Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6wid; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.5 Å)
- Summary
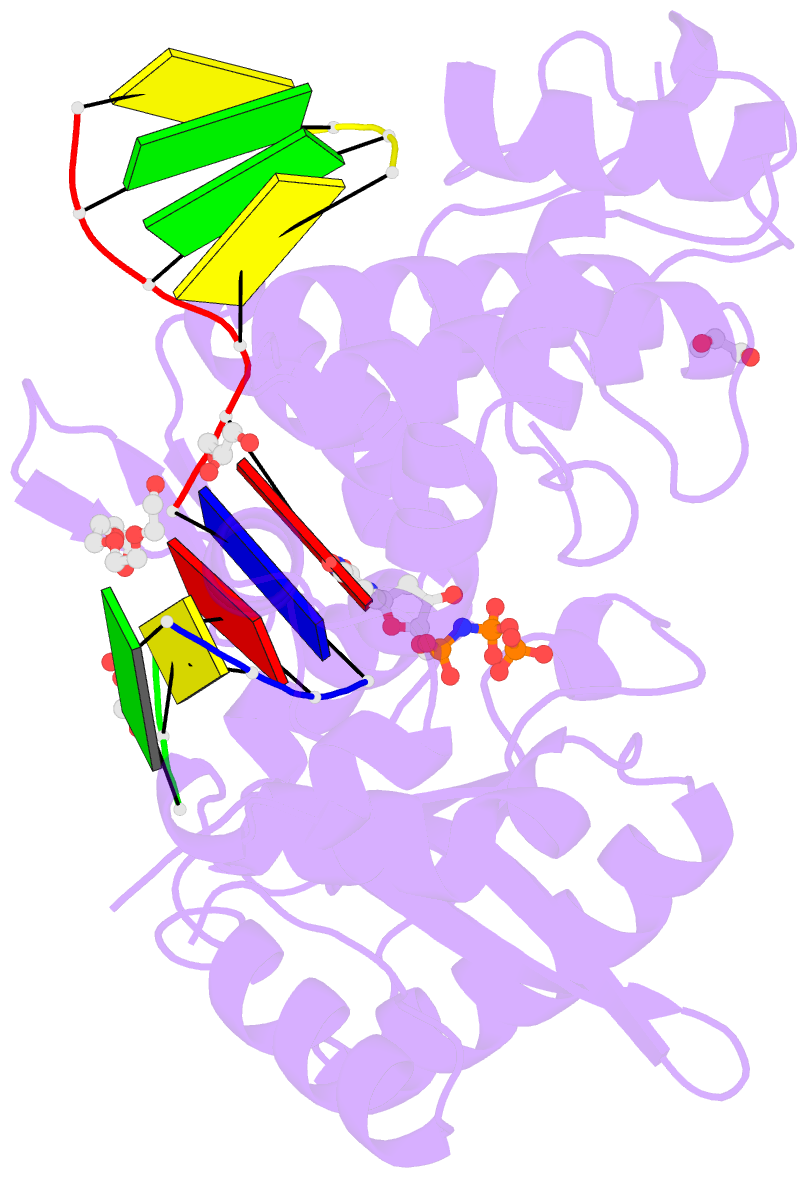
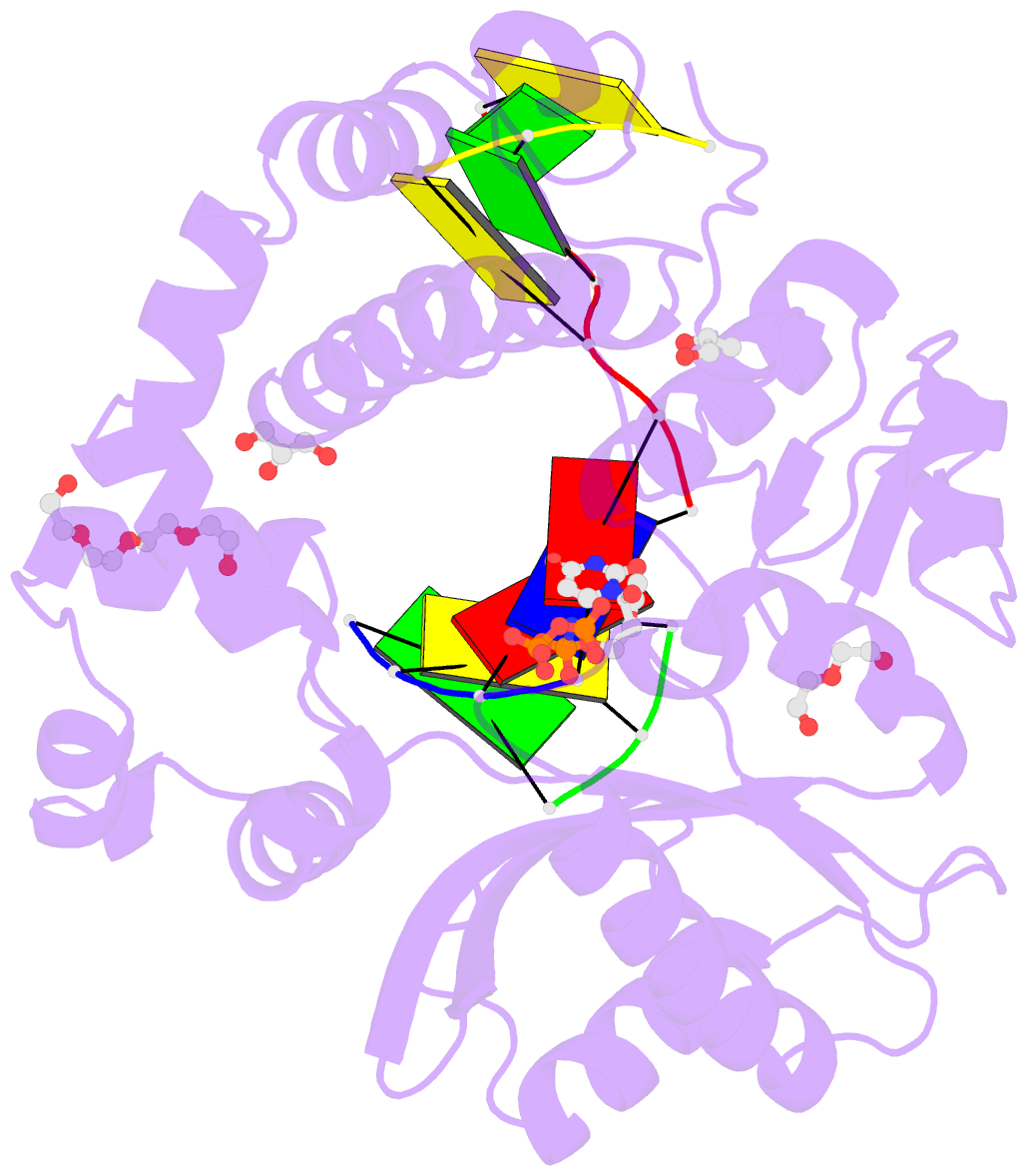
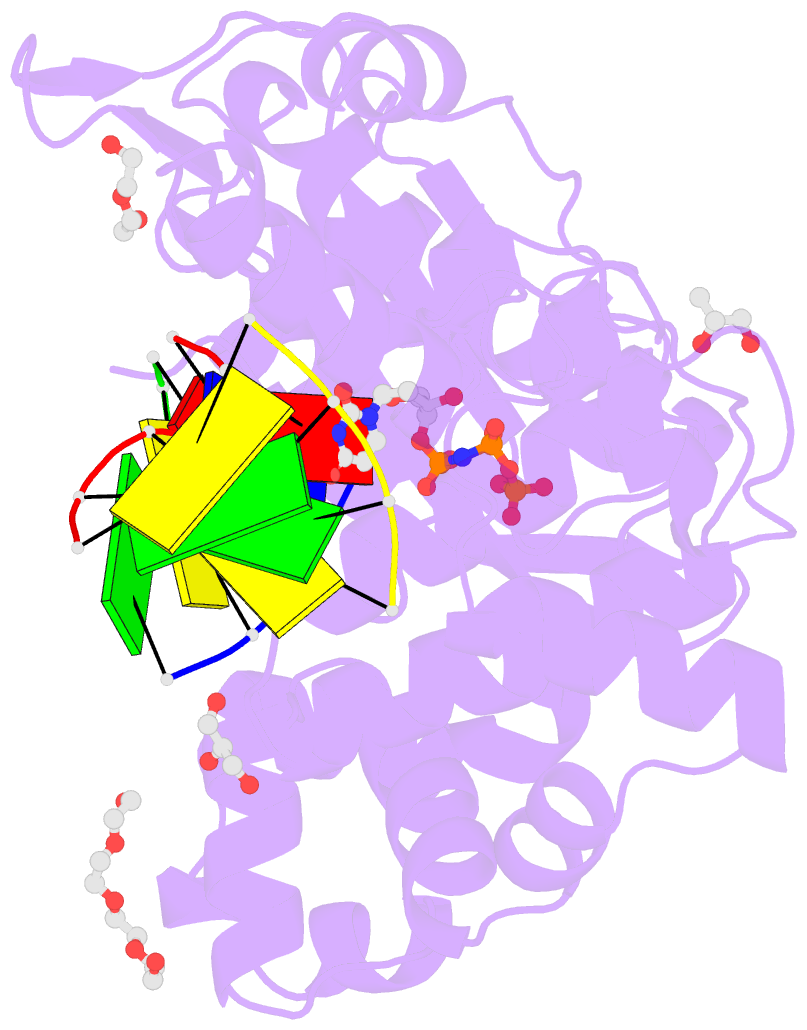
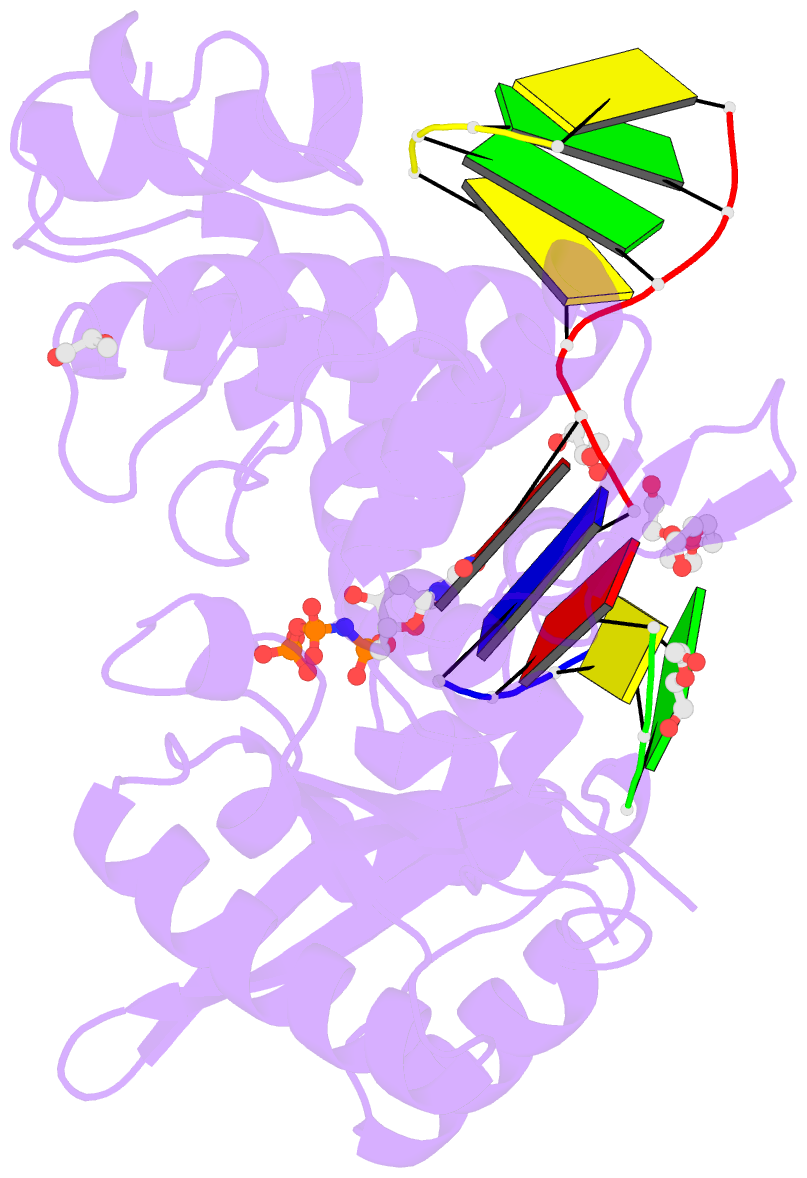
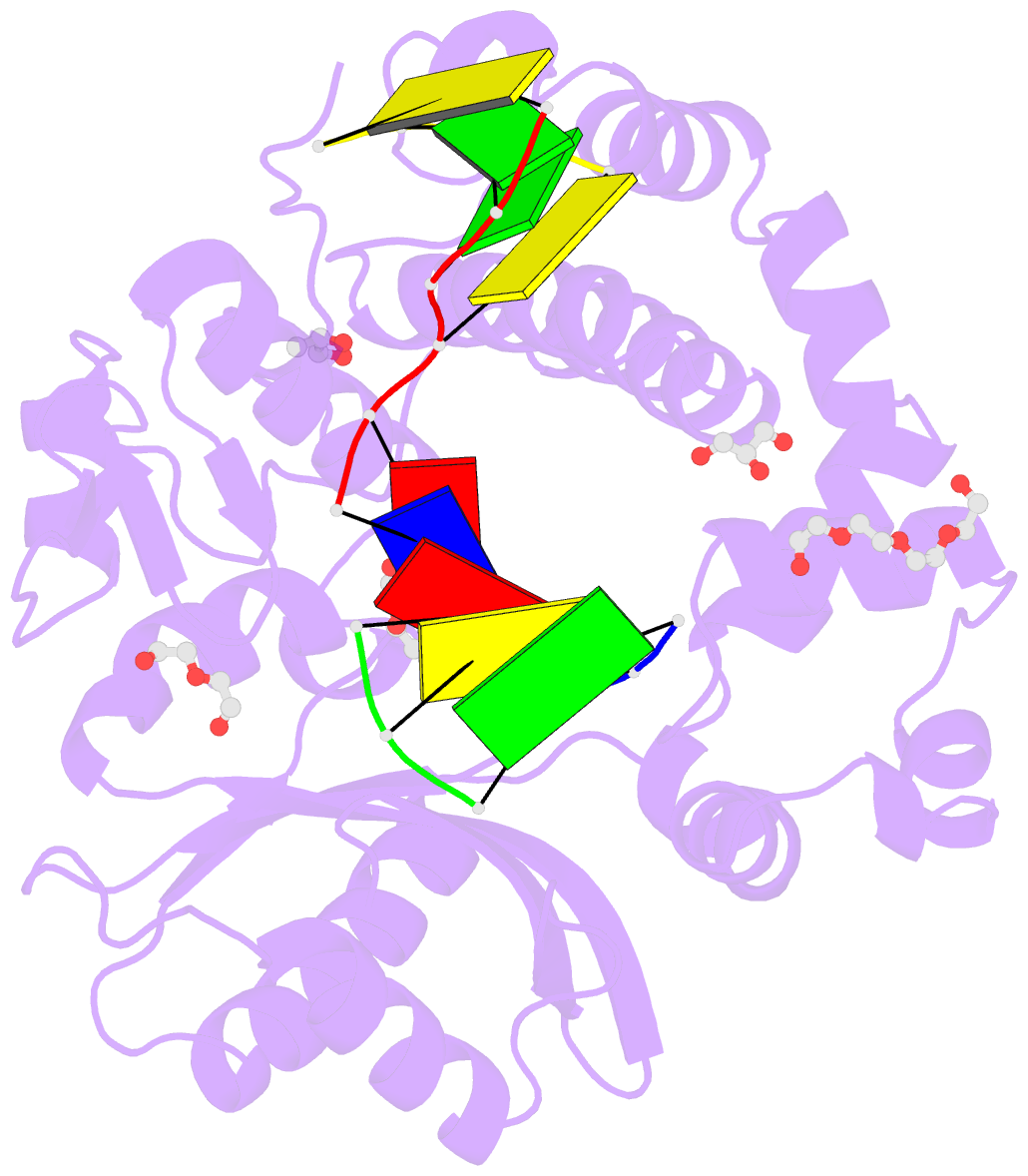
