Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6xh2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (1.71 Å)
- Summary
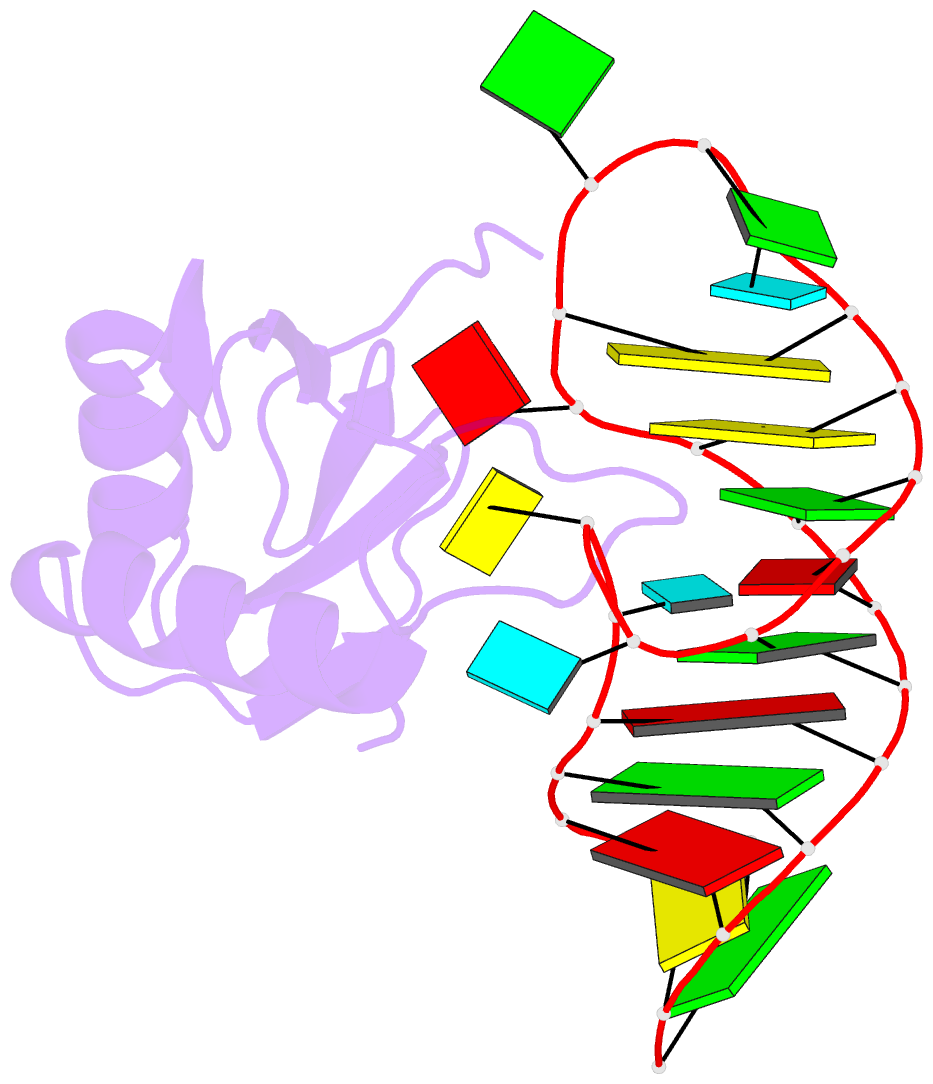
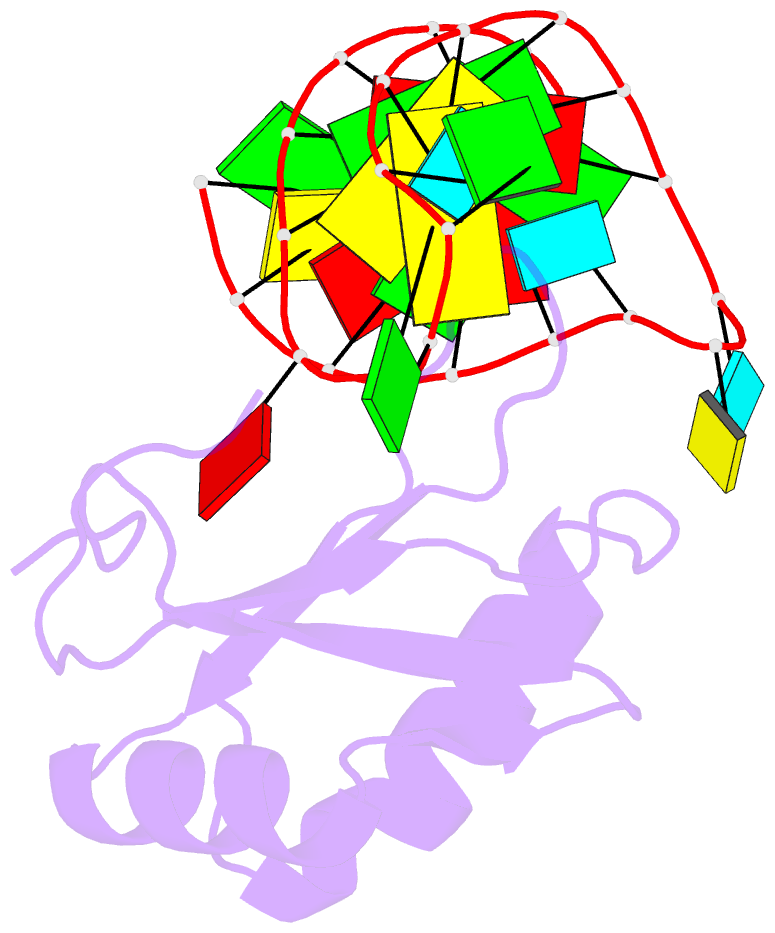
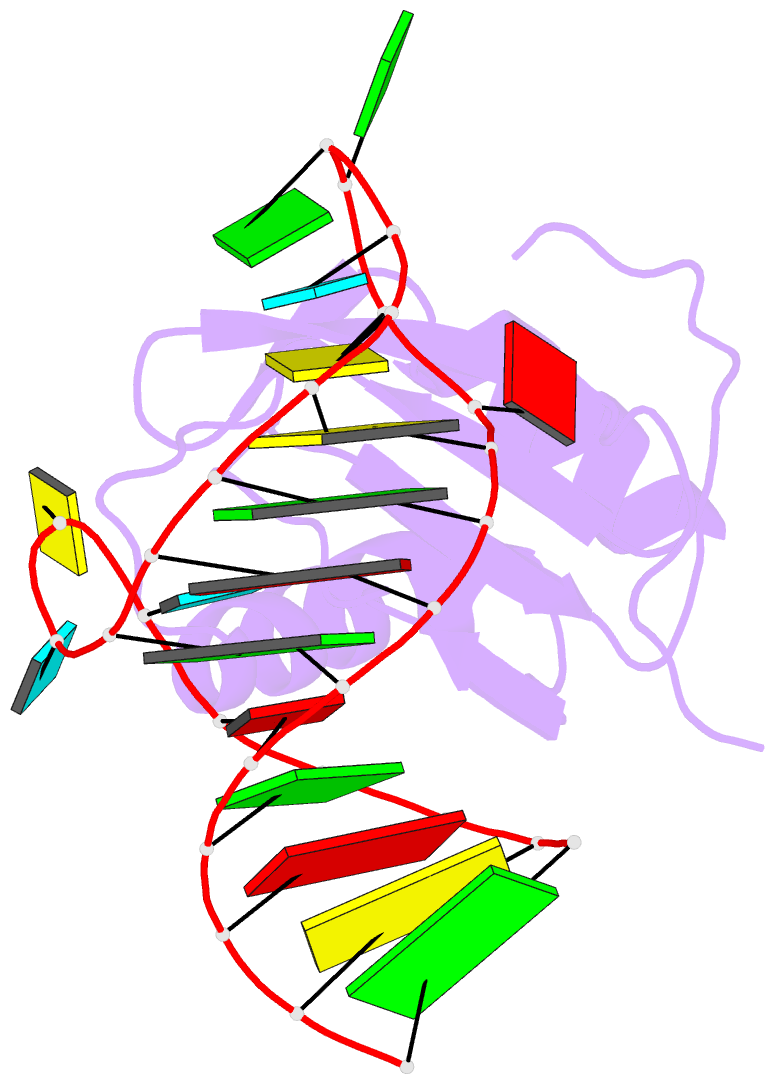
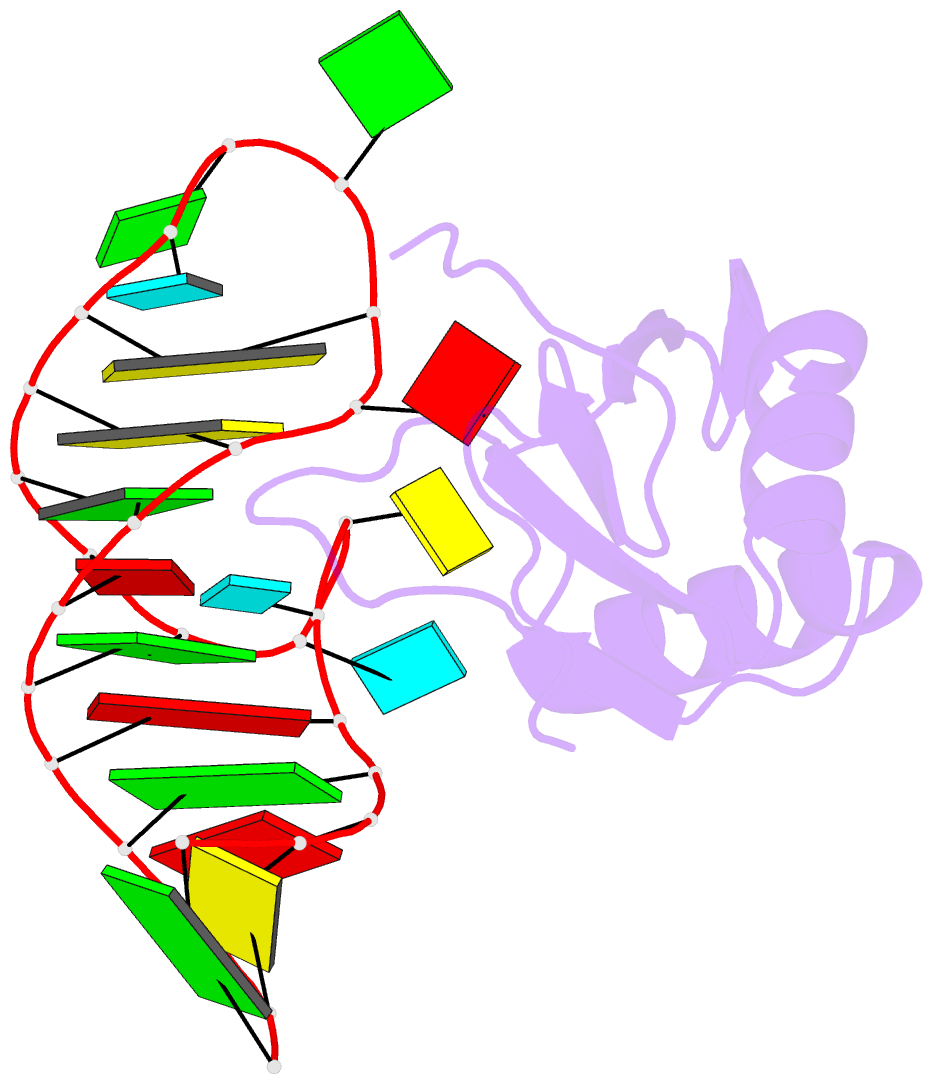
- Co-crystal structure of hiv-1 tar RNA in complex with lab-evolved rrm 6.6
- Reference
- Chavali SS, Mali SM, Jenkins JL, Fasan R, Wedekind JE (2020): "Co-crystal structures of HIV TAR RNA bound to lab-evolved proteins show key roles for arginine relevant to the design of cyclic peptide TAR inhibitors." J.Biol.Chem., 295, 16470-16486. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015444.
- Abstract
