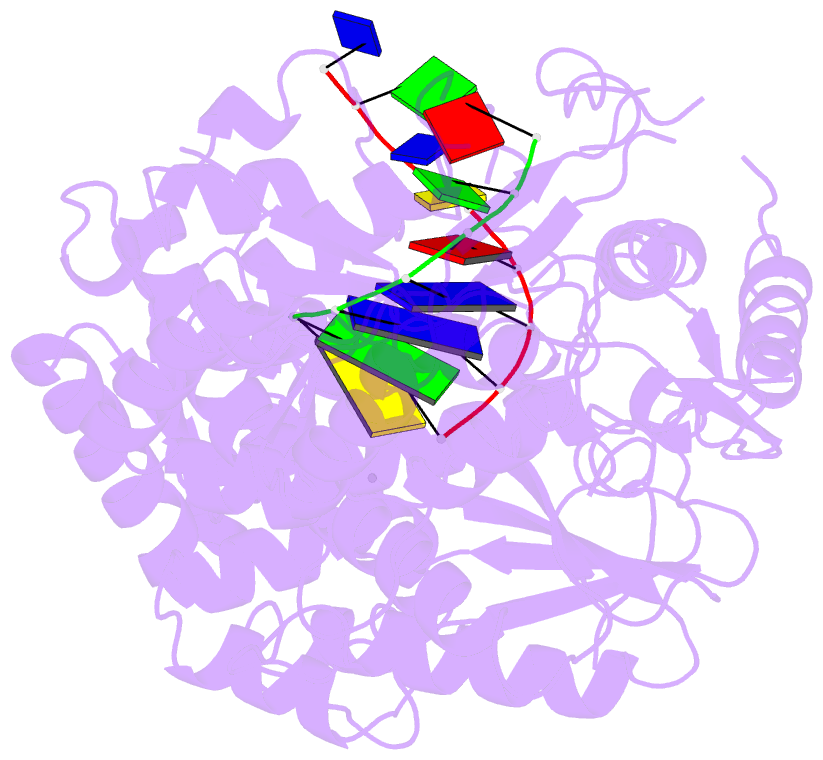
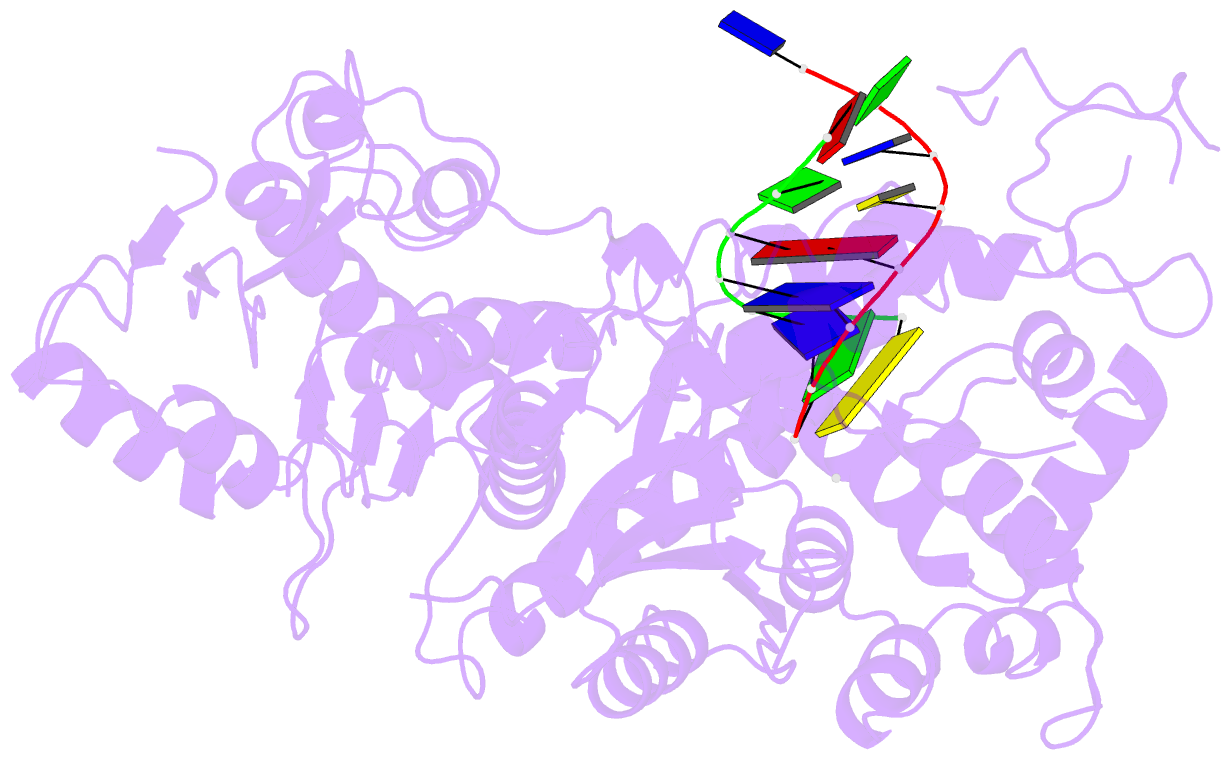
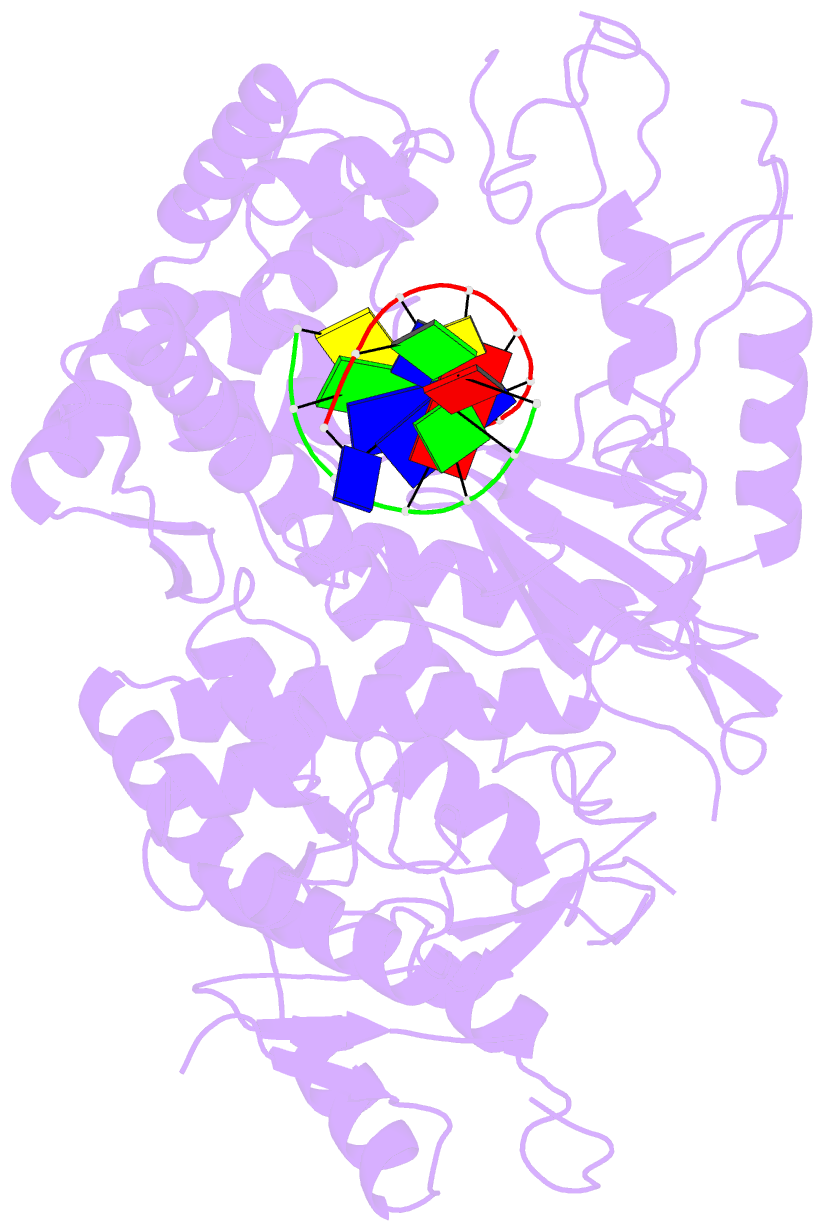
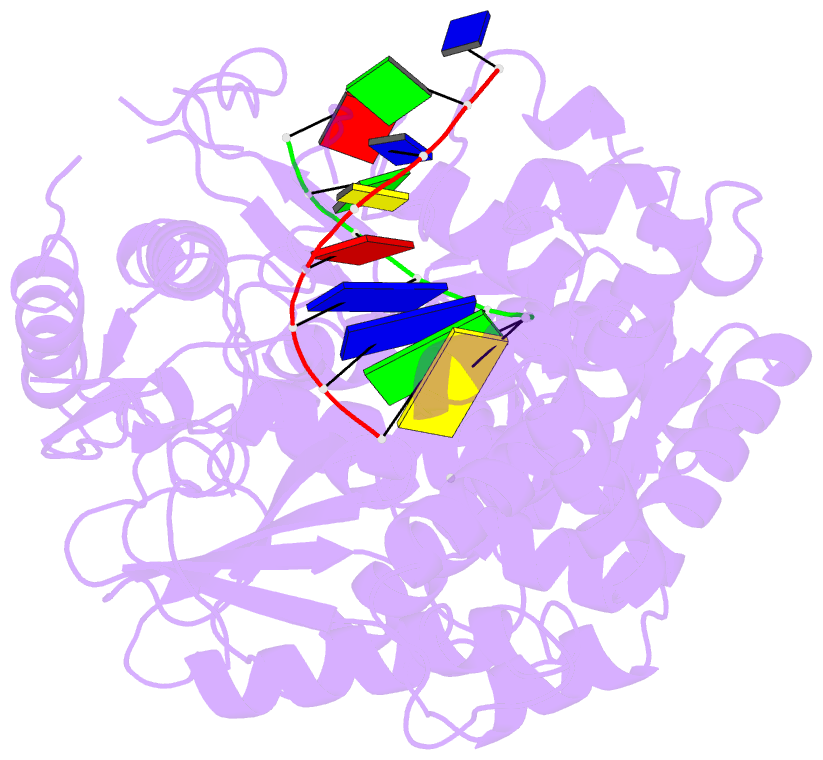
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6xbu; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.29 Å)
- Summary
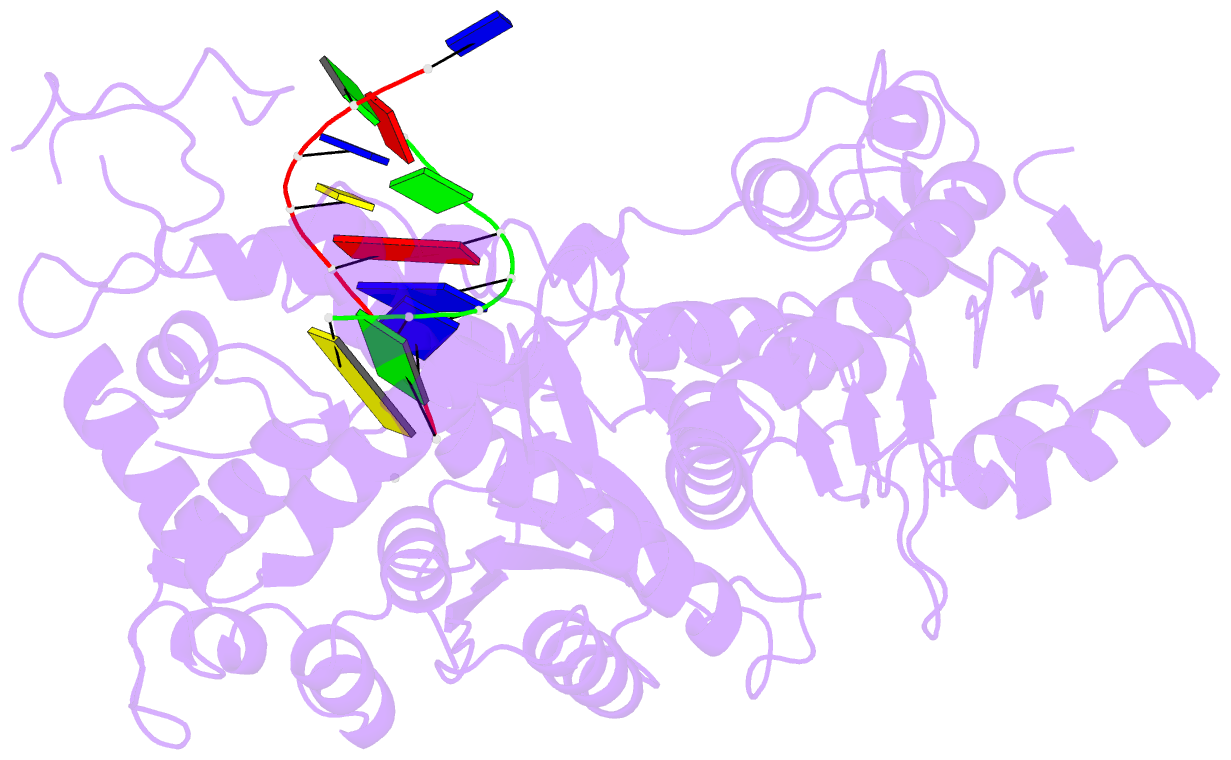
- Polymerase domain of polymerase-theta
- Reference
- Chandramouly G, Zhao J, McDevitt S, Rusanov T, Hoang T, Borisonnik N, Treddinick T, Lopezcolorado FW, Kent T, Siddique LA, Mallon J, Huhn J, Shoda Z, Kashkina E, Brambati A, Stark JM, Chen XS, Pomerantz RT (2021): "Pol theta reverse transcribes RNA and promotes RNA-templated DNA repair." Sci Adv, 7. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf1771.
- Abstract
- Genome-embedded ribonucleotides arrest replicative DNA polymerases (Pols) and cause DNA breaks. Whether mammalian DNA repair Pols efficiently use template ribonucleotides and promote RNA-templated DNA repair synthesis remains unknown. We find that human Polθ reverse transcribes RNA, similar to retroviral reverse transcriptases (RTs). Polθ exhibits a significantly higher velocity and fidelity of deoxyribonucleotide incorporation on RNA versus DNA. The 3.2-Å crystal structure of Polθ on a DNA/RNA primer-template with bound deoxyribonucleotide reveals that the enzyme undergoes a major structural transformation within the thumb subdomain to accommodate A-form DNA/RNA and forms multiple hydrogen bonds with template ribose 2'-hydroxyl groups like retroviral RTs. Last, we find that Polθ promotes RNA-templated DNA repair in mammalian cells. These findings suggest that Polθ was selected to accommodate template ribonucleotides during DNA repair.