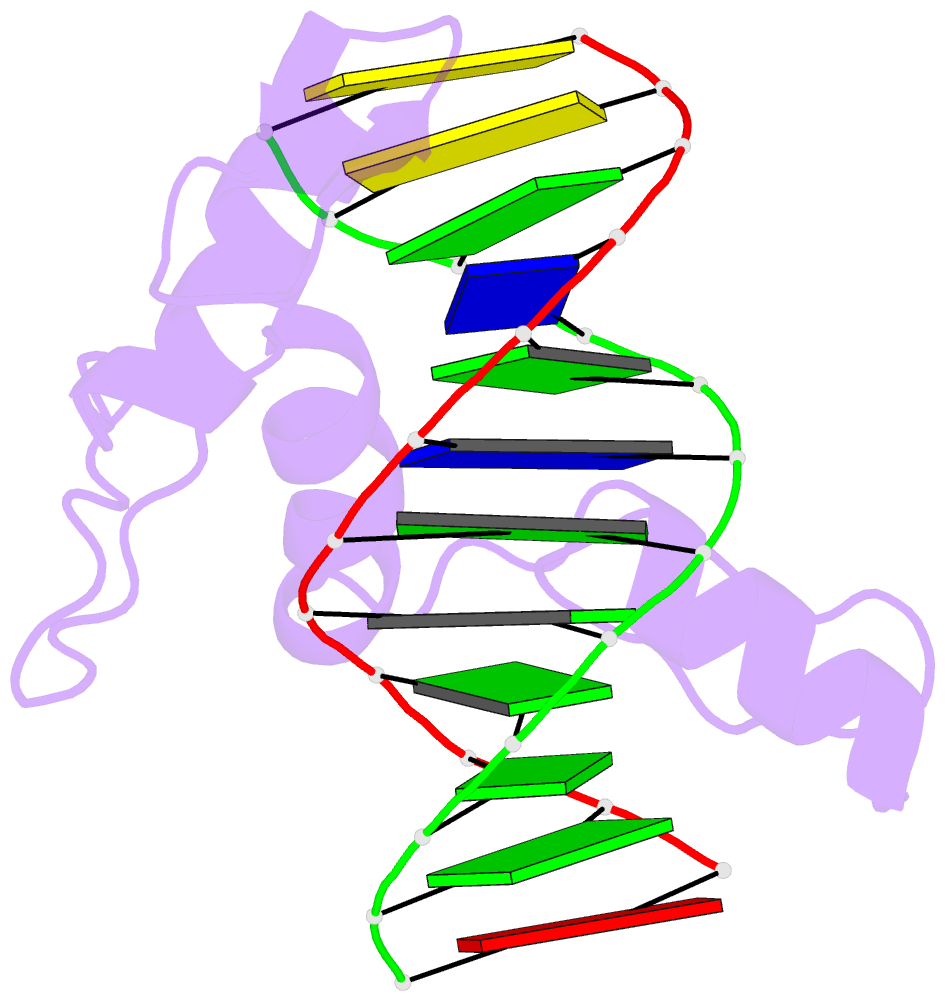
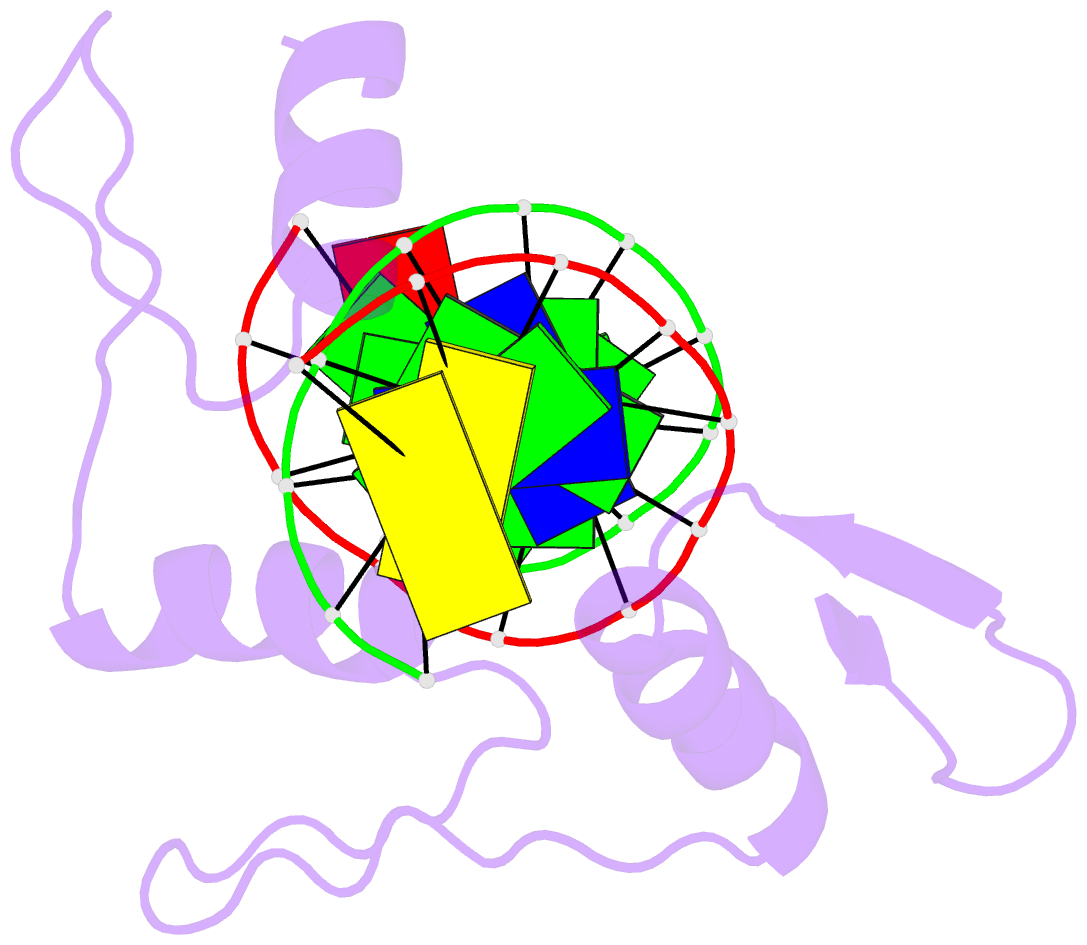
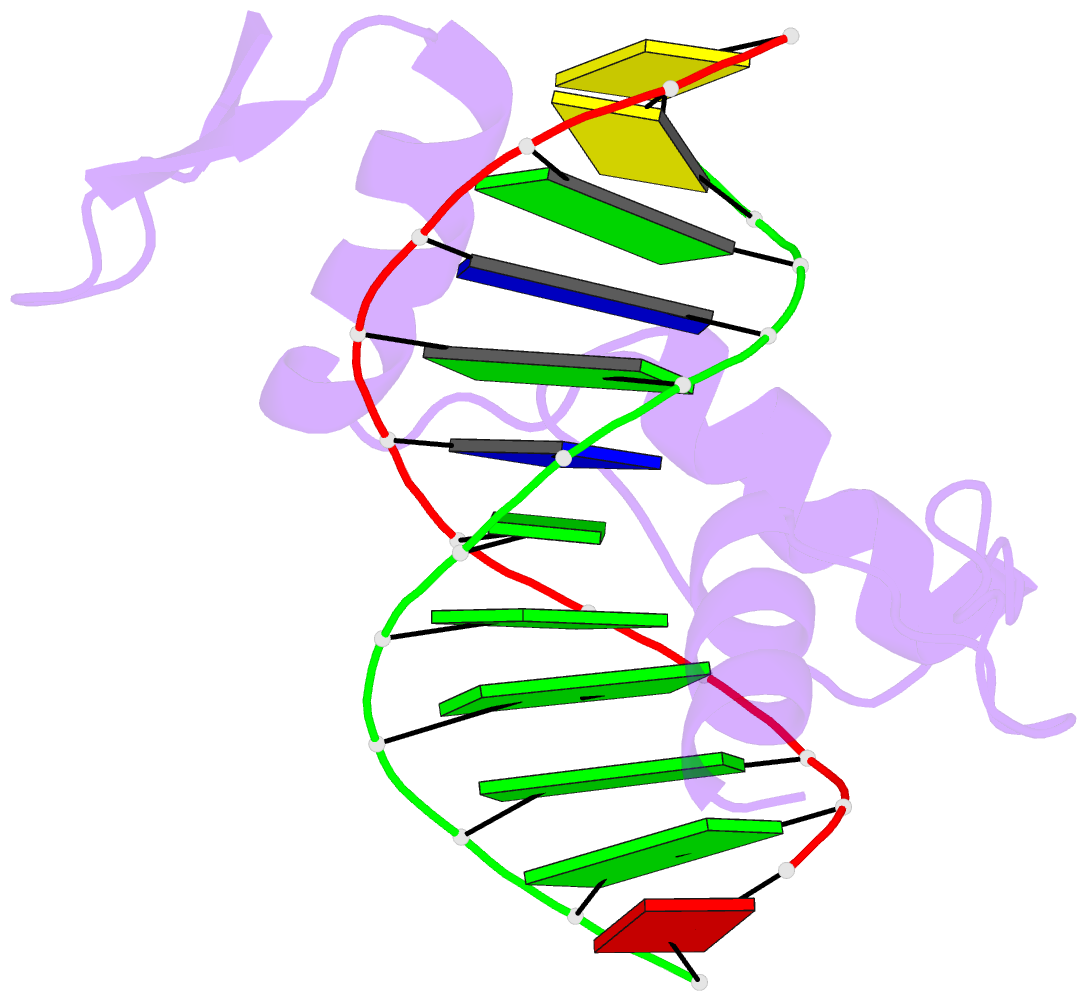
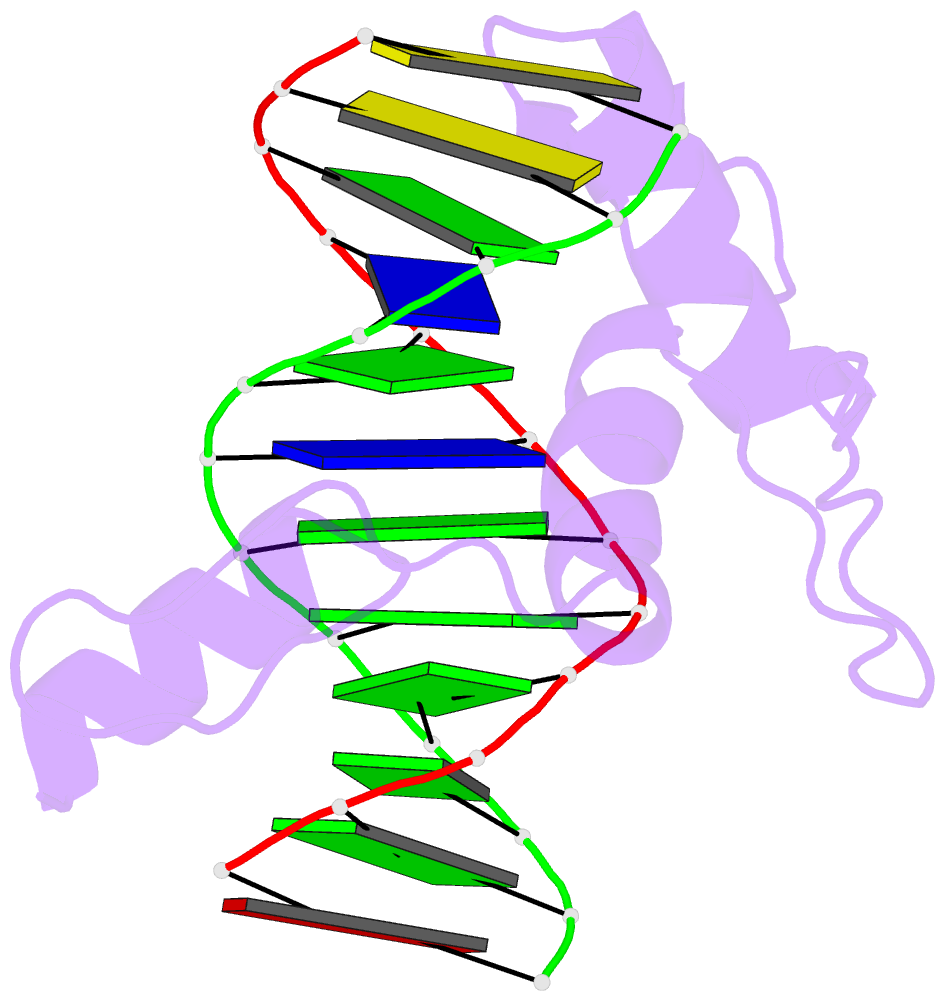
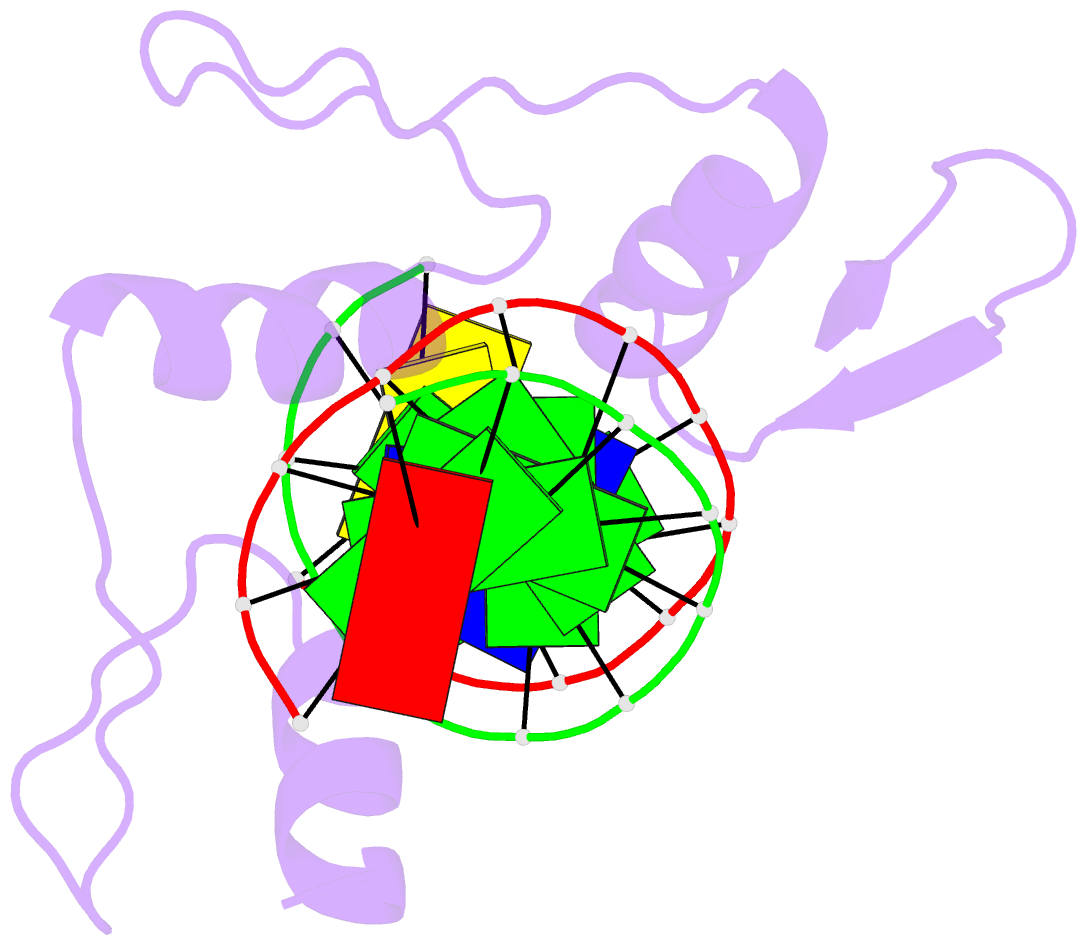
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6vtx; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.14 Å)
- Summary
- Crystal structure of human klf4 zinc finger DNA binding domain in complex with nanog DNA
- Reference
- Sharma R, Choi KJ, Quan MD, Sharma S, Sankaran B, Park H, LaGrone A, Kim JJ, MacKenzie KR, Ferreon ACM, Kim C, Ferreon JC (2021): "Liquid condensation of reprogramming factor KLF4 with DNA provides a mechanism for chromatin organization." Nat Commun, 12, 5579. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25761-7.
- Abstract
- Expression of a few master transcription factors can reprogram the epigenetic landscape and three-dimensional chromatin topology of differentiated cells and achieve pluripotency. During reprogramming, thousands of long-range chromatin contacts are altered, and changes in promoter association with enhancers dramatically influence transcription. Molecular participants at these sites have been identified, but how this re-organization might be orchestrated is not known. Biomolecular condensation is implicated in subcellular organization, including the recruitment of RNA polymerase in transcriptional activation. Here, we show that reprogramming factor KLF4 undergoes biomolecular condensation even in the absence of its intrinsically disordered region. Liquid-liquid condensation of the isolated KLF4 DNA binding domain with a DNA fragment from the NANOG proximal promoter is enhanced by CpG methylation of a KLF4 cognate binding site. We propose KLF4-mediated condensation as one mechanism for selectively organizing and re-organizing the genome based on the local sequence and epigenetic state.