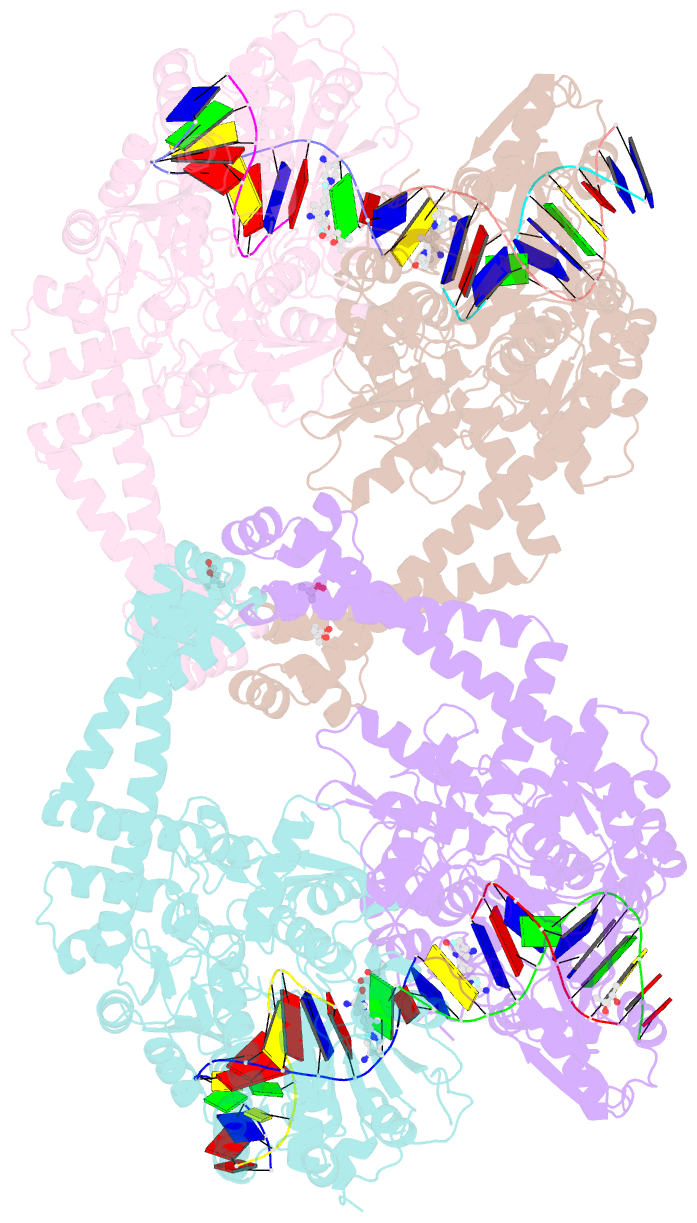
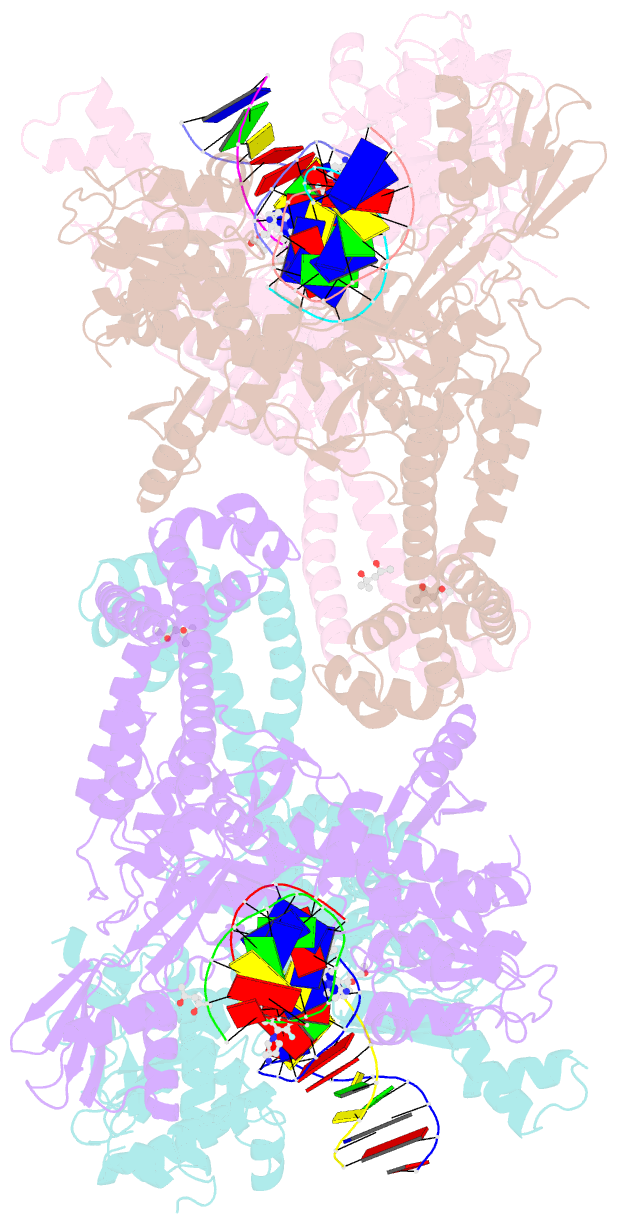
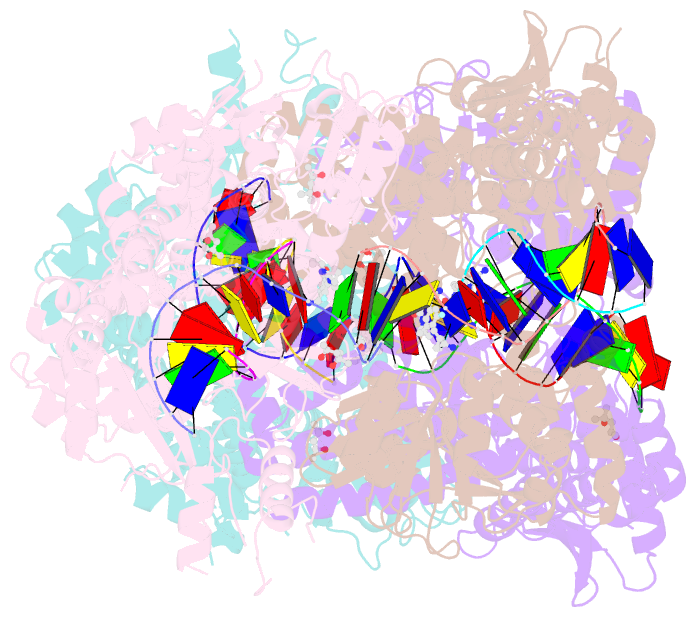
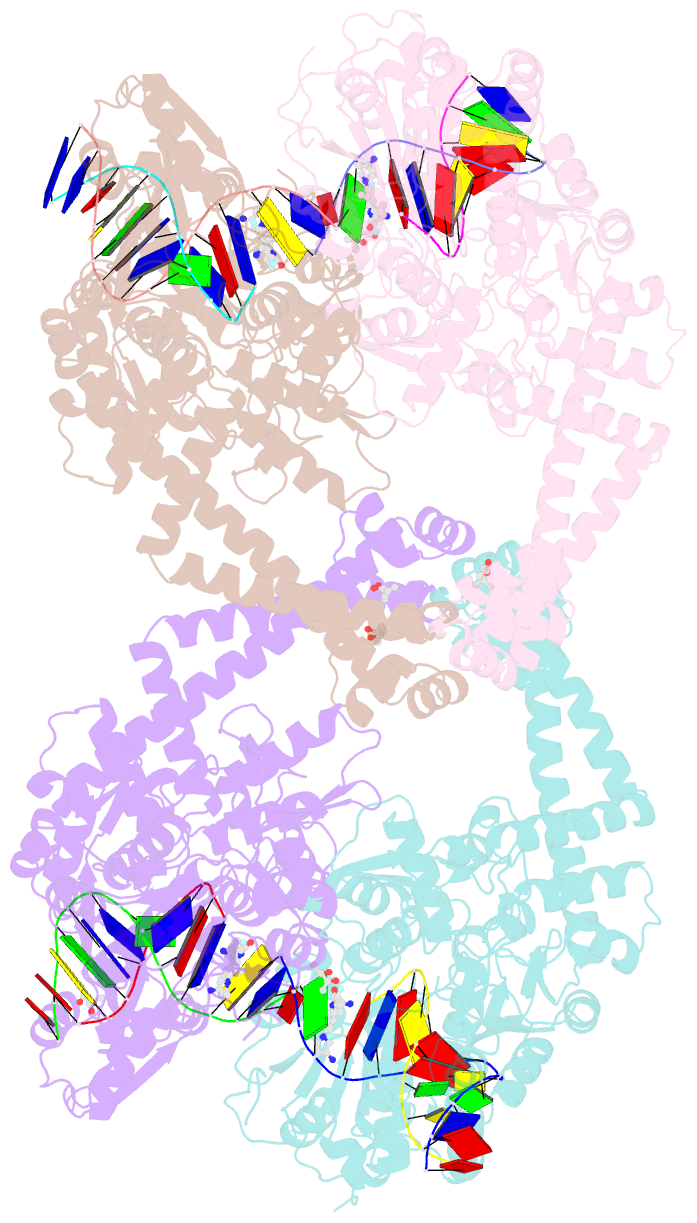
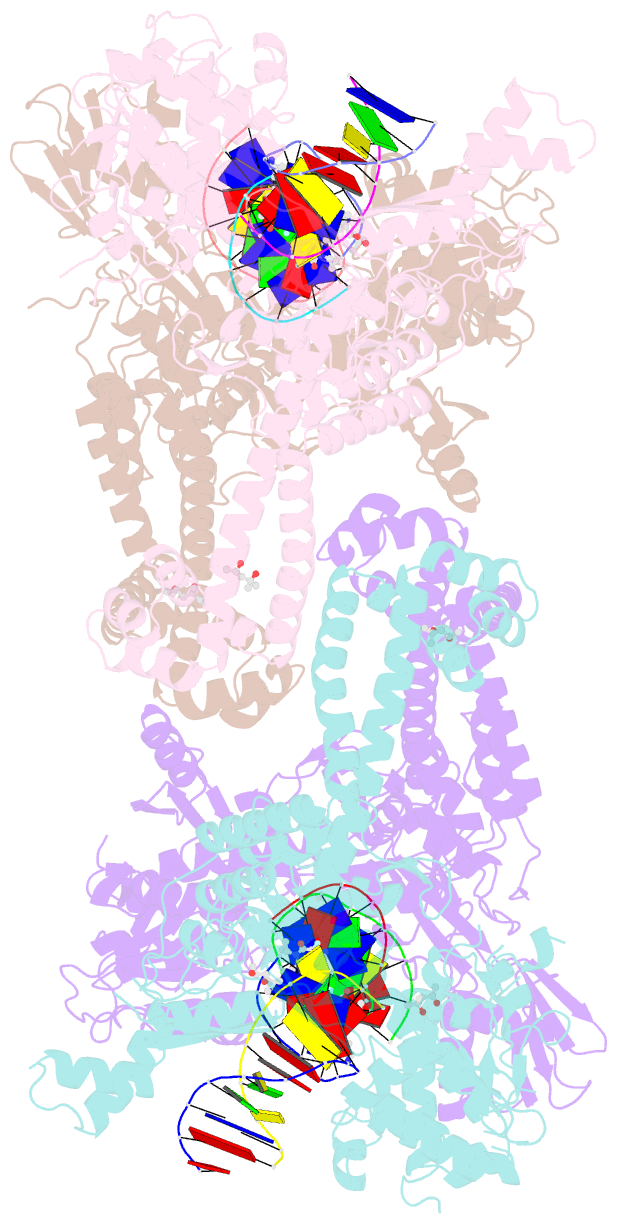
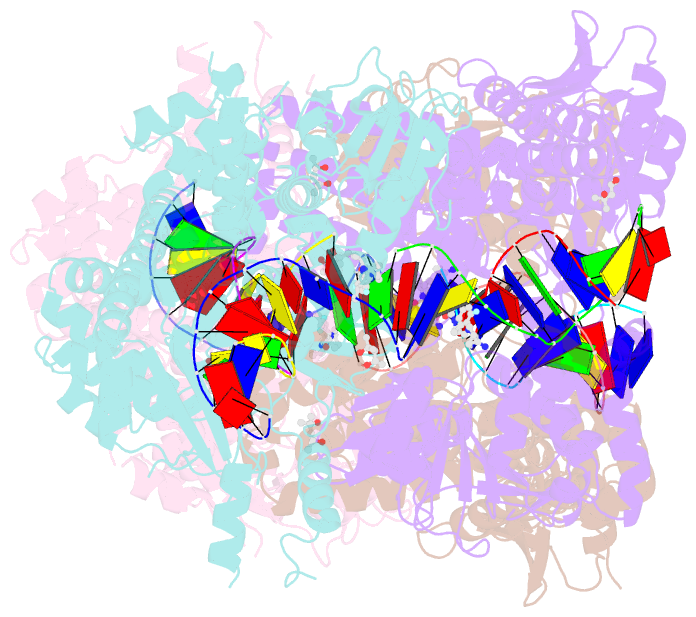
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6waa; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- isomerase-DNA-isomerase inhibitor
- Method
- X-ray (3.2 Å)
- Summary
- K. pneumoniae topoisomerase iv (pare-parc) in complex with DNA and compound 34 (7-[(1s,5r)-1-amino-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-3-yl]-4-(aminomethyl)-1-cyclopropyl-3,6-difluoro-8-methylquinolin-2(1h)-one)
- Reference
- Skepper CK, Armstrong D, Balibar CJ, Bauer D, Bellamacina C, Benton BM, Bussiere D, De Pascale G, De Vicente J, Dean CR, Dhumale B, Fisher LM, Fuller J, Fulsunder M, Holder LM, Hu C, Kantariya B, Lapointe G, Leeds JA, Li X, Lu P, Lvov A, Ma S, Madhavan S, Malekar S, McKenney D, Mergo W, Metzger L, Moser HE, Mutnick D, Noeske J, Osborne C, Patel A, Patel D, Patel T, Prajapati K, Prosen KR, Reck F, Richie DL, Rico A, Sanderson MR, Satasia S, Sawyer WS, Selvarajah J, Shah N, Shanghavi K, Shu W, Thompson KV, Traebert M, Vala A, Vala L, Veselkov DA, Vo J, Wang M, Widya M, Williams SL, Xu Y, Yue Q, Zang R, Zhou B, Rivkin A (2020): "Topoisomerase Inhibitors Addressing Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria." J.Med.Chem., 63, 7773-7816. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00347.
- Abstract
- Since their discovery over 5 decades ago, quinolone antibiotics have found enormous success as broad spectrum agents that exert their activity through dual inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. Increasing rates of resistance, driven largely by target-based mutations in the GyrA/ParC quinolone resistance determining region, have eroded the utility and threaten the future use of this vital class of antibiotics. Herein we describe the discovery and optimization of a series of 4-(aminomethyl)quinolin-2(1H)-ones, exemplified by