- RNA-protein interfaces control key replication events during the HIV-1 life cycle. The viral trans-activator of transcription (Tat) protein uses an archetypal arginine-rich motif (ARM) to recruit the host positive transcription elongation factor b (pTEFb) complex onto the viral trans-activation response (TAR) RNA, leading to activation of HIV transcription. Efforts to block this interaction have stimulated production of biologics designed to disrupt this essential RNA-protein interface. Here, we present four co-crystal structures of lab-evolved TAR-binding proteins (TBPs) in complex with HIV-1 TAR. Our results reveal that high-affinity binding requires a distinct sequence and spacing of arginines within a specific β2-β3 hairpin loop that arose during selection. Although loops with as many as five arginines were analyzed, only three arginines could bind simultaneously with major-groove guanines. Amino acids that promote backbone interactions within the β2-β3 loop were also observed to be important for high-affinity interactions. Based on structural and affinity analyses, we designed two cyclic peptide mimics of the TAR-binding β2-β3 loop sequences present in two high-affinity TBPs (KD values of 4.2 ± 0.3 and 3.0 ± 0.3 nm). Our efforts yielded low-molecular weight compounds that bind TAR with low micromolar affinity (KD values ranging from 3.6 to 22 μm). Significantly, one cyclic compound within this series blocked binding of the Tat-ARM peptide to TAR in solution assays, whereas its linear counterpart did not. Overall, this work provides insight into protein-mediated TAR recognition and lays the ground for the development of cyclic peptide inhibitors of a vital HIV-1 RNA-protein interaction.