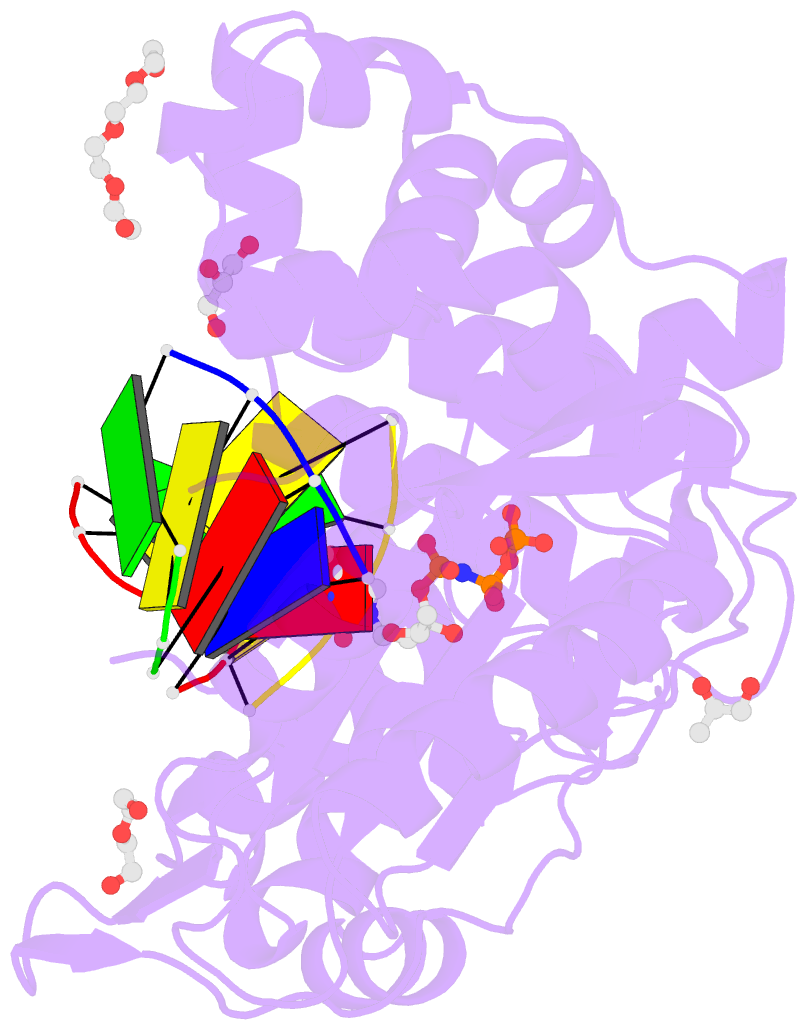
- Nucleotide incorporation intermediate into quaternary complex of human polymerase mu on a complementary DNA double-strand break substrate
- Reference
- Kaminski AM, Pryor JM, Ramsden DA, Kunkel TA, Pedersen LC, Bebenek K (2020): "Structural snapshots of human DNA polymerase mu engaged on a DNA double-strand break." Nat Commun, 11, 4784. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18506-5.
- Abstract
- Genomic integrity is threatened by cytotoxic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which must be resolved efficiently to prevent sequence loss, chromosomal rearrangements/translocations, or cell death. Polymerase μ (Polμ) participates in DSB repair via the nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway, by filling small sequence gaps in broken ends to create substrates ultimately ligatable by DNA Ligase IV. Here we present structures of human Polμ engaging a DSB substrate. Synapsis is mediated solely by Polμ, facilitated by single-nucleotide homology at the break site, wherein both ends of the discontinuous template strand are stabilized by a hydrogen bonding network. The active site in the quaternary Pol μ complex is poised for catalysis and nucleotide incoporation proceeds in crystallo. These structures demonstrate that Polμ may address complementary DSB substrates during NHEJ in a manner indistinguishable from single-strand breaks.